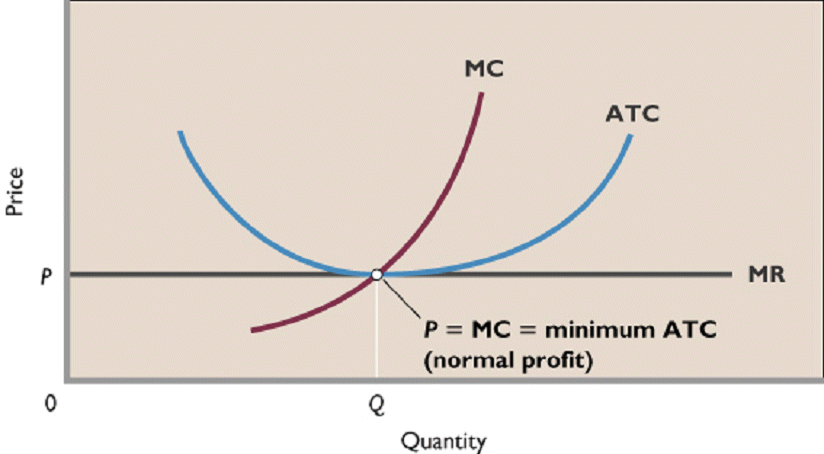
Why is the short run supply curve positively sloped?
Why is the aggregate supply curve positively sloped in the short run? In the short-run, the aggregate supply curve is upward sloping because some nominal input prices are fixed and as the output rises, more production processes experience bottlenecks.
What is supply curve with example?
Supply Curve Example Should the price of soybeans rise, farmers will have an incentive to plant less corn and more soybeans, and the total quantity of soybeans on the market will increase. The degree to which rising price translates into rising quantity is called supply elasticity or price elasticity of supply.
What does short run aggregate supply curve shows?
The short-run aggregate supply curve is an upward-sloping curve that shows the quantity of total output that will be produced at each price level in the short run. Wage and price stickiness account for the short-run aggregate supply curve’s upward slope.
What causes shifts in the supply curve?
- The entry of new producers into the market
- A government subsidy to cover some of the supply costs of firms
- A fall in the world price of imported components and raw materials
- A reduction in the size of an indirect tax on producers
- An improvement in labour productivity which lowers unit labour costs
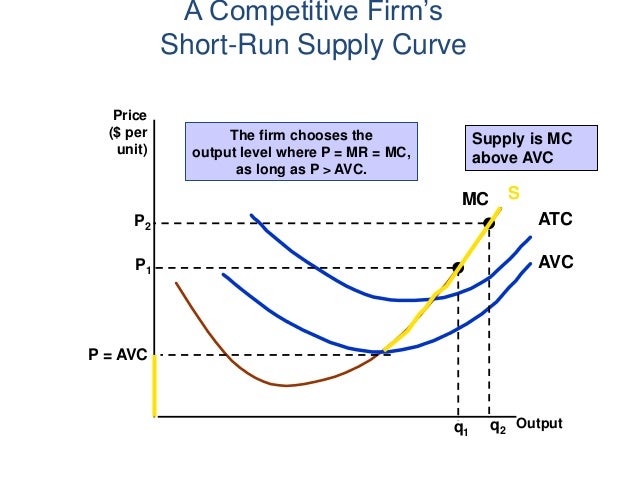
What is the supply curve of a firm in the short run and in the long run?
The short‐run market supply curve is just the horizontal summation of all the individual firm's supply curves. The long‐run market supply curve is found by examining the responsiveness of short‐run market supply to a change in market demand. Consider the market demand and supply curves depicted in Figures (a) and (b).
What happens to supply in the short run?
In the short run, aggregate supply responds to higher demand (and prices) by increasing the use of current inputs in the production process. In the short run, the level of capital is fixed, and a company cannot, for example, erect a new factory or introduce a new technology to increase production efficiency.
What is the supply curve of a firm in long run?
The rising segment of the firm's MC curve (Starting from the break-even point, when price= average cost) represents the firm's supply curve in the long run. The long-run is a period in which supply can be changed by changing all the factors of production. There is no distinction between fixed and variable factors.
Why is short-run supply curve upward sloping?
The short-run aggregate supply curve is upward sloping because the quantity supplied increases when the price rises. In the short-run, firms have one fixed factor of production (usually capital ). When the curve shifts outward the output and real GDP increase at a given price.
Why short-run aggregate supply curve is horizontal?
This is because capital, which encompasses assets such as buildings and machinery, takes time to implement. Also, as wages are assumed to be static in the short run, increases in labor only result in increased quantity, but not price. This is why the SRAS curve is almost horizontal at this stage.
Why is a long run supply curve flatter than a short run supply curve?
The correct answer is a. Firms can enter and exit a market more easily in the long run than in the short run.
Why is the supply curve perfectly elastic in the long run?
All firms have identical cost conditions. Hence, in the case of a constant cost industry, the long-run supply curve LSC is a horizontal straight line (i.e., perfectly elastic) at the price OP, which is equal to the minimum average cost. This means that whatever the output supplied, the price would remain the same.
Why long run supply curve is vertical?
The LRAS is vertical because, in the long-run, the potential output an economy can produce isn't related to the price level. There are only two things that matter for potential output: 1) the quantity and the quality of a country's resources, and 2) how it can combine those resources to produce aggregate output.
What happens in the short run?
The short run is a concept that states that, within a certain period in the future, at least one input is fixed while others are variable. In economics, it expresses the idea that an economy behaves differently depending on the length of time it has to react to certain stimuli.
When supply increases in the short run what is the profit of the producer?
The correct answer is OPTION A: Increases. The producer's goal when selecting how much production to offer is to maximize profits while keeping two constraints in mind: consumer demand and manufacturing expenses. The price at which a perfectly competitive firm can sell its output is determined by consumer demand.
How do you find short run supply?
Procedurefind the short run supply function of each firm, which involves. ... add together the short run supply functions to get the aggregate short run supply (if there are n identical firms, then we multiply each firm's supply by n)add together the consumers' demand functions to get the aggregate demand.More items...
How do you find quantity supplied in the short run?
7:5213:38Deriving the Short-Run Supply Curve - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipNow we notice here at a price of 2 each firm is producing one unit. So if each firm is producing oneMoreNow we notice here at a price of 2 each firm is producing one unit. So if each firm is producing one unit and there are 100 firms then the total market supply is not surprisingly 100 units.
Why does the short run individual supply curve hold true?
It holds true because a firm will not produce if the market price is lesser than the shut-down price. Ultimately, the short-run individual supply curve demonstrates how the producer’s profit-maximizing output is strictly dependent on the market price and holds the fixed cost as sunk.
How to calculate short run supply curve?
The short-run industry supply curve is calculated by taking an individual producer’s supply curve, setting it equal to quantity, and then multiplying it by the number of producers in the market
Why are fixed costs irrelevant in short run production?
Since fixed costs are considered to be sunk in the short run, they are irrelevant in the short-run production decision process. It is because, in the short run, fixed cost is paid regardless of the amount produced. A firm will only shut down production if the market price is lower than the minimum average variable cost of the product.
What is an indifference curve?
Indifference Curve An indifference curve is a contour line where utility remains constant across all points on the line. In economics, an indifference curve is
What is short run supply?
Short-run supply is defined as the current supply given a firm’s capital expenditure on fixed assets – such as property, plant, and equipment.
What happens if the market price is less than the minimum average total cost?
Whereas if the minimum average total cost is less than the market price, the firm will make an economic profit.
What is short run equilibrium?
The short-run market equilibrium is the point where the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded, where the number of producers is held fixed.
What is the long run supply curve?
Now look at the Fig. 24.3 (b). Corresponding to OP price, the long-run supply curve is LSC, which is a horizontal straight line parallel to the X-axis. This means that whatever the output along the X-axis, price is the same OP where the marginal cost and average cost are equal. The cost remains the same, because it is a constant cost industry.
Why does the long run supply curve slope upwards?
This means that the long-run supply curve LSC slopes upwards to the right as the output supplied increases. That is, more will be supplied at higher prices. This is probably typical of the actual competitive world, because higher prices have to be paid for the scarce productive resources to attract them from other uses so that production in this particular industry may be increased. Thus, we see that in the case of an increasing cost industry, the long-run supply curve slopes upward to the right.
What is the difference between LMC and LAC?
In the Fig. 24.3 (a) which relates to a firm, LMC is the long-run marginal cost curve, and LAC is the long-run average cost curve. They intersect at R which means that at the point R, the marginal cost is equal to the average cost. Here they are also equal to price OP. The output at this point is OM. Thus, at the output OM, MC = AC = Price.
What is SMC curve?
First look at the Fig. 24.2 (a), which relates to a single firm. Along the axis OX are represented the output supplied and along OY the prices. SMC curve is the short-run marginal cost curve, and, as mentioned above, it is the short-run supply curve of the firm. But only that portion of SMC curve which lies above the short-run average variable cost (SAVC), which means the thick portion above the dotted portion.
What is the marginal cost curve of a firm?
If, on the other hand, the price is less than the marginal cost, it is incurring a loss, and it will reduce its output till the marginal cost and the price are made equal. Hence, the marginal cost curve of the firm is the supply curve of the perfectly competitive firm in the short-run.
What happens when the cost curves rise?
This means that the additional supplies of the product will be forthcoming at higher prices, whether the additional supplies come from the expansion of the existing firms or from the new firms which may have entered the industry. All this is shown in the following diagram (Fig. 24.4).
How does cost of production increase?
In the case of an increasing cost industry, the cost of production increases as the existing firms expand or the new firms enter into the industry to meet an increase in demand. The external diseconomies outweigh the external economies. The increased demand for the productive resources required to produce larger output to meet increased demand for the product raises their prices resulting in higher cost of production.
What is supply curve?
The supply curve shows the maximum quantities per unit of time which sellers will place in the market at various prices. At a higher price, a greater quantity will be supplied and, at a lower price, a smaller quantity will be supplied.
When does a firm produce output?
Under perfect competition, a firm will produce that amount of output when P = MC. As price is given to a firm, the price line becomes parallel to the horizontal axis.
What is the equilibrium point of a firm?
At a price OP, the firm is in equilibrium at point R since at this point all the conditions for equilibrium are satisfied. Corresponding to this equilibrium point, the firm produces OQ output. The total revenue that the firm expects to earn from the sale of OQ output is OPRQ. But costs are higher than revenue since AVC and SAC curves lie above the OP price line.
What happens when the price is below AVC?
As AVC exceeds price, the firm should go out of business. So, when price is below AVC (i.e., P < AVC), the short run equilibrium output is zero.
What is the equilibrium quantity of output?
Corresponding to the price OP 2, the equilibrium quantity of output is OQ 2, total revenue is OP 2 NQ 2, total cost is OP 2 NQ 2. As costs equal revenue, the firm must go on producing. At point N, MC = minimum SAC. This point is called ‘break-even point’. Similarly, at price OP 3, the firm will produce and supply OQ 3 since it earns excess profit.
Is the MC curve positive or negative?
As is known to all, the MC curve is U-shaped having both negative and positive slopes while supply curve is positive sloping. So we must not consider negative or downward sloping portion of the MC curve. Only rising portion (i.e., upward sloping) of MC is the supply curve. To be more specific, rising portion of the MC the ...
Is the short run supply curve upward sloping?
Thus, like the individual supply curve, short run industry supply curve is upward sloping. It is drawn in the same way as we draw the market demand curve from the demand curve of an individual.
What is short run supply curve?
Short run supply curve of a perfectly competitive firm is that portion of marginal cost curve which is above average variable cost curve. According to C.E. Ferguson, “The short run supply curve of a firm in perfect competition is precisely its Marginal Cost Curve for all rates of output equal to or greater than the rate of output associated with minimum average variable cost.”
How is the supply curve determined in the long run?
In the long run, industry’s supply curve is determined by the supply curve of firms in the long run. Long run supply curve in the long run is not lateral summation of the short run supply curves. Industry’s long run supply curve depends upon the change in the optimum size of firms and change in the number of firms.
What is the position of marginal cost curve?
So that position of marginal cost curve will determine the supply curve which is above the minimum average variable cost. The point where minimum average cost is equal to marginal cost is called optimum production. Thus Long Run Supply Curve of a firm is that portion of its marginal cost curve that lies above the minimum point of the average cost curve.
What is supply curve in industry?
An industry is a blend of firms producing homogeneous goods. That way, supply curve of an industry is a lateral summation of all firms. This can be made clear with the help of a Fig. 2.
What happens if price is below OP?
From fig. 1 it is clear that there is no supply if price is below OP. At price less than OP, the firm will not be covering its average variable cost. At OP price, OM is the supply. In this case, firms’ marginal revenue and marginal cost cut each other at A, OM is equilibrium output. If price goes up to OP1, the firm will produce OM1 output. This firm’s short run supply curve starts from A upwards i.e., thick line AB.
What is supply curve?
According to Dorfman, “Supply curve is that curve which indicates various quantities supplied by the firm at different prices”. The concept of supply curve applies only under the conditions of perfect competition.
Which part of the short run marginal cost curves of the firms lie above the average variable cost?
Thus, under perfect competition, lateral summation of that part of short run marginal cost curves of the firms which lie above the average variable cost constitutes the supply curve of the industry. According to Stonier and Hague, “short run supply curve of a competitive industry will always slope upwards since the short run marginal cost curve of the industrial firms always slope upward.”
What is the supply curve of a firm?
In the short run, the firm’s supply curve is its MC curve above AVC (at B). Below this point it will shut down. Hence the firm would be willing to supply at P, but not at P1.
Why does a firm need to cover variable costs?
This is largely because covering variable cost ensures than an output can be produced in the future. If variable costs cannot be covered then no further output can be made. In addition, fixed costs have already been paid for prior to any marginal decision to supply, so will not enter into the firm’s short run calculations.

What Are Short Run Costs?
The Short-Run Production Decision
- Since fixed costs are considered to be sunk in the short run, they are irrelevant in the short-run production decision process. It is because, in the short run, fixed cost is paid regardless of the amount produced. A firm will only shut down production if the market price is lower than the minimum average variable cost of the product. Therefore, the shut-down price is equal to the mi…
Short-Run Supply Curve
- The short-run individual supply curve is the individual’s marginal cost at all points greater than the minimum average variable cost. It holds true because a firm will not produce if the market price is lesser than the shut-down price. Ultimately, the short-run individual supply curve demonstrates how the producer’s profit-maximizing output is stri...
Short-Run Industry Supply Curve
- A short-run industry supply curve illustrates how quantity supplied in the market is dependent on the market price, assuming that the number of producers in the market is fixed. The short-run market equilibrium is the point where the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded, where the number of producers is held fixed. This is also known as the allocative efficient point.
Calculating The Short-Run Industry Supply Curve
- The short-run industry supply curve is calculated by taking an individual producer’s supply curve, setting it equal to quantity, and then multiplying it by the number of producers in the market For example, consider a producer with the following supply curve: P = 2Q + 1 Assuming that there are 10 producers in the market and there is a market demand curve of: P = -1Q + 10 First, set the ind…