What is the principle of electrical impedance cell counting?
Principle of Electrical-Impedance Cell Counting In an electrolyte solution, which conducts electricity, blood cells counted by electrical impedance are diluted. The electrical current passes through the opening or through the opening of the measuring device in the electrolyte solution from one electrode to another.
How does the impedance change as a cell passes through?
The impedance changes as a cell passes through. The change in impedance is proportional to cell volume, resulting in a cell count and measure of volume. The principle of impedance counting, also known as the Coulter principle after its inventor Wallace Coulter, is the passage of cells suspended in a known dilution through a small orifice.
What is the traditional method for counting cells?
Learn more The traditional method for counting cells is electrical impedance, also known as the Coulter Principle. Whole blood is passed between two electrodes through an aperture so narrow that only one cell can pass through at a time. The impedance changes as a cell passes through.
What are the principles of cell counting automation?
Principles of Cell Counting Automation - Light Scatter Materials scatter light at wavelengths at which they do not absorb Cell size Larger particles have larger amounts of scatter on the forward side
What is the impedance of an electric circuit?
What was the first instrument to count blood cells?
How does an electrolyte conduct electricity?
How to count red cells?
What is the refraction index of a cell?
How are white cells counted?
What were the first instruments used in hematology?
See 2 more
Which principle is used in automated cell counter?
The technology was principally developed to count blood cells quickly by measuring the changes in electrical conductance as cells suspended in a conductive fluid passed through a small orifice. Presently, over 98% of automated cell counters incorporate this technology, which is referred to as the Coulter Principle.
What is the principle of automated impedance cell counters quizlet?
The impedance principle of cell counting is based on the detection and measurement of changes in electrical resistance produced by cells as they traverse a small aperture.
What is the principle of automated hematology analyzer?
Fully automated hematology analyzers employ two principal methods of counting blood cells: volumetric impedance and light-scatter technique. Both employ variations in the handling of samples before the count, such as automatic dilution and separation of samples into aliquots.
What is the cell counting principle of electrical impedance?
The traditional method for counting cells is electrical impedance, also known as the Coulter Principle. It is used in almost every hematology analyzer. Whole blood is passed between two electrodes through an aperture so narrow that only one cell can pass through at a time.
What is the principle of Coulter Counter?
The Coulter counter uses the principle that the electrical resistance of a conducting liquid is increased by the addition of an insulating material. Particles are assessed individually. To obtain adequate sensitivity, the volume of liquid measured must be similar to the volume of the particle.
Which principle in hematology automation involves detection and measurement of changes in electrical current between two electrodes?
The Coulter Principle is based on the detection and measurement of changes in electrical resistance produced by a particle or cell suspended in a conductive liquid (diluent) traversing through a small aperture.
How does an auto analyzer work?
AutoAnalyzers automate repetitive sample analysis steps which would otherwise be done manually by a technician, for such medical tests as the ones mentioned previously. This way, an AutoAnalyzer can analyze hundreds of samples every day with one operating technician.
What is the principle of CBC?
The overarching principle governing the activities of the CBC is to advance scientific understanding of behaviour change in promoting well-being for individuals and for society, including physical, mental, social and environmental wellbeing.
What are the advantages of using an automated hematology analyzer?
Advantages of Automated Hematology Analyzer Speed with efficient handling of a large number of samples. Accuracy and precision in quantitative blood tests. Ability to perform multiple tests on a single platform. Significant reduction of labor requirements.
How is Haemoglobin value determined by automated cell counters?
Measurement of Hb is based on the linear relationship between the amount of light absorbed in a given absorption band and the sample absorption source concentration (Beer's Law) (Skoog DA, West DM, 1965). Many automatic counters use an absorbance reading cyanmethaemoglobin process at wavelengths of 525 or 540 nm.
What is the principle of Sysmex?
Principles of measurement Blood is sampled and diluted, and moves through a tube thin enough that cells pass by one at a time. Characteristics about the cell are measured using lasers (fluorescence flow cytometry) or electrical impedance.
How does automated hematology analyzers measure hematocrit?
Automated Hematology Analyzers HCT The number of RBCs is multiplied by the mean RBC volume (MCV) of the sample RBCs to calculate the volume of the red cell component of the sample. This calculated RBC volume is subsequently divided by the total sample volume to produce a calculated HCT value.
What is the purpose of the diluent when performing a CBC on the automated cell counter quizlet?
Dilute the sample to minimize the number of red blood cells in the squares being counted.
Which parameters are measured directly on the automated cell counter in this hematology laboratory and how are they measured?
The WBC, RBC, hemoglobin, and platelet parameters are considered to be measured directly. A 60- to 70-μm aperture is used in the RBC/platelet transducer assembly for counting and volumetrically sizing of RBCs and platelets by the electronic impedance method.
Which parameters are measured directly on the automated cell counter in this hematology department?
We've talked about four parameters directly measured by the analyzer: the red blood cell count, the mean corpuscular volume, the hemoglobin concentration, and the red cell distribution width. The other parameters that make up the CBC are then calculated by the computer result, based on the measured data.
What is the greatest limitation of automated cell counters?
LimitationsSome automated cell counters falsely increase or decrease cell counts. They might not be able to differentiate between nucleated red blood cells and small clumps of platelets.The automated cell counters have high running costs.They make workflow expensive.
(PPT) Automated Hematology Cell Counters - Academia.edu
Rohitakarista (RHT), a classical Ayurvedic preparation which is used in splenomegaly, was studied for its effect on different hematologic parameters after chronic administrations for 41 days to male Sprague-Dawley rats.
Manual vs. Automated Cell Counters - DeNovix
Cell counting is a procedure with a choice of numerous diverse techniques, most of which rely on specialized laboratory appliances. Despite the variety of cell counters available for modern-day life science applications, they can typically be divided into one of two sub-groups: manual and automated cell counters.
What is automated cell counting?
Automated cell counters offer a convenient solution to the challenges facing life science researchers today by providing precise results in a fraction of the time taken for manual cell counting. CellDrop™ systems from DeNovix build on the fundamental throughput benefits of established automated cell counting principles with a suite of additional usability advantages.
What is a DeNovix cell counter?
If you would like to talk about quotes or pay-as-you-go contracts for a CellDrop automated cell counter, simply contact a member of the DeNovix team today.
What is a cell drop?
CellDrop Automated Cell Counters systematize the basic principles of manual cell counting. Samples are assayed with an appropriate staining reagent and a volume is pipetted into a sample chamber formed between two optical-grade sapphire surfaces. Maintaining precise control of sample chamber height and field of view enables the calculation of the exact volume of cells counted, delivering accurate cell enumeration and viability assessment. Cells are simply wiped from the surface with a dry laboratory wipe ready for the next sample.
What is coincidence in biology?
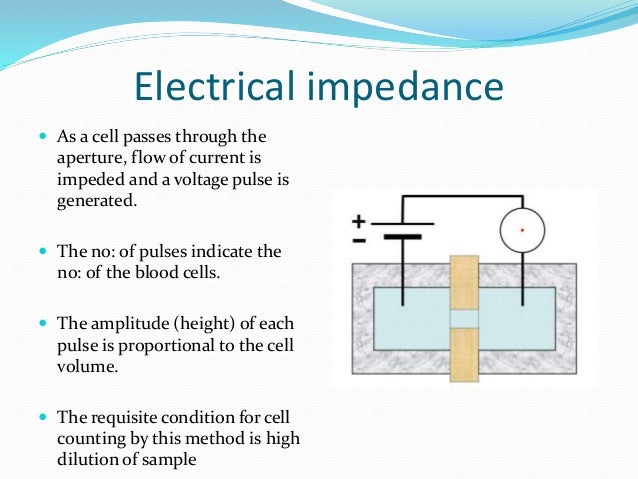
coincidence refers to two (or more) cells passing through the aperture at the same time. instead of counting them as two cells, the instrument would count them as one large cell
What causes a decrease in voltage?
an electrical current, momentarily cause a decrease in the voltage. Each time a cell
What law is used to determine if blood cells have increased resistance to electrical currents?
based on the fact that there is increased resistance when blood cells with poor conductivity pass through an electrical field (based on Ohm's Law: V= I*R).
What is the purpose of a sheath fluid coupling sample?
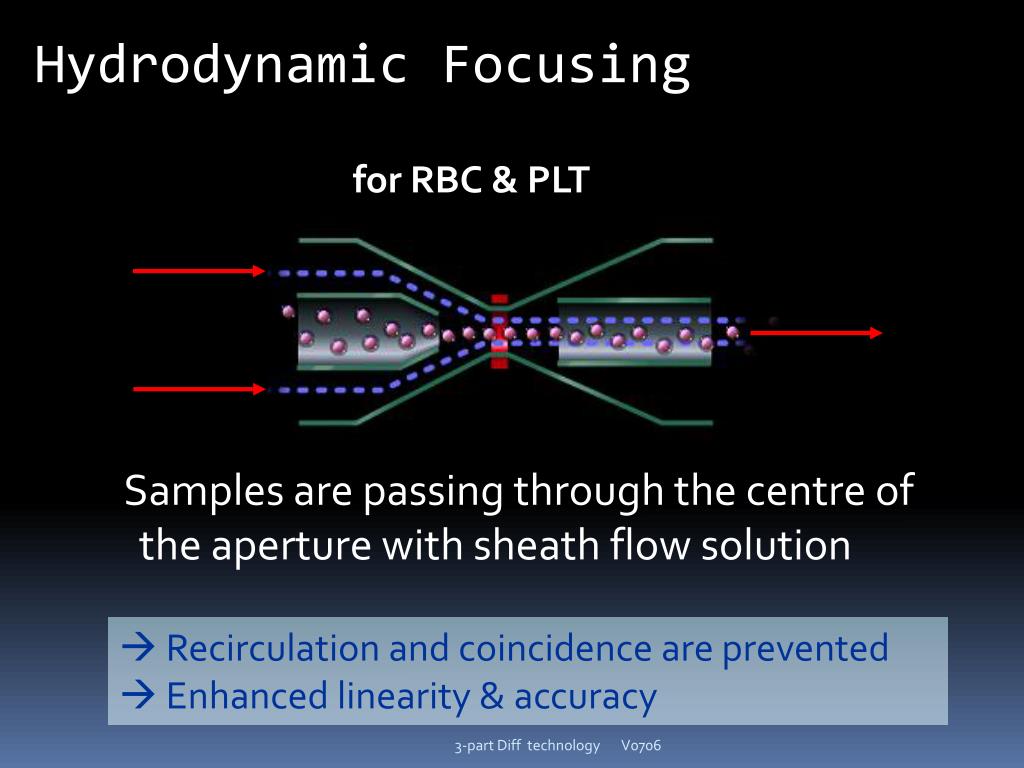
Coupling sample with sheath fluid (cell pact) applies force on cells so alighned in single line
What mode to use to base off DNA in platelets?
Use flourescent mode, base off DNA in platelets
Is the number of pulses equivalent to the number of blood cells?
The number of pulses is equivalent to the blood cell number. The amplitude (i.e., height of the pulse) is proportional to the cell volume.
What is the method of counting cells?
Electrical Impedance Methodology. The traditional method for counting cells is electrical impedance, also known as the Coulter Principle. Whole blood is passed between two electrodes through an aperture so narrow that only one cell can pass through at a time. The impedance changes as a cell passes through.
What phenomenon can cause falsely increased cell counts?
Figure 2. The phenomenon called “recirculation” that can cause falsely increased cell counts.
How many red cell indices are processed in a day?
Where a minimum of 100 test requests are processed each day, there should be no significant day-to-day variability in the means of the red cell indices obtained by an automated blood counter, provided that the population of patients remains stable and that samples from a particular clinical source (e.g. renal or oncology patients) are not processed all in the same set, disproportionately influencing the mean. Assuming that the sample population is stable, any significant change in the means of the red cell indices will indicate a change in instrument calibration or a drift owing to a fault in its function. The procedure was developed by Bull 5,6 using a computerised algorithm to estimate the daily patient means of absolute values for mean cell volume (MCV), mean cell haemoglobin (MCH) and mean cell haemoglobin concentration (MCHC). In laboratories using manual methods, a simple adaptation of the same principle can be applied, confined to MCHC and excluding results from any specific clinic that are likely to be biased. From the daily means for all measurements on 10 consecutive working days, an overall daily mean and SD are established. The mean MCHC is then calculated at the end of each day. If the test does not vary by more than ± 2SD, it is considered to be satisfactory, but may be misleading if there is a simultaneous error in the same direction in both Hb and Hct. The results may be displayed graphically as illustrated in Figure 25-3.
What is the clinical history of a hemostatic defect?
If the patient is suspected of a hemostatic defect, then the clinical history is usually very informative in the differentiation of a platelet defect from a coagulation defect (see Table 39-4 in Chapter 39 ). A typical panel of screening tests includes a full blood count; a blood smear (especially if there are abnormalities or flags from the blood counter); coagulation tests such as the activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), prothrombin time (PT), and thrombin time (TT); and a VWF screen (ristocetin cofactor assay, VWF antigen, and factor VIII coagulant activity). The full blood count is essential in the work-up of patients as modern blood counters can detect abnormalities in platelet number, platelet size distribution, or platelet volume (e.g., macrothrombocytopenia; see Chapter 27) and other problems with both red cells and white cells that may give rise to an acquired platelet defect, e.g., myelodysplasia. If abnormalities in either platelet count, size (MPV), or distribution are flagged by the instrument, then a blood smear should be examined to confirm any defect (s) in platelet size and granule content, as well as any abnormalities in the red cells (e.g., schistocytes in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura/hemolytic uremic syndrome) or leukocytes (e.g., neutrophil inclusions). Because VWD is the most common bleeding diathesis and also presents with bleeding symptoms similar to (rarer) platelet defects, this can be eliminated or diagnosed by performing the three VWF tests listed previously. The APTT, PT, and TT screens will determine whether the patient has a coagulation defect; if so, the defect can be confirmed by specific assays for the appropriate coagulation factors.
What is the impedance of an electric circuit?
The impedance of the electric circuit induces a pulse. Those pulses are known to be cells. The impedance size is proportional to the size of the cell which causes it. The instrument thus not only tracks how many cells move through the aperture but also the size of each cell.
What was the first instrument to count blood cells?
Coulter patented a system which used the electrical impedance process, also known as aperture impedance, to count blood cells. This innovation made the blood cell counts production quicker, smoother, and more accessible. The first instruments of hematology conducted only counts of the RBC and the white blood cell (WBC).
How does an electrolyte conduct electricity?
In an electrolyte solution, which conducts electricity, blood cells counted by electrical impedance are diluted . The electrical current passes through the opening or through the opening of the measuring device in the electrolyte solution from one electrode to another.
How to count red cells?
Red cells can be counted by aperture impedance, lightscattering techniques – using Laser LED or tungsten or a combination of the two technologies.
What is the refraction index of a cell?
This is known as the cell refractive index. The refraction index is determined by the cell’s form and volume while volume has the greater effect on the sca tter.
How are white cells counted?
White cells can be counted by a variety of technologies and divided into a large number of categories. Both have benefits and drawbacks. The creation of sheath flow-based counting systems , which allow single cells to move through the sensing region, has led to multi-parameter analysis on the same cell by integrating the signals from multiple sensors. The sensing region can be either electrical, conductive, impedant or a mixture of both, depending on the manufacturer, and the sensors can be mounted to look forward to light scatter, side scatter, small- or wide-angle scatter, polarized light scatter, or fluorescence.
What were the first instruments used in hematology?
The first instruments of hematology conducted only counts of the RBC and the white blood cell (WBC). Later, measurement of hemoglobin was introduced. Instruments are now available that include values for 60 or more parameters, either direct or estimated. Only the RBCs, WBCs, hemoglobin, platelets, and reticulocytes are specifically counted ...
