What is the objective of assembly line balancing and how does it relate to the definition of a process?
Definition: Assembly Line Balancing (ALB) optimizes the mass production process by dividing tasks into workstations and allocating equal processing time to each one without any delay. The assembly line in which the workstations have equal processing time with less or no ideal time is said to be a perfect one.
What is the importance of line balancing?
Line balancing ensures that all operators and machines work together in a balanced fashion. No operator or machine should be overburdened or idle. By minimizing downtime, line balancing reduces waiting waste.
What is the goal of line balancing what happens when a line is unbalanced?
The main goal of line balancing is to achieve a set of task groupings at workstations in the line that have equal time requirements to attain high utilization of labor and equipment. Unbalanced lines have bottlenecks at some workstations and idle time at others.
What is the assembly line balancing problem?
The assembly line balancing problem (ALBP) involves distributing the tasks needed to manufacture any unit of the products to be assembled among the work stations along a manufacturing line. It is usually assumed that the required tasks cannot be split, that is, each must each be performed at a single station.
What is meant by assembly line balancing?
ALB, or simply line balancing, is arranging the individual processing and assembly tasks at the workstations so that the total time required at each workstation is approximately the same. From: Production Planning and Control, 2019.
What are the types of assembly line balancing?
There are two types of line balancing that include Static Balance and Dynamic Balance.
How do you do production line balancing?
Steps in Assembly Line BalancingOutline your workstation sequence and draw a precedence diagram. ... Estimate the needed cycle time for each workstation. ... Calculate the hypothetical number of workstations you will need. ... Start assigning tasks to the workstations until the process times are equal.More items...
What is cycle time in assembly line balancing?
Cycle time is one of the important data for the line balancing at any production line. The time required to finish one product, or the total time takes before the product leaves the workstation and move to the next workstation is called cycle time.
How do you solve a line balancing problem?
For solving line balancing problems a number of methods are available, for example Heuristic, linear programming model, dynamic programming and comsoal (a computer method for sequencing operations for assembly lines). For intermittent flow system normally heuristic methods are preferred.
How does an assembly line work?
Assembly lines are manufacturing systems in which work-in-progress moves from station to station in a sequential fashion. At each workstation, new parts are added or new assemblies take place, resulting in a finished product at the end.
What is the disadvantage of assembly line balancing Mcq?
The main disadvantage is its inflexibility.} 13. For an assembly line if balance delay is high then efficiency will be low and vice versa.
What is line balancing PDF?
Assembly Line Balancing is the problem of assigning operations to workstations along an assembly line; in such a way that the assignment be optimal in some case. The minimization of the number of workstations and maximization of the production efficiency are the most common goals in the line balancing.
What is line balancing in plant layout?
Line balancing is used to achieve the same level of production at each station [5]. Systematic layout planning (SLP) is used to improve spatial distances between facilities (machines and work stations) and also improve the flow of material at a plant.
What are some of the benefits of balancing cycle time and takt time?
Achieve a consistent flow of production. Eliminate the waste of overproduction by producing to meet actual customer demand. Encourage the development of standardized work instructions thus promoting quality and efficiency. Enable managers to set real time targets for production.
Which method of line balancing is the most efficient method?
Heuristic Method of Line Balancing: Heuristic approach produced very good results when Wester and Kilbridge applied it to T.V. assembly line problems (with 133 steps).
How do you solve a line balancing problem?
0:1716:08Line Balancing Example - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipFirst. We are going to identify task. Times and precedence relationships. In our Excel project thisMoreFirst. We are going to identify task. Times and precedence relationships. In our Excel project this part will be provided. Second we are going to determine cycle time and then determine theoretical
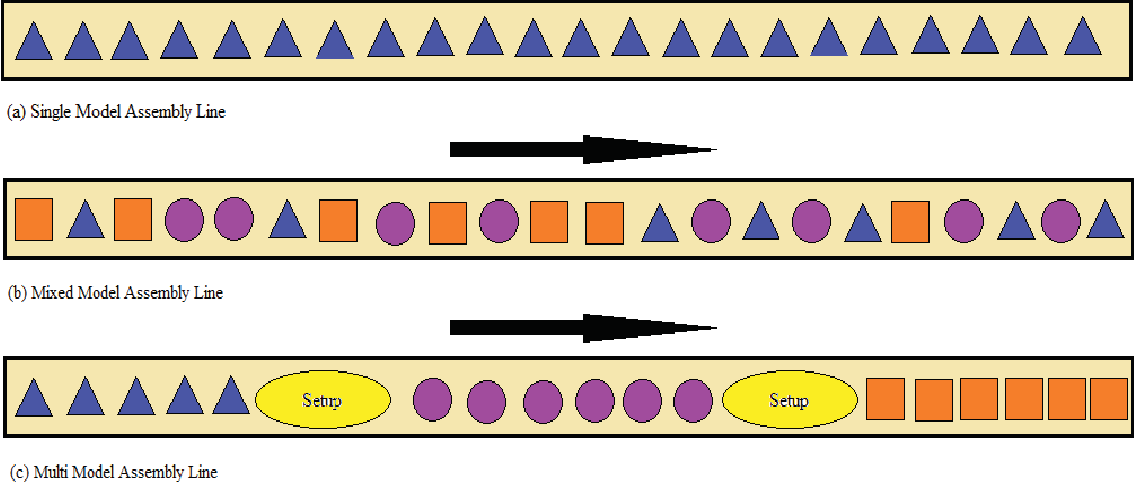
What is assembly line balancing?
Assembly line balancing is a production strategy that sets an intended rate of production to produce a particular product within a particular time frame. Also, the assembly line needs to be designed effectively and tasks needs to be distributed among workers, machines and work stations ensuring that every line segments in the production process can be met within the time frame and available production capacity. Assembly line balancing can also be defined as assigning proper number of workers or machines for each operations of an assembly line so as to meet required production rate with minimum or zero ideal time.
How many workers are on an assembly line?
The assembly line has 5 workers (work stations) stationed on the line as follows where back tracking is not allowed.
1. INTRODUCTION
Assembly line balancing is a production strategy that sets an intended rate of production to produce a particular product within a particular time frame.
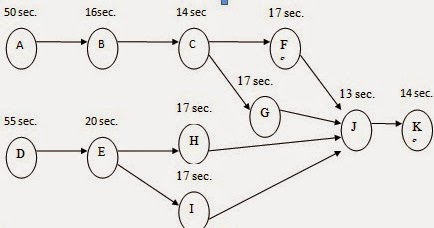
2. ASSEMBLY LINE PROBLEM
Problem: The below product in a factory is assembled in an assembly line. This process needs to be re-arranged to find a balance that minimizes the workstation cycle time.
3. CONCLUSION
In the above example we could clearly understand that with proper arrangement and allocation of activities and tasks to individual workstations in assembly, we could increase production by 14%.