
What is the basic structure of muscle tissue?
Structure
- Myofibril. The structural peculiarities of skeletal muscle are the alternate light and dark bands or shades (transverse striation) and thick longitudinal strands.
- Distribution. Striated muscle is called skeletal muscle as it is generally attached to the bone of the skeleton. ...
- Function. ...
What are the three types of muscles and their functions?
What are the 3 types of skeletal muscle?
- Skeletal Muscle. Skeletal muscle, attached to bones, is responsible for skeletal movements.
- Smooth Muscle.
- Cardiac Muscle.
What are the different types of muscle tissue?
Types of Muscular Tissue
- Skeletal Muscle Tissue. These muscles are attached to the skeleton and help in its movement. ...
- Smooth Muscle Tissue. These are non-striated, involuntary muscles controlled by the Autonomous Nervous System. ...
- Cardiac Muscle Tissue. These are found only in the heart. ...
What are the three types of muscle cells?
What are the parts of muscular system and their functions?
- Skeletal muscle. Skeletal muscles are the only muscles that can be consciously controlled. …
- Smooth muscle. Smooth muscle lines the inside of blood vessels and organs, such as the stomach, and is also known as visceral muscle. …
- Cardiac muscle.
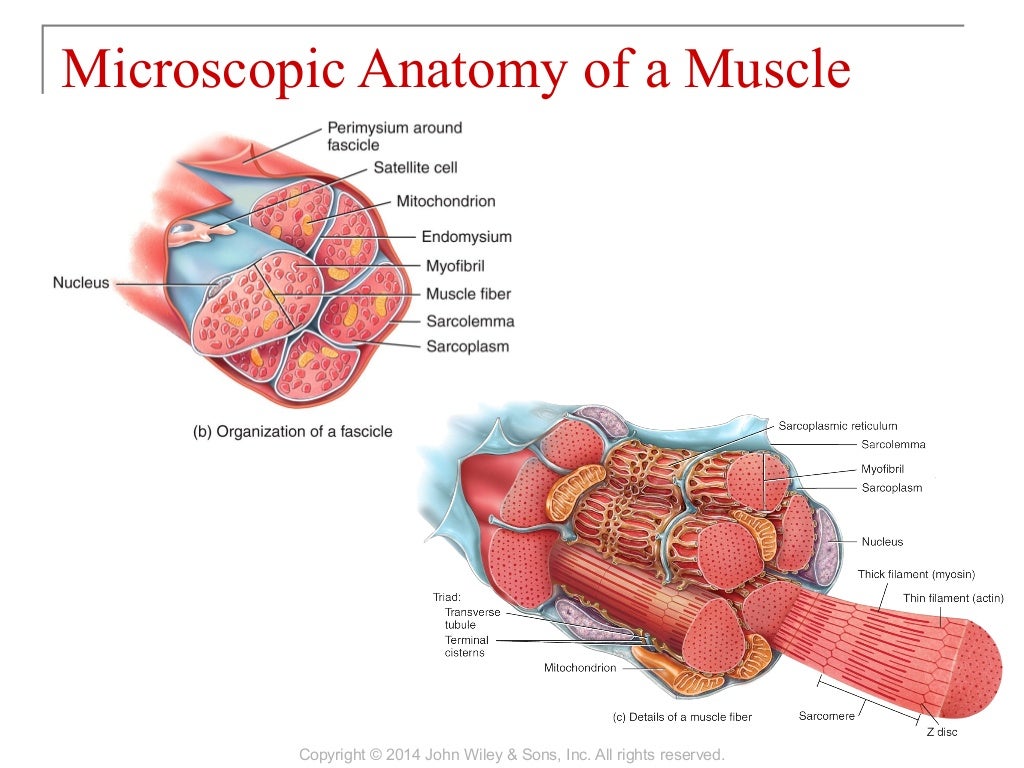
What is common to all muscle types?
All muscle tissues have 4 characteristics in common:excitability.contractility.extensibility - they can be stretched.elasticity - they return to normal length after stretching.
Which option is a main type of muscle tissue?
Skeletal muscle tissue is attached to bones by tendons. It allows voluntary body movements. Skeletal muscle is the most common type of muscle tissue in the human body.
What are the 3 types of muscles and which is the most common type of muscle?
The three main types of muscle include:Skeletal muscle – the specialised tissue that is attached to bones and allows movement. ... Smooth muscle – located in various internal structures including the digestive tract, uterus and blood vessels such as arteries. ... Cardiac muscle – the muscle specific to the heart.
What is the most common type of smooth muscle?
unitary smooth muscleTermed unitary smooth muscle or visceral muscle, this type of smooth muscle is the most common observed in the human body, forming the walls of hollow organs. Single-unit smooth muscle produces slow, steady contractions that allow substances, such as food in the digestive tract, to move through the body.
What do all 3 types of muscle tissue have in common?
All three muscle tissues have some properties in common; they all exhibit a quality called excitability as their plasma membranes can change their electrical states (from polarized to depolarized) and send an electrical wave called an action potential along the entire length of the membrane.
What is the muscular tissue?
Muscle tissue is composed of cells that have the special ability to shorten or contract in order to produce movement of the body parts. The tissue is highly cellular and is well supplied with blood vessels.
What is muscle tissue made up of?
Muscle tissue is a composite tissue which is composed of (1) muscle cells, specialized for contraction, (2) connective tissue, (3) nerve fibers and (4) blood vessels.
Where is skeletal muscle tissue found?
Where are the skeletal muscles located? There are skeletal muscles throughout your body. They're located between bones.
What is the 6 major types of muscles?
6.3: Types of Muscle TissueWork Those Eye Muscles!What is Muscle Tissue?Skeletal Muscle Tissue. Skeletal Muscle Pairs. Skeletal Muscle Structure. Slow- and Fast-Twitch Skeletal Muscle Fibers.Smooth Muscle. Structure of Smooth Muscle. Functions of Smooth Muscle.Cardiac Muscle. Feature: Human Body in the News.
What are smooth muscle tissue?
Smooth muscle consists of thick and thin filaments that are not arranged into sarcomeres giving it a non-striated pattern. On microscopic examination, it will appear homogenous. Smooth muscle cytoplasm contains a large amount of actin and myosin. Actin and myosin act as the main proteins involved in muscle contraction.
Which muscles are known as the smooth muscles?
Smooth muscle, found in the walls of the hollow internal organs such as blood vessels, the gastrointestinal tract, bladder, and uterus, is under control of the autonomic nervous system. Smooth muscle cannot be controlled consciously and thus acts involuntarily.
What type of muscle is the skeletal muscle?
Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles under the control of the somatic nervous system. The other types of muscle are cardiac muscle which is also striated and smooth muscle which is non-striated; both of these types of muscle tissue are classified as involuntary, or, under the control of the autonomic nervous system.
What is the 6 major types of muscles?
6.3: Types of Muscle TissueWork Those Eye Muscles!What is Muscle Tissue?Skeletal Muscle Tissue. Skeletal Muscle Pairs. Skeletal Muscle Structure. Slow- and Fast-Twitch Skeletal Muscle Fibers.Smooth Muscle. Structure of Smooth Muscle. Functions of Smooth Muscle.Cardiac Muscle. Feature: Human Body in the News.
What is tissue types of tissue?
Overview. There are 4 basic types of tissue: connective tissue, epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. Connective tissue supports other tissues and binds them together (bone, blood, and lymph tissues).
What type of muscle tissue is voluntary?
Skeletal muscle: Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles, meaning you control how and when they move and work.
Which of the following is not a type of muscle tissue?
Rough is not a form of muscle tissue. The proper types are listed below: Cardiac- this is the muscle tissue within the heart, whose contractions pump blood around the body. Smooth- this is the muscle that surrounds organs such as blood vessels, intestines and the stomach.
What is the most common muscle type in the human body?
Skeletal muscles are used whenever you move your eyes or run a marathon. Skeletal muscle contractions are voluntary and controlled by the central n...
Which is the most abundant type of muscle in a human or animal body?
It is the only form of tissue that possesses cells that can contract. Tendons connect skeletal muscle tissue to bones. It allows for voluntary moti...
What is the structure of a muscle that supports voluntary movements of the body?
Skeletal muscles are the voluntary muscles that are linked to bones via tendons and allow the body to move on its own. Muscle tissue is made up of...
What are the skeletal muscles in the body?
Skeletal muscle, also known as voluntary muscle in vertebrates, is the most prevalent of the body's three types of muscles. Tendons connect skeleta...
What are some examples of smooth muscles?
Smooth muscle occurs in multiple locations throughout the body. It is found in the lining of the digestive organs, the walls of vessels, the walls...
What is cardiac muscle tissue?
Cardiac muscle tissue composes the muscular walls of the heart. It is striated and contains intercalated discs. The individual cells contain a sing...
Where are smooth muscles found in the body?
Smooth muscles are found in the digestive system, the reproductive system, the renal system, and throughout the vessels of the circulatory system....
What are the 3 types of muscle tissue and their functions?
Cardiac muscle is found in the heart and results in the beating of the heart. Smooth muscle is found in many organs throughout the body and control...
What is the difference between smooth muscle and skeletal muscle?
Skeletal muscle is composed of striated muscle cells. This is the first and most easily identifiable difference between skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. The individual cells in skeletal muscle tissue are long, straight, and contain multiple nuclei. These cells are not connected by intercalated discs like cardiac muscle and instead typically run the entire length of the muscle. Skeletal muscle appears highly organized. Examine the skeletal muscle example below.
What is the most common muscle in the body?
Skeletal muscle is the most common muscle in the body. Skeletal muscle is voluntary muscle (controlled when an individual chooses to use them) via somatic neurons and is responsible for supporting the skeleton and movement of the body. This muscle tissue allows for walking, running, sitting, and raising the arm among many other movements. The cells in muscle tissue are long and large in diameter compared to the cells in cardiac and smooth muscle tissue. This is because the contractions in skeletal muscle are stronger, and the strength of a contraction is proportional to the cross section of a muscle fiber.
What is smooth muscle?
Smooth muscle characteristics are very different than skeletal and cardiac muscle types. Smooth muscle (also called visceral muscle) gets its name from the smooth appearance it has under a microscope. Unlike cardiac and skeletal muscle tissue, the actin and myosin filaments of smooth muscle tissue are not as well organized and pronounced. Thus, it has no apparent striation. Smooth muscle also appears more "messy." The muscle cells are not organized in straight lines or branching patterns but instead appear wispy and spindled. Each smooth muscle cell contains a single nucleus. Examine the example of smooth muscle tissue below.
What is muscle tissue?
Muscle tissue is a specialized contractile tissue in the body. When stimulated by an action potential (or electrical stimulating signal), muscle fibers contract and shorten. All movements in the body are cause by muscular contraction; thus, life would not be possible without muscle tissue.
How many types of muscle tissue are there?
There are three types of muscle tissue in the body:
Which muscle tissue is striated and contains intercalated discs?
Cardiac muscle tissue composes the muscular walls of the heart. It is striated and contains intercalated discs. The individual cells contain a single nuclei. This muscle tissue does not experience fatigue.
Which muscle tissue is ideal for continuous contractions like those found in the digestive system?
Unitary smooth muscle tissue: Unitary smooth muscle tissue is ideal for continuous contractions like those found in the digestive system.
Overview
Muscles are soft tissues. Many stretchy fibers make up your muscles. You have more than 600 muscles in your body. Different types of muscles have different jobs. Some muscles help you run, jump or perform delicate tasks like threading a needle. Other muscles allow you to breathe or digest food.
Function
Muscles play a role in nearly every system and function of the body. Different kinds of muscles help with:
Anatomy
All types of muscle tissue look similar. But there are slight differences in their appearance:
Conditions and Disorders
A wide range of disorders, diseases, drugs and injuries can cause problems with how the muscles work. They include:
Frequently Asked Questions
If you have muscle weakness or muscle pain that comes on suddenly, call your provider right away. Get emergency medical help if you have trouble breathing or swallowing, or if you have vision changes, chest pain or problems with balance. These could be signs of a serious health condition.
What is the difference between skeletal muscle and connective tissue?
Skeletal muscles differ in length, in depth and in thickness. Each muscle is interspersed with connective tissue and fat and is surrounded by connective tissue (called the epimysium or muscle sheath) which may vary in thickness over different parts of the muscle.
What is a muscle made of?
A single muscle is made up of many “bundles” (or fasciculi) of muscle cells or fibers held together by connect ive tissue (perimysium). The size of the bundles varies in different muscles in the same animal and in different species. When the fiber bundles are small, the meat has a fine grain.
How big are muscle fibers?
Muscle fibers vary greatly in length and have an average diameter of about 0.0002 inch. Muscles that are used for locomotion and power (e.g., in the legs and shoulders) have more connective tissue and yield less tender meat.
What are the three types of muscle tissue?
Muscle tissue can be of three types: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. Skeletal muscle is attached directly or indirectly to the bone and facilitates movement and/or gives support to the body. From an economic standpoint, skeletal muscle is the most important and it is the major component of the carcass. Cardiac, as the name implies, is the muscle ...
Which muscle is the heart?
Cardiac, as the name implies, is the muscle which forms the heart. Smooth muscles, also called visceral muscles, are found in the digestive and reproductive tracts as well as throughout the blood vessels, capillaries and arteries of the circulatory system. Skeletal muscles differ in length, in depth and in thickness.
