
What is temperature cycling or thermal cycle testing?
Temperature Cycling or Thermal Cycle testing is performed on materials to determine the resistance of exposure to alternating extremes of high and low temperatures. Thermal mismatch of materials can cause solder joint cracking, warpage, damage to leads and markings, and hermetic seal failures.
What is thermal shock testing or temperature cycle testing?
What is Thermal Shock Testing or Temperature Cycle Testing? Both thermal shock testing and temperature cycle testing exposes a device under test (DUT) to alternating high and low air temperatures to accelerate failures caused due to repeated temperature variations during normal use conditions.
What is Thermal Cycling (TC 200) Test?
It is defined as an environmental stress test used to evaluate the reliability of the material or the product and to identify any manufacturing defects early by inducing failure modes through the thermal fatigue. It is one of the main qualifying tests carried out on PV modules. How is the Thermal Cycling (TC 200) test performed?
What is the difference between isothermal and thermal cycling data?
The isothermal data are from tests at 450°C, and the thermal cycling data were produced in temperature cycles between 100 and 450°C with a 200 s period. Further information on these experiments can be found in Daehn and González-Doncel.
What is thermal cycling used for?
Stresses such as thermal cycling, where chips are repetitively cycled from very low temperatures (as low as −160°C) to high temperatures (as high as 300°C), have been devised to test device resilience to thermal expansion differences or other structural weakness.
What is thermal cycle?
The thermal cycle is a heat therapy treatment that involves alternating hot and cold temperatures, followed by a rest period. This relaxation ritual is based on a 2,000-year-old tradition founded in Nordic countries.
What is thermal cycling in solar?
What Is Thermal Cycling (TC)? As day and night cycles each day, and the weather changes throughout different seasons, Thermal Cycling works by putting solar panels through temperature extremes (-40°C to 85°C according to IEC standard) to simulate the impact of weather.
What is thermal cycling in knife making?
Thermal Cycling “Thermal cycling” is very non-specific, it just means heating and cooling steel. It probably isn't specific enough for our purposes, but it is a common phrase used by knifemakers to refer to the steps they perform after forging but before the final heat treatment.
How long is a thermal cycle?
The thermal cycle duration is 90 min with 15-min ramps between temperature extremes and 30 min dwells at each temperature extreme.
How do you do a thermal shock test?
3:3015:09Thermal/Temperature Shock Testing - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipOn your thermal shock chamber type between the hot and cold boxes of the thermal shock chamberMoreOn your thermal shock chamber type between the hot and cold boxes of the thermal shock chamber typically the transition between hot and cold boxes.
What is damp heat test?
What is the Damp Heat test? The PV Damp Heat Test is an accelerated environmental aging test that determines the ability of the solar module to withstand long-term exposure to high temperature and penetration of humidity.
What is humidity freeze?
What is Humidity Freeze HF 10 Test ? The humidity freeze HF 10 test is an environmental test that is designed to define the module's ability to endure the effects of high temperatures combined with humidity, then followed by very low temperatures. The module is exposed to 10 complete cycles in a harmonized profile.
What IEC 61215?
IEC 61215-1:2021 lays down requirements for the design qualification of terrestrial photovoltaic modules suitable for long-term operation in open-air climates. The useful service life of modules so qualified will depend on their design, their environment and the conditions under which they are operated.
What temperature should you quench a knife at?
Step 2: Quench (The block ensures that both sides of the blade are evenly cooled.) Many knifemakers recommend using canola oil heated to around 130℉, saying that water tends to cool the steel too quickly, which can lead to cracking, especially if the blade is on the thin side.
What temperature do you quench steel?
The steel is tempered to reduce some of the hardness and increase ductility. It's heated for a set period of time at a temperature that falls between 400° F and 1,105° F. Sometimes, if further ductility is needed, a higher temperature is used- around 1,300° F.
What temperature do you temper 1095 steel?
Tempering. AISI 1095 carbon steel can be tempered at 372 to 705°C (700 to 1300°F). It has Rockwell C 55 hardness.
Why is a thermal cycler used in PCR?
Thermocyclers, or thermal cyclers, are instruments used to amplify DNA and RNA samples by the polymerase chain reaction. The thermocycler raises and lowers the temperature of the samples in a holding block in discrete, pre-programmed steps, allowing for denaturation and reannealing of samples with various reagents.
What is the difference between thermal shock and thermal cycling?
Thermal shock testing determines whether the electronic product under test is capable of withstanding sudden temperature changes. Thermal cycle testing is conducted to identify the failure mechanisms caused by a mismatch in the coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) of materials.
What are basic thermodynamic cycles?
A thermodynamic cycle consists of a linked sequence of thermodynamic processes that involve transfer of heat and work into and out of the system, while varying pressure, temperature, and other state variables within the system, and eventually return the system to its initial state.
What is thermocline layer?
A thermocline is the transition layer between the warmer mixed water at the surface and the cooler deep water below. It is relatively easy to tell when you have reached the thermocline in a body of water because there is a sudden change in temperature.
Why do you heat a circuit board pad?
Heating the circuit board pad and component by touching only the pad allows the capacitor to heat slow enough to avoid the huge thermal stress relieved by cracking the ceramic.
Is thermal cycling elastic?
Let’s assume the temperature range for the thermal cycling does experience thermal shock and does not cross material transition points (freezing or melting, for example), thus the bulk material’s motion is relatively elastic, meaning the material retains its properties such as tensile strength, hardness, etc.
What is thermal cycling?
Thermal cycling can be regarded as one of the most severe among all thermal environments. Damage due to thermal cycling has been evidenced in a number of components, for example, turbine blades and brake drums that are traditionally made from metals or superalloys.
What causes thermal cycling damage?
Under thermal cycling, alternating plastic strains in the matrix give rise to low-cycle fatigue characterized by interface cavitation and debonding. Typical examples of interface damage include: voids in W fiber-reinforced copper matrix composites 116 and in boron fiber–1100 aluminum matrix composites 120; interface cracks in boron fiber–6061 aluminum matrix composites, 130 and Cf–5056 aluminum matrix composites. 131,132 Fig. 25 shows the voids and interface debonds that were generated after 1000 thermal cycles between ambient temperature and 320°C. The microdamage caused by interface debonding will result in macroscopic damage with a reduction in mechanical properties and dimensional changes of the MMCs. Dimensional change is considered a serious degradation. A number of analytical models 132–134 have been developed to explain the process of microdamage leading to dimensional change.
What are HST bistem thermal shields made of?
(2008) for space environmental durability. The shields were comprised of 2 mil (0.051 mm) aluminized-Teflon fluorinated ethylene propylene (Al-FEP) rings fused together into a circular bellows shape. Because the circular thermal shields had solar, antisolar, and solar-grazing surfaces and were exposed to the space environment for a long duration, it provided a unique opportunity to study the solar effects on the environmental degradation of Al-FEP. Tensile testing verified that near-solar-facing surfaces lost their mechanical strength and elasticity, while the antisolar-facing surfaces maintained their ductility. A polar plot of the elongation at failure versus solar angle for retrieved HST BSTS weld tensile samples is provided in Fig. 28.26. The study shows the detrimental effect of solar exposure on FEP insulation in the space environment. Antisolar-facing surfaces experienced only marginal degradation in space, but solar-facing surfaces experienced severe degradation due to the additional radiation exposure (soft X-rays and UV radiation) combined with increased on-orbit heating for Sun-facing surfaces.
How does temperature affect rock strength?
The influence of temperature upon the strength of rock is significant at great depths where the temperatures approach the melting point of the rock constituents. The reduction in strength, stiffness, and fracture toughness could be of importance to drilling engineers.
Can ER measurements detect temperature?
To detect the transformation temperatures, ER measurements can be useful and a good probe for identifying both temperature- and stress-induced transformations involving SMA crystallographic phases. Uchil et al. [ 23] investigated 40% cold-worked Nitinol phase transformations as a function of heat treatment by measuring ER variations with temperature. They observed that resistivity increases at martensite → austenite transformation and decreases at austenite → martensite transformation. Moreover, if the R-phase is present, resistivity approaches a maximum value, and during the cooling step, when resistivity increases, it is possible to evaluate the R-phase start and finish temperatures.
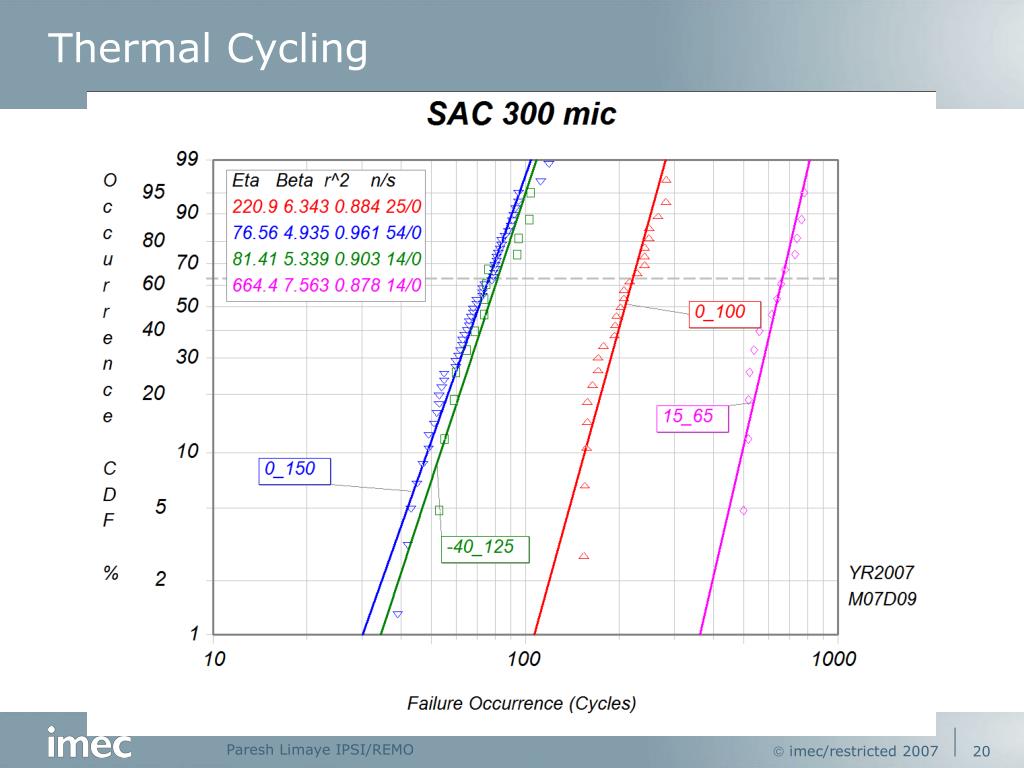
Is IMC thickness a good correlation with fatigue life prediction?
The reduction is more significant with increasing IMC thickness. The finite element model results with a thick IMC layer of 6 μm resulted in good correlation with the TC test fatigue life prediction result. However, dynamically modeling IMC layer in the FEA model is still one challenging job and needs to put more efforts on this problem.
Who implemented an experimental setup to measure the electrical properties of NiTi alloys with R-phase upon variations in temperature?
Antonucci et al. [ 10] implemented an experimental setup to measure the electrical properties of NiTi alloys with R-phase upon variations in temperature ( Fig. 5.17 ).
What is thermal cycling?
Temperature Cycling or Thermal Cycle testing is performed on materials to determine the resistance of exposure to alternating extremes of high and low temperatures. Thermal mismatch of materials can cause solder joint cracking, warpage, damage to leads and markings, and hermetic seal failures.
What is PTC cycling?
Powered Temperature Cycling (PTC) uses the same extreme temperature exposures as traditional temperature cycling but with the addition of simultaneous operating and electrical biases periodically applied and removed. PTC is used to simulate the worst case conditions in application environments.
What is PTC used for?
PTC is used to simulate the worst case conditions in application environment s. Adhesives such as silicones, epoxies and polyurethanes can also be tested for thermal cycling resistance where the bonded materials may have different coefficients of thermal expansion and contraction.
What is Paragon Systems Testing?
Paragon Systems Testing is a highly experienced thermal shock testing lab where we assist our customers in setting up a test using the proper test conditions. So, if you do not know what test conditions that you should use or what specification to choose, then we will help you because we are thermal shock testing experts!
What factors influence the test parameters?
Factors that can influence the test parameters comprise of the thermal mass of the device under test, the number of and the airflow around the device under test that depends on the DUT spacing within the chamber . The dwell time at each and every temperature are required to be included in the test specification in addition to tolerances around the high and low temperatures. Test methods can also specify minimum rates of temperature change.
Can a DUT be tested in a single chamber?
However larger DUT can possibly be tested in single compartment chambers. Some equipment uses separate hot and cold chambers with an elevator mechanism that transports the device under test between two or more chambers. This leads to a more rapid rate of change in the air temperature.
Can thermal shock equipment be used in multiple chambers?
Equipment with single or multiple chambers can be utilized in performing thermal shock testing. While using single chamber thermal shock equipment, the DUT or samples will be in one chamber and the chamber air temperature is rapidly cooled and heated.

Types of Damage Caused by Thermal Cycling
Material Phase Transition
Thermal Shock
Accumulated Cyclic Damage
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion Mismatch
Understand The Failure Mechanism Caused by Thermal Cycling
- This very brief introduction to thermal cycling and the ways it can damage your product implies that you must understand the specific failure mechanisms before designing your thermal cycling based life test. The thermal cycling profile will replicate the same path to failure as seen in normal use. If you accelerate the life testing by cycling more ...
Conclusion
Related