What Are the Four Roles That DNA Must Play in Cells?
- Replication. DNA exists in a double-helical arrangement, in which each base along one strand binds to a complementary base on the other strand.
- Encoding Information. The base sequences of A, T, C and G along a DNA strand are organized into units called genes. ...
- Mutation and Recombination. DNA plays a role in the evolution of a species. ...
- Gene Expression. ...
What is the role of RNA in cell differentiation?
Since RNA translates and transcribes the DNA code into proteins (the structures of a cell), it also plays a role in cell differentiation. Environmental factors can also influence gene expression and cell differentiation.
What is the role of gene expression in cell differentiation?
This process by which information from a gene is used to make the structures of a cell is called gene expression. Since RNA translates and transcribes the DNA code into proteins (the structures of a cell), it also plays a role in cell differentiation.
What is cell differentiation and why is it important?
Cell differentiation is the process by which cells become specialized in order to perform different functions. Multicellular organisms begin as just one single cell—a fertilized egg.
What is the role of transcription factors in cell differentiation?
One of the keys to the cell differentiation process is transcription factors. These hormones and chemicals direct the activities surrounding DNA, determining what gets transcribed and what is ignored.
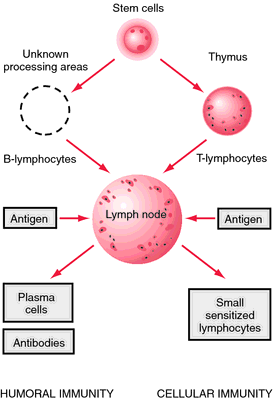
Does DNA regulate cell differentiation?
Cellular differentiation is a complex process that involves the coordinated regulation of genes by a multitude of cellular pathways. Differentiation is controlled a number of DNA binding proteins that are aberrantly expressed in PDAC.
What factors influence cell differentiation?
5 Major Factors that Regulates Cell DifferentiationCytoplasmic influence or cell differentiation: General influence of cytoplasm on the early cell differentiation has been demonstrated by numerous experiments with egg cells. ... Protein turn-over: ... Cell-Cell interactions: ... Embryonic induction: ... Hormones:
How genes are involved in cell differentiation?
The answer lies in the way each cell deploys its genome. In other words, the particular combination of genes that are turned on (expressed) or turned off (repressed) dictates cellular morphology (shape) and function.
How do cells become differentiated?
In order for a cell to differentiate into its specialized form and function, it need only manipulate those genes (and thus those proteins) that will be expressed, and not those that will remain silent. The primary mechanism by which genes are turned “on” or “off” is through transcription factors.
What factor is most important during cell differentiation?
Gene StructureGene Structure - This is the most important factor when it comes to cell differentiation. Each of the viable genes contains important information that determine the cell type and physical attributes of the animal (host).
What leads to cell differentiation during development transcription factors?
The differentiation of MSCs into specific mature cell types is controlled by various cytokines, growth factors, extracellular matrix molecules, and transcription factors (TFs).
What is cell differentiation?
Cell differentiation is the process by which dividing cells change their functional or phenotypical type. All cells presumably derive from stem cells and obtain their functions as they mature.
What is the role of DNA in differentiation?
Roles of DNA and RNA in Cell Differentiation. Dexoyribonucleic Acid, or DNA, controls the way cells function. It also determines what type of specialized cells will be made. Stem cells are cells that have the ability to become any type of specialized cell in the body.
What happens to DNA after sperm and egg cells unite?
After an egg cell and sperm cell unite to begin forming a new organism, all of the DNA in each cell of that organism will be virtually identical. If every part of the DNA in each cell is the same, then how do cells become different types of cells? Let’s look more closely at DNA to find out.
Why do multicellular organisms need different types of cells?
Multicellular organisms need many different types of cells to carry out the same life processes. Each of these special types of cells has a different structure that helps it perform a specific function.
What are some examples of environmental factors that influence gene expression?
Another example of environmental factors influencing gene expression is metamorphosis. Metamorphosis is regulated by external and internal factors, including temperature, available resources, and hormones. For example, a tadpole in a pond will go through many physical changes as it responds to the environment.
What are the three specialized cells in animals?
Some cells must be able to move (like sperm cells), while other cells need to contract (like muscle cells). Three of the many specialized cell types in animals include red blood cells, muscle cells, and skin cells.
Why are plants specialized cells?
In plants, cells are specialized for the roles they play in the plant’s survival.
What is the process by which information from a gene is used to make the structures of a cell?
This process by which information from a gene is used to make the structures of a cell is called gene expression . Since RNA translates and transcribes the DNA code into proteins (the structures of a cell), it also plays a role in cell differentiation.
What is the process of differentiation?
Cellular differentiation , or simply cell differentiation, is the process through which a cell undergoes changes in gene expression to become a more specific type of cell. The process of cell differentiation allows multi-cellular organisms to create uniquely functional cell types and body plans. The process of cell differentiation is driven by genetics, and their interaction with the environment.
What is the name of the cell that can differentiate into an entire organism?
In this case, one of the cells remains identical to the parent stem cell. In the other cell, chemical triggers activate the process of cell differentiation, and the cell will start to express the DNA of a specific cell type. Stem cells which can differentiate into entire organisms are known as embryonic stem cells and are said to be totipotent.
What happens if a cell expresses all of the proteins at once?
However, if this cell expressed all of these proteins at once it would not be functional. This cell must divide repeatedly, and the cells must begin the process of cell differentiation as they divide.
What is the original mass of cells that have not undergone differentiation?
The original mass of cells, which have not undergone differentiation, are known as stem cells. Unlike normal cell division, which creates two identical daughter cells, the division of stem cells is asymmetric cell division. In this case, one of the cells remains identical to the parent stem cell. In the other cell, chemical triggers activate ...
What is the layer of cells that sloughs off as the roots move through the soil?
In the roots a layer of cells forms around the meristem, forming the root cap. This layer of cells sloughs off as the roots move through the soil, and are consistently replaced by the meristem. On the inside of the meristem, cell differentiation happens in a different direction.
Which type of stem cell can divide into a narrow range of cells?
Stem cells which can differentiate into entire organisms are known as embryonic stem cells and are said to be totipotent. By contrast, the body also has many cells which are only pluripotent. These cells have already undergone some cell differentiation. These stem cells can only divide into a narrow range of cell types.
Can stem cells only divide?
These stem cells can only divide into a narrow range of cell types. Bone marrow, for instance, contains somatic stem cells which can only become red blood cells. These cells are necessary for the constant replenishment of blood cells, which are mostly inactive besides their oxygen-carrying ability.

Cell Differentiation Definition
- Cellular differentiation, or simply cell differentiation, is the process through which a cell undergoes changes in gene expression to become a more specific type of cell. The process of cell differentiation allows multi-cellular organisms to create uniquely functional cell types and body plans. The process of cell differentiation is driven by genetics, and their interaction with the envir…
Cell Differentiation Examples
- In Animals
After the process of fertilization in animals, a single-celled organism called the zygote is formed. The zygote is totipotent, and will eventually become an entire organism. Even the largest animal on Earth, the blue whale, starts as a single cell. The complex tissues and organ systems, which a… - In Plants
While the plantlifecycle sometimes seems alien and complex, the process of cell differentiation is very similar. While there are different hormones involved, all plants also develop from a single cell. A seed is simply a protective housing for the zygote, which also provides a food supply. It is ver…
Cell Differentiation Process
- One of the keys to the cell differentiation process is transcription factors. These hormones and chemicals direct the activities surrounding DNA, determining what gets transcribed and what is ignored. The factors present in cells from birth to death are determined by the body, and other cells in the vicinity. For instance, the pancreas or thyroid m...
Quiz
- 1. Why is cell differentiation an important process? A. It allows for multi-cellular life forms B. It creates new species C.We could do without it 2. What is the difference between cell differentiation and development? A. Development does not include differentiation B. Cell differentiation is part of development C.There is no difference 3. If each stem cell divides into m…