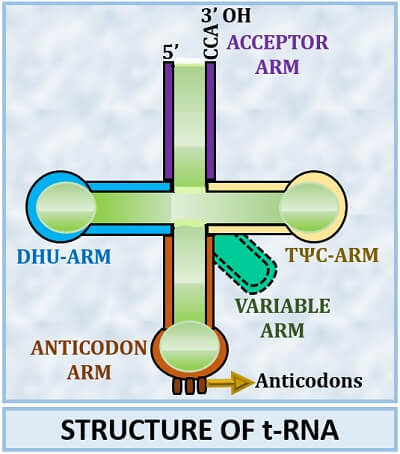
How do you convert mRNA to tRNA?
How do you convert mRNA to tRNA? To translate messenger RNA, or mRNA, use an amino acid table to help you figure out the codon sequence in transfer DNA known as tRNA. Genes in DNA are like coded recipes for proteins.
Is tRNA a ribosome?
tRNAs are ribonucleic acids and therefore capable of forming hydrogen bonds with mRNA. Additionally, they can also form ester linkages with amino acids, and therefore, can physically bring mRNA and amino acids together during the process of translation.
What is true about anticodons?
Anticodons are sequences of nucleotides that are complementary to codons. They are found in tRNAs, and allow the tRNAs to bring the correct amino acid in line with an mRNA during protein production. During protein production, amino acids are bound together into a string, much like beads on a necklace.
What is an example of an anticodon?
three unpaired nucleotides, called an anticodon. The anticodon of any one tRNA fits perfectly into the mRNA codon that codes for the amino acid attached to that tRNA; for example, the mRNA codon UUU, which codes for the amino acid phenylalanine, will be bound by the anticodon AAA.

What is the role for tRNA?
Transfer RNA (abbreviated tRNA) is a small RNA molecule that plays a key role in protein synthesis. Transfer RNA serves as a link (or adaptor) between the messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule and the growing chain of amino acids that make up a protein.
What is the role of tRNA rRNA?
Messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules carry the coding sequences for protein synthesis and are called transcripts; ribosomal RNA (rRNA) molecules form the core of a cell's ribosomes (the structures in which protein synthesis takes place); and transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules carry amino acids to the ribosomes during protein ...
Does tRNA contain anticodons?
Second, tRNA contains a trinucleotide sequence, the anticodon, which is complementary to the codon in mRNA representing its amino acid. The anticodon enables the tRNA to recognize the codon through complementary base pairing.
Does tRNA use codons or anticodons?
tRNAs bring their amino acids to the mRNA in a specific order. This order is determined by the attraction between a codon, a sequence of three nucleotides on the mRNA, and a complementary nucleotide triplet on the tRNA, called an anticodon.
What are the roles of tRNA and rRNA in translation?
The tRNA (transport RNA) carries the amino acid to the rRNA. The rRNA (ribosomal RNA) makes up the ribosome. The ribosome builds the protein according to the instructions written in the mRNA with the amino acids ferried in by the tRNA.
What are the major functions of mRNA tRNA and rRNA?
Difference between mRNA, tRNA and rRNAmRNAtRNArRNAmRNA carries codons for the translation processThey carry anticodons, specific to particular amino acidCodons or anticodons are absent4 more rows
What is the difference between rRNA and tRNA?
The main difference among mRNA tRNA and rRNA is that mRNA carries the coding instructions of an amino acid sequence of a protein while tRNA carries specific amino acids to the ribosome to form the polypeptide chain, and rRNA is associated with proteins to form ribosomes.
What are the functions of mRNA tRNA and rRNA quizlet?
Terms in this set (3)tRNA. transfer RNA; type of RNA that carries amino acids to the ribosome.mRNA. messenger RNA; type of RNA that carries instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome.ribosomal RNA. type of RNA molecule READS THE DNA SEQUENCE that plays a structural role in ribosomes.
What is tRNA in biology?
Transfer RNA (tRNA) Transfer RNA (tRNA) is a small RNA molecule that participates in protein synthesis. Each tRNA molecule has two important areas: a trinucleotide region called the anticodon and a region for attaching a specific amino acid. During translation, each time an amino acid is added to the growing chain, ...
What is transfer RNA?
Transfer RNA is that key link between transcribing RNA and translating that RNA into protein. The transfer RNA matches up via the anticodon to the specific codons in the messenger RNA, and that transfer RNA carries the amino acid that that codon encodes for.
What happens to amino acids in translation?
During translation, each time an amino acid is added to the growing chain, a tRNA molecule forms base pairs with its complementary sequence on the messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule, ensuring that the appropriate amino acid is inserted into the protein.
How many anticodons does a tRNA have?
Each tRNA carries one amino acid, and has one anticodon. When the anticodon successfully pairs up with an mRNA codon, the cellular machinery knows that the correct amino acid is in place to be added to the growing protein. Anticodons are necessary to complete the process of turning the information stored in DNA into functional proteins ...
How do anticodons work?
How Anticodons Work. When genetic information is to be turned into a protein, the sequence of events goes like this: Genetic information in the cell’s genome is transcribed into mobile pieces of RNA using base-pairing rules. Each nucleotide has only one other nucleotide which pairs up with it.
What is an anticodon?
Anticodon Definition. Anticodons are sequences of nucleotides that are complementary to codons. They are found in tRNAs, and allow the tRNAs to bring the correct amino acid in line with an mRNA during protein production. During protein production, amino acids are bound together into a string, much like beads on a necklace.
What enzymes bind amino acids together?
Enzymes catalyze the bonding of amino acids together as tRNA anticodons bind to the correct mRNA codon. When the tRNA’s amino acid has been added to the protein chain, the tRNA leaves to pick up a new amino acid to bring to a new mRNA. Interestingly, this means that the tRNA anticodon has the RNA version of the same nucleotide sequence ...
What is the function of tRNAs?
The “transfer RNAs” or “tRNAs” that string proteins together each have one anticodon that corresponds to one mRNA codon, and one amino acid attached. When the correct tRNA finds the mRNA, its amino acid is added to the growing protein chain. Enzymes catalyze the bonding of amino acids together as tRNA anticodons bind to the correct mRNA codon.
How does RNA polymerase make protein?
By pairing the correct RNA nucleotide with each DNA nucleotide, RNA polymerase creates a strand of RNA that contains all the correct information to make the protein. This “messenger RNA,” or “mRNA,” then travels to a ribosome, the site of protein production.
Why does DNA use thymine instead of uracil?
It is thought that DNA uses Thymine instead of Uracil because, as the cell’s “master blueprints,” information stored in DNA must remain stable over a long period of time. RNAs are only copies of DNA made for specific purposes, and are used by the cell for only a short period of time before being discarded.