
The structure and function of sensory, relay and motor neurons.
| Structure | WHAT IS IT? |
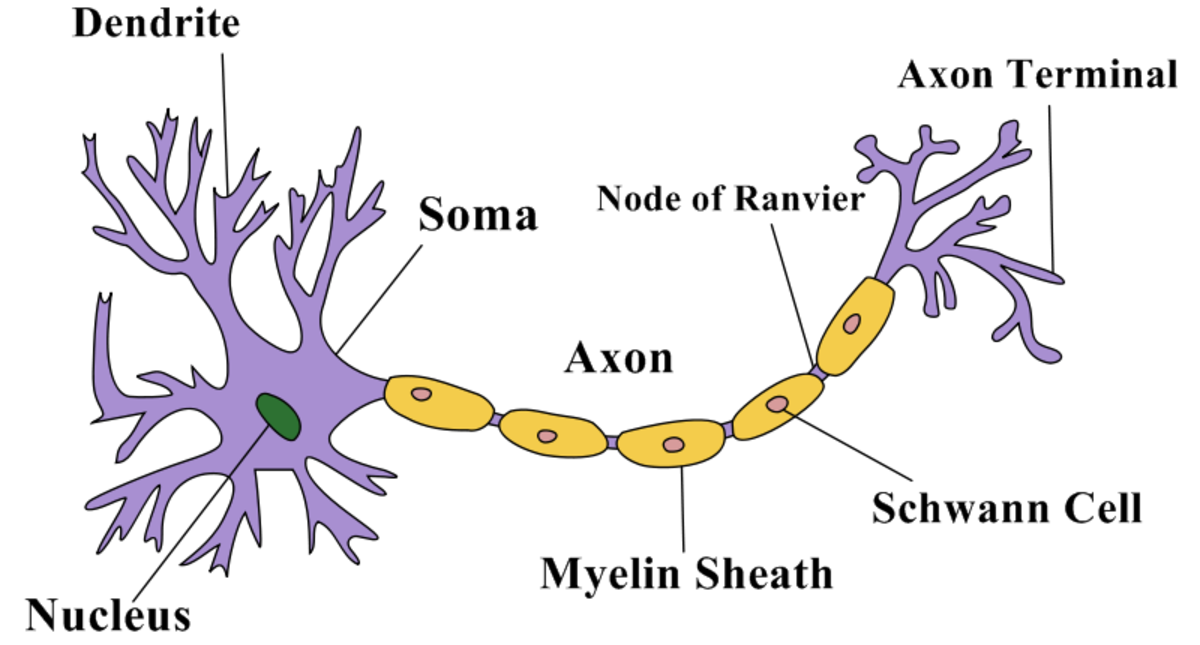
| Cell body | This includes a nucleus which contains t ... |
| Axon | This is a long extension from the cell b ... |
| Myelin sheath | This insulates or protects the axon from ... |
| Terminal button | Sends signals to an adjacent cell (anoth ... |
How is the structure of a neuron related to its function?
Answer: The structure of a neuron allows it to rapidly transmit nerve impulses to other cells. The axon of many neurons has an outer layer called a myelin sheath (see Figure above). Regularly spaced nodes, or gaps, in the myelin sheath allow nerve impulses to skip along the axon very rapidly.
Which structures carry sensory information into the neuron?
- The soma is the cell body where the nucleus lies, and which controls the cells and is also where proteins are produced to maintain the functioning of the neuron.
- The dendrites are the branch-like structures found at the ends of the neuron. ...
- The axon is the long extension structure stemming from the soma. ...
How does the structure of a neuron suit its function?
- The mass of cytoplasm present in the nerve cell is called neuro-plasm.
- Some cytoplasmic organelles like Mitochondria, Golgi-bodies, Endoplasmic Reticulum, Ribosome, Lysosome etc.
- It contains a prominent spherical nucleus with one or two nuclei but there is no centrosome.
- Neuron also consist Nissl’s granules. ...
What are the 3 types of neurons and their functions?
Types of neurons
- Sensory neurons. Sensory neurons are triggered by physical and chemical inputs from your environment. Sound, touch, heat, and light are physical inputs.
- Motor neurons. Motor neurons play a role in movement, including voluntary and involuntary movements. ...
- Interneurons. Interneurons are neural intermediaries found in your brain and spinal cord. ...
What is the function of sensory neurons?
Sensory neurons are the nerve cells that are activated by sensory input from the environment - for example, when you touch a hot surface with your fingertips, the sensory neurons will be the ones firing and sending off signals to the rest of the nervous system about the information they have received.
What is the structure of the sensory neurons?
Sensory neurons have dendrites on both ends and are connected by a long axon that has a cell body in the middle. Motor neurons have a cell body on one end and dendrites on the other end, with a long axon in the middle.
What is the structure and function of neurons?
Neurons are the structural and functional unit of the nervous system. All neurons have three different parts – dendrites, cell body and axon. The neuron structure is specially adapted to carry messages over large distances in the body quickly in the form of electrical signals.
What is the function of sensory neurons quizlet?
Sensory neurons are nerve cells within the nervous system responsible for converting external stimuli from the organism's environment into internal electrical impulses.
What is the structure of the sensory?
A sensory system consists of sensory neurons (including the sensory receptor cells), neural pathways, and parts of the brain involved in sensory perception. Commonly recognized sensory systems are those for vision, hearing, touch, taste, smell, and balance.
What structure are sensory cell bodies located?
Sensory neurons have their cell bodies in the spinal (dorsal root) ganglion. Their axons travel through the dorsal root into the gray matter of the cord. Within the gray matter are interneurons with which the sensory neurons may connect.
How is the structure of the neuron ideal for its function?
Neurons have long extensions that extend out from the cell body called dendrites and axons. Dendrites are extensions of neurons that receive signals and conduct them toward the cell body. Axons are extensions of neurons that conduct signals away from the cell body to other cells.
Between which structures do sensory neurons carry nerve impulses?
Two main types of neurons are sensory neurons and motor neurons.Sensory neurons carry nerve impulses from sense organs and internal organs to the central nervous system.Motor neurons carry nerve impulses from the central nervous system to organs, glands, and muscles—the opposite direction.
What are sensory neurons quizlet?
sensory neuron. cells that carry information from the body parts (senses) to the brain; allow you to sense. interneuron. nerve cells that carry information from one cell to another.
What are the functional differences between sensory neurons interneurons and motor neurons quizlet?
Sensory neurons carry signals from the outer parts of your body (periphery) into the central nervous system. Motor neurons (motoneurons) carry signals from the central nervous system to the outer parts (muscles, skin, glands) of your body. Interneurons connect various neurons within the brain and spinal cord.
Where are the sensory neurons located?
The cell bodies of the sensory neurons are located in the dorsal ganglia of the spinal cord.
What is the structure of a sensory neuron?
Structure of Sensory Neurons. A typical neuron is comprised of dendrites, an axon, and a cell body, and the sensory neurons are no exception. Most sensory neurons are pseudounipolar, which means they have a single axon extending from the cell body that forms two extensions: the dendrites and the axon. The sensory neuron “begins” with the dendrites, ...
What is sensory neuron?
A sensory neuron (sometimes referred to as an afferent neuron) is a nerve cell that detects and responds to external signals. Sensory neurons receive information via their receptors, which are part of the peripheral nervous system, and convert this information into electrical impulses. These impulses act as signals and are passed on to ...
What is the stimulus that triggers the sensory neuron to send a signal?
The stimulus triggers the sensory neuron to send a signal then carries information towards the central nervous system. Specifically, depolarization is initiated at the sensory receptors and transmitted along the dendrites to the cell body and then to the axon. At the axon terminal, the signal initiates the release of chemicals into the synapse.
How does the brain respond to stimuli?
To accurately respond to stimuli, the brain relies on information communicated by sensory neurons. Sensory neurons detect inputs from the environment, convert them into signals (electrical impulses), and pass the information on to the brain and spinal cord, where a response can be generated.
What are the three types of neurons?
There are three main types of neurons: sensory neurons, relay neurons, and motor neurons.
Where does the transduction of sensory signals take place?
The transduction of the signal takes place in the sensory receptor at the dendritic end of the neuron.
Which part of the brain receives sensory information?
The spinal cord and brain then receive and respond to this information. There are various types of sensory neurons that differ in their structure, location, and stimuli to which they respond. Morphology of a typical sensory neuron.
What are Sensory Neurons?
To understand what a sensory neuron is, it is important to first define a neuron.
Sensory Neuron Function
Sensory neurons interpret environmental stimuli that exist in several forms. Sound waves, for example, cause physical changes within the ear that will activate sensory neurons. Molecules broken down from ingested food cause sensory neurons in the tongue and mouth to respond.
Sensory Neuron Structure
As with other neurons, a sensory neuron consists of a cell body, several dendrites, and an axon. The nucleus, cytoplasm, and the organelles of the cell are centralized within the cell body. The dendrites of a sensory neuron resemble the branches of a tree. In fact, the overall collection of dendrites is often called a dendritic tree.
Sensory Neurons Location
Sensory neurons are found in the sensory organs associated with the five primary senses such as the eyes, nose, ears, tongue, and skin. More accurately, the dendrites of sensory neurons reside in the sensory organs. The cell bodies of these cells are grouped in the spinal cord in a specialized area called the dorsal root ganglia.
Five Primary Senses
Sensory neurons allow an individual to experience vision, smell, taste, touch, and hearing. Each of these will be described in further detail below.
Smell and Taste
The sense of smell is also called olfaction. When chocolate chip cookies are baking in the oven, tiny odor molecules from the magical aroma pass through the air and into the nose. Here, odor molecules, called odorants, are trapped and eventually dissolved in the mucus lining.
Sight
A specialized structure in the very back of the eye called the retina houses cells called photoreceptors. Photoreceptors are divided into two categories: rods and cones. Rods and cones are unique cells that are activated by photons of light traveling from surrounding objects.
What are the roles of neurons in the body?
There are three main neurons, all of which have different roles to play — Sensory, Relay and Motor Neuron. Structure.
How many neurons are there in the nervous system?
The neurons form pathways in the brain and throughout the body by being connected to one another by synapses. There are about 100 billion neuron s or nerve cells in the average nervous system. Neurons vary in size and shape. The neurons are specialised for communication whether this ...
What is the grey matter in the brain?
This is what gives the brain its grey colour (“grey matter”). This is a long extension from the cell body and can be up to a meter in length. Usually has two or more branches, called collateral branches. This insulates or protects the axon from external influences that might affect transmission of the nerve impulse.
Where are sensory neurons located?
The cell bodies of other PNS neurons, such as the sensory neurons that provide information about touch, position, pain, and temperature, are located outside of the CNS, where they are found in clusters known as ganglia. The axons of peripheral neurons that travel a common route are bundled together to form nerves.
Which type of neuron receives information from other neurons?
Interneurons. Interneurons, which are found only in the CNS, connect one neuron to another. They receive information from other neurons (either sensory neurons or interneurons) and transmit information to other neurons (either motor neurons or interneurons).
What are the parts of the nervous system?
The human nervous system 1 The central nervous system ( CNS) consists of the brain and the spinal cord. It is in the CNS that all of the analysis of information takes place. 2 The peripheral nervous system ( PNS ), which consists of the neurons and parts of neurons found outside of the CNS, includes sensory neurons and motor neurons. Sensory neurons bring signals into the CNS, and motor neurons carry signals out of the CNS.
How do neurons work together?
Neurons form networks. A single neuron can’t do very much by itself, and nervous system function depends on groups of neurons that work together. Individual neurons connect to other neurons to stimulate or inhibit their activity, forming circuits that can process incoming information and carry out a response.
How do motor neurons get information?
Motor neurons get information from other neurons and convey commands to your muscles, organs and glands. For instance, if you picked up a hot coal, it motor neurons innervating the muscles in your fingers would cause your hand to let go.
How many input signals do neurons receive?
Most neurons receive many input signals throughout their dendritic trees. A single neuron may have more than one set of dendrites, and may receive many thousands of input signals. Whether or not a neuron is excited into firing an impulse depends on the sum of all of the excitatory and inhibitory signals it receives.
What are the cells that make up the nervous system?
Like the heart, lungs, and stomach, the nervous system is made up of specialized cells. These include nerve cells (or neurons) and glial cells (or glia ).
What are sensory neurons?
Sensory Neurons. The sensory neurons convert signals from the external environment into corresponding internal stimuli. The sensory inputs activate the sensory neurons and carry sensory information to the brain and spinal cord. They are pseudounipolar in structure.
Which type of neuron is responsible for the transmission of information?
There are several different types of neurons that facilitate the transmission of information. The sensory neurons carry information from the sensory receptor cells present throughout the body to the brain.
How does action potential affect other neurons?
In chemical synapses, the action potential affects other neurons through a gap present between two neurons known as the synapse. The action potential is carried along the axon to a postsynaptic ending that initiates the release of chemical messengers known as neurotransmitters.
What is the unit of the nervous system that transmits information to different parts of the body?
Neuron Definition. “Neurons are the fundamental unit of the nervous system specialized to transmit information to different parts of the body.”.
Where are motor neurons located?
Motor Neurons. These are multipolar and are located in the central nervous system extending their axons outside the central nervous system. This is the most common type of neuron and transmits information from the brain to the muscles of the body.
What happens when two neurons are connected by a gap junction?
When two neurons are connected by a gap junction, it results in an electrical synapse. These gaps include ion channels that help in the direct transmission of a positive electrical signal. These are much faster than chemical synapses.

Definition
Overview of Neurons
- Neurons are cells of the nervous systemthat can transmit electrical impulses to facilitate communications between the brain and the rest of the body. There are three main types of neurons: sensory neurons, relay neurons, and motor neurons. Motor neurons control movement, sensory neurons allow us to feel sensations, and relay neurons allow motor neurons and sensor…
Structure of Sensory Neurons
- A typical neuron is comprised of dendrites, an axon, and a cell body, and the sensory neurons are no exception. Most sensory neurons are pseudounipolar, which means they have a single axon extending from the cellbody that forms two extensions: the dendrites and the axon. The sensory neuron “begins” with the dendrites, as this is where the signal is received from the external envir…
Location of Sensory Neurons
- The cell bodies of sensory neurons cluster together at regions called the dorsal ganglia of the spinal cord, sometimes called the dorsal root ganglia. Note that the term ganglia simply means a collection of cell bodies. Sensory neurons begin in the periphery. For example, in the skin, we can perceive tactile stimuli that detect touch, pain, and cold because of the sensory neurons located …
Function of Sensory Neurons
- Sensory neurons make up all the senses in the body, even those of which you are not consciously aware! The function of sensory neurons is to detect and transmit signals from a peripheral region to a more central location in the central nervous system, i.e., the spinal cord or the brain. The transduction of the signal takes place in the sensory receptorat the dendritic end of the neuron. …
Sensory Neurons vs. Motor Neurons
- To put it simply, sensory neurons are for “feeling,” and motor neurons are for “doing.” Motor neurons are efferent (meaning they carry information out towards the periphery from the central nervous system). In contrast, sensory neurons are efferent (they carry information in towards the central nervous system from the periphery). Motor neurons tend to have a multipolar morpholog…
Types of Sensory Neurons
- Sensory neurons can be classified in various ways, including by their morphology, location, and the stimulus they are responsible for detecting. Below are some examples of sensory neurons classified by the type of stimulus to which they respond. 1. Olfactory sensory neurons are bipolar neurons located in the nasal cavity. They are activated by odor molecules in the air and give us o…