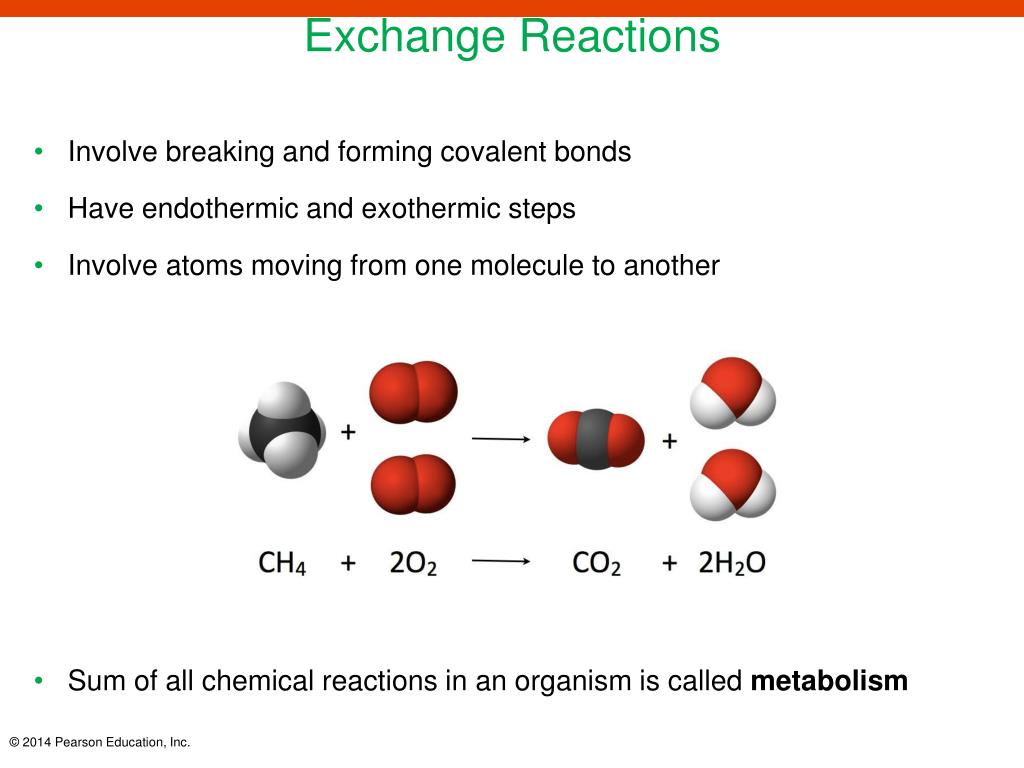
Which is the best example of synthesis?
Examples of sentence structures that demonstrate synthesis: Synthesis that indicates agreement/support: Source A asserts that…. Source B agrees when he or she states…. According to both A & B…. The combined conclusions of sources B & C seem to indicate that…. The evidence shows that…. Source B is correct that….
What are examples of a synthesis reaction?
Synthesis Reaction Examples
- Polymerization Reactions
- Organometallic Chemistry
- Metal-Catalyzed Reactions
- Flow Chemistry
- Design of Experiments (DoE)
- Low Temperature Chemistry
- Elevated Pressure Chemistry ( Hydrogenation Reactions)
- Enzyme Catalyzed Reactions Biocatalysis
- Oligonucleotide Synthesis
What is an example of synthesizing?
things. For example, when you report to a friend the things that several other friends have said about a song or movie, you are engaging in synthesis. However, synthesizing is much more than simply reporting. Synthesis is related to, but not the same as, classification, division, or comparison and contrast.
What best describes the process of synthesis?
The process of protein synthesis occurs in two major steps driven by enzymes inside a cell. First, deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) is transcribed to ribonucleic acid ( RNA) with the enzyme RNA polymerase. Second, the RNA is then translated into a protein molecule by ribosomes in the cell.

What is the most common type of synthesizer?
Subtractive synthesis is the method of starting with a harmonically rich waveform created by an oscillator and attenuating it with a filter to create your desired timbre. This type of synthesis is the most commonly used. It's associated with the classic synths that started it all.
What are the 3 types of synthesis?
While there are roughly 20 known types of synthesis, in this tutorial we will cover the three most popular ones: subtractive, FM and wavetable.
Which type of synthesis uses mathematical equations to process different aspects of sound?
Subtractive Synthesis Subtractive is the most common method that gave birth to the concept of sound synthesis. And is also one of the most popular synthesis types of all, perhaps due to its inherent simplicity and application.
What is type of synthesis?
Note that synthesizing is not the same as summarizing. There are two types of syntheses: explanatory syntheses and argumentative syntheses. Explanatory syntheses seek to bring sources together to explain a perspective and the reasoning behind it.
What are the 2 kinds of synthesis?
10 Types of Synthesis, Explained: FM, Vector, and MoreSubtractive Synthesis. Subtractive synthesis is perhaps the most common form. ... FM Synthesis. ... Sample-Based Synthesis. ... Wavetable Synthesis. ... Vector Synthesis. ... Additive Synthesis. ... Spectral Synthesis. ... Physical Modeling.More items...•
What are the types of synthesis in research?
A Review and Analysis of Approaches to Research Synthesis - PMC....Torraco [14] suggests they can be represented in four forms:A research agenda,A taxonomy or conceptual classification of constructs,Alternative models/conceptual framework, and.Metatheory.
What is the difference between additive synthesis and subtractive synthesis?
The difference between additive and subtractive synthesis is that the latter deconstructs sounds rather than building it up. It uses filters to attenuate partials of an audio signal to create the timbre.
What was the first type of synthesis to be invented?
One of the first synthesizers that would be recognised as such by modern musicians was created in 1964 after Bob Moog met Herbert Deutsch, and the former was inspired to create a voltage-controlled oscillator and amplifier module with a keyboard – but it wasn't until 1967 that Mr Moog called his diverse modular system ...
What is additive synthesis used for?
Additive synthesis is a technique which builds sounds from the bottom up, by incrementally adding simple waveforms together to achieve the desired resultss. Additive synthesis can be used to very accurately model almost any musical instrument, given enough computational resources.
What is an example of a synthesis?
It's simply a matter of making connections or putting things together. We synthesize information naturally to help others see the connections between things. For example, when you report to a friend the things that several other friends have said about a song or movie, you are engaging in synthesis.
What is direct synthesis in chemistry?
A synthesis reaction or direct combination reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which two or more simple substances combine to form a more complex product. The reactants may be elements or compounds, while the product is always a compound.
How do you do synthesis in research?
To effectively synthesize the literature, you must first critically read the research on your topic. Then, you need to think about how all of the ideas and findings are connected. One great way to think about synthesis is to think about the authors of the research discussing the topic at a research conference.
What is synthesis in the human body?
It is the process of combining two or more components to produce an entity. In biochemistry, it refers to the production of an organic compound in a living thing, especially as aided by enzymes. There are several syntheses occurring in the cell or organism.
What was the first type of synthesis to be invented?
One of the first synthesizers that would be recognised as such by modern musicians was created in 1964 after Bob Moog met Herbert Deutsch, and the former was inspired to create a voltage-controlled oscillator and amplifier module with a keyboard – but it wasn't until 1967 that Mr Moog called his diverse modular system ...
What are the types of nanomaterials synthesis method?
2. Methods of synthesis of metal nanoparticles1 The polyol method. The Polyol method is a chemical method for the synthesis of nanoparticles. ... 2 Microemulsions. An emulsion is a liquid in liquid dispersion. ... 3 Thermal decomposition. ... 4 Electrochemical synthesis.
What are synthesis of sentences?
Synthesis means the combination of a number of simple sentences into one new sentence – simple, compound or complex. The following are the chief ways of combining two or more simple sentences into one large simple sentence. By using a participle. He sprang up to his feet.
What is additive synthesis?
Additive synthesis is based on the principle that any sound can be expressed as a sum of simple sine waves. That means that any timbre, no matter how lush or complex, can be synthesized by combining enough sine waves of different frequencies and amplitudes. This had big implications for the earliest generation of synths.
What is the most common waveform used in subtractive synthesis?
It’s associated with the classic synths that started it all. The waveforms most commonly used in subtractive synthesis is are square, saw, sine and triangle. . A square wave has a naturally rich, buzzy sound with lots of overtones.
Why are additive synths digital?
That’s why most modern additive synths are digital—You need a lot of horsepower to run enough individual sine oscillators to create highly complex sounds. But today’s VST plugins are definitely up to the task. Modern additive synthesis is robust and cable of some truly amazing sounds.
What is granular wave synthesis?
Granular is a variation on wavetable synthesis where samples are broken down into microsecond fragments called “grains” and rearranged and manipulated.
What is wavetable synth?
Instead of traditional oscillators, wavetable synths load each individual slice of a digital sample into a “cell” in a table.
What is FM in synthesis?
FM or Frequency Modulation is a synthesis method that changes the timbre of one wave by modulating it with another.
How are different pitches created?
Different pitches are created by speeding up or slowing down the sample lookup rate.
What is synthesis?
Sound synthesis is the process of using electronics to create an electrical pressure soundwave from scratch and then controlling and modifying it.
What is the most common method of sound synthesis?
Subtractive is the most common method that gave birth to the concept of sound synthesis. And is also one of the most popular synthesis types of all, perhaps due to its inherent simplicity and application.
What is subtractive synthesis?
Subtractive synthesis is the most closely associated with the analog synthesizers of the ‘60s and ‘70s. In which the harmonics of simple waveforms, such as the ones previously mentioned, are attenuated with a voltage-controlled resonant low-pass filter.
What is the process of resynthesis?
The process of Resynthesis is highly connected to Additive Synthesis. In essence, Resynthesis involves analyzing the harmonic structure of a sampled sound and trying to recreate that structure. Additive Synthesis is essentially Resynthesis, excluding the fact that Resynthesis is the recreation of a specific existing sound, not a general instrument tone. Given this connection, additive synthesis is quite often used in Resynthesis processes.
What is wavetable synthesizer?
Wavetable Synthesis employs the use of a table with various switchable frequencies played in certain orders (wavetables). As a key is pressed, the sound moves in order through the wavetable, not spontaneously changing the waveform, but smoothly changing its shape into the various waves in the table.
How many waveforms are used in synthesis?
The basic concept behind any synthesis is that you are working primarily with 4 basic waveforms:
Why are synthesis methods combined?
Many of these synthesis methods are combined or layered within single programs to accommodate the creation of unique synthesizers. In understanding these methods, experimenting, and combining them, you´ll end up becoming the creative force behind sound-synthesis.
What is additive synthesis?
Additive synthesis is the type of synthesis which most closely emulates how sounds are produced in nature. Lots of sine waves at different frequencies are summed together to make complex waveforms. The problem with these synthesisers is that natural sounds are very complicated in their harmonic structure over time, so to accurately recreate a natural sound hundreds of individual sine-waves would need to be used which is why it was not used very often before the digital age but now was computer CPU becomes more powerful we are seeing a re-emergence of additive synthesis in software VST and AU form. Many new VSTs are boasting the power of a combination of different synthesis including the ability to load your own sounds into the synthesiser which then re-synthesises the sound using additive synthesis, allowing you the flexibility to edit the sound on an individual sine wave basis.
What is granular synthesis?
Granular synthesis is where a sample is cut up into tiny grains. These grains can then be manipulated either by duration, size, amount, pitch or amplitude. These can be used to create some completely crazy sounds. This type of synthesiser typically lends itself to long evolving textures and soundscapes due to its time stretching capabilities
How does subtractive synthesis work?
Subtractive synthesis works by starting with a complex waveform and subtracting sound away from it to give you the sound you want. Usually the sounds are made with between 1 and 3 oscillators and these will then be passed through filters where the sound can be filtered and sculpted into the final sound. As you can imagine the types of filters used are crucial to the end result as well as the envelopes used.#N#Subtractive synthesis generally creates very rich warm sounds (think anything Moog) however due to the analog circuitry there was often imperfections in drift and tuning.
What is FM synthesis?
Fm synthesis was the first affordable method of digital synthesis. It is renowned for making very realistic and harmonically rich sounds, in particular it is very good at emulating bell, glass and metal instruments. In FM the oscillators are called operators and rather than adding them together they can be set to modulate each other. The routing in which they are set to modulate is known as an algorithm and this makes a large impact on the final sound. One of the operators will be the carrier which is the main operator getting modulated.
Which synths use phase distortion?
The Casio CZ-1 one of few synths to use phase distortion successfully.
Is a synthesis an aha?
Often teachers identify a synthesis as an aha readers experience after combining multiple thoughts and thinking beyond the text. And this is accurate. However, the concept of an “aha” may be misinterpreted as including only brand-new understandings. There are actually three different types of syntheses.
Is a synthesis a new understanding?
In fact, if this is the only definition provided to students, many will think they rarely synthesize. However, a synthesis doesn’t have to be a new understanding, but a deeper realization of an initial thought.
How to identify a synthesis?
Remember, the key to identifying a synthesis or direct combination reaction is to recognize two or more reactants form a more complex product molecule.
What is a synthesis reaction?
Updated December 02, 2019. A synthesis reaction or direct combination reaction is one of the most common types of chemical reaction. In a synthesis reaction, two or more chemical species combine to form a more complex product: A + B → AB. In this form, a synthesis reaction is easy to recognize because you have more reactants than products.
Why is synthesis reaction easy to recognize?
In this form, a synthesis reaction is easy to recognize because you have more reactants than products. Two or more reactants combine to make one larger compound. One way to think of synthesis reactions is that they are the reverse of a decomposition reaction .
What will form a carbonate?
A metallic oxide and carbon dioxide will form a carbonate.
How many ATP molecules does ATP synthase make?from quizlet.com
ATP synthase makes about 28 molecules of ATP for each molecule of glucose. Glyolysis + Aerobic Respiration = 32 ATP.
What are some examples of simple sugars?from diabetestalk.net
The family of carbohydrates includes both simple and complex sugars. Glucose and fructose are examples of simple sugars, and starch, glycogen, and cellulose are all examples of complex sugars. The complex sugars are also called polysaccharides and are made of multiple monosaccharide molecules.
What are the three main pathways of metabolism?from diabetestalk.net
There are three groups of molecules that form the core building blocks and fuel substrates in the body: carbohydrates (glucose and other sugars); proteins and their constituent amino acids; and lipids and their constituent fatty acids. The biochemical processes that allow these molecules to be synthesized and stored (anabolism) or broken down to generate energy (catabolism) are referred to as metabolic pathways. Glucose metabolism involves the anabolic pathways of gluconeogenesis and glycogenesis, and the catabolic pathways of glycogenolysis and glycolysis. Lipid metabolism involves the anabolic pathways of fatty acid synthesis and lipogenesis and the catabolic pathways of lipolysis and fatty acid oxidation. Protein metabolism involves the anabolic pathways of amino acid synthesis and protein synthesis and the catabolic pathways of proteolysis and amino acid oxidation. Under conditions when glucose levels inside the cell are low (such as fasting, sustained exercise, starvation or diabetes), lipid and protein catabolism includes the synthesis (ketogenesis) and utilization (ketolysis) of ketone bodies. The end products of glycolysis, fatty acid oxidation, amino acid oxidation and ketone body degradation can be oxidised to carbon dioxide and water via the sequential actions of the tricarboxylic acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation, generating many molecules of the high energy substrate adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Interplay between metabolic pathways The interplay between glucose metabolism, lipid metabolism, ketone body metabolism and protein and amino acid metabolism is summarized in Figure 1. Amino acids can be a source of glucose synthesis as well as energy production and excess glucose that is not required for energy production can be stored as glycogen or metabo Continue reading >>
How is glucose produced in the body?from diabetestalk.net
Physiology • Glucose in the blood is derived from three main sources: ○ ▪ Glucose is the end-product of carbohydrate digestion, absorbed by enterocytes. ▪ Increased blood glucose concentrations occur 2 to 4 hours after a meal in simple-stomached animals. ○ Hepatic production ▪ Gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis within hepatic cells produce glucose when metabolically necessary. □ Gluconeogenesis converts noncarbohydrate sources, primarily amino acids (from protein) and glycerol (from fat), in simple-stomached animals. □ Glycogenolysis converts glycogen (poly-glucose) stored in hepatocytes to glucose through hydrolysis. ▪ Gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis within hepatic cells produce glucose when metabolically necessary. □ Gluconeogenesis converts noncarbohydrate sources, primarily amino acids (from protein) and glycerol (from fat), in simple-stomached animals. □ Glycogenolysis converts glycogen (poly-glucose) stored in hepatocytes to glucose through hydrolysis. ○ ▪ Gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis within renal epithelial cells can result in the formation of glucose when metabolically necessary. • The plasma concentration of glucose is controlled by a number of hormones, in particular, insulin and glucagon. The physiology of glucose homeostasis is controlled primarily by insulin release in response to elevated glucose levels (postprandial), although in birds, glucagon appears to serve as the primary regulator. Significant species variations in glucose levels have been noted. In general, levels are lowest in reptiles (60 to 100 mg/dL) and highest in birds (200 to 500 mg/dL), with mammals in between (100 to 200 mg/dL). Glucose that is not needed for energy is stored in the form of glycogen as a source of potential energy, readily available whe Continue reading >>
What enzyme is used to form acetyl CoA?from quizlet.com
An enzyme derived from the B vitamin pantothenic acid, to form acetyl CoA. The CoA escorts the acetic acid into the first reaction of the cirtci acid cycle. CoA is then stripped and recycled.
Which metabolic pathway involves the anabolic pathways of gluconeogenesis and glycogenesis?from diabetestalk.net
Glucose metabolism involves the anabolic pathways of gluconeogenesis and glycogenesis, and the catabolic pathways of glycogenolysis and glycolysis. Lipid metabolism involves the anabolic pathways of fatty acid synthesis and lipogenesis and the catabolic pathways of lipolysis and fatty acid oxidation.
What are the two gases that are central to energy metabolism?from diabetestalk.net
Duringthe eighteenth century, the initial studies, developed by Joseph Black, JosephPriestley, Carl Wilhelm Scheele, and Antoine Lavoisier, played a special rolein identifying two gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide, that are central to energymetabolism. Lavoisier, the French nobleman who owns the title of "father ofmodern chemistry," characterized the composition of the air we breathe andconducted the first experiments on energy conservation and transformation inthe organism. Oneof Lavoisier's main questions at this time was: How does oxygen's role incombustion relate to the process of respiration in living organisms? Using acalorimeter to make quantitative measurements with guinea pigs and later onwith himself and his assistant, he demonstrated that respiration is a slow formof combustion (Figure 1). Based on the concept that oxygen burned the carbon infood, Lavoisier showed that the exhaled air contained carbon dioxide, which wasformed from the reaction between oxygen (present in the air) and organicmolecules inside the organism. Lavoisier also observed that heat is continuallyproduced by the body during respiration. It was then, in the middle of the nineteenthcentury, that Justus Liebig conducted animal studies and recognized thatproteins, carbohydrates, and fats were oxidized in the body. Finally,pioneering contributions to metabolism and nutrition came from the studies of aLiebig's protg, Carl von Voit, and his talented student, Max Rubner. Voitdemonstrated that oxygen consumption is the result of cellular metabolism, while Rubner measured the major energy value of certain foods in orderto calculate the caloric values that are still used today. For example, carbohydrates and proteins produce approximately4 kcal/g of energy, whereas lipids can generate up to 9 kcal/g Continue reading >>
Additive Synthesis
Subtractive Synthesis
- Subtractive synthesis is the method of starting with a harmonically rich waveform created by an oscillator and attenuating it with a filterto create your desired timbre. This type of synthesis is the most commonly used. It’s associated with the classic synths that started it all. The waveforms most commonly used in subtractive synthesis is are square, saw, sine and triangle.. A square w…
FM Synthesis
- FM or Frequency Modulation is a synthesis method that changes the timbre of one wave by modulating it with another. The first commercially available FM synth was the massively popular Yamaha DX7 which basically defined the sound of the 80s. Compared to other forms of synthesis FM is fairly young. If the “FM” part of FM synthesis is sounding familiar, you’re on the right track. …
Wavetable Synthesis
- Wavetable synthesis is a method of synthesizing sound using sample-based waveforms as oscillators. Instead of traditional oscillators, wavetable synths load each individual slice of a digital sample into a “cell” in a table. The synth scrolls through the slices in the table one by one to output the sample as a sound. Different pitches are created by speeding up or slowing down th…
Other Types of Synthesis
- With the most common synthesis methods out of the way, there are a few outliers that are worth mentioning. These types of synthesis are related to the other styles I’ve covered, but with some differences that make them unique.
Synthesthesia
- We’re so spoiled for choice in the free VST era that it can be a struggle to figure out which tools are right for the job. With a little knowledge of the types of synthesis, you can learn anything synth by looking under the hood, rather than just checking out the paint job. So now that you know how they work, go find the style of synthesis that best suits your music productionflow!
What Is Synthesis?
What Is An Oscillator?
- An Oscillator is an electronic sound source. It is the device which creates the electrical pressure soundwave in a synthesizer. Oscillators can be analog or digital.
Cv, Gates & Midi
- Before digital control, analog synthesizers used an interconnecting arrangement of controlled voltage/gate signals to trigger their various components. For example, a key/note played on a keyboard would send a control voltage to an oscillator to tell it what pitch to produce, and another control voltage to an envelope which in turn would "instruct" an amplifier "shape" the volume env…
Patches
- In the early days of synthesis when only modular systems were available, sounds were created by connecting modules with patch cords and adjusting settings on each module. The settings and patch cord connections for a sound came to be referred to as patches. Recalling a patch was a laborious process until performance synthesizers began to integrate microprocessor control and …
Types/Methods of Synthesis
- The basic conceptbehind any synthesis is that you are working primarily with 4 basic waveforms: Layering and modulating them with each other in certain frequencies. Then you shape the sound with amplifiers and filter envelopesto achieve desired longevity. You are used to identifying musical intervals by their specific ever-present sound quality. You can do the same wi…
Wavetable
- A wavetable is a collection of single-cycle waveforms, or essentially samples of audio, that get played back on a loop to produce a periodic waveform or a continuous sound or tone. The speed of which those waveforms are played back, or the speed between each loop cycle, determines what you and I would call pitch or frequency. and in the digitally audio world, a MIDI note is esse…
Subtractive Synthesis
- Subtractive is the most common method that gave birth to the concept of sound synthesis. And is also one of the most popular synthesis types of all, perhaps due to its inherent simplicity and application. This type of synthesis is a very simple signal chain of an oscillator (or the combination of multiple oscillators) running through a filter (EQ curve) which is then sent to an amplifier for ga…
Additive
- Additive synthesis is a sound synthesis technique that creates timbre by adding sinewaves together. What this type of synthesis does, is trying to achieve the same result as Subtractive Synthesis, but approaching the method from a “constructive philosophy”, rather than just carving harmonics out. The sounds that are heard in everyday life are not characterized by a single freq…
FM
- FM (Frequency Modulation) synthesis was one of the first digital synthesis methods. It first appeared in the legendary Yamaha DX7. The way that FM synthesis works is that a simple waveform called a carrier (sine, saw, square, triangle) is modulated by another wave, called a modulator. The result is a far more complex waveform. This type was the first commercially succ…
Find Your Own Sound
- With these four synthesis types, you can create almost any sound you want. In the modern computer-era, the availability of VSTs in the market offers plenty of choices to pick from on our constant search to discover new sounds we´re all in. Contemporary music is always hungry for new timbres. Synth plugins are going to be your best friends here. With such a vast abundance …
Subtractive Synthesis
FM Synthesis
- FM, which stands for frequency modulation, is a digital form of synthesis whereby one waveform modulates another. Although there is analog FM synthesis (also known as "exponential FM synthesis" or sometimes "cross modulation"), usually, when people talk about FM, they're talking about the digital kind. Specifically, they're likely referring to the patented form of linear FM synth…
Sample-Based Synthesis
- Sample-based synthesis involves recording (or sampling) a sound into digital memory. Although commonplace now, in the late '70s and early '80s this was a novel and often expensive form of synthesis. Some of the first were the Fairlight CMI and New England Digital Synclavier—which were enormously expensive at the time. Later samplers, particularly Akai's rackmount S series a…
Wavetable Synthesis
- First developed by Wolfgang Palm in the late '70s, wavetable synthesis has become extremely popular as of late, due largely to its flexibility and ability to create evolving sounds. At its heart are digital oscillators that use wavetables, or groupings of single-cycle waveforms. Playback can move laterally across the waveforms, resulting in unique expressions of movement and sonic ch…
Vector Synthesis
- In contrast to wavetable synthesis, which interpolates between waveforms stacked side by side, vector synthesis gives the user control over the volume balance of four sampled waveforms arranged as if occupying four corners of a two-dimensional plane, with a joystick to crossfade between them. Vector synthesis debuted with Sequential Circuits' Prophet VS, and also appeare…
Additive Synthesis
- Where subtractive synthesis involves starting with harmonically rich sounds and paring back, additive synthesis is the opposite, using a number of harmonic partials of sine waves that, when added together (hence the name), create harmonically rich sounds. A Hammond organ, with its drawbars, is an example of a kind of additive synthesis. The 24-harmonic oscillator in Mutable In…
Spectral Synthesis
- Spectral synthesis is a kind of resynthesis that transforms a sound into a number of spectral bins, where each "bin" is a representation of its frequencies. The sound's noise content is also represented. This content is then displayed on a spectrogram, which represents the frequencies in terms of pitch as well as density. This allows for unique and targeted shaping of sound at the fre…
Physical Modeling
- Where basic subtractive synthesis can mimic the sound of physical acoustic instruments, physical modeling goes one further and digitally recreates the processes whereby a sound is made. This involves using digital signal processing (DSP) to recreate the various properties that make up the sound, usually the exciter (such as a bow on a stringed instrument or breath for a woodwind), th…
Granular Synthesis
- Granular synthesis is a kind of sample synthesis but one that acts almost microscopically on the sample, breaking it down into tiny parts, or grains, and allowing playback to jump around to different grains in the sample. Grain size, volume, position, etc., can be manipulated, resulting in new sounds. Tasty Chips GR-1 is a dedicated granular synthesis machine, while the Waldorf Qu…
West Coast Synthesis
- We started our tour of synthesis types with subtractive on the East Coast, so it seems fitting that we end on the West Coast. At the same time that Bob Moog was developing his subtractive analog synthesis in New York, Don Buchla was perfecting what would come to be called West Coast synthesis in San Francisco. Unlike East Coast subtractive synthesis, which starts with a c…