Stomata On A Marijuana Leaf
- Exactly What are Stomata. Stomata are the door and windows of the leaves. ...
- Stomata Responses to Climate. Stomata operate in their own solar cycles, not so different from our own circadian rhythms. ...
- Stomata responses to CO2 and Light Intensity. ...
- Controlling Stomata with Cannabis Grow Lights. ...
- Moisture and Stomata. ...
What substance do enters the leaf through the stomata?
Stomata are the tiny openings present on the epidermis of leaves. We can see stomata under the light microscope. In some of the plants, stomata are present on stems and other parts of plants. Stomata play an important role in gaseous exchange and photosynthesis. They control by transpiration rate by opening and closing.
What role do stomata play in leaves?
Nov 15, 2021 · Stomata are microscopic pores found mostly on the underside of leaves. The primary function of stomata is to allow gaseous exchange during photosynthesis and respiration between the plant’s internal tissues and the atmosphere. The process of transpiration also takes place through stomata.
How does stomata release water from a leaf?
Stomata are tiny pores or opening on the surface of a leaf. Stomata play an important role in gaseous exchange and photosynthesis. They control by transpiration rate by opening and closing. Functions of stomata: It helps in the transpiration of water, i.e., the loss of …
What does stomata do for a plant?
In botany, a stoma (plural "stomata"), also called a stomate (plural "stomates") (from Greek στόμα, "mouth"), is a pore, found in the epidermis of leaves, stems, and other organs, that facilitates gas exchange. Dicotyledons usually have more stomata on the lower surface of …
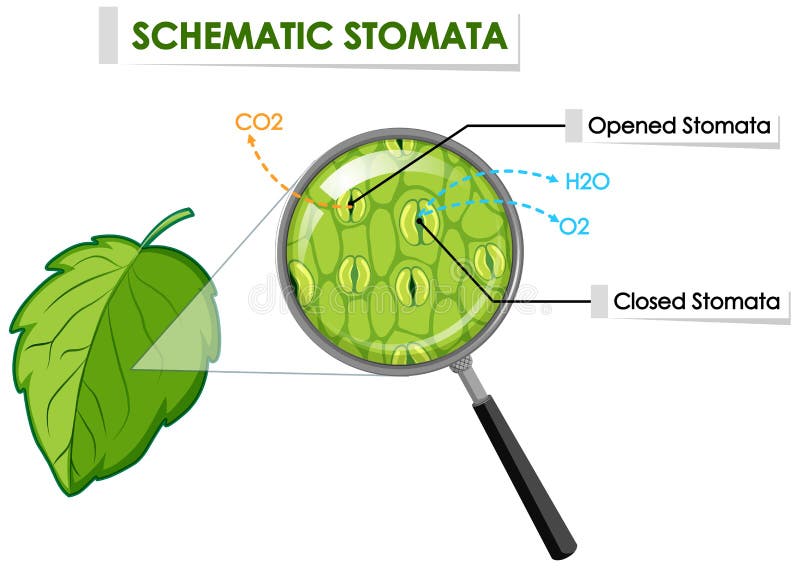
Where are stomata found in the plant cells?
In all green plants, stomata are found in the epidermis of leaves, stems, and other parts.
Why do plants need stomata?
Stomata are the specialized pores or openings present in the epidermis of plant cells, which play a crucial role in gaseous exchange during the pro...
What are the Guard Cells?
Two bean-shaped cells surrounding a stoma are called Guard Cells. They play a crucial role during the process of photosynthesis.
Explain the structure of stomata.
Stomata are the tiny, kidney, or bean-shaped pores or openings present in the epidermis of the cell. The stomatal opening has specialized guard cel...
List the types of stomata.
There are different types of stomata and are classified based on various criteria: Based on the structure: Paracytic. Tetracytic. Actinocytic. Gram...
Where are the stomata located?
The majority of stomata are located on the underside of plant leaves reducing their exposure to heat and air current. In aquatic plants, stomata are located on the upper surface of the leaves. A stoma (singular for stomata) is surrounded by two types of specialized plant cells that differ from other plant epidermal cells.
What do stomata do?
Stomata allow a plant to take in carbon dioxide, which is needed for photosynthesis. They also help to reduce water loss by closing when conditions are hot or dry. Stomata look like tiny mouths which open and close as they assist in transpiration.
What are the different types of stomata?
Stomata can be grouped into different types base on the number and characteristics of the surrounding subsidiary cells. Examples of different types of stomata include: 1 Anomocytic Stomata: Possess irregularly shaped cells, similar to epidermal cells, that surround each stoma. 2 Anisocytic Stomata: Features include an unequal number of subsidiary cells (three) surrounding each stoma. Two of these cells are significantly larger than the third. 3 Diacytic Stomata: Stomata are surrounded by two subsidiary cells that are perpendicular to each stoma. 4 Paracytic Stomata: Two subsidiary cells are arranged parallel to the guard cells and stomatal pore. 5 Gramineous Stomata: The guard cells are narrow in the middle and wider at the ends. The subsidiary cells are parallel to the guard cells.
What are the tiny openings in plant tissue that allow for gas exchange?
Stomata are tiny openings or pores in plant tissue that allow for gas exchange. Stomata are typically found in plant leaves but can also be found in some stems. Specialized cells known as guard cells surround stomata and function to open and close stomatal pores. Stomata allow a plant to take in carbon dioxide, which is needed for photosynthesis.
Why are stomata open during the day?
Stomata are open during the day because this is when photosynthesis typically occurs. In photosynthesis, plants use carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight to produce glucose, water, and oxygen. Glucose is used as a food source, while oxygen and water vapor escape through open stomata into the surrounding environment.
What are guard cells?
Guard cells are large crescent-shaped cells, two of which surround a stoma and are connected to at both ends. These cells enlarge and contract to open and close stomatal pores. Guard cells also contain chloroplasts, the light-capturing organelles in plants. Subsidiary cells, also called accessory cells, surround and support guard cells.
Who is Regina Bailey?
A.S., Nursing, Chattahoochee Technical College. Regina Bailey is a board-certified registered nurse, science writer and educator. Her work has been featured in "Kaplan AP Biology" and "The Internet for Cellular and Molecular Biologists.". Stomata are tiny openings or pores in plant tissue that allow for gas exchange.
