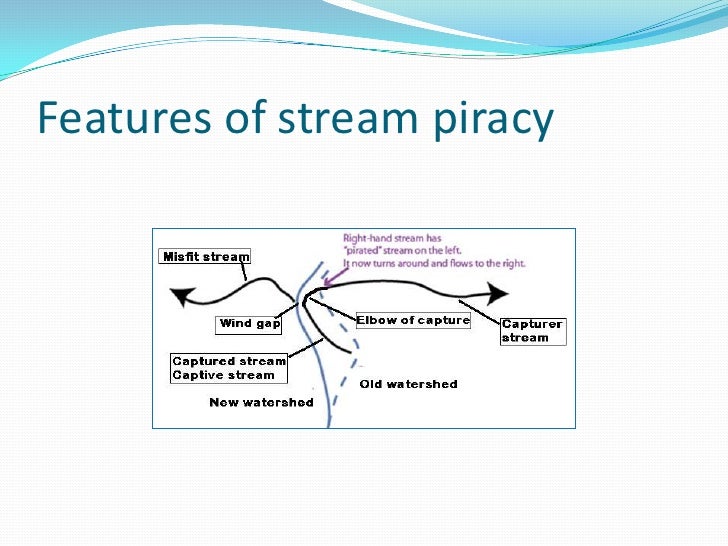
The suspended load of a flow of fluid, such as a river, is the portion of its sediment uplifted by the fluid’s flow in the process of sediment transportation. It is kept suspended by the fluid’s turbulence. The suspended load generally consists of smaller particles, like clay
Clay
Clay is a finely-grained natural rock or soil material that combines one or more clay minerals with possible traces of quartz, metal oxides and organic matter. Geologic clay deposits are mostly composed of phyllosilicate minerals containing variable amounts of water trapped in the mineral …
What is the suspended load of a stream?
The suspended load is generally made up of lighter‐weight, finer‐grained particles such as silt and clay. Most of the sediment in a stream is carried as suspended load. It does not contribute greatly to stream erosion, since it is not in frictional contact with the stream bed. Bed load.
What is the difference between suspended load and bed load?
The suspended load generally consists of smaller particles, like clay, silt, and fine sands. The suspended load is one of the three layers of the fluvial sediment transportation system. The bed load consists of the larger sediment which is transported by saltation, rolling, and dragging on the riverbed.
What type of load is a river?
a river load is a river load. What would happen at the mouth of a river with a river's suspended load and bed load? A river's suspended load and bed load may accumulate at the river's mouth and form a delta. It is a land form created by the deposition of sediments. What are the two types of load?
What is the maximum sediment load that a stream can transport?
the maximum sediment load that a stream can transport heavy particles that move along the bottom of the stream Usually the greatest fraction of a river's load is carried as its bed load dissolved load suspended load wind suspended load A grain of clay is most likely to be carried by a river in its in its bed load in its dissolved load
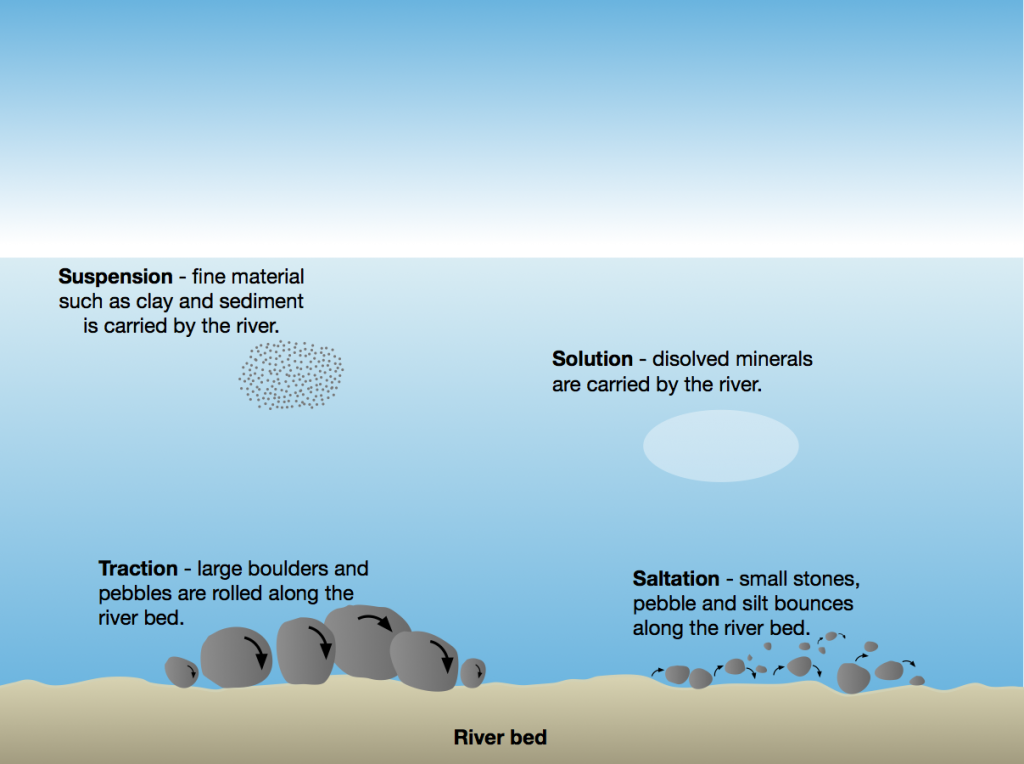
What is a suspended stream load?
Suspended load is composed of fine sediment particles suspended and transported through the stream. These materials are too large to be dissolved, but too small to lie on the bed of the stream (Mangelsdorf, 1990). Stream flow keeps these suspended materials, such as clay and silt, from settling on the stream bed.
What is the bed load of a river?
Gravel and sand is dragged, rolled and bounced along the bottom of the river. This is called the bed load. Finer sand and mud that is supported by the water column is called the suspended load. Some minerals are dissolved in the water.
What is a suspended load in geology?
The suspended load is the fine-grained (clay and silt) sediment that remains in water during transportation. The bed load consists of the coarser fractions of the sediment (sands and gravels), moves by rolling, sliding, or saltation actions.
What is load of a river?
The load is the total amount of sediment being transported. There are 3 types of sediment load in the river: dissolved, suspended, and bed load. The dissolved load is made up of the solutes that are generally derived from chemical weathering of bedrock and soils.
What is as suspended load?
Definition of Suspended load: Suspended load refers to that part of the total sediment transport which is maintained in suspension by turbulence in the flowing water for considerable periods of time without contact with the stream bed. It moves with practically the same velocity as that of the flowing water..
What is the difference between bed load and suspended load?
The bed load consists of the larger sediment which is transported by saltation, rolling, and dragging on the riverbed. The suspended load is the middle layer that consists of the smaller sediment that's suspended.
What is suspended load quizlet?
Suspended load is. Fine sand, silt, and clay particles in suspension. bed load is. particles that are too heavy to be carried in suspension that roll or bounce along the bottom.
Can you work under a suspended load?
The load should never be raised higher than necessary or left suspended in the air. As the load is lifted higher, the fall zone increases in size, as well. Never allow anyone to walk near or work under a suspended load. As always, stay safe out there!
How is suspended sediment load calculated?
Determine total suspended-sediment discharge (in tons for the period of interest by multiplying the mean daily suspended-sediment discharge (from step h) by the total number of days in the period.
What are the three loads of a stream?
The total load (quantity of sediment) of a stream can be described as consisting of three components: the bed load - materials bounced along the stream bottom. the suspended load - material carried in suspension in the stream water. the dissolved load - material carried as dissolved solids in the stream water.
How does a river carry its load?
The load bounces in line with the rise and fall in the velocity of the river; Saltation – small pebbles and stones are bounced along the river bed; Traction – large boulders and rocks are rolled along the river bed. The load carried this way is called bed load.
Why do rivers deposit their load?
When a river loses energy, it will drop or deposit some of the material it is carrying. Deposition may take place when a river enters an area of shallow water or when the volume of water decreases - for example, after a flood or during times of drought.
What do you mean by bed load?
Definition of bed load : sediment not in suspension rolled or dragged along a stream bottom.
What is known as bed load?
Bed load refers to the discharge of sediment particles which are too heavy to be suspended by the turbulent action of the flow. These particles move by rolling, sliding and skipping (“WIND ACTION; SEDIMENT TRANSPORT; also pr Vol.
How bed load is measured?
Direct measurements of bedload have traditionally been made by placing samplers in contact with the bed, allowing the sediment transported as bedload to accumulate (or be trapped) inside the sampler for a certain amount of time, after which the sampler is raised to the surface and the material is emptied and weighed to ...
What are the 3 types of stream load?
The total load (quantity of sediment) of a stream can be described as consisting of three components: the bed load - materials bounced along the stream bottom. the suspended load - material carried in suspension in the stream water. the dissolved load - material carried as dissolved solids in the stream water.
What is suspended load?
The suspended load is generally made up of lighter‐weight, finer‐grained particles such as silt and clay. Most of the sediment in a stream is carried as suspended load. It does not contribute greatly to stream erosion, since it is not in frictional contact with the stream bed. Bed load.
What is the maximum load of sediment that a stream can transport?
The maximum load of sediment that a stream can transport is called its capacity . Capacity is directly proportional to the discharge: the greater the amount of water flowing in the stream, the greater the amount of sediment it can carry.
What is the majority of sediment load in a stream?
The majority of a stream's sediment load is carried in solution (dissolved load) or in suspension. The remainder is called the bed load.
How does traction occur?
Traction occurs when these fragments move along by rolling and sliding. Turbulent or eddying currents can temporarily lift these larger grains into the overlying flow of water—the grains advance by short jumps or skips until the surge diminishes and then fall back to the bottom because of their greater weight.
What is stream competence?
A stream's competence is a measure of the largest‐sized particle it can transport; competence is directly proportional to a stream's velocity, which can vary seasonally. Because of increased capacity and competence, a single flood event can cause more erosion than a hundred years of standard flow. Previous Stream Erosion.
Why is saltation load included in bedload?
The saltation load is included in bedload because grain excursions into the fluid are short-lived. Saltating grains tend to travel much farther in air than their watery counterparts because the grain-to-fluid density contrast is much greater.
What is the bedload process?
Both bedload and suspension load are important processes in the generation of sedimentary structures. In particular, bedload transport of loose sand is the critical process for growth of bedforms and their internal cross-stratification (crossbedding). The description of bedforms (crossbeds) and the flow conditions ( flow regime) under which they form have been described in other posts.
How does saltation affect traction?
As flow velocities increase, so too will the lift component of fluid forces and grains may temporarily leave the traction carpet, bouncing along with the flow; this process is called saltation. The saltation load is included in bedload because grain excursions into the fluid are short-lived. Saltating grains tend to travel much farther in air than their watery counterparts because the grain-to-fluid density contrast is much greater. Stand on any sandy beach on a blusterous day and you will witness first-hand the effects of grain saltation. Saltation produces many collisions, and not just against your bare legs. Saltation collisions also result in grain abrasion.
What is the threshold velocity of sediment?
As the name suggests, this element of sediment movement consists of loose, granular particles at the sediment-water interface (such as a stream bed or tidal flat). Air or water that moves across the bed will being to move grains if the flow velocity is great enough to overcome the force of gravity and any resistance at grain contacts. This is the threshold velocity.
What is the force involved in grain movement?
Here, fluid flowing over a sediment bed produces shear stresses that can be resolved into a component of drag (parallel to the bed) and a lift component normal to the bed. At the threshold velocity when the resultant fluid force on grains is greater than gravity, grains begin to roll, slide and jostle along the bed like a moving carpet – the traction carpet.
How does turbulence affect the rate of settling?
Thus, the rate of settling depends on the size, shape and density of particles, and the viscosity of the fluid. In general, settling through air is much more rapid than through water.
Is settling through air more rapid than through water?
In general, settling through air is much more rapid than through water. Both bedload and suspension load are important processes in the generation of sedimentary structures. In particular, bedload transport of loose sand is the critical process for growth of bedforms and their internal cross-stratification (crossbedding).
What happens if two streams are identical?
If two streams are identical in every respect except for gradient, the stream with the higher gradient would have the greater velocity.
Is a depositional feature parallel to its stream channel?
both a depositional feature and essentially parallel to its stream channel
Is an aquifer saturated?
The aquifer is generally in clined, and it is saturated to an elevation above the point where the well penetrates the aquifer. When the well penetrates the aquifer, the water rises only to the bottom of the aquitard above the aquifer. The well penetrates an aquifer underlain by an impermeable bed.
