What is the trend in atomic radius on the periodic table?
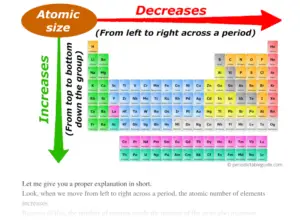
Atomic Radius Trend on the Periodic Table Atomic radii increase toward the bottom left corner of the periodic table, with Francium having the largest atomic radius. Atoms decrease in size across the period and increase in size down the group. Let’s break down the trend into its period and group trends.
What happens to atomic radius as you move down a group?
Atomic Radius Trend 2: Atomic Radii Increase as You Move Down a Group The second atomic radius periodic trend is that atomic radii increase as you move downwards in a group in the periodic table. For each group you move down, the atom gets an additional electron shell.
How do atomic radii change across the periodic table?
One atomic radius trend occurs as you move left to right across the periodic table (moving within a period), and the other trend occurs when you move from the top of the periodic table down (moving within a group). Below is a periodic table with arrows showing how atomic radii change to help you understand and visualize each atomic radius trend.
Why does the radius of an atom decrease down the period?
This is because while the number of electrons increases down the period, they only add to the same main energy level, and therefore do not expand the electron cloud. Down the period, however, the number of protons also increases. This increased positive charge attracts or pulls, the electrons in closer to the nucleus, decreasing the atomic radius.

What is the trend in atomic radius going down a group?
Atomic radius is the distance from the atom's nucleus to the outer edge of the electron cloud. In general, atomic radius decreases across a period and increases down a group.
Why does the atomic radius increase from top to bottom of the periodic table?
The number of energy levels increases as you move down a group as the number of electrons increases. Each subsequent energy level is further from the nucleus than the last. Therefore, the atomic radius increases as the group and energy levels increase. .
What is the trend of the atomic radius?
Atomic Radius Trend 1: Atomic Radii Decrease From Left to Right Across a Period. The first atomic radius periodic trend is that atomic size decreases as you move left to right across a period. Within a period of elements, each new electron is added to the same shell.
How does atomic radius change in group and period?
Solution : As we go down in a group, atomic radius gradually increases.
Reason: As we go down in a group, new shells are opened and electrons which enter in them are attracted weakly by the nucleus.
As we go from left to right in a period, atomic radius gradually decreases.
How does atomic radius change as you go down the periodic table?
On the periodic table, atomic radius generally decreases as you move from left to right across a period (due to increasing nuclear charge) and increases as you move down a group (due to the increasing number of electron shells).
Why atomic radius increases down a group?
In general, the atomic radius decreases and increases in a group over a time. The number of energy levels (n) increases in a group downwards, since there is a larger distance between the nucleus and the outermost orbital. This results in an atomic radius that is greater.
Why does atomic radius increase down Group 2?
Group 2 Elements are called Alkali Earth Metals. They are called s-block elements because their highest energy electrons appear in the s subshell. Progressing down group 2, the atomic radius increases due to the extra shell of electrons for each element. Going down the group, the first ionisation energy decreases.
Why atomic radius decreases across a period and increases down a group?
Atomic radius decreases across a period because valance electrons are being added to the same energy level at the same time the nucleus is increasing in protons. The increase in nuclear charge attracts the electrons more strongly, pulling them closer to the nucleus.
What makes atomic radius increase?
An atom gets larger as the number of electronic shells increase; therefore the radius of atoms increases as you go down a certain group in the periodic table of elements. In general, the size of an atom will decrease as you move from left to the right of a certain period.
How does atomic radius change from top to bottom in a group in the periodic table quizlet?
The radius increases as you go from top to bottom in the periodic table.
What happens to the atomic radius as it moves from top to bottom in a group and left to right in period?
As the atomic number increases in a period, the electron enters in the same shell. Thus, they are more and more strongly attracted towards the nucleus. As a result of this force of attraction from the nucleus, the atomic radii gradually decreases.
Why does atomic size increase down a group and decrease left to right?
In a period, the size of an atom decreases from left to right. This is because the nuclear charge, i.e., the atomic number increases from left to right in the same period, thereby bringing the outermost shell closer to the nucleus. (d) Metallic character increases down the group and decreases across a period.
What Are the Atomic Radius Trends? What Causes Them?
There are two main atomic radius trends. One atomic radius trend occurs as you move left to right across the periodic table (moving within a period), and the other trend occurs when you move from the top of the periodic table down (moving within a group). Below is a periodic table with arrows showing how atomic radii change to help you understand and visualize each atomic radius trend. At the end of this section is a chart with the estimated empirical atomic radius for each element.
What is the first atomic radius trend?
The first atomic radius periodic trend is that atomic size decreases as you move left to right across a period. Within a period of elements, each new electron is added to the same shell. When an electron is added, a new proton is also added to the nucleus, which gives the nucleus a stronger positive charge and a greater nuclear attraction.
Why don't noble gas atoms follow atomic radius trends?
Because noble gas atoms bond differently, their radii can't be compared to the radii of other atoms, so they don't follow atomic radius trends. Other exceptions include the lanthanide series and actinide series at the bottom of the periodic table.
How are noble gases held together?
Each of the noble gases has their outermost electron shell completely filled, which means multiple noble gas atoms are held together by Van der Waals forces rather than through bonds. Van der Waals forces aren't as strong as covalent bonds, so two atoms connected by Van der Waals forces don't get as close to each other as two atoms connected by a covalent bond. This means the radii of the noble gases would be overestimated if we attempted to find their empirical radii, so none of the noble gases have an empirical radius and thus don't follow the atomic radius trends.
Why do valence electrons have a larger radius?
So, because of electron shielding, the valence electrons don’t get particularly close to the center of the atom, and because they can’t get that close, the atom has a larger radius. As an example, potassium (K) has a larger average atomic radius (220 pm)than sodium (Na) does (180 pm). The potassium atom has an extra electron shell compared to ...
What is the unit of a chemical element?
An atom is a basic unit of a chemical element, such as hydrogen, helium, potassium, etc. A radius is the distance between the center of an object and its outer edge. An atomic radius is one-half the distance between the nuclei of two atoms. Atomic radii are measured in picometers (one picometer is equal to one trillionth of a meter).
What happens when more protons are added to the nucleus?
This means that, as more protons are added, the nucleus gets a stronger positive charge which then attracts the electrons more strongly and pulls them closer to the atom’s nucleus. The electrons being pulled closer to the nucleus makes the atom’s radius smaller.
Why does the atomic radius increase as you move down a column?
The atomic radius increases as you move down a column because for every new row of the table a new electron shell is added to the atom. A corollary to this is that because there are more electrons per atom as the atomic number increases, the atomic radius may decrease as you make your way across the table left to right.
What Is Atomic Radius?
Atomic radius refers to the size of the atom. Yet this value isn’t as easy to pin down as you might think. First of all, it’s important to be aware of the fact that although the term atomic radius is used to refer to an atom’s size, there isn’t an agreed-upon definition for this value. Various methods of measuring atomic radius are used, including the ionic radius, the metallic radius, the covalent radius, and the Van der Waals radius.
How Is Atomic Radius Measured?
Measurement of the atomic radius is done by measuring the distance between the nuclei of two different atoms that are just barely touching. The diameter of the distance between the two nuclei is divided by two to get the radius. When measuring atomic radius you must remember that the atoms being measured can’t share a chemical bond between them. This is because a chemical bond means that the electron shells of the atoms overlap or that they share an outer shell.
What is the ionic radius of an atom?
Ionic radius refers to the measure of an atom’s ion when in a crystal lattice, and it’s typically half the distance between the nuclei of two different ions which are barely touching. The covalent radius is the size of an atom that makes up a portion of a covalent bond.
What is the trend in ionization energy?
The ionization energy trend refers to how the amount of ionization energy needed to remove an electron from a gaseous neutral atom changes across the periodic table. Elements on the right side of the periodic table usually need more ionization energy to become a cation while elements on the left side of the table typically become cations more easily. In other words, ionization energy increases as one moves across the table from left to right.
What are the trends in the periodic table?
Other trends found in the periodic table include the electronegativity trend, the ionization energy trend, and the electron affinity trend. The electronegativity trend reflects the fact that the electronegativity value of an atom increases as you move left ...
What happens when electrons drop from an atom?
When the electrons drop from an atom the atom often drops its outermost electron shell as well, which has the effect of making the atomic radius larger than the ionic radius. In contrast to the fact that some atoms are more stable with a positive charge, some are more stable with a net negative charge.
Which direction does atomic size decrease in the periodic table?
Atomic size decreases from left to right in the Periodic Table.
What happens to the valence electrons as the proton number increases?
As a result, the valence electrons are held closer to the nucleus, and the atomic radius decreases. The chart below shows the relative sizes of atoms. (from crystalmaker.com)