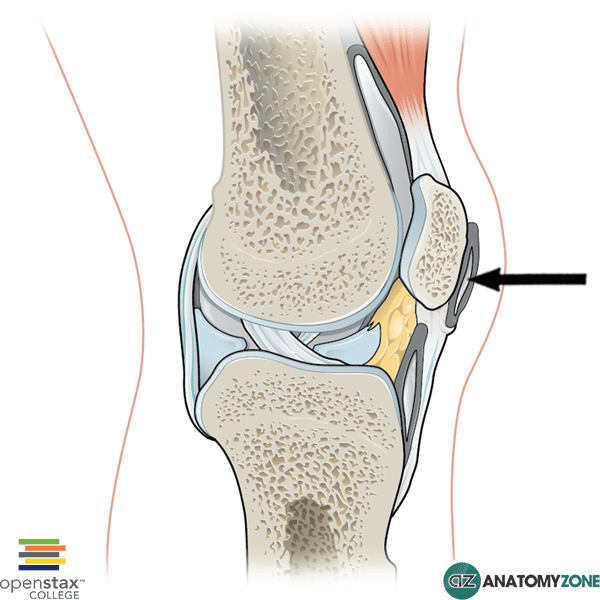
Suprapatellar Bursitis. Suprapatellar bursitis, which extends superiorly from beneath the patella (kneecap), occurs when the suprapatellar bursa becomes swollen and inflamed. Pain will often be felt above the kneecap and can even radiate into the thigh. More commonly suprapatellar bursitis is simply referred to as knee bursitis.
Where is the suprapatellar bursa located in the knee?
It is located proximal to the knee joint, between the prefemoral and suprapatellar fat pads. As with all bursae, its purpose is to reduce friction between moving structures. In most (~85%) people, the suprapatellar bursa communicates with the knee joint proper.
What is the anatomy and pathophysiology of suprapatellar bursitis?
It usually communicates with the cavity of the knee joint and is pathologically distended with blood or synovial fluid in suprapatellar bursitis ("water on the knee"). A large space between the lower part of the femur and the tendon of the quadriceps femoris muscle. It usually communicates with the cavity of the knee joint.
What is prepatellar bursa?
Prepatellar bursa is located at the top of the knee over the kneecap. Bursitis of the prepatellar bursa is sometimes called carpet layer’s knee, housemaid’s knee or roofer’s knee. It can be caused by a direct blow to the knee or from being in a prolonged kneeling position.
Is my suprapatellar bursa discrete or continuous?
In most patients, the suprapatellar bursa is continuous with the joint space. According to the expert opinions I solicited, it is unlikely that a knee with a discrete isolated bursa will look any different than a continuous bursa.

What causes Suprapatellar bursitis?
It can be caused by a direct blow to the knee or from being in a prolonged kneeling position. Infrapatellar bursa is located below the kneecap, under the large patella tendon. It is commonly associated with patella tendonitis or from a repetitive jumping injury called “jumper's knee.”
What does Suprapatellar mean?
[ sōō′prə-pə-tĕl′ər ] n. A large bursa between the lower part of the thigh and the tendon of the quadriceps muscle, usually communicating with the cavity of the knee joint.
How is Suprapatellar bursitis treated?
Most cases of suprapatellar bursitis will resolve over several weeks with conservative treatment. This can include things like rest, OTC pain medications, and icing. More severe or recurring bursitis may be treated with methods such as draining or removal of the suprapatellar bursa.
What is the most commonly damaged bursa in the knee?
Prepatellar Bursitis. Prepatellar bursitis is a common and treatable condition that causes the front of your knee to swell. It happens when the bursa sac in front of your knee cap becomes inflamed. Most cases of prepatellar bursitis can be treated from home with rest.
How long does knee bursitis last?
With the proper treatment, knee bursitis can be healed in an average of two to eight weeks. You must practice proper stretching, strengthening, and exercise for a speedy recovery from this condition.
What does bursitis in your knee feel like?
In general, the affected portion of your knee might feel warm, tender and swollen when you put pressure on it. You might also feel pain when you move or even at rest. A sharp blow to the knee can cause symptoms to appear rapidly.
What happens if knee bursitis is left untreated?
Chronic pain: Untreated bursitis can lead to a permanent thickening or enlargement of the bursa, which can cause chronic inflammation and pain. Muscle atrophy: Long term reduced use of joint can lead to decreased physical activity and loss of surrounding muscle.
Is walking good for knee bursitis?
Exercise is often prescribed to improve joint pain, so walking could be a vital part of managing your bursitis symptoms.
Do you need surgery for bursitis in the knee?
If you have severe chronic or recurrent bursitis and don't respond to other treatments, your doctor might recommend surgery to remove the bursa.
Will knee bursa heal itself?
Prepatellar bursitis that is caused by an injury will usually go away on its own. The body will absorb the blood in the bursa over several weeks, and the bursa should return to normal. If swelling in the bursa is causing a slow recovery, a needle may be inserted to drain the blood and speed up the process.
Does knee bursitis show up on MRI?
On MRI, prepatellar bursitis appears as an oval fluid-signal-intensity lesion between the subcutaneous tissue and the patella [Figure 1].
How long does it take a bursa sac to heal?
Bursitis is when a joint becomes painful and swollen. It can usually be treated at home and should go away in a few weeks.
What is a Suprapatellar knee joint effusion?
A knee joint effusion will demonstrate swelling around the patella and distend of the suprapatellar space. Patients may have a restricted range of motion along with pain with ambulation.
What is a opposite word of Suprapatellar?
Medical Definition of infrapatellar : situated below the patella or its ligament the infrapatellar bursa of the knee.
Does joint effusion go away?
Effusion is a symptom of an injury or other condition affecting a joint. In almost all cases, if the underlying condition is identified and treated, the effusion will go away. Joint effusion that happens for no apparent reason or with a fever should be checked by a doctor as soon as possible.
How do you treat a knee effusion?
What can I do at home to treat joint effusion?Heat, especially moist heat, can help with joint effusion and joint pain. ... Ice works well on swollen joints. ... Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce stress on your joints.Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen (Advil®, Motrin®) and naproxen (Aleve®).More items...•
Where is the suprapatellar bursa located?
It is located proximal to the knee joint, between the prefemoral and suprapatellar fat pads. As with all bursae, its purpose is to reduce friction between moving structures.
What is the purpose of suprapatellar bursa?
As with all bursae, its purpose is to reduce friction between moving structures. In most (~85%) people, the suprapatellar bursa communicates with the knee joint proper. Thus, it is useful to assess for bursal distension on x-ray, as this generally indicates the presence of a knee effusion.
Does the suprapatellar bursa communicate with the knee joint?
the suprapatellar bursa does not communicate with the knee joint in ~15% of people, remaining separated by an embryonic septum 2,3. knee effusion. synovial chondromatosis.
What happens when the joint recesses are communicated with the suprapatellar bursa?
Communication with the joint recesses usually results in fluid accumulation in the suprapatellar bursa directly abutting the SPFP, where as there is little or no communication with areas surrounding the IPFP.
Where is the bursa located in the knee?
a large bursa between the inferior part of the femur and the tendon of the quadriceps femoris muscle. It usually communicates with the cavity of the knee joint and is pathologically distended with blood or synovial fluid in suprapatellar bursitis ("water on the knee").
What order is the inferior patella released?
Under the guide of an arthroscope, it was released from the inferior patella with a blunt needle drill in the following order: inner and outer groove, suprapatellar bursa, bilateral retinaculum, patellar joint, intercondylar fossa, bilateral compartment, and adhes- ions between the femur and the quadriceps.
Is the vastus medialis split?
The vastus medialis was not split if its patellar insertion was not lower than the upper pole of the patella, and the suprapatellar bursa was only partially opened.
Is the bursa around the knee present?
A bursa around the knee was classified as present when there was more than 5 mm of synovial liquid in the suprapatellar bursa and as absent when there was less than 5 mm. [11] Other fluid-filled bursae were considered present or absent and described based on their locations.
What is suprapatellar bursitis?
Suprapatellar Bursitis is a pathological condition involving the knee in which there is inflammation of the suprapatellar bursa of the knee. 1 A bursa is a fluid filled sac which prevents friction in between the bones by rubbing against each other. Repetitive overuse is the primary cause of Suprapatellar Bursitis, although a bacterial infection, ...
What is the procedure to bring down a suprapatellar bursa?
This procedure is called aspiration. This is done when excessive fluid is accumulated within the bursa. Aspiration is quite a beneficial procedure to bring down ...
What is swelling over the upper portion of the patella?
Swelling over the upper portion of the patella can be symptom of suprapatellar bursitis
Can steroid injections help with suprapatellar bursitis?
For cases where overuse or trauma is the cause of the condition then steroid injections are quite beneficial in alleviating the symptoms of pain and calming down the inflammation associated with suprapatellar bursitis. In case if a bacterial infection is found to be the cause of the condition, then the patient will be first treated with a course ...
Can a motor vehicle accident cause suprapatellar bursitis?
A direct trauma to the knee while playing contact sports like hockey, falls, motor vehicle collisions can cause suprapatellar bursitis. Infection either in the knee through an open wound or infection spread to the knee from other areas of the body can also cause suprapatellar bursitis. 2.
Can repetitive overuse cause suprapatellar bursitis?
Repetitive overuse is the primary cause of Suprapatellar Bursitis, although a bacterial infection, a direct trauma, or even degenerative conditions like osteoporosis can cause Suprapatellar Bursitis. The primary presenting feature of Suprapatellar Bursitis is severe pain in the knee with inability to ambulate for long distances or standing ...
Can you stand for a long time with suprapatellar bursitis?
It also becomes extremely difficult for the affected individual to stand for a prolonged period of time as a result of Suprapatellar Bursitis. For treating a condition like Suprapatellar Bursitis, the individual needs medical care as well as certain lifestyle modifications so as to get relief from the symptoms.
How to treat suprapatellar bursitis?
Initial treatment of suprapatellar bursitis includes avoiding activities that produce pain or stress of the suprapatellar bursa and associated tendons (jumping, running, and kneeling.) The use of ice to reduce inflammation and pain. NSAIDS (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) Physical Therapy.
Where is the prepatellar bursa located?
Prepatellar bursa is located at the top of the knee over the kneecap. Bursitis of the prepatellar bursa is sometimes called carpet layer’s knee, housemaid’s knee or roofer’s knee. It can be caused by a direct blow to the knee or from being in a prolonged kneeling position.
What happens if you blow your suprapatellar bursa?
A direct blow to the suprapatellar bursa can produce inflammation and irritation.
What is the bursa in the knee?
A bursa is a fluid filled sack that serves to reduce friction between tendons, and between tendons and bone. The four major bursae of the knee are: Suprapatellar bursa is located between the distal femur (leg bone) and the quadriceps tendon. It permits free movement of the quadriceps tendon over the distal femur.
What is the bursa of the roofer's knee called?
Bursitis of the prepatellar bursa is sometimes called carpet layer’s knee, housemaid’s knee or roofer’s knee. It can be caused by a direct blow to the knee or from being in a prolonged kneeling position. Infrapatellar bursa is located below the kneecap, under the large patella tendon.
How long does it take to recover from suprapatellar bursitis?
In general, patients respond well to conservative treatment of suprapatellar bursitis. It is important that once the pain and inflammation is reduced and motion and strength are restored that the patient gradually returns back to full activities. Instruction in daily activities or sport performance is helpful to reduce the chance of a reoccurrence of the bursitis. In most cases full return to activity will take from 2-6 weeks depending on the severity of the condition. As a preventive measure individuals should: 1 Make modifications in work or daily activities such and kneeling, squatting or wearing protective equipment to avoid prolonged pressure or unexpected blows on the suprapatellar bursa. 2 Maintain strength and flexibility to reduce stress on the suprapatellar bursa and tendons of the knee. 3 Avoid highly repetitive activities whenever possible.
What are the activities that stress the suprapatellar bursa?
Pain with activities that stress the suprapatellar bursa like kneeling, jumping, running or activities that cause stress on the tendons that are lubricated by the suprapatellar bursa.
What is suprapatellar bursitis?
Suprapatellar bursitis, also known as suprapatellar synovitis, popliteal cyst suprapatellar recess or suprapatellar pouch, is a painful condition that occurs when the fluid within the joint becomes infected.
Where is the suprapatellar pouch?
The suprapatellar pouch can be found under the kneecap and is also known as the popliteal space. It is found in humans, monkeys, and other primates. It can also be found in some quadrupeds such as dogs and horses. The suprapatellar pouch is a potential space and not a cavity. It can communicate with the underlying synovial joint capsule or synovial membrane.
How to remove fluid from suprapatellar pouch?
A needle is inserted into the suprapatellar pouch through an incision behind the knee, and a syringe plunger is used to aspirate any fluids that have accumulated inside it. The process can be repeated until all synovial fluid has been removed from this location in order to treat the inflammation.
What is the term for the fatty tissue around the knee area?
Suprapatellar fat pad impingement is a condition in which the fatty tissue around the knee area, called suprpatellar fat pad, gets trapped between two points of contact at or near this joint. When one of these surfaces moves vertically (up and down) with respect to the other surface, then it causes irritation on the fat tissue.
Why does my suprapatellar joint hurt?
Causes: suprapatellar pain can be caused by a variety of factors, including patellofemoral problems. It is also common in patients with iliotibial band syndrome or shin splints and other conditions that cause inflammation of the bone or cartilage under the kneecap.
Why does my synovial membrane hurt?
It usually responds well to treatment with anti-inflammatory medications like ibuprofen, but if not adequately treated it can lead to chronic inflammation of the synovial membrane surrounding the knee joint, leading to osteoarthritis.
What is the fat pad on the femur?
The suprapatellar fat pad is a small, triangular-shaped cushion of adipose tissue and fibrous tissue that sits on the distal end of the femur. It helps to protect the surrounding ligaments from friction during knee flexion.
When do knees lose their septum?
Embryologically, we all have an imperforate suprapatellar septum, but from around the 5th month of gestation on, most knees develop a perforation or complete loss of the septum, yielding a continuous joint space. 2
Can you use synovial fluid for septic arthritis?
This is a very important topic, as the ability to access synovial fluid for analysis is the only way to definitively rule out, or rule in septic arthritis, and can drastically alter the treatment and disposition of a patient presenting with a swollen, painful joint. Most ED practitioners are proficient at arthrocentesis of knee joints with a blind approach, but ultrasound has become an invaluable asset in assisting access to other joints, such as the ankle, hip, wrist, elbow, and shoulder. Many of these joints are infrequently tapped, have smaller volumes of fluid, or do not have a straightforward landmark approach to them.
Should we tap the bursa as opposed to the knee joint?
Though there was consensus that we should not be purposefully tapping the bursa as opposed to the knee joint, there seemed to be different opinions on whether or not the bursa was truly continuous with the joint, and if the suprapatellar approach to aspiration samples joint or bursa (or both!). The slim pickings of anatomical studies on the bursa actually reflect this ambiguity: 16% of suprapatellar bursae are not continuous with the knee joint.1
Is tapping the bursa easy?
Looking at anatomy renderings, tapping the bursa seems pretty easy, especially when clinical knee effusions make the bursa seem so big and juicy:
Is a suprapatellar bursa continuous?
In most patients, the suprapatellar bursa is continuous with the joint space. According to the expert opinions I solicited, it is unlikely that a knee with a discrete isolated bursa will look any different than a continuous bursa. Because the knee joint extends proximally beyond the patella regardless of bursa anatomy, there will likely always be the familiar “fullness” above the patella in a large knee effusion. I am speculating, but it seems unlikely that a suprapatellar diagonal approach to knee aspiration would sample a septated bursa and not the joint space, since a septated bursa would likely remain small and be displaced superiorly/proximally.
