
What is a nucleosome made up of?
A nucleosome consists of a strand of DNA, eight core histone proteins, and one linker protein. Euchromatin is the less dense form of chromatin that allows for transcription. Active chromatin is another name for euchromatin because it allows for gene transcription.
How are the nucleosomes connected to the adjacent nucleosome core?
The nucleosome core is connected to the adjacent nucleosome core through a segment of linker DNA, which often associates with the linker histone protein (H1 or H5).
What is the structure of a histone nucleosome?
The nucleosome structure consists of DNA and a histone protein complex. One strand of DNA is coiled around one core histone octamer to create a histone nucleosome. Each core histone octamer is comprised of two copies of four core histone proteins for a total of 8 proteins in all:
How many base pairs are in a nucleosome?
A single nucleosome consists of about 150 base pairs of DNA sequence wrapped around a core of histone proteins. The nucleosomes are arranged like beads on a string. They are repeatedly folded in on themselves to form a chromosome.
Why is the structure of a nucleosome so important?
Nucleosomes are thought to carry epigenetically inherited information in the form of covalent modifications of their core histones. Nucleosome positions in the genome are not random, and it is important to know where each nucleosome is located because this determines the accessibility of the DNA to regulatory proteins.
What is nucleosome draw the structure of it?
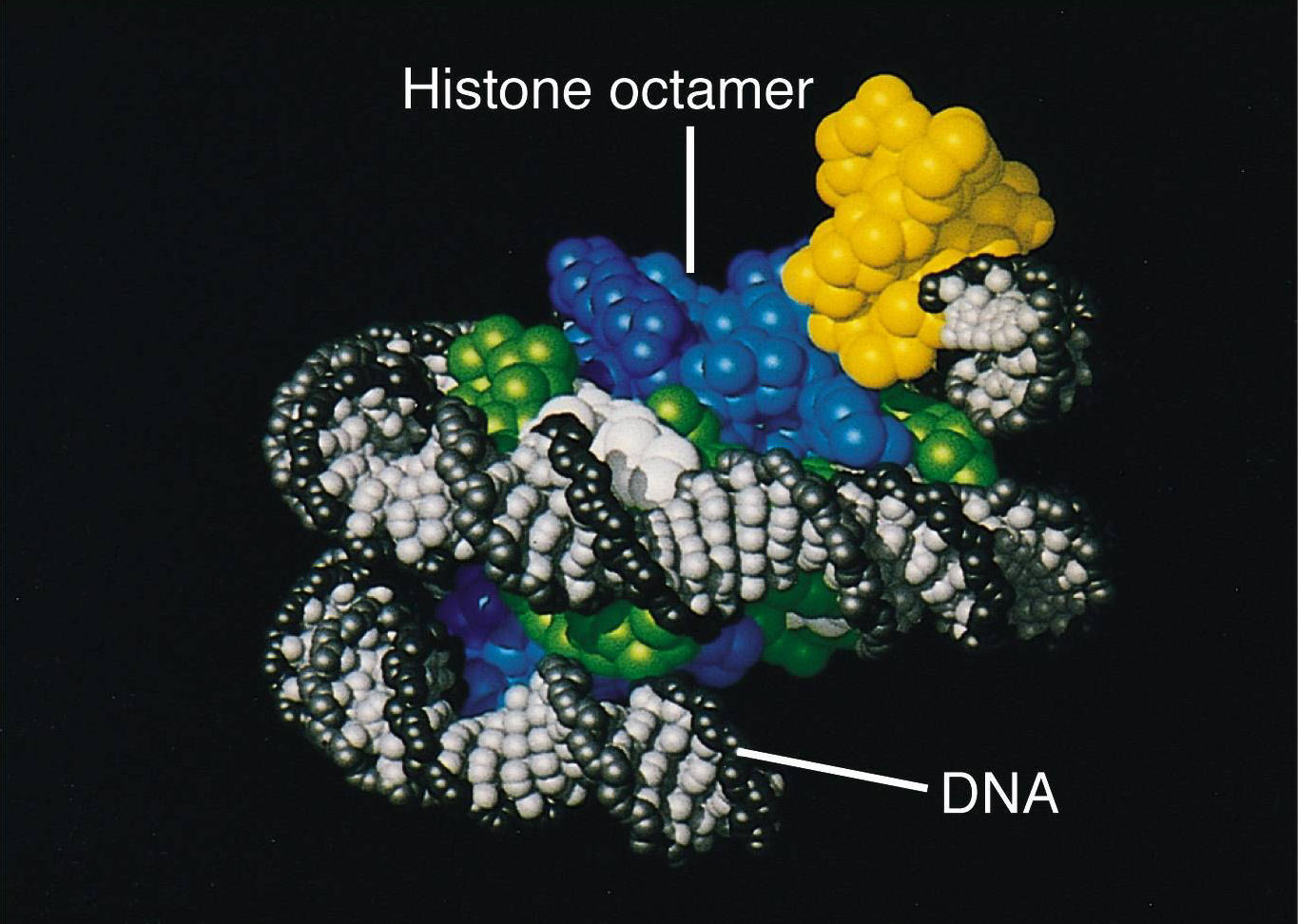
The nucleosome is the fundamental subunit of chromatin. Every nucleosome is composed of less than two turns of DNA wound around a set of eight proteins called histones, which are called histone octamers. One histone octamer comprises two copies of each of the histone proteins H2A, H2B, H3, and H4.
What is the main function of nucleosome?
A nucleosome on a promoter prevents the initiation of transcription. The association of nucleosomes with most genomic DNA prevents initiation from cryptic promoters. The nucleosome thus serves not only as a general gene repressor, but also as a repressor of all transcription (genic, intragenic, and intergenic).
Which histone is a structural component of nucleosome?
The nucleosome is the smallest structural component of chromatin, and is produced through interactions between DNA and histone proteins. Here, a histone octamer is formed from the histones H2A, H2B, H3 and H4, although in some cases other histone variants may also be found in the core (e.g., H2A.
What is a nucleosome Class 12?
Nucleosomes are the repeating unit in the eukaryotic chromatin and give the appearance of beads on a string. A single nucleosome has around 150 base pairs of DNA. The eukaryotic cells undergo DNA packaging to accommodate the- large lengths of the DNA molecules into the nucleus of each cell.
What is nucleosome very short answer?
A nucleosome is a section of DNA that is wrapped around a core of proteins. Inside the nucleus, DNA forms a complex with proteins called chromatin, which allows the DNA to be condensed into a smaller volume. When the chromatin is extended and viewed under a microscope, the structure resembles beads on a string.
What are nucleosomes made of?
A single nucleosome consists of about 150 base pairs of DNA sequence wrapped around a core of histone proteins. In forming a chromosome, the nucleosomes repeatedly fold in on themselves to tighten and condense the packaged DNA.
Where are nucleosomes found?
the nucleusNucleosome is found in the nucleus of the eukaryotic cell. It is the basic unit of DNA packaging into chromosomes. Nucleosomes are the repeating units in the chromatin thread, which give the beaded appearance. In the nucleosome DNA is wound around the core of histone octamer.
How many base pairs are in a nucleosome?
The basic repeating structural (and functional) unit of chromatin is the nucleosome, which contains eight histone proteins and about 146 base pairs of DNA (Van Holde, 1988; Wolffe, 1999).
Which of the following structure are present in core particle of nucleosome?
The nucleosome core particle consists of fourteen turns of B-form DNA around an octamer of histone proteins. The octamer contains two copies each of four different proteins: H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. One can think of this arrangement as the dimerization of tetramers. These four proteins are arranged with C2 Symmetry .
What is nucleosome model of chromosome?
Nucleosome model is a scientific model which explains the organization of DNA and associated proteins in the chromosome. It also further explains the exact mechanism of the folding of the DNA in the nucleus. The model was proposed by Roger Kornberg in 1974 and is the most accepted model of chromatin organization.
What is nucleosome PDF?
The nucleosome core particle consists of an octameric. protein core around which 147 base pairs of DNA are. wrapped in 1.65 turns of a left-handed superhelix.
Nucleosomes
What is a nucelosome? The nucleosome definition is a repeating unit within a chromosome that consists of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and a histone. DNA is the genetic code for nearly every living organism, and histones are complexes of proteins. Histones:
Nucleosome Structure
The nucleosome structure consists of DNA and a histone protein complex. One strand of DNA is coiled around one core histone octamer to create a histone nucleosome. Each core histone octamer is comprised of two copies of four core histone proteins for a total of 8 proteins in all:
Components of a Nucleosome
What are nucleosomes made of? As mentioned, nucleosomes are made up of:
Importance of Nucleosomes
Euchromatin is the less dense form of chromatin that allows for transcription. Active chromatin is another name for euchromatin because it allows for gene transcription.
Nucleosome Model
In this activity, students are going to be applying their knowledge of the nucleosome to create two three dimensional models and comparing them.
What is the nucleosome?
A nucleosome is a structure in your chromosomes, or bundled DNA. Each nucleosome has a core particle, DNA, and a linker protein. The proteins in the core particle and linker proteins are called histones. The DNA will wrap around the core particle about 1.65 times and is secured by the linker protein. This figure shows a drawing of a nucleosome.
What is the arrangement of nucleosomes called?
This arrangement is said to look like beads on a thread. Several nucleosomes together are called chromatin. Chromosomes are bundles of tightly packed chromatin.
What is the name of the part of the cell cycle where DNA is not packaged into chromosomes?
When a cell is not undergoing cell division, its DNA is not packaged into chromosomes. This part of the cell cycle is called interphase. Thus, DNA in this form is called interphase chromatin. The DNA is spread out throughout the nucleus and looks like a plate of spaghetti. Interphase chromatin can be of two types.
How many histones are in a nucleosome?
The protein portion of a nucleosome is made of histones. There are five major families of histones, which include H1, H2A, H2B, H3, H4, and H5. The core particle has eight total histones. One H2A and H2B bind together to form a dimer, or two proteins bound together. An H3 and an H4 will bind to also form a dimer.
What is the protein portion of DNA?
The protein portion is made of small units called histones. The core particle is made of four types of histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4). DNA wraps around the core particle. Either the H1 histone or the H5 histone will be used to bind the DNA to the core particle. To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member.
What is the form of DNA that is not broken when a cell divides?
This ensures that the DNA is not broken and helps ensure transfer into daughter cells. DNA in this form is called chromosomal chromatin. When a cell is not undergoing cell division, its DNA is not packaged into chromosomes.
How many times does DNA wrap around the core?
The DNA will wrap around the core particle about 1.65 times and is secured by the linker protein. This figure shows a drawing of a nucleosome. Nucleosome Structure. About 200 bases of DNA are involved with each nucleosome.
How many base pairs are in a nucleosome?
The bead and the connecting string (seen in Fig. 19.7) constitute one repeat unit. Structurally it contains about 200 base pairs (bp) of DNA and all the 5 histones. ADVERTISEMENTS:
What is the role of H1 in the nucleosome?
According to Kornberg and Klug (1981), H1 leads to folding of the 10 nm fibre to form the solenoid.
What happens when chromatin is digested with micro-coccal nuclease?
When chromatin is digested with micro-coccal nuclease, it produces oligomeric DNA fragments of specific lengths which correspond with the repeat unit observed in EM. The core particles are most resistant to degradation by nuclease and the linkers are the most nuclease sensitive regions.
How many turns of DNA are in a core?
It is calculated that each core particle is associated with 1.75 turns of DNA. Although it is often stated that nucleosomes are present in inactive, non-transcribing chromatin, there are some conflicting reports on this aspect. EM observations have shown the absence of nucleosomes at the sites of rRNA transcription.
Which type of DNA is transcribed by pronase digestion?
Pronase digestion of the 10 nm fibre leaves a DNAse sensitive 2 nm fibre which contains the single DNA double helix. It is now well known that only a small fraction of eukaryotic chromatin is transcribed (active chromatin) in a particular nucleus while most of it is silent (inactive chromatin).
Does EM show nucleosomes?
EM observations have shown the absence of nucleosomes at the sites of rRNA transcription. However, nucleosomes have been observed in chromatin regions involved in non-ribosomal RNA synthesis. Some studies on the structure of chromatin have shown the presence of nucleosomes in both active and inactive chromatin.
What are the building blocks of DNA?
The nucleosomes are structural building blocks of the packing of DNA within a chromosome. The packing problem of how to fit a very, very long stretch of DNA, which is about a yard of DNA, inside a very small cell, which is about a hundredth of a millimeter in diameter, has fascinated scientists for a long time. And it turns out how the cell does this--now--remember that each cell in the body has this problem--is that it coils and super coils the DNA in a multitude of complex ways. The fundamental building block of that coiling are nucleosomes, which are blocks of essentially little spheres of histone proteins around which the DNA is wrapped, and they look literally like beads on a string, except the beads have the DNA wrapped around them instead of having the DNA go through them, as in the case of a bead on a string.
What is the basic repeating unit of eukaryotic chromatin?
A nucleosome is the basic repeating unit of eukaryotic chromatin. In a human cell, about six feet of DNA must be packaged into a nucleus with a diameter less than a human hair. A single nucleosome consists of about 150 base pairs of DNA sequence wrapped around a core of histone proteins.
Nucleosome is a Unit of Chromatin
Nucleosomes are considered as the basic unit of chromatin as if the cells are the basic unit of life. Thus, the basic structural and functional unit of chromatin is the nucleosome which is made up of eight histone proteins, so it is also called as histone octomer.
Structure of Nucleosome
When chromatin or whole chromosomes are let to read in air or water interface and examined under an electron microscope, a fibres of length 250 Angstrom are noted.
