Expenditure Plans. A two-way link exists between aggregate expenditure and real GDP: •An increase in real GDP increases aggregate expenditure. •An increase in aggregate expenditure increases real GDP. Consumption Function and Saving Function. Consumption and saving are influenced by: •Disposable income. •Wealth.
How does the aggregate demand curve show real GDP?
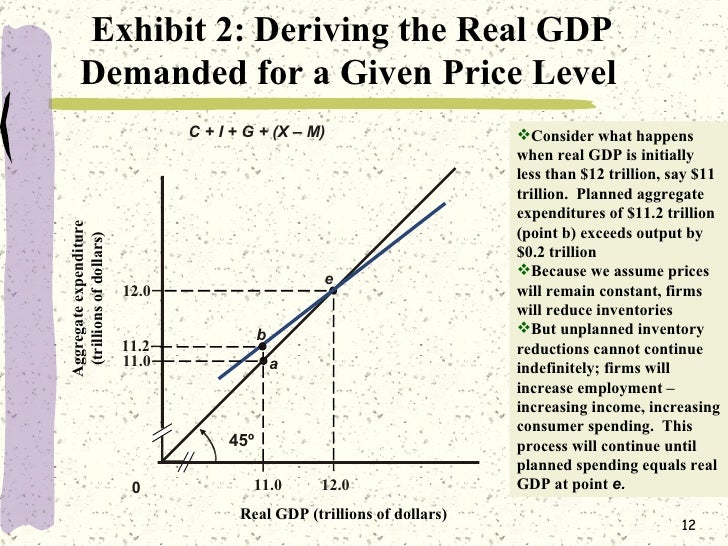
The aggregate demand curve thus shows the equilibrium real GDP from the aggregate expenditures model at each price level. In the aggregate expenditures model, a change in autonomous aggregate expenditures changes equilibrium real GDP by the multiplier times the change in autonomous aggregate expenditures.
What is the relationship between consumption expenditure and real GDP?
Consumption expenditure and imports are influenced by real GDP. When real GDP increases, consumption expenditure and imports increase. What is the relationship between aggregate planned expenditure and real GDP at equilibrium expenditure? At equilibrium expenditure, aggregate planned expenditure ______ real GDP.
What is the difference between real GDP and aggregate planned expenditure?
D. decreases; real GDP being less than aggregate planned expenditure If real GDP is $500 billion, explain the process that moves the economy toward equilibrium expenditure. When real GDP is $500 billion, aggregate planned expenditure is $ 445 billion.
How do autonomous aggregate expenditures affect the aggregate expenditures model?
In the aggregate expenditures model, a change in autonomous aggregate expenditures changes equilibrium real GDP by the multiplier times the change in autonomous aggregate expenditures. That model, however, assumes a constant price level. How can we incorporate the concept of the multiplier into the model of aggregate demand and aggregate supply?

Is aggregate expenditure and GDP the same?
The aggregate expenditure is one of the methods that is used to calculate the total sum of all the economic activities in an economy, also known as the gross domestic product (GDP).
What is the relationship between aggregate planned expenditure and real GDP at equilibrium expenditure quizlet?
Equilibrium expenditure occurs when aggregate planned expenditure equals real GDP. Disposable income is the aggregate income minus taxes plus transfer payment .
What happens when aggregate expenditure increases?
An increase in autonomous aggregate expenditures shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right; a reduction shifts it to the left.
What is the relationship between aggregate expenditures and aggregate demand?
An increase in the expenditure by consumption (C) or investment (I) causes the aggregate expenditure to rise which pushes the economy towards a higher equilibrium. Aggregate Expenditure – Equilibrium: In this graph, equilibrium is reached when the total demand (AD) equals the total amount of output (Y).
What is the relationship between aggregate planned expenditure and real GDP at equilibrium expenditure?
Equilibrium expenditure is the level of aggregate expenditure when aggregate planned expenditure equals real GDP. Equilibrium expenditure equals the real GDP at which the AE curve intersects the 45° line.
What happens if real GDP exceeds aggregate expenditures?
If aggregate expenditures exceed real GDP, then firms will increase their output and real GDP will rise. If aggregate expenditures equal real GDP, then firms will leave their output unchanged; we have achieved equilibrium in the aggregate expenditures model. At equilibrium, there is no unplanned investment.
When aggregate expenditure is less than GDP Which of the following is true?
When aggregate expenditure is less than GDP, which of the following is true? There was an unplanned increase in inventories. if aggregate expenditure is greater than GDP, how will the economy reach macroeconomic equilibrium? Inventories will decline, and GDP and employment will rise.
When aggregate expenditures are less than the GDP inventories will?
If aggregate expenditures are less than real GDP, it means that people are planning to buy fewer goods and services than are currently being produced. Since not all goods and services will be sold, inventories will pile up. When producers see inventories building up, they decrease production, and real GDP falls. 3.
What causes an increase in aggregate expenditures?
Compared to the simplified aggregate expenditures model, the aggregate expenditures curve shifts up by the amount of government purchases and net exports.An even more realistic view of the economy might assume that imports are induced, since as a country's real GDP rises it will buy more goods and services, some of ...
When planned aggregate expenditure is less than real GDP as in the diagram to the right what happens to firms inventories quizlet?
When planned aggregate expenditure is less than real GDP, as in the diagram to the right, what happens to firms' inventories? Inventories accumulate if production is not scaled back. the vertical distance between AE and the 45° line at the level of potential real GDP.
What is the relationship between aggregate expenditures and aggregate demand quizlet?
Aggregate expenditure shows the amount of desired spending from given levels of income, while aggregate demand shows the amount of desired spending from given levels of prices.
Why is there an inverse relationship between the level of aggregate expenditure and the general price levels?
The explanation of this inverse relationship is based on the real-balances effect, the interest-rate effect, and the foreign-purchases effect. In this case, as the price level rises, the quantity of real domestic output decreases.
When aggregate expenditure is greater than GDP inventories will and GDP and total employment will?
What is the effect on inventories, GDP, and employment when aggregate expenditure (total spending) exceeds GDP? Inventories decrease, GDP increases, and employment increases. You just studied 106 terms!
When aggregate expenditure is less than GDP Which of the following is true?
When aggregate expenditure is less than GDP, which of the following is true? There was an unplanned increase in inventories. if aggregate expenditure is greater than GDP, how will the economy reach macroeconomic equilibrium? Inventories will decline, and GDP and employment will rise.
When real GDP is $1 trillion What are aggregate planned expenditure autonomous expenditure and induced expenditure?
When real GDP is $1 trillion, what are aggregate planned expenditure, autonomous expenditure, and induced expenditure? When real GDP is 1 trillion, Aggregate planned expenditure = $2.3 trillion + $0.5 trillion + $0.5 trillion + $0.7 trillion−$0.5 trillion, which is $3.5 trillion.
When the aggregate expenditure line intersects the 45o line at a level of GDP below potential GDP?
In the Keynesian cross diagram, if the aggregate expenditure line intersects the 45-degree line at the level of potential GDP, then the economy is in sound shape. There is no recession, and unemployment is at the natural rate–what we call full employment.
Why do aggregate expenditures vary with the price level?
Aggregate expenditures will vary with the price level because of the wealth effect, the interest rate effect, and the international trade effect. The higher the price level, the lower the aggregate expenditures curve and the lower the equilibrium level of real GDP.
What is aggregate expenditure curve?
An aggregate expenditures curve assumes a fixed price level. If the price level were to change, the levels of consumption, investment, and net exports would all change, producing a new aggregate expenditures curve and a new equilibrium solution in the aggregate expenditures model.
Why is there a different level of equilibrium real GDP for each price level?
More generally, there will be a different level of equilibrium real GDP for every price level; the higher the price level, the lower the equilibrium value of real GDP. Because there is a different aggregate expenditures curve for each price level , there is a different equilibrium real GDP for each price level.
How does a higher price level affect the real quantity of money?
Similarly, a higher price level reduces the real quantity of money , raises interest rates, and reduces investment. This is called the interest rate effect. Finally, a change in the domestic price level will affect exports and imports.
What is the tendency for price level changes to change real wealth and consumption?
The tendency for price level changes to change real wealth and consumption is called the wealth effect . Because changes in the price level also affect the real quantity of money, we can expect a change in the price level to change the interest rate.
How does price level affect real wealth?
A change in the price level changes people’s real wealth. Suppose, for example, that your wealth includes $10,000 in a bond account. An increase in the price level would reduce the real value of this money, reduce your real wealth, and thus reduce your consumption.
