1. the activated form of coagulation factor II (prothrombin), which catalyzes the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin. 2. a preparation of this compound prepared from prothrombin of bovine origin, used as a topical hemostatic.
Full Answer
What is the history of topical thrombin?
The first clinical use of topical bovine thrombin dates back to more than 60 years ago. In the 1970s, FDA approval of thrombin was grandfathered in. The use of topical thrombin has been described for over 100 uses, including spinal, neurologic, general, orthopedic, cardiac, thoracic, vascular, gynecologic, and dental procedures. 5,9
What is thrombin used to treat?
Thrombin is used to prevent and stop bleeding whenever oozing blood and minor bleeding from microvessels is accessible. Thrombin is available under the following different brand names: Recothrom, Thrombogen, and Thrombin JMI.
What is recothrom (recombinant topical thrombin)?
Recombinant topical thrombin (Recothrom [ZymoGenetics]) was FDA approved in 2008. This product is produced utilizing recombinant DNA and has comparable efficacy compared to bovine thrombin but is free from bovine or human plasma.
What if I am allergic to thrombin (topical)?
If you are allergic to thrombin (topical); any part of thrombin (topical); or any other drugs, foods, or substances. Tell your doctor about the allergy and what signs you had.
What is topical thrombin used for?
Thrombin is a topical hemostatic agent used to control and minimize blood loss during surgical procedures, is utilized in conjunction or as an alternative to standard surgical techniques.
What is used as topical anticoagulant?
Topical thrombin has a direct clotting effect on exposed blood. The active hemostats include topical (bovine) thrombin (Thrombin-JMI), topical (human) thrombin (Evithrom), and topical (recombinant) thrombin (Recothrom).
How do you make topical thrombin?
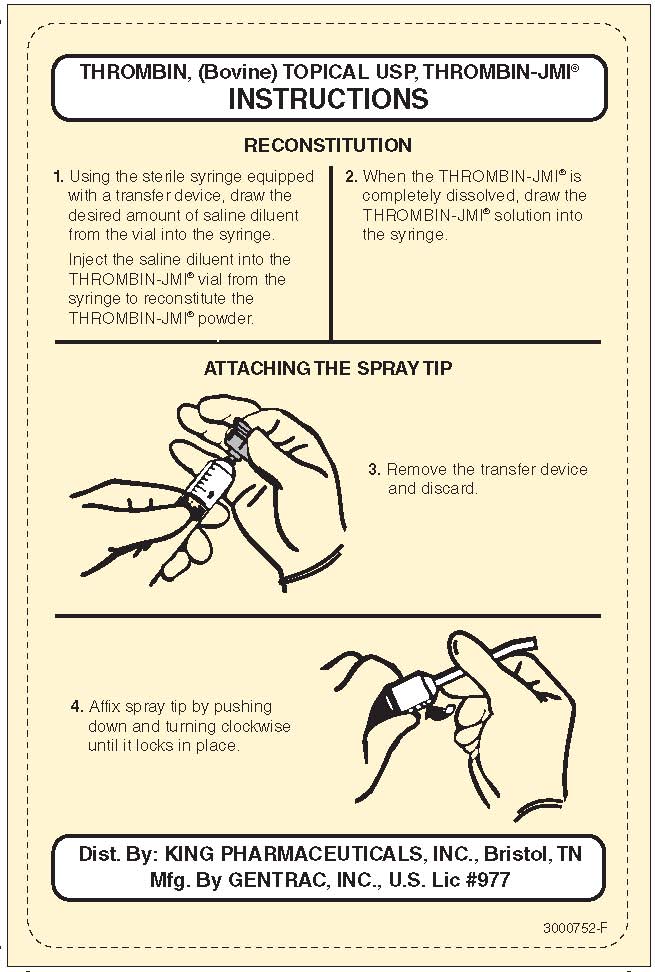
Prepare THROMBIN-JMI solution to desired strength. Immerse sponge strips of the desired size in THROMBIN-JMI solution. Knead the sponge strips vigorously with moistened, gloved fingers to remove trapped air, thereby facilitating saturation of the sponge. Apply saturated sponge to bleeding area.
Can topical thrombin cause thrombosis?
THROMBIN-JMI can cause fatal severe bleeding or thrombosis . Thrombos is may result from the development of antibodies against bovine thrombin. Bleeding may res ult from the development of antibodies against factor V.
What are 3 types of anticoagulants?
There are three main types of anticoagulant medications:Vitamin K antagonists.Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs)Low molecular weight heparins (LMWH)
What's the meaning of thrombin?
Definition of thrombin : a proteolytic enzyme that is formed from prothrombin and facilitates the clotting of blood by catalyzing conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin.
Can topical thrombin be injected?
Conclusion: Simple iatrogenic femoral pseudoaneurysms, regardless of size or concomitant anticoagulation therapy, can be treated with a single injection of up to 1,000 units of topical thrombin and require no follow-up.
Where is topical thrombin stored?
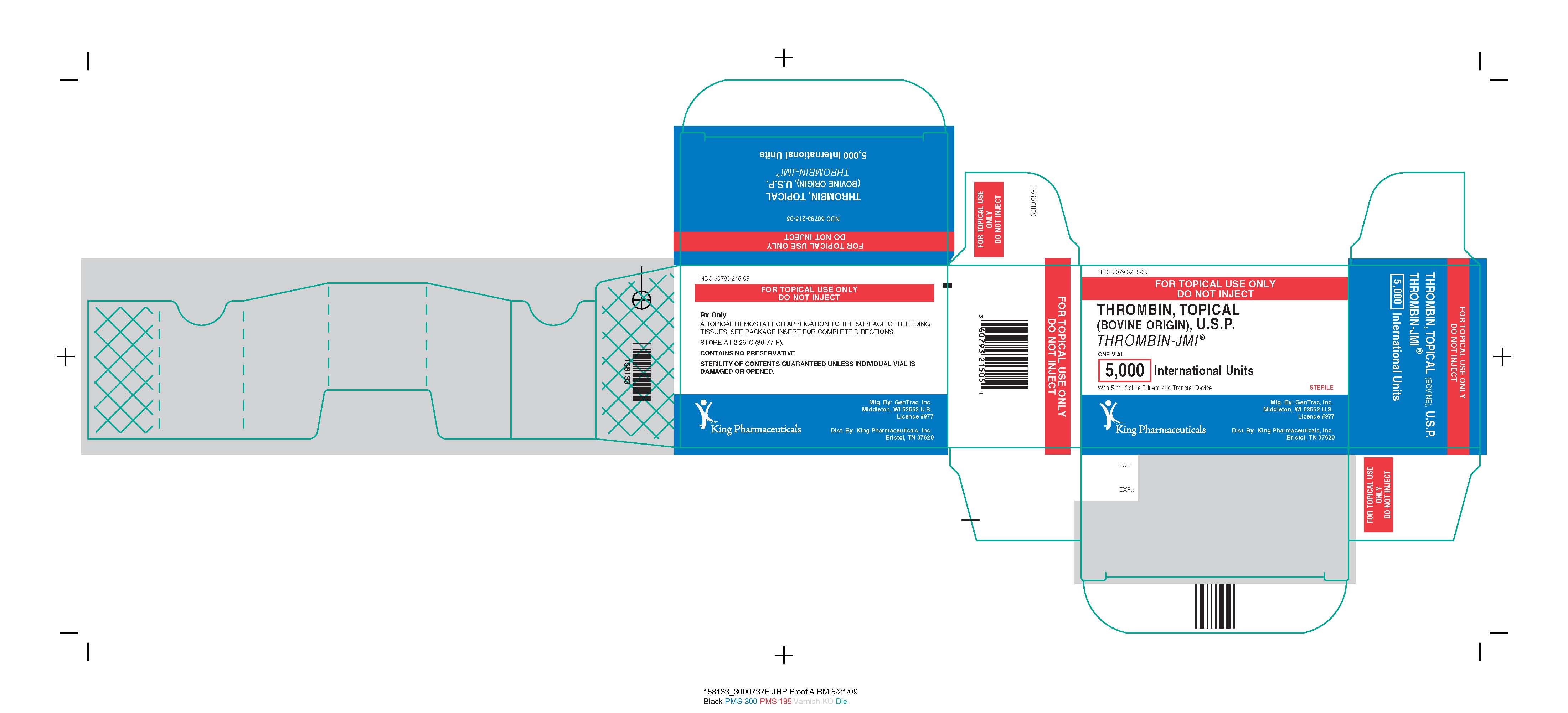
CAUTION: Solutions should be used promptly upon removal from the container. However, the solution may be refrigerated at 2°-8°C for up to 24 hours, or may be stored at room temperature for up to 4 hours after reconstitution. , one vial of diluent and one spray pump and actuator.
Is Gelfoam and Surgifoam the same thing?
Gelfoam is available in the form of a compressed sponge, while Surgifoam is available in both forms, as a sponge and as a flowable matrix. These products can be used dry, with saline solution, or together with topical thrombin.
How long does fibrin glue last?
Biodegradation of this fibrin sealant occurs over 30 days [65]. The effectiveness of this product has been demonstrated in a multicenter, prospective, randomized trial [65, 70] including cardiac, hepatic [71], general surgical, and orthopedic patients (cancellous bone bleeding) [72].
What is bone wax made of?
Bone wax is a mixture of beeswax (70%) and Vaseline (30%). It is a non-absorbable material, becoming soft and malleable in the hand when warmed.
How do you dissolve thrombin?
The product is soluble in water (10 mg/mL), yielding a clear solution. Stock solutions can be prepared at a concentration of 100 units/mL in a 0.1% (w/v) BSA solution. Stock solutions remain active for one week at 0–5 °C. Solutions are most stable at pH 6.5, as a pH >7 will greatly reduce thrombin activity.
What is thrombin used for?
The initial thrombin was bovine in origin, but its use has been complicated by the formation of antibodies that cross react with human coagulation factors. This has been associated with life threatening bleeding and in some circumstances anaphylaxis and death. Human thrombin, isolated from pooled plasma of donors, has been developed in an effort to minimize these risks, but its downside is the potential of transmitting blood-borne pathogens and limited availability. Recently a recombinant thrombin has been developed and approved for use by the FDA. It has the advantage of being minimally antigenic and devoid of the risk if viral transmission. Thrombin is often used in conjunction with other hemostatic aids, including absorbable agents (like gelfoam, collagen, and cellulose), and with fibrinogen in fibrin glues. The last part of this review will discuss these agents in detail, and review their clinical applications.
What is the function of thrombin?
Thrombin has a number of well studied biological activities, which serve to achieve coagulation and hemostasis. With tissue injury and bleeding, exposed collagen and released tissue factor cause activation of the intrinsic and extrinsic coagulation pathways. Both pathways lead to activation of factor X which along with activated factor V forms a complex that cleaves the prothrombin protein into the active thrombin molecule. Thrombin production is the final coagulation step required to cleave fibrinogen into fibrin which provides a hemostatic lattice for platelet aggregation and thrombus formation at the site of injury (Figure 1).
How long has thrombin been used?
Thrombin has a long history as a vehicle to affect hemostasis. Descriptions can be found in the European literature as early as 1892 for the use of thrombin (Brister et al 1994). Early on, thrombin was used by barbers and boxers, for hemostasis of shaving cuts and fight lacerations. Records citing thrombin use in surgery date back to the 1940s. Since then its use has grown exponentially, and now thrombin is used in more than 1 million patients in the United States each year at a cost of US$250 million (Lawson 2006). Recently there have been new developments in thrombin, namely FDA approval in human thrombin, and development of a recombinant thrombin.
What are the blue boxes and arrows in the coagulation cascade?
Diagram of coagulation cascade. Blue boxes and arrows include various hemostatic agents with their mechanism of actions. (+) these agents affect the entire coagulation cascade by concentration and creating of a matrix for coagulation factors at the bleeding site. Red arrows indicate the inhibition caused by bovine generated antibodies to thrombin, factor V, and platelet antiphospholipids.
How serious are the adverse events of evithrom?
Two subjects (1.3%) in the Evithrom®group experienced a severe adverse event: respiratory arrest and post-procedural hematoma in one subject and an extradural hematoma in the other. Three subjects in the bovine thrombin group experienced severe adverse events: hyperhidrosis, pyrexia, and post-procedural hematoma. None of the adverse events reported was considered causally related to Evithrom®or bovine thrombin administration. No deaths were reported during the study period (Omrix Biopharmaceuticals 2007).
When was thrombin first approved?
In 2007, the FDA finally approved the first stand alone human thrombin preparation, Evithrom®(Omrix Biopharmaceuticals, Ltd, New York, NY, USA) (US Food and Drug Administration 2007). Previously, human thrombin was only used in FDA approved combination products, namely Floseal®(Baxter; Deerfield, IL, USA), and the fibrin glues (to be discussed in greater detail later).
Can bovine thrombin cause thrombosis?
In a study with 88 hemodialysis patients (Sands et al 2000) and another case report with 1 cardiac patient (Fastenau et al 1999), the authors demonstrated certain patients exposed to bovine thrombin preparations could developed antiphospholipid antibodies causing subsequent thrombosis. More bovine thrombin induced antibodies continued to be discovered, as mice experiments by Schoenecker et al in 2001 demonstrated autoantibodies similar to those found in autoimmune disorders like SLE could be caused by bovine thrombin exposure (Schoenecker et al 2001).
Can bovine derived thrombin cause bleeding?
US BOXED WARNING:#N#-SEVERE BLEEDING AND THROMBOSIS COMPLICATIONS: The bovine-derived formulation can cause fatal bleeding or thrombosis. Thrombosis may result from the development of antibodies against bovine thrombin. Bleeding may result from the development of antibodies against factor V, and these antibodies may cross-react with human factor V and lead to its deficiency. Do not re-expose patients to the bovine-derived formulation if there are known or suspected antibodies to bovine thrombin and/or factor V. Monitor patients for abnormal coagulation laboratory values, bleeding, or thrombosis.#N#Do not inject.
Can you refrigerate thrombin?
For thrombin topical marketed as Evithrom:#N#Do not refreeze thrombin topical once it has been thawed. Do not refrigerate thrombin topical once it has reached at room temperature. Discard unused product after 24 hours at room temperature.
When was topical thrombin first used?
The first clinical use of topical bovine thrombin dates back to more than 60 years ago. In the 1970s, FDA approval of thrombin was grandfathered in. The use of topical thrombin has been described for over 100 uses, including spinal, neurologic, general, orthopedic, cardiac, thoracic, vascular, gynecologic, and dental procedures. 5,9
What is the function of thrombin?
The active hemostats include topical (bovine) thrombin (Thrombin-JMI), topical (human) thrombin (Evithrom), and topical (recombinant) thrombin (Recothrom). These agents are indicated as an aid to hemostasis whenever ongoing oozing blood and minor bleeding from capillaries and small venules are accessible. The active agents stimulate activity in the coagulation cascade and promote the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin ( FIGURE 1 ). 8
What is a topical hemostat?
Topical hemostats are used in the setting of surgery or trauma as adjuncts to maintain hemostasis. Topical hemostat products include gelatin sponges, collagens, fibrin sealants, and active thrombin preparations. These agents are applied locally to stop blood flow. 1. Current health care has an emphasis on outcomes.
How long does it take for a coagulopathy to appear?
12 The reported time of clinical presentation of IMC is quite variable and may occur within 10 days with a mean of 32 days to months after exposure. Over 60 cases with known or presumed surgical exposure to bovine thrombin have been published. Bleeding was noted in approximately one half of these cases. Currently, there is a low clinical awareness for IMC. 5,13-15 Although the newly formulated bovine-derived Thrombin-JMI contains significantly reduced levels of contaminants, coagulopathies can still occur. 10,16
How long can evithrom be stored?
Once reconstituted, the product can be stored in the refrigerator for 30 days and at room temperature for 24 hours. 22. Recombinant topical thrombin (Recothrom [ZymoGenetics]) was FDA approved in 2008.
When was thrombin JMI approved?
Thrombin-JMI (King Pharmaceuticals) was approved in 1995. 10 It is estimated that between 500,000 and 1 million patients have exposure to bovine thrombin on an annual basis in the U.S. With a broad indication for use, bovine thrombin has two vial sizes and can be sprayed on or applied with a sponge.
What is hemorrhagic IMC?
Hemorrhagic IMC is a diagnostic challenge. The clinical presentation may be quite variable and masked by other conditions such as anticoagulant or antiplatelet therapy, vitamin K or liver disease, disseminated intravascular coagulation, acidosis and hypothermia, and hemodilution due to blood loss. 17,18 The management of hemorrhagic IMC often requires a hematology consult. Supportive care with extended follow-up of laboratory tests can manage a patient in the absence of overt bleeding. For the bleeding patient, packed red blood cells, platelet transfusions and immunosuppressive therapy (corticosteroids, cyclosporine), chemotherapy (cyclophosphamide, vincristine), or epsilon aminocaproic acid may be required. 12,19-21
What is thrombin in blood?
Thrombin is implicated in the physiology of blood clots. Its presence indicates the existence of a clot. In 2013 a system for detecting the presence of thrombin was developed in mice. It combines peptide-coated iron oxide attached to "reporter chemicals".
What is the function of thrombin?
Thrombin in turn acts as a serine protease that converts soluble fibrinogen into insoluble strands of fibrin, as well as catalyzing many other coagulation-related reactions.
What is prothrombin complex concentrate?
Prothrombin complex concentrate and fresh frozen plasma are prothrombin-rich coagulation factor preparations that can be used to correct deficiencies (usually due to medication) of prothrombin. Indications include intractable bleeding due to warfarin .
What are the effects of gla residues on prothrombin?
In the presence of calcium, the Gla residues promote the binding of prothrombin to phospholipid bilayers. Deficiency of vitamin K or administration of the anticoagulant warfarin inhibits the production of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid residues, slowing the activation of the coagulation cascade.
What is fibrinogen used for?
Thrombin, combined with fibrinogen, is sold under the brand name Fibrimex for use as a binding agent for meat. Both proteins in Fibrimex derives from porcine or bovine blood. According to the manufacturer it can be used to produce new kinds of mixed meats (for example combining beef and fish seamlessly).
How much antithrombin is in the blood?
In human adults, the normal blood level of antithrombin activity has been measured to be around 1.1 units/mL. Newborn levels of thrombin steadily increase after birth to reach normal adult levels, from a level of around 0.5 units/mL 1 day after birth, to a level of around 0.9 units/mL after 6 months of life.
What is the function of thrombin and thrombomodulin?
Thrombin bound to thrombomodulin activates protein C, an inhibitor of the coagulation cascade. The activation of protein C is greatly enhanced following the binding of thrombin to thrombomodulin, an integral membrane protein expressed by endothelial cells. Activated protein C inactivates factors Va and VIIIa. Binding of activated protein C to protein S leads to a modest increase in its activity. Thrombin is also inactivated by antithrombin, a serine protease inhibitor .
Why is thrombin used?
Thrombin is used to prevent and stop bleeding whenever oozing blood and minor bleeding from micro vessels is accessible.
What are the side effects of thrombin?
Immune hypersensitivity reaction. Blood clotting disorder. Other side effects of thrombin include: General allergic reactions. Antibody formation. This document does not contain all possible side effects and others may occur. Check with your physician for additional information about side effects.
What Are Warnings and Precautions for Thrombin?
This medication contains thrombin. Do not take Recothrom, Thrombogen, or Thrombin JMI if you are allergic to thrombin or any ingredients contained in this drug .
Is bovine thrombin asymptomatic?
The use of topical bovine thrombin preparations has occasionally been associated with abnormalities in hemostasis ranging from asymptomatic alterations in laboratory determinations, such as prothrombin time (PT) and partial thromboplastin time (PTT), to severe bleeding or thrombosis, which rarely have been fatal.
Can you re-expose bovine thrombin?
Any interventions should consider the immunologic basis of this condition. Patients with antibodies to bovine thrombin preparations should not be re-exposed to these products.
Does thrombin interact with other drugs?
Thrombin has no listed interactions with other drugs.
Is recothrom safe for children?
Recothrom is approved in children for hemostasis whenever oozing blood and minor bleeding from microvessels is accessible. Children under 1 month of age: Safety and efficacy not established. Children over 1 month of age: Dose depends on area to be treated (Recothrom) Children and adolescents: May soak in up to 10 mL of absorbable gelatin sponge ...
