What is the total revenue rule?
Total revenue profits are a product of subtracting total costs from total revenue. What is the profit maximizing rule? The Profit Maximization Rule states that if a firm chooses to maximize its profits , it must choose that level of output where Marginal Cost (MC) is equal to Marginal Revenue (MR) and the Marginal Cost curve is rising.
How to increase total revenue?
Top 10 Ways To Immediately Increase Your Revenue
- Raise Your Prices. ...
- Up-Sell. ...
- Cross-Sell. ...
- Bundle Better. ...
- Offer Volume or Frequent Buyer Discounts. ...
- Offer Complementary Products or Services. ...
- Communicate Often. ...
- Have a Special Event. ...
- Promote Others. ...
- Say “No” to Bad Customers. ...
Does total revenue equal total sales?
Total sales refers to the total number of units you sell, regardless of how much money you bring in or whether or not you make a profit. If you use the term “sales” to refer to the amount of money you bring in, your total sales would be your total dollar volume. Revenues are the monies you generate from sales or other activities.
What is the average revenue curve?
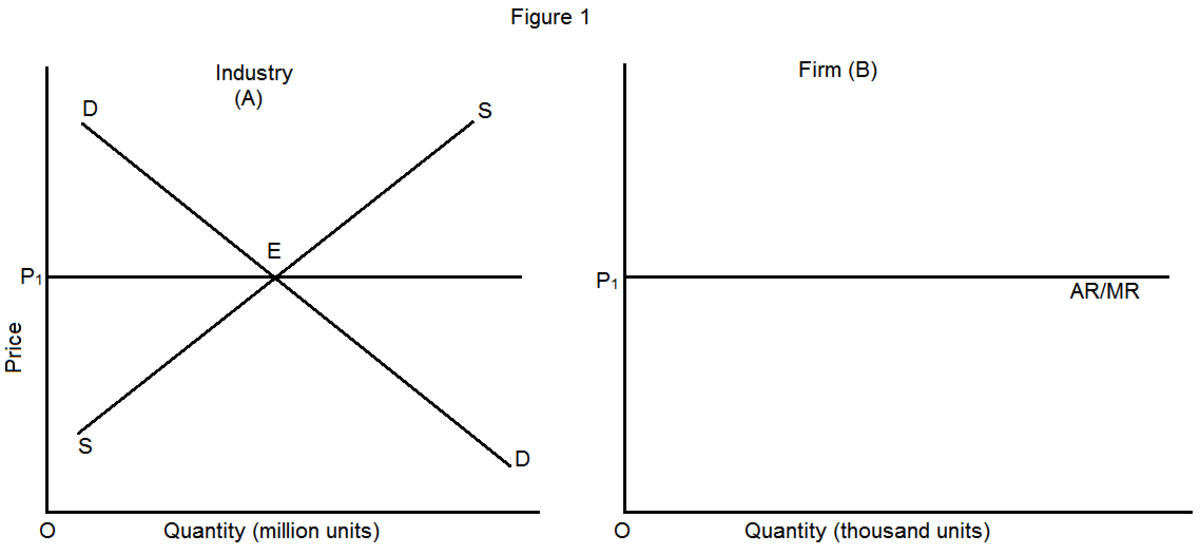
The curve represents the relation between the average revenue a firm receives from production and the quantity of the output which is produced. The average revenue curve reflects the degree of market control which is controlled by the firm. For a perfectly competitive firm with no market control, the average revenue curve is only a horizontal line.

What is meant by total revenue?
Total revenue is the total amount of money a company brings in from selling its goods and services. It determines how well a company is bringing in money from its core operations based on demand and price.
How does the total revenue curve look?
A total revenue curve is a straight line coming out of the origin. The slope of a total revenue curve is MR; it equals the market price (P) and AR in perfect competition. Marginal revenue and average revenue are thus a single horizontal line at the market price, as shown in Panel (b).
What is total revenue curve of a monopoly?
TOTAL REVENUE CURVE, MONOPOLY: A curve that graphically represents the relation between the total revenue received by a monopoly firm for selling its output and the quantity of output sold. It is combined with a monopoly firm's total cost curve to determine economic profit and the profit maximizing level of production.
Why is total revenue important?
Total revenue is the amount a company or business owner receives for the services or products they sell in a specific period of time. The total revenue formula helps business owners to decide whether they should raise their prices, or offer a discount on their goods.
What is total revenue formula?
Total Revenue Formula The formula for Total Revenue is as follows: Number of Products Sold x Price Per Product = Total Revenue. The formula to know your business' revenue is to multiply the total amount of products or services sold by the price of those products or services.
What is the shape of TR curve under perfect competition?
TR curve under perfect competition is a straight line, sloping upward from the origin.
What is marginal revenue curve?
The marginal revenue curve is a horizontal line at the market price, implying perfectly elastic demand and is equal to the demand curve. Under monopoly, one firm is a sole seller in the market with a differentiated product.
What is the slope of total revenue?
At the point of maximum total revenue m the slope of the total revenue curve is zero and the marginal revenue is therefore also zero. The marginal revenue curve thus crosses the horizontal axis at the quantity at which the total revenue is maximum.
Why is the total revenue curve concave?
Unlike under perfect competition, a firm under imperfect competition such as under monopoly can sell more only by lowering its price. Therefore, the average revenue curve is downward sloping and its corresponding marginal revenue curve lies below it.
Why is the total revenue curve a straight line?
The total revenue is an upward sloping straight line through the origin at a constant rate in perfect competition because the price of commodity remains constant for each level of output for a price taking firm.
How does a total revenue curve of a price taking firm look like why does it look so?
The total revenue curve for a firm in a perfectly competitive market is an upward sloping curve because the price or AR remains constant and MR is also equal to AR. Thus TR can only be influenced by altering the output sold as the price remains constant.
How do you draw a revenue curve?
How To Draw The Marginal Revenue CurveAverage Revenue = The Total Revenue of the firm divided by the total units of goods/services sold. ... Marginal Revenue = The additional revenue gained from the firm selling the next unit of goods/services. ... AR = mQ + C.TR = AR * Q = ( mQ + C ) * Q = mQ2 + CQ.MR = d(TR) / d(Q) = 2mQ + C.More items...•
What is AR curve?
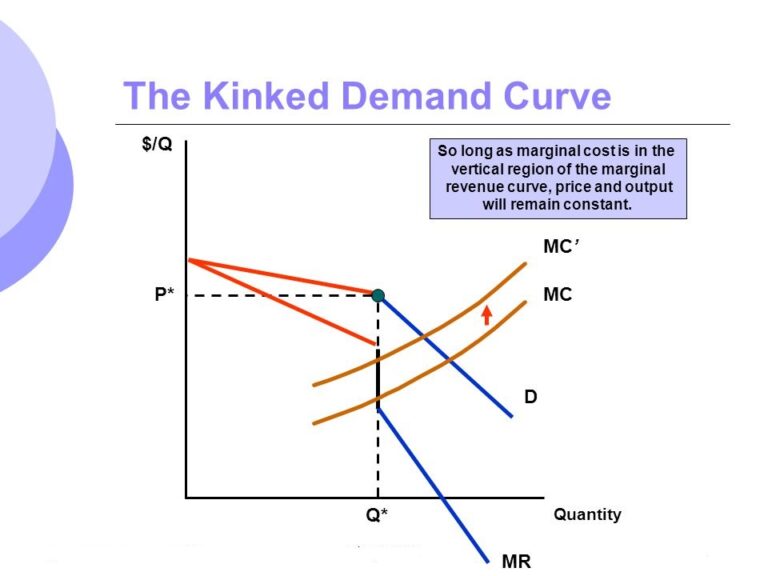
2. In pure monopoly, AR curve is a rectangular hyperbola and MR curve coincides with the horizontal axis. 3. In all other markets, AR curve slopes downwards and MR curve lies below it. In oligopoly, however, AR curve cannot be drawn with definiteness but the practice is to draw downward sloping AR and MR curves.
What happens to the AR curve when it is under oligopoly?
If it is done so, he may not be in a position to raise his sales. Thus AR curve becomes less elastic from K onwards and correspondingly MR curve falls vertically from a to b and then slopes at a lower level.
Why does demand/AR curve have a negative slope?
This is because the monopolist seller ordinarily has to accept a lower price for his product, as he increases his sales. Under imperfect competition conditions, total revenue increases at a diminishing rate.
What happens to revenue under imperfect competition?
Under imperfect competition conditions, total revenue increases at a diminishing rate. It becomes maximum and then begins to decline.
When a firm is working under conditions of monopoly or imperfect competition, its demand curve or AR curve is less?
When a firm is working under conditions of monopoly or imperfect competition, its demand curve or AR curve is less than perfectly elastic, the exact degree of elasticity being different in different market situations depending upon the number of sellers and the nature of product.
Is marginal revenue the same as AR?
In table 5 we find that as output increases, AR remains the same i.e. Rs. 5. Total revenue increases but at a constant rate. Marginal revenue is also constant i.e. Rs. 5 and is equal to AR.
Is marginal unit bringing in Rs. 4?
The marginal unit is not bringing in Rs. 4 which is its price, but only Rs. 2. This is because the additional one unit is sold at Re. one less and the first 2 units which could have been sold for Rs. 5 are also sold at Rs. 4. i.e., Re. one less.
What is total revenue formula?
The total revenue formula demands the calculation of the total number of units sold by the company as the first step. The next step in the formula for total revenue is to determine the average price per unit of the goods sold. For finding total revenue, you need to multiply both:
How to find total revenue?
How to find total revenue? – As a first step, you need to calculate the total number of units sold by your company. It can be products or services. The second step is to determine the average price per unit sold.
How to value a company based on revenue?
Thereby checking the gross profit or revenue of the company. Next is to check whether a company is able to earn higher even after deducting the sales expenses.
What is the formula for net income?
The expenses are usually the operating expenses. If the net income is positive, the conclusion is the company is earning profits. If it’s negative then it is undergoing loss.
What is the second step in the net revenue equation?
Then the second step is to determine the deductions that you need to consider in the net revenue equation. The amount to be accumulated for deductions is from discounts, sales returns, and commissions. They are cumulatively called selling expenses.
What is gross revenue?
The simplest way to define gross revenue is the total sum of all the money earned by the company. It includes the amount earned from the sale of goods and services, sale of shares, sale of property and equipment, and interest. It is included in the company’s income statement. Under the gross annual revenue head, you can find details of the total income and the expenses that need to be deducted from it to calculate the net revenue or the net income.
Why is total revenue important?
The importance of total revenue is to understand the difference between the total revenue and total costs. The more is the difference, the more a company can maximize its profits. The importance of marginal revenue is to find out how much a company can increase revenue by selling additional products or services.
How to calculate total revenue?
To calculate total revenue (TR), multiply the price per unit (P) and quantity of the product sold (Q).
What are the advantages of the total revenue test?
The total revenue test can help a business in its pricing strategy. Using the test, you can determine the extent of a product or service's elasticity or inelasticity. Price elasticity is the extent to which a product's (or service's) price affects consumer demand.
What happens when a price increase increases the total revenue?
If a price increase also increases the total revenue for the period, then the product's demand is inelastic—the price increase has little impact on the quantity demanded. Here, the business can increase its products' prices to increase total revenue.
Why does total revenue have a limit?
The total revenue test has a limit because, despite a product's demand elasticity or inelasticity, demand for all products eventually drops off over time. Therefore, it means that your results may at best produce results that hold for a limited time.
What is ProfitWell metrics?
ProfitWell Metrics is a practical solution for businesses looking to find sound strategies for tracking their revenue. The software provides accurate, real-time subscription analytics and reporting on one platform.
Can you use total revenue to test for price elasticity of supply?
No, you cannot use the total revenue test to test for price elasticity of supply. The reason is that total revenue and price always move in one direction, regardless of the price elasticity of supply degree.
What Is a Total Revenue Test?
A total revenue test approximates the price elasticity of demand by measuring the change in total revenue from a change in the price of a product or service. Price elasticity refers to the extent to which the price of a product or service affects consumer demand for it; when the price affects demand, the price is said to be elastic, but when it does not or does not to a lesser degree, it is said to be inelastic. The total revenue test assumes all other factors that may influence revenue will remain constant during the testing period.
Does an increase in price increase total revenue?
In fact, an increase in price would be more likely to lead to an increase in total revenue , because an inelastic demand indicates that price is not one of the most important factors influencing consumer demand for the product.
What is total revenue?
Total revenue is the total amount of money a company brings in from selling its goods and services. It determines how well a company is bringing in money from its core operations based on demand and price.
How to calculate total revenue?
Total revenue is the full amount of total sales of goods and services. It is calculated by multiplying the total amount of goods and services sold by their prices.
How is marginal revenue calculated?
It is calculated by multiplying the total amount of goods and services sold by the price of the goods and services. Marginal revenue is directly related to total revenue because it measures the increase in total revenue from selling one additional unit of a good or service. Total revenue is important because, in the effort to grow profits, ...
How to find marginal revenue?
To calculate marginal revenue, divide the change in total revenue by the change in the quantity sold. Therefore, the marginal revenue is the slope of the total revenue curve. Use the total revenue to calculate marginal revenue.
What is revenue in accounting?
Revenue is the total amount of money a company brings in from selling its goods and services at a specific price. The starting point for any income statement is revenue that will eventually lead to net income after expenses are deducted. Total revenue is the full amount of total sales of goods and services. It is calculated by multiplying the total ...
How does total revenue change?
Total revenue changes with respect to price, and quantity can be visually demonstrated on a graph, in which a demand curve is drawn, that signals the price and quantity that would maximize total revenue.
What are the two forms of revenue?
Two of the most common forms of revenue are total revenue and marginal revenue.