Full Answer
Is it normal to have a visible carotid pulse?
While the normal carotid pulse is typically palpable, not all are visible. Hyperdynamic states (e.g., sepsis) can make the pulse visible. These videos demonstrate the typical features of an arterial pulse.
What is the average carotid pulse rate?
The pulse felt on the neck is called the carotid pulse. When felt on the groin, it is called the femoral pulse. The normal apical pulse rate of an adult is 60 to 100 beats. Complete answer to this is here.
What is a normal internal carotid artery velocity?
The usual normal velocity of the common carotid artery is 30-40 cm/sec, but the velocity scale setting should be adjusted for each patient. What’s a good investment for 2022?
What is the normal tibial pulse rate?
Your pulse rate, also known as your heart rate, is the number of times your heart beats per minute. A normal resting heart rate should be between 60 to 100 beats per minute, but it can vary from minute to minute. Is 72 a good resting heart rate?
What is an abnormal carotid pulse?
Abnormalities of the carotid pulse may involve an alteration in the amplitude of the pulse peak, a distortion of the upstroke or downstroke, or any combination of these changes.
What is the average carotid pulse rate?
Children 10 years and older, and adults (including seniors): 60 to 100 beats per minute. Well-trained athletes: 40 to 60 beats per minute.
Is it normal for your carotid artery to pulsate?
Overview. The carotid arteries take oxygenated blood from the heart to the brain. The pulse from the carotids may be felt on either side of the front of the neck just below the angle of the jaw. This rhythmic "beat" is caused by varying volumes of blood being pushed out of the heart toward the extremities.
Is carotid pulse same as heart rate?
A pulse is the heart rate, or the number of times your heart beats in one minute. The pulse can be measured using the radial artery in the wrist or the carotid artery in the neck. Heart rates vary from person to person. Knowing your heart rate can help you gauge your heart health.
What are good numbers for carotid artery?
The usual normal velocity of the common carotid artery is 30-40 cm/sec [19], but the velocity scale setting should be adjusted for each patient.
What are the signs and symptoms of a blocked carotid artery?
Carotid Artery Blockage SymptomsBlurred vision or vision loss.Confusion.Memory loss.Numbness or weakness in part of your body or one side of your body.Problems with thinking, reasoning, memory and speech.
What does pulse 2+ mean?
Zero refers to a nonpalpable pulse, 1+ is a barely detectable pulse, 2+ is slightly diminished but greater than 1+, 3+ is a normal pulse and should be easily palpable, and 4+ is “bounding” (e.g., stronger than normal).
Why is my carotid pulse stronger on one side?
Carotid Artery Pulses Stronger on Left Side But you can feel your carotid artery on the left, right? Don't worry; it is not a disorder or something. It happens because of variations in the positioning of the artery.
Can you feel a blockage in your carotid artery?
Carotid artery disease often does not cause symptoms until the blockage or narrowing is severe. One sign may be a bruit (whooshing sound) that your doctor hears when listening to your artery with a stethoscope.
What is a good pulse rate?
Answer From Edward R. Laskowski, M.D. A normal resting heart rate for adults ranges from 60 to 100 beats per minute.
What is normal pulse by age?
Normal Heart Rate by Age ChartAgeNormal Resting Heart RateChildren 5 to 6 years old75 to 115 bpmChildren 7 to 9 years old70 to 110 bpmChildren 10 years and older and adults (including seniors)60 to 100 bpmAthletes in top condition40 to 60 bpm4 more rows•Nov 3, 2022
How does the carotid pulse different from the jugular pulse?
Commonly, a prominent pulsation is mistaken for that of the carotid artery rather than of the JVP. To differentiate, press on the RUQ while watching the neck. The JVP should rise in all individuals with this maneuver; whereas a carotid pulsation should not change.
What does a strong pulse in your neck mean?
A bounding pulse is a strong throbbing felt over one of the arteries in the body. It is due to a forceful heartbeat. The carotid arteries take oxygenated blood from the heart to the brain. The pulse from the carotids may be felt on either side of thefront of the neck just below the angle of the jaw.
What does pulse 2+ mean?
Zero refers to a nonpalpable pulse, 1+ is a barely detectable pulse, 2+ is slightly diminished but greater than 1+, 3+ is a normal pulse and should be easily palpable, and 4+ is “bounding” (e.g., stronger than normal).
What percentage of carotid artery requires surgery?
Surgery is usually advised for carotid narrowing of more than 70%. Surgical treatment decreases the risk for stroke after symptoms such as TIA or minor stroke.
What is the purpose of a carotid pulse examination?
Examination of the carotid pulse is generally directed toward evaluating the status of the heart. While palpation of the carotid pulse is the most important component, the examination should also include inspection and auscultation.
Why is there an inequality in the pulse amplitude in the carotid arteries?
An inequality between the pulse amplitude in the two carotid arteries usually reflects atherosclerosis. Other possible explanations include aortic dissection, arteritis, or embolus. Kinking of the carotid artery is occasionally seen in a hypertensive patient and may simulate an aneurysm.
How does arterial distensibility affect pulse pressure?
As the rate of ventricular ejection accelerates, the arterial wall stiffens and the pulse pressure increases. The amplitude of the pulse pressure can also be modified by the "peripheral runoff.".
What is the purpose of palpation of the carotid pulse?
Palpation of an arterial pulse may be directed toward assessing cardiac performance, determining cardiac rate and rhythm, establishing the integrity of the peripheral arterial blood supply, or localizing peripheral lesions. Examination of the carotid pulse is generally directed toward evaluating the status of the heart.
Why is palpation of the carotid pulse after a premature beat important?
Palpation of the carotid pulse after a premature beat may be very helpful because certain pulse abnormalities are accentuated following a premature contraction. Basic Science.
How does the height of the pulse affect the stroke volume?
Consequently, a given stroke volume will produce a larger pulse pressure if the mean arterial pressure is elevated . Arterial distensibility is also inversely related to the rate of rise of intraluminal pressure. As the rate of ventricular ejection accelerates, the arterial wall stiffens and the pulse pressure increases. The amplitude of the pulse pressure can also be modified by the "peripheral runoff." An accelerated runoff will lower the diastolic pressure and result in higher amplitude of the pulse pressure.
What is the carotid pulse?
The carotid pulse is characterized by a smooth, relatively rapid upstroke and a smooth, more gradual downstroke, interrupted only briefly at the pulse peak. These palpable pulsatile changes in the carotid arterial diameter are virtually identical to the intraluminal pressure pulse.
Why do doctors listen for carotid bruits?
Many physicians listen for bruits over the carotid arteries because asymptomatic carotid bruits are associated with an increased incidence of cerebrovascular and cardiac events in older patients ( Chapters 413 and 414Chapter 413Chapter 414 ). In asymptomatic patients, the presence of a carotid bruit increases the likelihood of a 70 to 90% stenotic lesion (LR 4 to 10), but the absence of a bruit is of uncertain value. Unfortunately, clinical data do not provide adequate data for judging the importance of detecting bruits in asymptomatic patients.
What is Pulsus Parvus et tardus?
Pulsus parvus et tardus describes a carotid pulse with a small volume (pulsus parvus) that rises slowly and has a delayed systolic peak (pulsus tardus; see Fig. 15.1 ). 22 It is routinely detected by palpation.
Why is the dicrotic wave followed by the dicrotic wave?
The dicrotic notch may be followed by the dicrotic wave (DW) because of the reflected pulse from the lower body. The carotid pulse trace is affected by valvular imperfections such as mitral insufficiency and aortic stenosis; however, it is not commonly employed in clinical diagnosis.
What is the CP of the aorta?
The carotid pulse (CP) is a pressure signal acquired over the carotid artery as it passes near the surface of the body at the neck. It delivers a pulse signal signifying the variations in arterial blood pressure and volume with each heartbeat. Because of the proximity of the recording site to the heart, the CP signal closely looks like the morphology of the pressure signal at the root of the aorta. The CP is a beneficial assistant to the PCG and can help in the recognition of S2 and its components. The CP increases sharply with the ejection of blood from the left ventricle to the aorta, reaching a peak called the percussion (P) wave. This is followed by a plateau or a secondary wave known as the tidal (T) wave, resulting from a reflected pulse returning from the upper body. Next, closure of the aortic valve results in a notch known as the dicrotic (D) notch. The dicrotic notch may be followed by the dicrotic wave (DW) because of the reflected pulse from the lower body. The carotid pulse trace is affected by valvular imperfections such as mitral insufficiency and aortic stenosis; however, it is not commonly employed in clinical diagnosis. The CP signals have a nominal bandwidth of 0–100 Hz and usually recorded with the PCG and ECG signals. Location of the CP transducer needs careful choice of a location on the neck as close to the carotid artery as possible, in which the pulse is felt the strongest, usually by a trained technician ( Rangayyan, 2015 ).
Why should carotid pulses be palpated?
The carotid pulses should be palpated for contour and timing in relation to the cardiac impulse. Abnormalities in the carotid pulse contour reflect underlying cardiac abnormalities (e.g., aortic stenosis) but are generally appreciated only after detecting an abnormal cardiac impulse or murmur ( Chapter 50 ).
What is Pulsus tardus?
Pulsus tardus depends on both obstruction to flow and the compliance of the vessel distal to the obstruction. The pulse waveform rises rapidly in stiff vessels but slowly in more compliant vessels that act like low-pass filters and remove the high frequency components of the waveform. 68 That the delay in the pulse reflects the severity of obstruction is a principle also used by Doppler sonography to gauge the severity of renal artery stenosis. 68
Where does aortic stenosis radiate?
The murmur of aortic stenosis radiates to the carotid arteries in the majority of patients as the turbulent jet is directed superiorly into the ascending aorta, allowing transmission of sound through the aorta to the carotid arteries. In a minority of patients, the murmur radiates to the apex, a pattern referred to as the Gallavardin phenomenon. 104
Carotid Pulse
The jugular venous pulse must be distinguished from the carotid pulse. There are important differences between arterial and venous pulses that allows the examiner to distinguish them at the bedside. The normal carotid arterial pulse is characterized by a single peak that is quick and sharp.
Patient 1
This patient was admitted to the hospital for an unrelated condition and was noted to have a normal carotid pulse visible at the bedside. While the normal carotid pulse is typically palpable, not all are visible. Hyperdynamic states (e.g., sepsis) can make the pulse visible. These videos demonstrate the typical features of an arterial pulse.
Patient 2
This is a young woman with cystic fibrosis who was admitted for an exacerbation. She was noted to have a visible normal carotid pulse.
Patient 3
This is a middle-aged woman who was admitted to the hospital with heart failure with preserved systolic function. She has a normal visible carotid pulse.
Patient 4
This is an older woman with metastatic carcinoid syndrome who developed infective endocarditis of the tricuspid and aortic valves. She has an easily visible arterial pulse in the neck; note the single outward pulsation that is quick and sharp.
What is the doppler trace of CCA?
Ultrasound of the CCA will have a doppler trace that is representative of both upstream and down stream influences. Any cardiac arhythmia or significant left heart valvular problems may be relected in the wave form (eg via a audible and visible ‘flutter’). Similarly, the CCA waveform is a combination of both ICA and ECA waveforms.
What causes high diastolic flow in the carotid artery?
Similarly, if there is low systolic, high diastolic flow in the common carotid artery this may be related to CCA origin or subclavian pathology.
Which artery has a smaller diameter?
Identify the origins of the ICA and ECA arteries. The ECA has small branches (usually the thyroglossal artery). The ECA also usually has a smaller diameter, arises laterally and has a higher resistance waveform (ie lower diastolic flow than a normal ICA).
What is the purpose of the mid-distal CCA slide?
From the mid-distal CCA slide and angle posteriorly to visualise the cervical transverse processes and the vertebral artery.
What is the best angle for doppler shift?
Ideally an angle of 0 degrees provides least error and greatest doppler shift. This is rarely acheivable but as we approach 0 degrees, our human inter-observer error error is diminishing.
What is the purpose of colour in vessel design?
Use colour to assess patency of vessel and the direction of flow.
What are the factors to consider when assessing vessels in B mode?
Begin the examination by assessing vessels in B-Mode, optimising factors such as frequency, depth, gain, TGC and focal zone.
How to assess carotid artery amplitude?
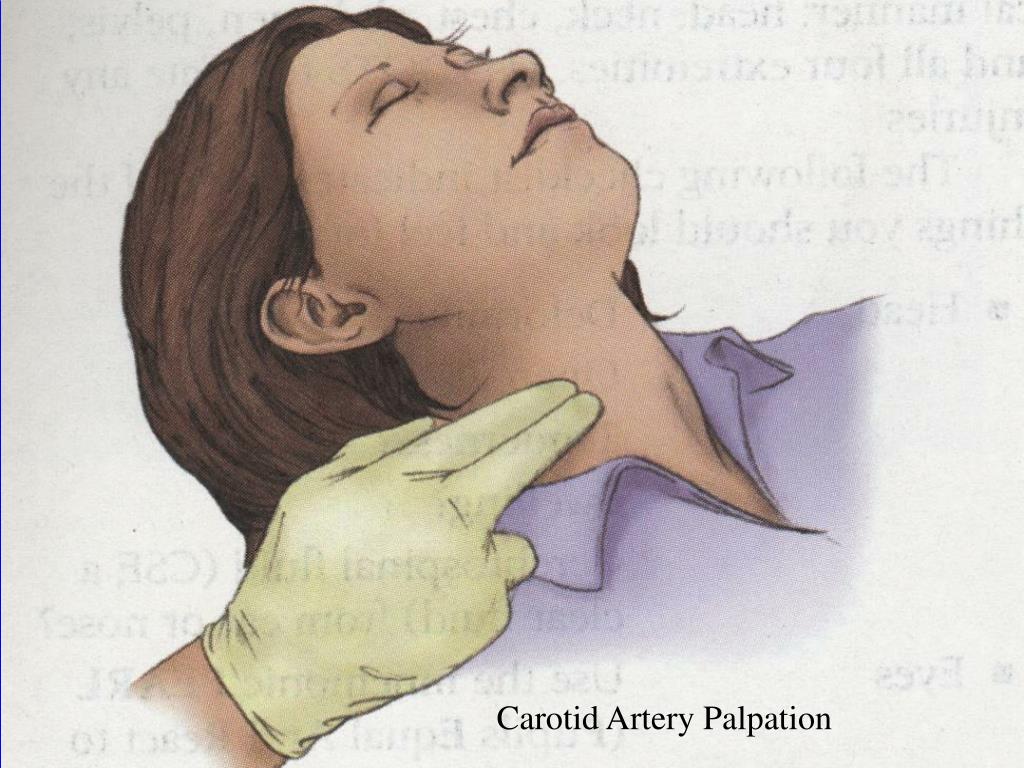
To assess amplitude and contour, the patient should be lying down with the head of the bed still elevated to about 30°. When feeling for the carotid artery, first inspect the neck for carotid pulsations. These may be visible just medial to the sternomastoidmuscles. Then place your left index and middle fingers (or left thumb11) on the right carotid artery in the lower third of the neck, press posteriorly, and feel for pulsations.
What happens after you measure JVP?
After you measure the JVP, move on to assessment of the carotid pulse. The carotid pulse provides valuable information about cardiac function and is especially
Which artery is most accurate for aortic pulsations?
The Brachial Artery. The carotid arteries reflect aortic pulsations more accurately, but in patients with carotid obstruction, kinking, or thrills, they are unsuitable. If so, assess the pulse in the brachial artery, applying e techniques described above for etermining amplitude and contour.
How to relax bicepstendon?
your hand under the patient's elbow and feel for the pulse just medial to the bicepstendon. The patient's arm should rest with the elbow extended, palm up. With your free hand, you may need to flex the elbow to a varying degree to get optimal muscular relaxation. Continue reading here: The Heart.
Do you hear a bruit in the carotid arteries?
You should also listen for bruits over the carotid arteries if the patient is middle-aged or elderly or if you suspect cerebrovascular disease. Ask the patient to hold breathing for a moment so that breath sounds do not obscure the vascular sound. Heart sounds alone do not constitute a bruit.
Can carotid sinus pressure cause a reflex drop in pulse rate?
Pressure on the carotid sinus may cause a reflex drop in pulse rate or blood pressure. See Table 3-9, Abnormalities of the Arterial Pulse and Pressure Waves (p. ■ The amplitude of the pulse. This correlates reasonably well with the pulse pressure.
Where to press on sternomastoid muscle?
Press just inside the medial border of a well-relaxed sternomastoid muscle, roughly at the level of the cricoid cartilage. Avoid pressing on the carotid sinus, which lies at the level of the top of the thyroidcartilage. For the left carotid artery, use your right fingers or thumb.
What is the name of the pulse that is felt over the brachial artery at the inner aspect of the elbow?
bisferious pulse pulsus bisferiens. brachial pulse that which is felt over the brachial artery at the inner aspect of the elbow; palpated before taking blood pressure to determine location for the stethoscope. capillary pulse Quincke's pulse.
What does it mean when your pulse is weaker?
If a pulse is noted to be weaker during inhalation and stronger during exhalation ( pulsus paradoxus ), this could indicate either greater reduction in the flow of blood to the left ventricle than is normal, as in constrictive pericarditis or pericardial effusion, or a grossly exaggerated inspiratory maneuver, as in tracheal obstruction, asthma, or emphysema.
Why is the examiner's thumb never used to take a pulse?
The examiner's thumb is never used to take a pulse because its own pulse is likely to be confused with that of the patient. Pressure should be light; if the artery is pressed too hard, the pulse will disappear entirely. The number of beats felt in exactly 1 minute is the pulse rate.
What is a jerky pulse?
jerky pulse one in which the artery is suddenly and markedly distended. paradoxical pulse one that markedly decreases in amplitude during inhalation, as often occurs in constrictive pericarditis. pistol-shot pulse Corrigan's pulse. plateau pulse one that is slowly rising and sustained.
Where is the carotid pulse felt?
carotid pulse the pulse felt over the carotid artery, which lies between the larynx and the sternocleidomastoid muscle in the neck; frequently used to assess effectiveness of cardiac massage during cardiopulmonary resuscitation. It can be felt by pushing the muscle to the side and pressing against the larynx, or, if the patient is dyspneic, by palpating the pulse at the groove in the muscle.
What is tricrotic pulse one?
tricrotic pulse one in which the tracing shows three marked expansions in one beat of the artery.
What is felt in the veins?
What is felt is not the blood pulsing through the arteries (as is commonly supposed) but a shock wave that travels along the walls of the arteries as the heart contracts. This shock wave is generated by the pounding of the blood as it is ejected from the heart under pressure. It is analogous to the hammering sound heard in steam pipes as the steam is forced into the pipes under pressure. A pulse in the veins is too weak to be felt, although sometimes it is measured by sphygmograph (see below); the tracing obtained is called a phlebogram.