Explore
The patellar tendon tests the nerves along the second through fourth lumbar vertebrae. (L2, L3, L4) The biceps tendon (C5, C6), triceps tendon (C6, C7, C8), and brachioradialis tendon test the cervical nerves along the 5th, 6th and 7th vertebrae (C5, C6, C7).
What nerve is tested for a patellar reflex test?
The patellar reflex is a deep tendon reflex, mediated by the spinal nerves from the levels L2, L3, and L4 in the spinal cord, predominantly in the root L4. The patellar reflex test is performed to determine the integrity of the neurological function, which is accomplished by hitting the patellar tendon below the knee cap with a test hammer [ 2 ].
What nerve is tested in patellar reflex?
What does an abnormal patellar reflex indicate? The normal response is a 'knee jerk'. This is an example of a reflex, which is an involuntary muscular response elicited by the rubber hammer tapping the associated tendon. When reflex responses are absent this could be a clue that the spinal cord, nerve root, peripheral nerve, or muscle has been damaged.
What does an abnormal patellar reflex indicate?
What is a normal patellar reflex? The patellar reflex occurs when an abrupt change arises in muscle length; in this case, it is produced by the tendon stretching, which is caused when the hammer stroke is applied [3, 4]. The normal response must be a sudden leg extension.
What is a normal reaction for the patellar reflex?

What is the purpose of the patellar reflex?
The primary purpose of the patellar reflex – the stretch reflex of the quadriceps femoris muscle – is to prevent excessive stretching of the quadriceps.
What happens when you test the patellar reflex?
0:071:01Patellar Reflex Test | Knee Reflex Examination of Deep TendonsYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe leg out and then that tendon will pop out and that is where you're gonna go okay after locatingMoreThe leg out and then that tendon will pop out and that is where you're gonna go okay after locating the tendon put your hand behind the knee just to support it have them relaxed.
What muscle does the patellar reflex test?
0:411:532-Minute Neuroscience: Knee-jerk Reflex - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWhen the patellar tendon of the quadriceps muscle is stretched the stretch is detected by stretchMoreWhen the patellar tendon of the quadriceps muscle is stretched the stretch is detected by stretch receptors known as muscle spindles that are found in the quadriceps muscle.
What does it mean if you have no knee reflex?
The normal response is a 'knee jerk'. This is an example of a reflex, which is an involuntary muscular response elicited by the rubber hammer tapping the associated tendon. When reflex responses are absent this could be a clue that the spinal cord, nerve root, peripheral nerve, or muscle has been damaged.
What does it mean when the doctor hits your knee and it doesn't move?
If your doctor taps on a tendon and there isn't a reflexive movement in the muscle, it's a sign of a health issue. Usually, absent reflexes are caused by an issue with the nerves in the tendon and muscle. You may have other muscle symptoms along with areflexia, like weakness, twitching, or atrophy.
What causes poor reflexes in legs?
The most common cause of low reflex response is peripheral neuropathy. Diabetes, anemia, and vitamin deficiency are possible causes of absent reflexes.
Why do doctors tap your knee?
Ed. INDIANAPOLIS (WISH) – The strike just below the kneecap is designed to test our reflexes, The tap should quickly fire your neuromuscular system triggering nerve receptors in the tendons. This kicks off nerve impulse transmission up the spinal cord.
What was the effect of muscle fatigue on your ability to produce the patellar reflex?
What was the effect of muscle fatigue on your ability to produce the patellar reflex? The response was lesser than usual. Pupillary light reflex: protects the retina(s). Corneal reflex: protects the eye from damage.
What causes the patellar reflex quizlet?
When patellar is stretched, the response is a rapid extension of the leg at the knee. The patellar reflux involves the rapid contraction of QUADRICEPS FEMORIS when a stretched patellar ligament is tapped. The result is rapid knee extension.
What happens during knee-jerk reflex?
The sharp tap on the tendon slightly stretches the quadriceps, the complex of muscles at the front of the upper leg. In reaction these muscles contract, and the contraction tends to straighten the leg in a kicking motion.
How is the knee-jerk reflex tested?
To test your knee jerk reflex, a doctor or nurse practitioner raps a small hammer on the tendon below your kneecap. A split second later, when you kick the person with the hammer, it's because the lightning-quick knee jerk reflex occurred within the spinal cord.
What is the purpose of the patellar reflex?
The primary purpose of the patellar reflex, which is the stretch reflex of the quadriceps femoris muscle in your anterior thigh, is to prevent the stretching of the quadriceps. The patellar reflex is illustrated in Figure 2. The patellar tendon attaches the quadriceps muscle to the tibia bone of the lower leg.
Why do doctors test the patellar reflex?
Medical author Dr Janice Rachel Mae explains that doctors routinely use reflex tests to check if there are any problems in the nervous system involved in movement, nerve functioning or health of the connective tissue in the knee or leg.
What does an abnormal patellar reflex indicate?
Abnormal patellar tendon reflexes can indicate neurological disease. [4] [5] [6] [7] In particular, diminished reflex responses are associated with the peripheral nervous system (PNS) disorders, while hyper reflexive responses are related to the central nervous system (CNS) disorders.
Does the patellar reflex involve the brain?
The normal knee-jerk or, “patellar jerk,” reflex is elicited when the knee is tapped below the knee cap (patella). Sensors that detect stretching of the tendon of this area send electrical impulses back to the spinal cord. The brain is never involved in the reflex.
What nerve causes knee jerk?
Although the knee jerk reflex is mediated by the L3 and L4 nerve roots, evidence exists that altered knee jerk expression may occur with exclusively L5 radiculopathy.
What is abnormal reflex?
Definition. An abnormal response to a stimulus applied to the sensory components of the nervous system. This may take the form of increased, decreased, or absent reflexes. [ from MeSH].
What happens during the patellar reflex?
Knee-jerk reflex, also called patellar reflex, sudden kicking movement of the lower leg in response to a sharp tap on the patellar tendon, which lies just below the kneecap. In reaction these muscles contract, and the contraction tends to straighten the leg in a kicking motion.
What is the hammer that pulls the patellar ligament back?
Instead then, doctors tap the patellar ligament with their little hammer (which is actually called a ‘reflex hammer’). When they do this, it causes the muscle spindle in the quadriceps muscle to stretch and that in turn triggers the reflex response to pull the muscle back.
Why This Test?
That’s all good and well then, but what do doctors stand to learn from all this? Do they just enjoy hitting people with tiny hammers? And why don’t they play MC Hammer at the same time ?
Can a doctor test your reflexes?
A doctor wanting to test your reflexes though is unlikely to try yanking your arm against your will. That would be awkward and the fact you knew it was coming would make it tricky for them to get accurate results.
Can a reflex test be used to detect cerebellar disease?
On the other hand, this test can be used to look for reflex problems – the absence of this reaction can be an early sign of cerebellar disease for instance.
Why is patellar reflex tested in infants?
The patellar reflex is often tested in infants to test the nervous system.
What is the patellar reflex?
The patellar reflex or knee-jerk (in American English knee reflex) is a stretch reflex which tests the L2, L3, and L4 segments of the spinal cord.
Which muscle is striked with a reflex hammer?
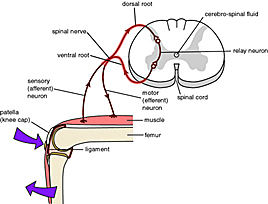
Striking of the patellar tendon with a reflex hammer just below the patella stretches the muscle spindle in the quadriceps muscle. This produces a signal which travels back to the spinal cord and synapses (without interneurons) at the level of L3 or L4 in the spinal cord, completely independent of higher centres.
Who invented the term "knee jerk"?
The term knee-jerk was recorded by Sir Michael Foster in his Textbook of physiology in 1877: "Striking the tendon below the patella gives rise to a sudden extension of the leg, known as the knee-jerk.".
Is the patellar reflex a monosynaptic reflex?
The patellar reflex is a clinical and classic example of the monosynaptic reflex arc. There is no interneuron in the pathway leading to contraction of the quadriceps muscle. Instead, the sensory neuron synapses directly on a motor neuron in the spinal cord. However, there is an inhibitory interneuron used to relax the antagonistic hamstring muscle ...
What is the purpose of patellar reflex test?
The patellar reflex test is done in order to check thesensory response when the doctor strikes the patellar tendon hammer a littleunder the knee cap. The main purpose is to determine the state of the nervoussystem; whether it is good or not, and whether there is any damage to the motornerve or spinal cord.
Why is patellar reflex important?
When it comes to the importance of the patellar reflex, itis important to mention that it plays a significant role in maintaining the postureand balance, thus allowing a person to walk without having to think about everysingle step. Patellar reflex test and its purpose.
What is the function of patella?
Patella is a bone in the knee, or, tobe more precise, it is the knee cap, and it functions as the knee extension,increasing the force of the tendon on the femur. Patellar reflex is actuallyanother term for the knee jerk, which is a typical reaction when, for example,a doctor taps on the patellar tendon, which is located under the knee, ...
What is the patellar reflex?
The patellar reflex is a deep tendon reflex, mediated by the spinal nerves from the levels L2, L3, and L4 in the spinal cord, predominantly in the root L4. The patellar reflex test is performed to determine the integrity of the neurological function, which is accomplished by hitting the patellar tendon below the knee cap with a test hammer [2].
What is the test for patellar tendon?
Test A. A physician gives a sharp tap on the patellar tendon with a standard clinical hammer. The physician evaluates the reflex response using the NINDS scale. Dafkin et al. [10] established using stepwise multiple regression analysis that different groups of subjective raters all relied on the change of the knee angle to assess the reflex. Therefore, the trained physician was asked to focus on this feature to provide his rating for the analyzed patients.
What scale is used to measure reflexes?
The result of the test is commonly rated using the scales of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) and the Mayo Clinic [6]; in this work, we use the former one. This scale measures the response magnitude assigning a different number of “crosses” (+), whereby zero crosses (0+) indicate an exam with no visible answer; one cross (1+) corresponds to a slight reflex; two crosses (2+) indicate a reflex in the lower half of the normal range; three crosses (3+) are a reflex in the upper half of the normal range; and four crosses (4+) mean the reflex is significantly enhanced [6].
How are classifiers tested?
Classifiers are tested with different combinations of the extracted features. Because the size of the dataset is relatively small, each classifier is tested using leave-one-out cross validation. Moreover, the data are preprocessed for feature reduction using principal component analysis (PCA).
What is reflex test?
These tests are actually part of a neurological exam done for spinal cord injuries or neuromuscular conditions— to check whether or not the nerves in the spine are still functioning.
What is the test called when you see if you have reflexes?
When people go for check-ups, doctors usually use a tool to see how patients’ reflexes respond to that tool. This is called the reflex test .
Why is it important to have reflex tests?
Why it is important to have reflex tests. Reflex tests help doctors recognize brain damages, spinal injuries and neuromuscular conditions. Doctors are then able to recommend that patients see neurologists or specialists who can further assist them with their illnesses.
What does a doctor do with the Achilles heel?
Ankle. Doctor holds the relaxed foot with one hand and strikes the Achilles’ heel with the reflex hammer. he same thing is done with the other foot. If the reactions are the same, then the nerves connected to the ankles are completely normal and functioning well.
What is the patient's position at the edge of a checkup bed?
The (adult) patient is seated straight at the edge of a checkup bed, arms and legs are relaxed with one hand on top of the other. The patient should be calm and relaxed.
Which backbone is connected to the nerves of the first and second backbones?
The ankle is connected to the nerves of the first and second backbones. The knee is connected to the nerves of the second through the fourth backbones. The abdomen is connected to the nerves of the eighth through the twelfth backbones.
Who invented the reflex hammer?
In 1888, a Philadelphia neurologist John Madison Taylor invented the first certified reflex hammer. Since then, it has been medically used for various reflex tests all over the world. Basically, neurologists or physicians are permitted to use this tool.
Why is the knee jerk reflex important?
The stimulation of the patellar tendon helps us contract and relax the quadriceps and hamstrings , making the reflex important for balance and movement, for example when you walk, accidentally trip, or rock back and forth, since the without the knee-jerk reflex the pull of gravity could make the knee bend, leading us to fall down. So, the next time you decide to go on a walk, pay attention to the stretch and contraction of your quadriceps and hamstrings and admire the rhythmic and accurate movement. Consider how incredibly fast and efficient the nervous system is, especially when you trip and look around to make sure that no one saw you.
What is the knee jerk reflex?
The knee-jerk reflex is a deep tendon reflex that is mediated by the nerves in the L2, L3, and L4 of the spinal cord 3. This reflex is a monosynaptic reflex, meaning that one neuron synapses onto a second neuron, leading to a response in the muscle. This monosynaptic connection is part of why the knee-jerk reflex is so fast. Additionally, the reflex only goes to the lumbar region of the spinal cord, instead of getting feedback from the brain first, increasing its speed. So what exactly happens when your patellar tendon is hit with the hammer (Fig. 1) 4?
How fast does it take for a patellar tendon to move?
The combination of these two sets of steps leads to the movement of the leg in response to a tap on the tendon. It takes about 30-50ms for the leg to move after the patellar tendon is tapped 5,6 which is incredibly fast, considering the number of steps involved in the reflex pathway.
Where is the stretch receptor located in the muscle?
The stretch of the tendon is detected through stretch receptors in the muscle spindle in the quadriceps muscle.
Which neuron synapses on a motor neuron?
In the gray matter of the spinal cord, the sensory neurons synapse on a motor neuron (this is the monosynaptic reflex).
What is a knee jerk reflex?
The Reflex Test. The knee-jerk reflex is what's known as a mono-synaptic response, because there is only one synapse in the circuit needed to complete the reflex. Within each body tendon is a stretch receptor. The stretch receptor can be stimulated by tapping the tendon with a rubber mallet, whereupon the associated muscle contracts slightly.
What Does Reflex Mean?
A reflex, or reflex action, is an involuntary and nearly instantaneous movement in response to a stimulus. A reflex is made possible by neural pathways called reflex arcs which can act on an impulse before that impulse reaches the brain. The reflex is then an automatic response to a stimulus that does not receive or need conscious thought.
What does it mean when your reflexes are slower?
One side of the body reacts slower to a reflex test - If your reflexes are slower on one side it may indicate early onset of progressive disease, or localized nerve damage.
What does it mean when your hyporeflexia is weak?
0 : No evidence of contraction (Hyporeflexia) - Weak or absent response may indicate damage to the nerves outside the spinal cord (peripheral neuropathy), damage to the motor neurons just before or just after they leave the spinal cord (motor neuron disease), or muscle disease. It usually indicates a disease that involves one or more of the components of the two-neuron reflex arc itself.
What is the Babinski test?
Babinski Test. Involves gently stroking the sole of the foot to assess proper development of the spine and cerebral cortex. An adult or older child who responds to the Babinski test with an extended big toe may have a lesion in the spinal cord or cerebral cortex. The speed and forcefulness of the reflex response varies.
How many nerve cells does a knee jerk use?
The knee-jerk response is any kind of reaction that is done automatically, without thought, and is one of the fastest and most primitive in the human body: it uses only two nerve cells via the spinal cord, and does not use the brain. However, the brain does preset the strength of the reflex. It only takes about 50 milliseconds between the tap and the start of the leg kick.
How to stimulate stretch receptor?
The stretch receptor can be stimulated by tapping the tendon with a rubber mallet, whereupon the associated muscle contracts slightly. This simple reflex forms the basis of the test performed by doctors during the examination of a patient's central and peripheral nervous system.
Overview
Clinical significance
After the tap of a hammer, the leg is normally extended once and comes to rest. The absence or decrease of this reflex is problematic, and known as Westphal's sign. This reflex may be diminished or absent in lower motor neuron lesions and during sleep. On the other hand, multiple oscillation of the leg (pendular reflex) following the tap may be a sign of cerebellar diseases. Exaggerated (brisk) deep tendon reflexes such as this can be found in upper motor neuron lesions,
Mechanism
Striking of the patellar tendon with a reflex hammer just below the patella stretches the muscle spindle in the quadriceps muscle. This produces a signal which travels back to the spinal cord and synapses (without interneurons) at the level of L3 or L4 in the spinal cord, completely independent of higher centres. From there, an alpha motor neuron conducts an efferent impulse back to the quadriceps femoris muscle, triggering contraction. This contraction, coordinated with the relaxa…
History
Wilhelm Heinrich Erb (1840–1921) and Carl Friedrich Westphal (1833–1890) simultaneously reported the patellar tendon or knee reflex in 1875. The term knee-jerk was recorded by Sir Michael Foster in his Textbook of physiology in 1877: "Striking the tendon below the patella gives rise to a sudden extension of the leg, known as the knee-jerk."
In popular culture
The term began to be used figuratively from the early 20th century onwards. O. O. McIntyre, in his New York Day-By-Day column in The Coshocton Tribune, October 1921, wrote: "Itinerant preacher stemming Broadway on a soap box. And gets only an occasional knee-jerk."
See also
• Tonic vibration reflex – Sustained contraction of vibrated muscle
• Motor control – Regulation of movement within organisms possessing a nervous system
• Jendrassik maneuver – Medical maneuver to test reflexes
Sources
• Gurfinkel' VS, Lipshits MI, Popov KE (1974). "Is the stretch reflex a basic mechanism in the system of regulation of human vertical posture?". Biofizika (in Russian). 19 (4): 744–8. PMID 4425696.
• Pinnock CA, Lin ES, Smith T (2003). "Physiology of the Nervous System". Fundamentals of Anaesthesia, 2nd Edition (2nd ed.). Greenwich Medical Media Ltd.