What is the molecular structure of Kevlar?
Molecular structure of Kevlar: bold represents a monomer unit, dashed lines indicate hydrogen bonds. When Kevlar is spun, the resulting fiber has a tensile strength of about 3,620 MPa (525,000 psi), and a relative density of 1.44 (0.052 lb/in 3 ). The polymer owes its high strength to the many inter-chain bonds.
Does Kevlar have a giant molecular structure?
So yes, Kevlar is made up of a lot of monomers. However, the monomers are actually not that big! That 'n' just signifies that the molecule in the brackets can be repeated as many times as one would like. Originally Answered: Does kevlar have a giant molecular structure? Kevlar is chemically aramid, a polyamid fiber similar to nylon and perlon.
What is kevlar made up of?
Kevlar is made from aromatic polyamide polymer that is synthetic or simply called as aramids. Kevlar is made inside a chemical laboratory just like any other synthetic materials. Since it is aromatic, it means that Kevlar also have tightly knitted molecules.
What is the difference between kevlar and Twaron?
The difference between Kevlar and Twaron is that kevlar cloth is woven and can be used for purposes such as mooring lines in marine applications. The Kevlar composite is also used to produce automotive components, fiber optics, and industrial garments. Twaron is a fiber that is solid and synthetic. It’s heat-proof, too.
What are the properties of a Kevlar?
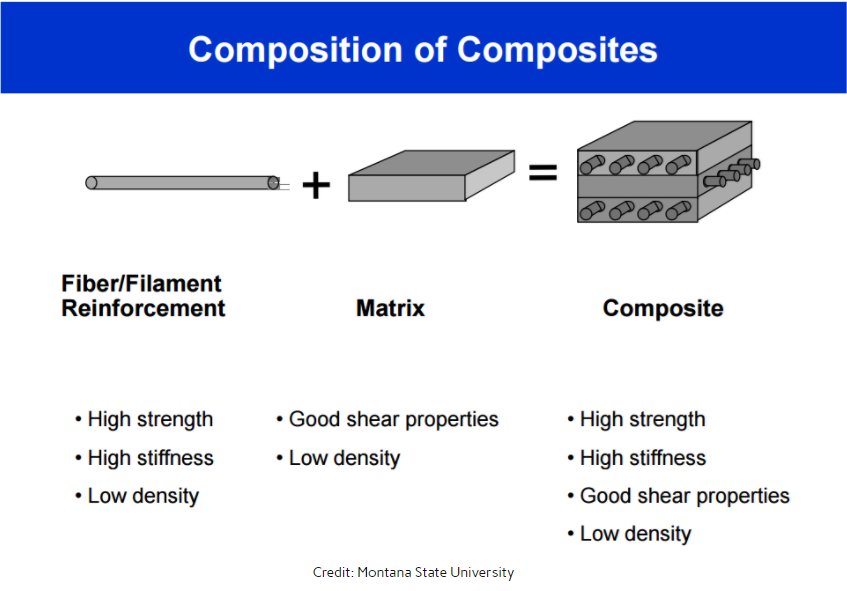
Kevlar has unique properties, such as high tensile strength, high toughness, and chemical stability at high temperatures in aromatic polyamides. Kevlar is widely-used as a friction material in the automotive industry and a combustion protection material in the aerospace industry.
What kind of bonding is Kevlar?
hydrogen bondingKevlar has a highly crystalline structure. Strong covalent bonding in the fiber direction and weak hydrogen bonding in the transverse direction result in highly anisotropic properties of Kevlar fiber.
What molecules make up Kevlar?
A single Kevlar polymer chain could have anywhere from five to a million segments bonded together. Each Kevlar segment or monomer is a chemical unit that contains 14 carbon atoms, 2 nitrogen atoms, 2 oxygen atoms and 10 hydrogen atoms.
Is Kevlar 100% bulletproof?
It's not 100 percent effective at stopping bullets from a handgun. Kevlar jackets are also not so effective with bullets fired from Assault rifles because they are traveling three times the speed of sound, way faster than those from a handgun. And that speed can help the bullet breakthrough the layers of the Kevlar.
What about Kevlar makes it so strong?
The chemical structure of Kevlar® is comprised of several repeating inter-chain bonds. These chains are cross-linked with hydrogen bonds, providing a tensile strength 10X greater than steel on an equal weight basis. Kevlar® fibers are so tightly spun that it is nearly impossible to separate them.
Why is Kevlar 5 times stronger than steel?
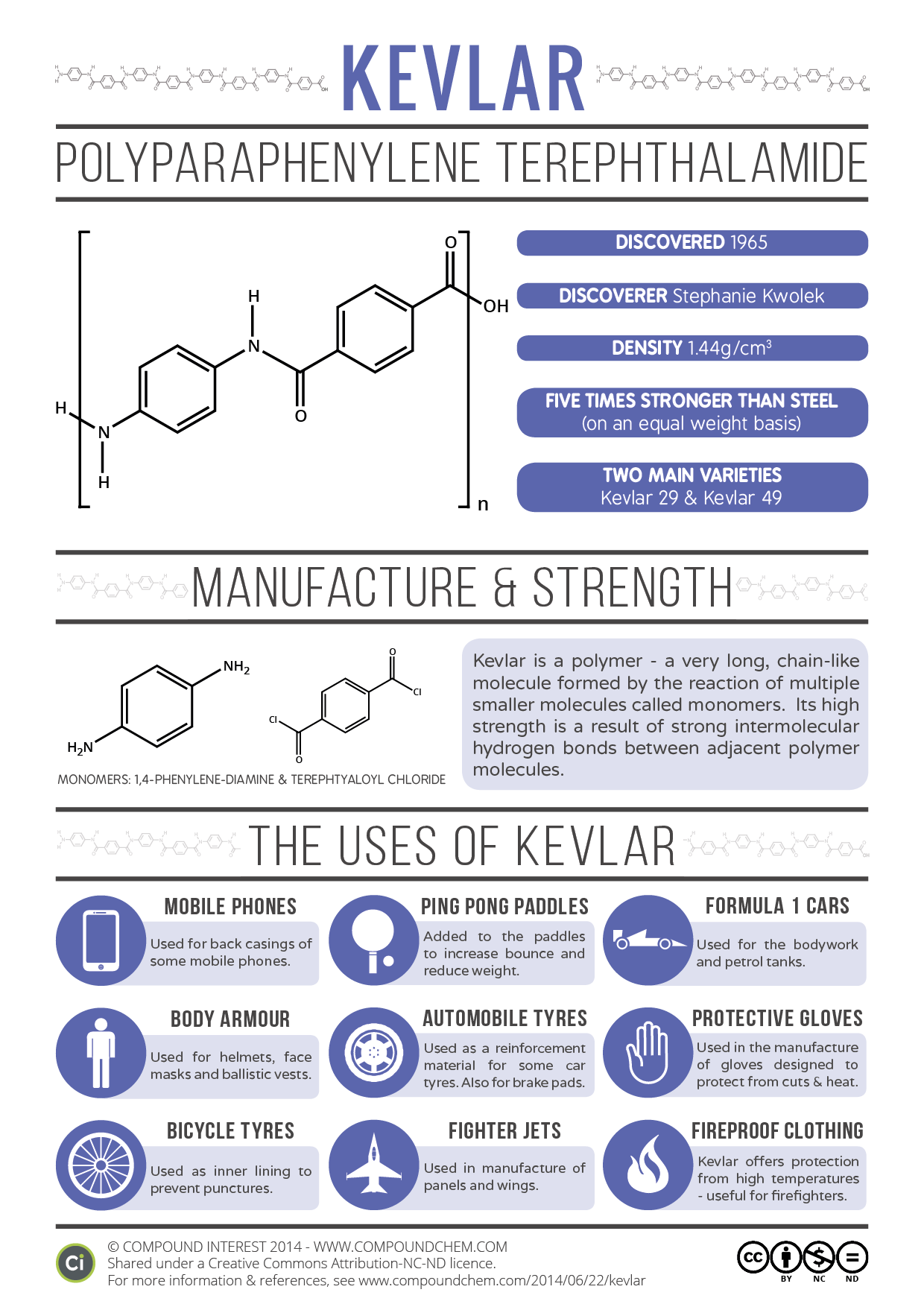
Kevlar, the accidental discovery of chemist Stephanie Kwolek, is one of the strongest and most versatile textiles, boasting a tensile strength-to-weight ratio so high it is actually five times stronger than steel. Kevlar is a synthetic material that is, to put it simply, a very strong woven plastic.
Can Kevlar stop a knife?
A Kevlar® vest with stab and spike rating will protect against edged and spiked attacks from objects such as knives, broken bottles and syringes.
Can Kevlar stop a bullet?
Kevlar is able to stop a bullet due to its molecular structure. It is a light, polyarylamide plastic fabric, which has a high tensile strength. this means it takes a huge amount of energy to make its fibres stretch even a little. Each Kevlar molecule looks like a long twisting coil.
Is all Kevlar bulletproof?
It's important to remember that no material is 100 percent bulletproof—and sometimes even Kevlar isn't enough.
How many layers of Kevlar does it take to stop a 9mm?
21 layers4) It was assessed that for a 9 mm Parabellum ammunition, which are most commonly used around the world, 21 layers of 200 GSM Kevlar is required as a minimum to stop the projectile.
Is Kevlar toxic?
INGESTION: Based on animal studies, KEVLAR® is nontoxic when eaten. INHALATION: KEVLAR® fiber is too big to inhale into the lungs, but fiber dust and fly from processing may be breathed into the nose and throat. Working unprotected in dusty conditions may cause upper respiratory irritation and cold-like symptoms.
Is Kevlar waterproof?
Once it is manufactured into its fiber form, it is then made into a thread that can be woven into fabric or other materials. This is how it is woven into body armor and bulletproof vests. An important thing to note about Kevlar is that it is not waterproof and can not be placed in direct sunlight.
Does Kevlar have hydrogen bonding?
In Kevlar, the attraction that holds the polymer strands together works on a principle similar to electrostatic attraction. The difference is that polymer strands of Kevlar are held together by hydrogen bonding (which you have probably guessed involves hydrogen).
Is Kevlar polar or nonpolar?
Kevlar molecules have polar groups accessible for hydrogen bonding. Water that enters the interior of the fibre can take the place of bonding between molecules and reduce the material's strength, while the available groups at the surface lead to good wetting properties.
Can you glue Kevlar?
Preferred adhesives for bonding Kevlar include Supreme 11HT, EP21TDCHT and EP3HT. High shear and peel strength epoxy adhesive system Supreme 11HT cures at room temperature. It exhibits resistance to stress cracking fatigue and impact.
Is Kevlar a compound?
Kevlar is a manufactured plastic, and it's made of a chemical compound called poly-para-phenylene terephthalamide. This chemical is made from creating a chemical reaction between an acid and a chemical solution containing nitrogen and hydrogen.
What is kevlar made of?
Kevlar is made from a condensation reaction of 1,4- para-phenylenediamine and terephthalic acid. The presence of amine groups on aromatic ring results in a rod-like structure which has high glass transition temperature and low solubility. The chains of polymer are connected to each other via Hydrogen bonding between adjacent polar amide groups ...
How strong is kevlar?
Kevlar fibers have tensile strength twice than Nylon 6,6 ranging from about 2.6 to 4.1 GPa. The mechanical properties of different grades are given in the table below:
What grades of Kevlar are there?
It is commonly available in grades like K-29, K-49, K-100, K-119, and K-129. Presently, Kevlar fiber is available in a number of variants: Kevlar K-29 – It is a high toughness grade used in industrial applications, such as cables, ...
What is the purpose of kevlar fiber?
In 1988, the second generation of Kevlar fiber was developed which offers ballistic resistance against 9mm FMJ.
How are fibers made?
Fibers are manufactured by melt spinning of PPD-T solution extruded through a spinneret and then directly solidification upon cooling . The solution is heated to attain required viscosity in induction heated extruders. This melt is passed at high pressure and constant rate from a spinneret and enters an air-cooled stream which solidifies it into a filament form. At the lower end of the spinning setup, a guided coverage converts these individual filaments to form a continuous spun yarn. This yarn is then wound onto bobbins or treated further for end-use applications.
What is K49 used for?
Kevlar K49 –It has a high modulus used in rope and cable products.
Which direction are the filaments of fibers extruded?
The extruded rod-like para-aramid structure has high anisotropic properties. The strength and stiffness is higher in the axial direction and lowers in the transverse direction.
What is the tensile strength of kevlar?
These chains are cross-linked with hydrogen bonds, providing a tensile strength 10X greater than steel on an equal weight basis.
What is the ballistic resistance of kevlar?
Ballistic resistance. Kevlar® fibers are so tightly spun that it is nearly impossible to separate them. When a bullet or other high-velocity projectile hits Kev lar®, the fibers essentially catch the projectile while absorbing and dissipating its energy.
Who makes Dupont kevlar?
Created by Stephanie Kwolek, DuPont ™ Kevlar ® is a heat-resistant para-aramid synthetic fiber with a molecular structure of many inter-chain bonds that make Kevlar ® incredibly strong.
Who is stronger than steel?
Stephanie Kwolek: stronger than steel. A pioneer in polymer research, Stephanie Kwolek accumulated several patents and awards throughout her career. Most notably, she is known for her groundbreaking work that led to the creation of Kevlar® - an incredibly strong material that continues to push the limits of possible.
What is a kevlar?
Kevlar is DuPonts name for aramid fibers. Aramid fibers are light weight, strong, and tough. Two types of aramid fiber are used in the aviation industry. Kevlar 49 which has a high stiffness and Kevlar 29 which has a low stiffness. An advantage of aramid fibers is their high resistance to impact damage, so they are often used in areas prone ...
What is kevlar laminate?
Kevlar is widely-used as a friction material in the automotive industry and a combustion protection material in the aerospace industry. The net shaping of Kevlar laminates is difficult using the conventional machine tools due to whiskers forming and loose fibers around the machine edges. In addition, the specific energy required for machining is higher than most of the engineering materials. Moreover, laser machining offers considerable advantages over the conventional techniques. Some of these advantages include a high-quality end product, precision of operation, and low cost. Laser cutting eliminates the whiskers emanating from the machined edges due to thermal effect. Although unwoven Kevlar laminates are easy to bend, the development of resolidified regions at the kerf edges and the formation of a heat-affected zone in the cut section increases brittleness of laser machined Kevlar laminates in this region. This, in turn, limits the practical application of the machined laminates.
What is aramid rope?
Aramid (used in Kevlar and Twaron brands ) rope has strength and stiffness comparable to steel wire rope. It is only occasionally used for offshore moorings, because it has a failure mode of axial compression fatigue, which can cause the rope to fail if fibers are subjected to compression. The first attempt to use large aramid fiber rope in a deepwater mooring system was in 1983 [9]. These aramid ropes were break tested to verify their strength. The aramid mooring lines were preset several months before a barge arrived in a manner that allowed them to become slack and rotate. This action caused axial compression fatigue in and near the bottom splices, which reduced the rope strength. When the barge was finally moored and the lines were tensioned to set the anchors, several of the aramid ropes failed. Prior to that incident, there was little understanding of axial compression fatigue. Note however that the axial compression can be avoided or minimized by good rope design, by maintaining a tension in the rope that does not allow fibers to see compression, and by using good termination techniques.
How to inspect kevlar?
One of the methods used to inspect the integrity of structures made from Kevlar is CT. CT is commonly used in the inspection of metals. However, this method is now being used for composites. Fidan [72] utilized microcomputerized tomography to visualize the internal damage impact on glass fiber–reinforced and glass fiber + aramid fiber–reinforced polyester composites. Low-velocity impacts were tested at 80 J energy. From the investigation, the micro-CT showed that the 3D-delamination pattern defect in glass-reinforced composites is more visible due to the nature of the glass fiber. However, the delamination pattern lost its effectiveness when aramid fiber was added to the glass fiber.
What is a vectran fiber?
Vectran is a polyester-based high-performance Liquide Crystal Polymer (LCP) produced by Ticona , and its performances are listed in Table 2.60. Its modulus is similar to Kevlar 29, but it has less strength loss. Vectran fiber shows a 0.02% creep at 30% of max load after 10,000 h, high chemical and abrasion resistance and high tensile strength. The UV endurance of Vectran is inferior to PET and PEN, but has better exposure degradation than aramids.
Is kevlar hard to cut?
Another disadvantage is that Kevlar is difficult to drill and cut. The fibers fuzz easily, and special scissors are needed to cut the material. Kevlar is often used for military ballistic and body armor applications. It has a natural yellow color and is available as dry fabric and prepreg material.
Is kevlar a composite?
It is usually made into composites. Kevlar can also be combined with other fibers to produce hybrid composites. The hybrid composites of Kevlar are tabulated in Table 16.1. Since Kevlar is used in many structural applications, NDT plays an important role in determining the integrity of the structure.
What materials are used in space suits?
Learn about some of the synthetic materials—nylon, Dacron, Mylar, Kevlar —from which space suits are made. Kevlar, trademarked name of poly-para-phenylene terephthalamide, a nylonlike polymer first produced by Du Pont in 1971.
Is kevlar stronger than steel?
Kevlar can be made into strong, tough, stiff, high-melting fibres, five times stronger per weight than steel; it is used in radial tires, heat- or flame-resistant fabrics, bulletproof clothing, and fibre-reinforced composite materials for aircraft panels, boat hulls, golf-club shafts, and lightweight bicycles. Britannica Quiz.
What exactly is Kevlar?
Kevlar is one of those magic modern materials people talk about all the time without ever really explaining any further. "It's made of Kevlar", they say, with a knowing nod, as though that were all the explanation you needed.
How is Kevlar made?
There are two main stages involved in making Kevlar. First you have to produce the basic plastic from which Kevlar is made (a chemical called poly-para-phenylene terephthalamide —no wonder they call it Kevlar). Second, you have to turn it into strong fibers. So the first step is all about chemistry; the second one is about turning your chemical product into a more useful, practical material.
How are polyamides made?
Polyamides like Kevlar are polymers (huge molecules made of many identical parts joined together in long chains) made by repeating amides over and over again. Amides are simply chemical compounds in which part of an organic (carbon-based) acid replaces one of the hydrogen atoms in ammonia (NH3). So the basic way of making a polyamide is to take an ammonia-like chemical and react it with an organic acid. This is an example of what chemists call a condensation reaction because two substances fuse together into one. [7]
How does kevlar get its properties?
Photo: Kevlar textiles get their properties partly from the inherent strength of the polymer from which the fibers are made and partly from the way the fibers are knitted tightly together , as shown here in a NASA ballistics test. Picture courtesy of NASA Glenn Research Center (NASA-GRC).
How long does it take for kevlar to degrade?
Kevlar can resist attacks from many different chemicals, though long exposure to strong acids or bases will degrade it over time. In DuPont's tests, Kevlar remained "virtually unchanged" after exposure to hot water for more than 200 days and its super-strong properties are "virtually unaffected" by moisture.
What is polyamide in concrete?
Polyamide means the ring-like aromatic molecules connect together to form long chains. These run inside (and parallel to) the fibers of Kevlar a bit like the steel bars ("rebar") in reinforced concrete.
What is kevlar vest used for?
Originally developed as a lightweight replacement for steel bracing in vehicle tires, it's probably best-known today for its use in things like body armor; by the time of Kwolek's death in 2014, one million Kevlar body vests had been sold—and countless lives saved.
What is kevlar pulp?
Kevlar® pulp (Figure 3.1) is a highly fibrillated form of the fiber that can be dispersed into many different matrix systems. The fibrillation (Figure 3.2) results in a high surface area of 7 m2/g to 10 m2/g (170 yd2/oz to 240 yd2/oz).
What is short kevlar?
Short Kevlar® pulp is available in a masterbatch form for easy, uniform dispersion in viscous elastomers. When Kevlar® pulp is blended with various elastomers it gives enhanced tensile strength (Table III-1) at elevated temperatures. It also increases the modulus (Figure 3.6), tear resistance, wear resistance and puncture resistance of the resulting compounds. To make it easier to incorporate pulp into elastomers,DuPont offers Kevlar® M/B a masterbatch concentrate. Kevlar® M/B can also be blended with other elastomers to give desired end-use properties.
How does RH affect kevlar?
Moisture regain is the tendency of most fibers to pick up or give off ambient atmospheric moisture until they reach an equilibrium moisture content at a given temperature and humidity level. Relative humidity (RH) has a significant effect on the rate of moisture absorption by Kevlar® and the equilibrium level reached. The higher the RH, the faster Kevlar® absorbs moisture during the initial phase of moisture gain, and the higher the final equilibrium level.Bone-dried Kevlar® will reach a slightly lower equilibrium moisture level than fiber that has never been bone dried. Figure 2.3 illustrates this effect for Kevlar® 29. Figure 2.4 illustrates the effect of RH on the equilibrium moisture content obtained from a bone-dry yarn of Kevlar® 49. This relationship is linear throughout the entire RH range.
How long does kevlar degrade?
At neutral pH (pH 7), the filament tenacity remains virtually unchanged after exposure at 149°F (65°C) for more than 200 days.
Is kevlar a UV ray?
Like other polymeric materials, Kevlar® is sensitive to UV (ultraviolet) light. Unprotected yarn tends to discolor from yellow to brown after prolonged exposure. Extended exposure to UV can also cause loss of mechanical properties, depending on wavelength, exposure time, radiation intensity and product geometry. Discoloration of fresh yarn after exposure to ordinary room light is normal and is not indicative of degradation.
Does arctic temperature affect tensile strength of kevlar?
Exposure to arctic conditions (-50°F [-46°C]) does not adversely influence the tensile properties of Kevlar® (Table II-6). The increase in modulus and the small decrease in break elongation at this low temperature can be attributed to a slight increase in molecular rigidity.
Does kevlar melt?
Kevlar® does not melt; it decomposes at relatively high temperatures (800°F to 900°F [427°C to 482°C] in air and approximately 1,000°F [538°C] in nitrogen), when tested with a temperature rise of 10°C/minute. Decomposition temperatures vary with the rate of temperature rise and the length of exposure.