
What is the accounting treatment of contingent liabilities?
So a contingent liability has no accounting treatment as such. However, considering that we follow a conservative approach to accounting, we must follow the practice of the disclosure. So a contingent liability, like contingent assets, will be disclosed in the final statements of a company as a footnote. i.e. notes to accounts. This will happen if
What are the three financial statements for contingent liabilities?
Three Financial Statements The three financial statements are the income statement, the balance sheet, and the statement of cash flows. These three core statements are if the contingency is probable and the related amount can be estimated with a reasonable level of accuracy. The most common example of a contingent liability is a product warranty.
When is a contingent liability recorded?
A contingent liability is recorded in the accounting records if the contingency is probable and the related amount can be estimated with a reasonable level of accuracy. The most common example of a contingent liability is a product warranty. Other examples include guarantees on debts
What are the criteria for qualifying contingent liabilities?
First, it must be possible to estimate the value of the contingent liability. If the value can be estimated, the liability must have a greater than 50 percent chance of being realized. Qualifying contingent liabilities are recorded as an expense on the income statement and a liability on the balance sheet.
How are contingent liabilities treated in the financial statements?
Contingent liabilities, although not yet realized, are recorded as journal entries. Contingent liabilities require a credit to the accrued liability account and a debit to an expense account. Once the obligation is realized, the balance sheet's liability account is debited and the cash account is credited.
Where does contingent liability appear in the financial statements?
A contingent liability is recorded first as an expense in the Profit & Loss Account and then on the liabilities side in the Balance sheet.
Are contingent liabilities included in financial statements?
A contingent liability is a potential obligation that may arise from an event that has not yet occurred. A contingent liability is not recognized in a company's financial statements. Instead, only disclose the existence of the contingent liability, unless the possibility of payment is remote.
Is contingent liability recorded in accounting records?
Key Takeaways. A contingent liability is a potential liability that may occur in the future, such as pending lawsuits or honoring product warranties. If the liability is likely to occur and the amount can be reasonably estimated, the liability should be recorded in the accounting records of a firm.
When should contingent liabilities be recorded?
Rules specify that contingent liabilities should be recorded in the accounts when it is probable that the future event will occur and the amount of the liability can be reasonably estimated. This means that a loss would be recorded (debit) and a liability established (credit) in advance of the settlement.
Is a contingent liability a current liability?
Current and contingent liabilities are both important financial matters for a business. The primary difference between the two is that a current liability is an amount that you already owe, whereas a contingent liability refers to an amount that you could potentially owe depending on how certain events transpire.
How are contingent assets recorded in the financial statements?
A contingent asset is not disclosed in the financial statements. It is usually disclosed in the report of the approving authority (Board of Directors in the case of a company, and, the corresponding approving authority in the case of any other enterprise), where an inflow of economic benefits is probable. 34.
What is contingent liability in accounting?
Definition: A contingent liability is defined as a liability which may arise depending on the outcome of a specific event. It is a possible obligation which may or may not arise depending on how a future event unfolds. A contingent liability is recorded when it can be estimated, else it should be disclosed.
Are contingent liabilities current liabilities?
Current and contingent liabilities are both important financial matters for a business. The primary difference between the two is that a current liability is an amount that you already owe, whereas a contingent liability refers to an amount that you could potentially owe depending on how certain events transpire.
How do you find contingent liabilities?
The liability is contingent on whether or not the event occurs. The most common source of contingent liabilities are outstanding lawsuits and product warranties. Auditors usually ask management to write a statement acknowledging they disclosed all known contingent liabilities.
Where is information about contingent liabilities disclosed?
A contingent liability is not recognised in the statement of financial position. However, unless the possibility of an outflow of economic resources is remote, a contingent liability is disclosed in the notes.
Which of the following should be disclosed in the financial statements as a contingent liability?
2. A contingent liability should be disclosed by note if it is probable that a transfer of economic benefits to settle it will be required, with no provision being made. 3.
What are contingent liabilities?
Contingent liabilities takes place when an outcome is uncertain in a future point of time, which may lead to debt or obligation for a corporation. These get treated through two factors- likelihood of occurrence & measurement.
Why is it important to record contingent liability?
Recording of contingent liability help in planning of different types of budget for the company.
What is GAAP compliance?
Under GAAP compliance, any potential liability losses depend on the future event which turns into actual expenses.
What is a probable contingency?
Probable contingency: These are most likely to be occur and the outcomes have to be estimated reasonably. It can be taken into an estimate when the probability is between (90-51%) and recognize an asset if you can estimate the amount fairly. If it is not rated, disclosure should be noted as liability (provision). These record an expense & an actual liability which is based on estimated amounts. Example: Warranty expenses.
How to assess financial position of an entity?
Assessing of financial position of the entity can be done by recording contingent liability in the books of accounts.
What are the three categories of liabilities?
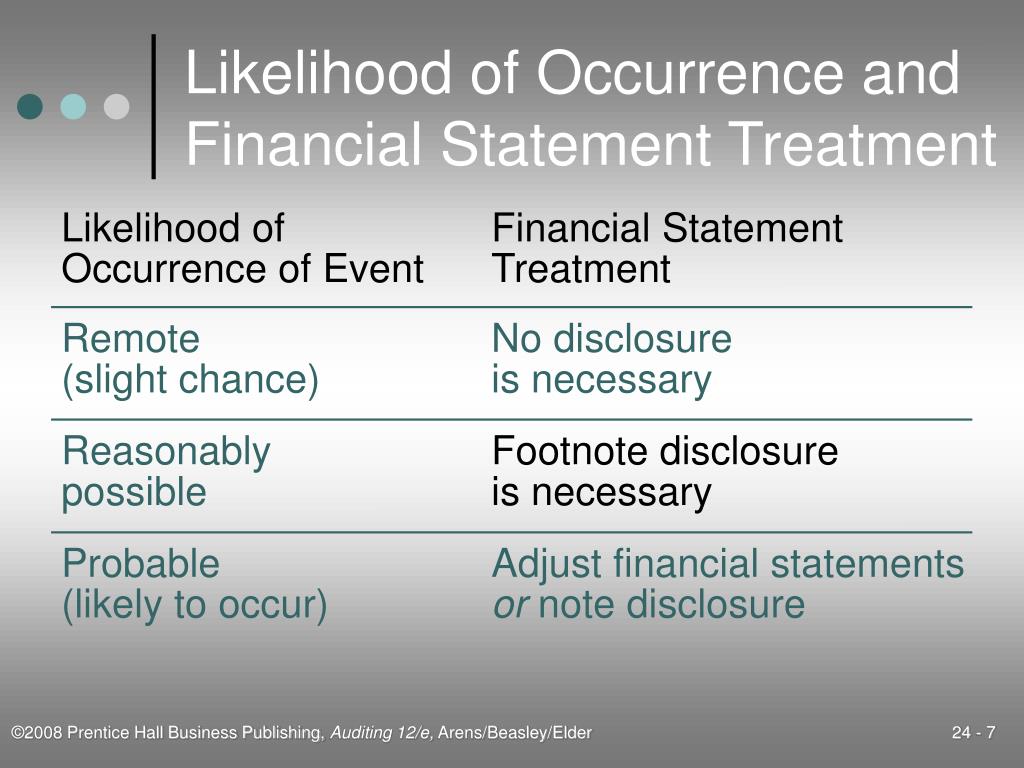
The accounting treatment for liabilities depends on the three categories: Probable, Possible and Remote. The measurement is the amount of estimable or not estimable which must be recorded and disclosed in the financial statements.
Why do we need a note to the financial statements?
A note to the financial statements may be needed to explain that the end of the financial year.
What is contingent liability?
A contingent liability is a liability that may or may not happen. This means there is uncertainty about recording such a liability in the financial accounts. This is because the happening or not happening of a contingent liability is not in the hand of us.
How many ways are contingent liability defined?
There are two ways contingent liability can be defined. One method involves a past event and the other one a future event. Let us take a look at the definition of a contingent liability.
Why are contingent liabilities only disclosed in notes to accounts?
Contingent liabilities, on the other hand, are only disclosed in the notes to accounts because they do not meet the criteria. If the management estimates a liability is probable, that the settlement of the obligation will most likely result in an outflow of economic resources it will be recognized as a provision.
What is provision in accounting?
A provision is a liability which can only be measured using a significant degree of estimation. This means that the obligation is already present but we cannot determine the exact amount of the obligation, only an estimate can be determined. Then in such a case, we make a provision for such a liability.
What is the chance of a company not paying damages?
Q: A company is facing litigation. Their lawyers inform them that there is a 70% chance that the company will not have to pay damages, and a 30% possibility of damages arising. How should the management recognize such a liability?
Is contingent liability recorded in financial statements?
Now let’s make one thing clear. Contingent liabilities are never recorded in the financial statements of a company. These obligations have not occurred yet but there is a possibility of them occurring in the future. So a contingent liability has no accounting treatment as such.
Can an obligation arise from past events?
An obligation may arise for the company from past events also. This happens when. It is not likely that an outflow of funds will be required to discharge the contingent liabilities. No reliable estimate can be made for the legal obligation. There is no prior precedence to enable the company to make such an estimate.
What are contingent liabilities?
Contingent liabilities, liabilities that depend on the outcome of an uncertain event, must pass two thresholds before they can be reported in financial statements. First, it must be possible to estimate the value of the contingent liability.
When should a company report contingent liability?
If a court is likely to rule in favor of the plaintiff, whether because there is strong evidence of wrongdoing or some other factor, the company should report a contingent liability equal to probable damages. This is true even if the company has liability insurance .
How many thresholds are required for contingent liabilities?
Contingent liabilities must pass two thresholds before they can be reported in financial statements: it must be possible to estimate the value of the contingent liability, and the liability must have greater than a 50% chance of being realized.
Why is it important to be warned about possible losses?
It's important that shareholders and lenders be warned about possible losses—an otherwise sound investment might look foolish after an undisclosed contingent liability is realized.
Do you have to include remote contingencies in financial statements?
Any probable contingency needs to be reflected in the financial statements—no exceptions. Remote contingencies should never be included. Contingencies that are neither probable nor remote should be disclosed in the footnotes of the financial statements.
Should a company consult experts before making decisions?
Company management should consult experts or research prior accounting cases before making determinations. In the event of an audit, the company must be able to explain and defend its contingent accounting decisions. Any probable contingency needs to be reflected in the financial statements—no exceptions.
Is contingent loss reflected on the balance sheet?
If the contingent loss is remote, meaning it has less than a 50% chance of occurring, the liability should not be reflected on the balance sheet. Any contingent liabilities that are questionable before their value can be determined should be disclosed in the footnotes to the financial statements.
What are contingencies in accounting?
Entities often make commitments that are future obligations that do not yet qualify as liabilities that must be reported. For accounting purposes, they are only described in the notes to financial statements. Contingencies are potential liabilities that might result because of a past event. The likelihood of loss or the actual amount of the loss is still uncertain. Loss contingencies are recognized when their likelihood is probable and this loss is subject to a reasonable estimation. Reasonably possible losses are only described in the notes and remote contingencies can be omitted entirely from financial statements. Estimations of such losses often prove to be incorrect and normally are simply fixed in the period discovered. However, if fraud, either purposely or through gross negligence, has occurred, amounts reported in prior years are restated. Contingent gains are only reported to decision makers through disclosure within the notes to the financial statements.
When is contingent loss recognized?
Question: According to U.S. GAAP, a contingent loss must be recognized when it is probable that it will occur and a reasonable estimation of the amount can be made. That rule has been in place now for over thirty years and is well understood in this country. Are contingent losses handled in the same way by IFRS?
Why are structured guidelines needed for reporting contingencies?
Because companies prefer to avoid (or at least minimize) the recognition of losses and liabilities, it is not surprising that structured guidelines are needed for reporting contingencies. Otherwise, few if any contingencies would ever be reported. U.S. GAAP in this area was established in 1975 when FASB issued its Statement Number Five, “Accounting for Contingencies.” This pronouncement requires the recognition of a loss contingency if
Why did Wysocki Corporation lose $800,000 in the first year?
For example, Wysocki Corporation recognized an estimated loss of $800,000 in Year One because of a lawsuit involving environmental damage. Assume the case is eventually settled in Year Two for $900,000. How is the additional loss of $100,000 reported? It relates to an action taken in Year One but the actual amount is not finalized until Year Two. The difference is not apparent until the later period.
What is a probable loss?
“Probable” is described in Statement Number Five as likely to occur and “remote” is a situation where the chance of occurrence is slight.
How to restate a previously reported income statement?
From a journal entry perspective, restatement of a previously reported income statement balance is accomplished by adjusting retained earnings. Revenues and expenses (as well as gains, losses, and any dividend paid figures) are closed into retained earnings at the end of each year. That is where the previous year error now resides.
What is a commitment in business?
Commitments. Commitments represent unexecuted contracts. For example, assume that a business places an order with a truck company for the purchase of a large truck. The business has made a commitment to pay for this new vehicle but only after it has been delivered. Although cash may be needed in the future, no event (delivery of the truck) has yet created a present obligation. There is not yet a liability to report; no journal entry is appropriate.

The Reporting Requirements of Contingent Liabilities
Contingent Liabilities
- Two classic examples of contingent liabilities include a company warrantyand a lawsuit against the company. Both represent possible losses to the company, and both depend on some uncertain future event. Suppose a lawsuit is filed against a company, and the plaintiff claims damages up to $250,000. It's impossible to know whether the company should report a continge…
Journal Entries
- A business accounting journal is used to record all business transactions. Each business transaction is recorded using the double-entry accountingmethod, with a credit entry to one account and a debit entry to another. Contingent liabilities, although not yet realized, are recorded as journal entries. Contingent liabilities require a credit to the accrued liability account and a deb…
GAAP Compliance
- Companies operating in the United States rely on the guidelines established in the generally accepted accounting principles(GAAP). Under GAAP, a contingent liability is defined as any potential future loss that depends on a "triggering event" to turn into an actual expense. It's important that shareholdersand lenders be warned about possible losses—an otherwise sound i…
The Bottom Line
- Contingent liabilities are those that are likely to be realized if specific events occur. These liabilities are categorized as being likely to occur and estimable, likely to occur but not estimable, or not likely to occur. Generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) require contingent liabilities that can be estimated and are more likely to occur to be recorded in a company's finan…