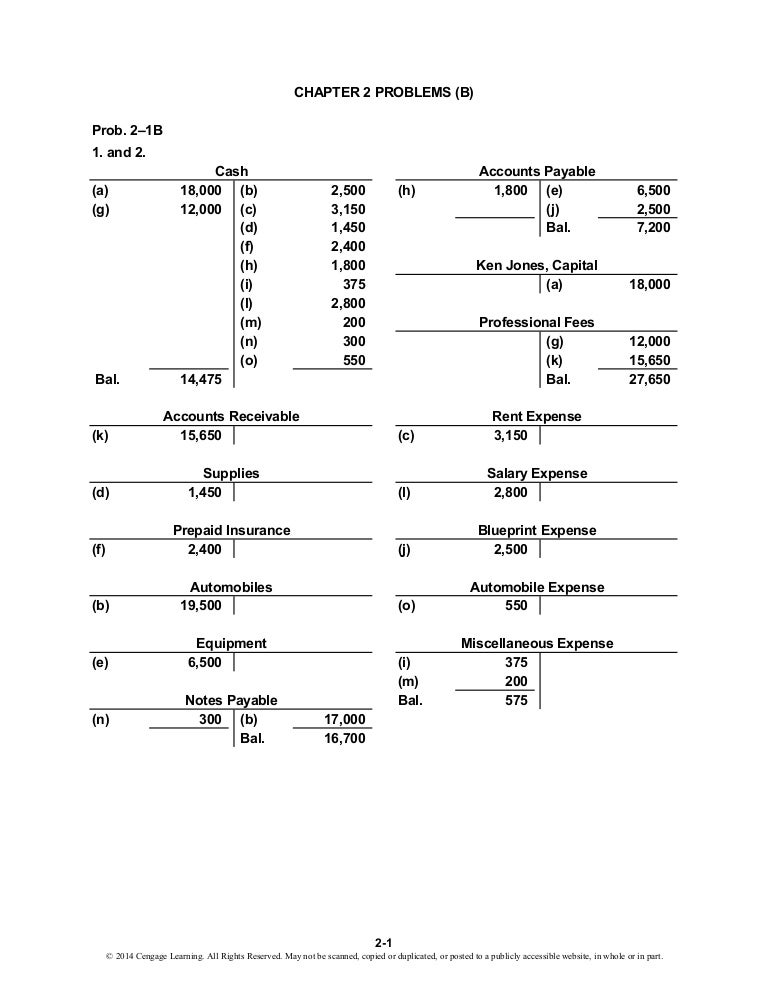
What was the purpose of the Clayton Antitrust Act Quizlet?
are:
- the Sherman Act;
- the Clayton Act; and.
- the Federal Trade Commission Act (FTCA).
What is Section 7 of the Clayton Act?
Section 7 of the Clayton Act. The section of the Clayton Antitrust Act prohibiting mergers, acquisitions, and certain joint ventures where the effect may be to substantially lessen competition. The Antitrust Division of the Department of Justice (DOJ), the Federal Trade Commission, state attorneys general, and private parties may challenge transactions under Section 7.
What is the significance of Clayton Act?
Clayton Antitrust Act
- Understanding the Clayton Antitrust Act. At the turn of the 20th century, a handful of large U.S. ...
- Special Considerations. The Clayton Antitrust Act is still in force today, essentially in its original form. ...
- Clayton Antitrust Act vs. Sherman Antitrust Act. ...
What does the Clayton Act prohibit?
- The Robinson-Patman Act prohibits price discrimination against small business.
- It was enacted to overcome ambiguity in the Sherman Act of 1890 and the Clayton Antitrust Act of 1914.
- The principal criticism of Robinson-Patman is that it protects competitors instead of encouraging and maintaining competition.
What was the purpose of the Clayton Act?
The Clayton Antitrust Act of 1914 continues to regulate U.S. business practices today. Intended to strengthen earlier antitrust legislation, the act prohibits anticompetitive mergers, predatory and discriminatory pricing, and other forms of unethical corporate behavior.
What was the purpose of the Clayton Antitrust Act quizlet?
The Clayton Antitrust Act attempts to prohibit certain actions that lead to anti-competitiveness. Outlaws price discrimination, prohibits tying contracts, prohibits stock acquisition of competing corporations, prohibits the formation of interlocking directorates (director of one firm, is board member on another firm).
What is the Clayton Act quizlet?
The Clayton Antitrust Act is an amendment passed by U.S. Congress in 1914 that provides further clarification and substance to the Sherman Antitrust Act of 1890 on topics such as price discrimination, price fixing and unfair business practices.
Which of the following was a purpose of the Clayton Act of 1914 quizlet?
The Clayton Act of 1914: outlawed price discrimination, tying contracts, acquisition of stocks of competing corporations, and interlocking directorates that lessen competition.
What are the four major provisions of the Clayton Act?
The Clayton Act, authored by Alabama congressman Henry Clayton, outlawed, among other things, anticompetitive mergers and acquisitions, interlocking directorates, and price discrimination.
Why was the Clayton Act of antitrust passed?
The US Congress passed the bill in June 1914, and President Woodrow Wilson later signed it into law. The Clayton Antitrust Act sought to address the weaknesses in the Sherman Act by expanding the list of prohibited business practices that would prevent a level playing field for all businesses.
Which of the following was true of the Clayton Antitrust Act quizlet?
Which of the following was true of the Clayton Anti-Trust Act? It outlawed price discrimination and exempted labor unions from anti-trust laws.
What did the Sherman and Clayton antitrust Acts accomplish quizlet?
Section 2 of the Sherman Act bans "monopolization". the wrongful acquisition of a monopoly. The Clayton Act prohibits anticompetitive mergers, tying arrangements, and exclusive dealing agreements. The Robinson-Patman Act bans price discrimination that reduces competition.
What was the main purpose of the Sherman Antitrust Act quizlet?
- The major purpose of the Sherman Antitrust Act was to prohibit monopolies and sustain competition so as to protect companies from each other and to protect consumers from unfair business practices.
Which of the following does the Clayton Antitrust Act specifically prohibit quizlet?
The Clayton Act forbids price discrimination, exclusive dealing, tying arrangements, requirements contracts, mergers restraining commerce or tending to create a monopoly, and interlocking directorates.
What did Clayton Antitrust Act do Apush?
The Clayton Antitrust Act gave the government greater power to break up monopolistic corporations than it had under the earlier Sherman Antitrust Act (1890).
Which of the following does the Clayton Antitrust Act specifically prohibit?
Section 7 of the Clayton Act prohibits mergers and acquisitions where the effect "may be substantially to lessen competition, or to tend to create a monopoly." As amended by the Robinson-Patman Act of 1936, the Clayton Act also bans certain discriminatory prices, services, and allowances in dealings between merchants.
What is the purpose of the Controlled Substances Act?
to enforce the Controlled Substances act, to gather intelligence, to train its officers, and to conduct research in the area of dangerous drugs and drug abuse. who as the authority to reschedule a drug, to bring an unscheduled drug under control, or to remove controls on scheduled drugs.
What is the purpose of the Rare Diseases Act?
to stimulate the development and market availability of products that are used for the treatment of rare diseases (rare disease is a condition that affects fewer than 200,000 in the US) what promotes the development of products that demonstrate promise for the diagnosis or treatment of rare diseases or conditions.
What is the Food and Drugs Act?
the Food and Drugs Act (1927) and Regulations (1953, 1954, 1979) the National Association of Pharmacy Regulatory Authorities (NAPRA) deals with.
What is the primary purpose of the United States Pharmacopeia (USP)/National Formulary?
what is the primary purpose of the United States Pharmacopeia (USP)/National Formulary. to provide standards for the identity, quality, strength, and purity of substances used in the practice of health care. what do manufacturers of drugs have to develop.