What are the two types of groundwater?
Groundwater is found in two zones. The unsaturated zone, immediately below the land surface, contains water and air in the open spaces, or pores. The saturated zone, a zone in which all the pores and rock fractures are filled with water, underlies the unsaturated zone.
What are the three types of groundwater?
Infiltration Galleries. Infiltration galleries are also known as horizontal wells as they are horizontal or nearly horizontal tunnels that are constructed through the water-bearing strata along the banks of the river. ... Infiltration Wells. ... Springs. ... Wells.
What is a simple definition of groundwater?
Ground water is water underground in saturated zones beneath the land surface. Contrary to popular belief, ground water does not form underground "rivers." It fills the pores and fractures in underground materials such as sand, gravel, and other rock.
What is example of groundwater?
The definition of groundwater, or ground water, is water located beneath the surface of the earth. The water that your well draws from under the ground is an example of groundwater. Water that exists beneath the earth's surface in underground streams and aquifers.
What type of water is groundwater?
Groundwater is defined as water that is found beneath the surface of the Earth in conditions of 100 percent saturation (if it is less than 100 percent saturation, then the water is considered soil moisture). Ninety-eight percent of Earth's available fresh water is groundwater.
What is groundwater called?
groundwater, water that occurs below the surface of Earth, where it occupies all or part of the void spaces in soils or geologic strata. It is also called subsurface water to distinguish it from surface water, which is found in large bodies like the oceans or lakes or which flows overland in streams.
How do you identify ground water?
The ground penetrating radar (GPR) system is used for underground water detection. GPR is a promising technology to detect and identify aquifer water or nonmetallic mines. One of the most serious components for the performance of GPR is the antenna system.
What is the main source of groundwater?
Most groundwater originates as meteoric water from precipitation in the form of rain or snow. If it is not lost by evaporation, transpiration or to stream runoff, water from these sources may infiltrate into the ground.
What is the source of groundwater?
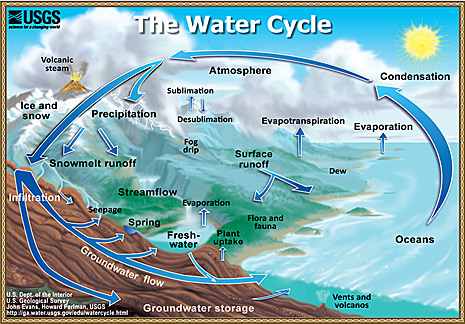
Groundwater sources are beneath the land surface and include springs and wells. As can be seen from the hydrologic cycle, when rain falls to the ground, some water flows along the land to streams or lakes, some water evaporates into the atmosphere, some is taken up by plants, and some seeps into the ground.
What is the difference between groundwater and underground water?
Water in the ground is stored in the spaces between rock particles (no, there are no underground rivers or lakes). Groundwater slowly moves underground, generally at a downward angle (because of gravity), and may eventually seep into streams, lakes, and oceans.
Is groundwater safe to drink?
Typically, groundwater is naturally clean and safe to drink. Because the soil on top acts as a filter, groundwater is usually free of micro-organisms that may cause disease. However, groundwater can become contaminated if the casings or caps for wells are not installed in the correct way.
How many types of groundwater are there?
There are two general types of aquifers: confined and unconfined. Confined aquifers have a layer of impenetrable rock or clay above them, while unconfined aquifers lie below a permeable layer of soil.
Are there different types of groundwater?
The most common groundwater source types are springs, hand-dug wells, or drilled boreholes. (But be careful, as drilled boreholes are often also called wells!). Many resources are available to support the choice of which groundwater source type to use in different environments or for different purposes.
What are different sources of groundwater?
Sources of groundwater are rainwater, lakes, ponds, springs and wells.
What are the four types of water?
Ground water. The ground absorbs water and retains it in soil and the pores of rocks. ... Flowing water. Water found in streams, rivers and lakes with underwater currents can be reasonably clean. ... Standing water. The term 'standing water' refers to any body of water that isn't flowing or in motion. ... Rainwater.
What is groundwater?
Groundwater is water that exists underground in saturated zones beneath the land surface. The upper surface of the saturated zone is called the water table. Contrary to popular belief, groundwater does not form underground rivers. It fills the pores and fractures in underground materials such as sand, gravel, and other rock, ...
Why is ground water important?
It provides half our drinking water and is essential to the vitality of agriculture and industry, as well as to the health of rivers, wetlands, and estuaries throughout the country .
How many people rely on groundwater for drinking water?
The quality of our Nation's waters: Water quality in principal aquifers of the United States, 1991-2010. About 130 million people in the United States rely on groundwater for drinking water, and the need for high-quality drinking-water supplies becomes more urgent as our population grows.
What is the purpose of the USGS?
USGS scientist tests groundwater samples for water quality. The USGS is near the midpoint of a complex undertaking to survey the quality of the nation’s largest drinking-water resource. From 2012 – 2023, the USGS is assessing groundwater throughout the country through extensive sampling.
How long does groundwater stay in an aquifer?
As a result, water could remain in an aquifer for hundreds or thousands of years. Groundwater is the source of about 40 percent of water used for public supplies and about 39 percent of water used for agriculture in the United States.
What is the USGS?
The USGS is near the midpoint of a complex undertaking to survey the quality of the nation’s largest drinking-water resource. From 2012 – 2023, the USGS is assessing groundwater throughout the country through extensive sampling. The latest results from five regional aquifers are now available.
How much groundwater was withdrawn in 2015?
In 2015, about 84,600 million gallons per day (Mgal/d) of groundwater were withdrawn in the United States for various uses including public supply, self-supplied domestic, industrial, mining, thermoelectric power, aquaculture, livestock, and irrigation.
How is groundwater recharged?
It is recharged by precipitation, snowmelt, or water seepage from other sources, including irrigation and leaks from water supply systems.
Why is groundwater extracted?
One important reason why groundwater is extracted through wells is to provide drinking water. In fact, groundwater provides drinking water for over 50 percent of the U.S. population, including almost 100 percent of the rural U.S. population. It is also used for domestic, industrial, and commercial purposes, though most groundwater is actually used ...
How do wells discharge groundwater?
To artificially discharge groundwater, a well must be drilled into an aquifer, and a well typically requires a pump to move water upward out of the aquifer. Artesian wells are drilled into aquifers that are bounded by an impenetrable rock layer from both above and below and water pressure from a recharging source located above the well outlet point will cause groundwater to be pushed upward through the artesian well, making the use of a pump unnecessary.
How long does groundwater stay in the aquifer?
The amount of time that groundwater remains in aquifers is called its residence time, which can vary widely, from a few days or weeks to 10 thousand years or more . The top of the saturated zone is called the water table, and sitting above the water table is the unsaturated zone, where the spaces in between rocks and sediments are filled ...
What are the threats to groundwater?
Another threat to groundwater is pollution by fertilizers, pesticides, and waste from septic tanks, all of which can seep down into aquifers from the soil surface. Groundwater is everywhere beneath the soil surface and can be ever-present in many places if allowed to recharge.
What is the water that has travelled down from the soil surface and collected in the spaces between sediments and the crack?
Groundwater. Water that has travelled down from the soil surface and collected in the spaces between sediments and the cracks within rock is called groundwater. Groundwater fills in all the empty spaces underground, in what is called the saturated zone, until it reaches an impenetrable layer of rock. Groundwater is contained and flows ...
Can you pump out too much groundwater?
We must take care, however, we do not pump out too much groundwater at once. This can cause wells to dry up if water inputs from recharging cannot keep up with our rate of groundwater removal. This has already happened in East Porterville, California, where an extended drought has led people to drill deeper wells, which has resulted in decreased groundwater levels and caused wells to further dry up. Another threat to groundwater is pollution by fertilizers, pesticides, and waste from septic tanks, all of which can seep down into aquifers from the soil surface.
Where is groundwater found?
Groundwater is the water found underground in the cracks and spaces in soil, sand and rock. It is stored in and moves slowly through geologic formations of soil, sand and rocks called aquifers.
How much do we depend on groundwater?
Groundwater supplies drinking water for 51% of the total U.S. population and 99% of the rural population.
What is groundwater recharge?
Groundwater is a source of recharge for lakes, rivers, and wetlands.
How does groundwater form?
Groundwater forms when precipitation, rain, snow, sleet, hail, or freezing rain soaks into the ground It settles into three main layers- the saturated zone, the water table, and the unsaturated zone. is recharged by precipitation.
What is the meaning of "aquifer"?
aquifer. underground layer of permeable rock from which groundwater can be removed. impermeable. not allowing a fluid to pass through. permeable. allowing a fluid to pass through. porosity. amount of air space between soil or rock particles. water table.
How far below the surface is the water table?
The water table can be anywhere from a foot to hundreds of feet below the surface. It is not always in the same place, and it may rise or fall, depending on the amount of precipitation and the amount that people pump out of the ground.
Is sand permeable?
Sand and gravel are highly permeable. Clays and soils with mixed particle sizes have low permeability.
What is groundwater?
Groundwater Facts. Groundwater is the water that fills cracks and other openings in beds of rocks and sand. Each drop of rain that soaks into the soils moves downward to the water table, which is the water level in the groundwater reservoir. Groundwater does not normally occur in underground streams, lakes, or veins.
Where is groundwater found?
Groundwater is the water that fills cracks and other openings in beds of rocks and sand. Each drop of rain that soaks into the soils moves downward to the water table, which is the water level in the groundwater reservoir. Groundwater does not normally occur in underground streams, lakes, or veins. Groundwater is found in soils ...
How much groundwater is used for irrigation?
16 In 1900, the U.S. used only 2.2 billion gallons of groundwater daily for irrigation from 17,000 wells.
How much groundwater is there in the world?
Some 2.78 million trillion gallons of groundwater, 30.1 percent of the world's freshwater, are estimated for the entire planet of Earth. 1 Of the total 349 billion gallons of freshwater the United States withdraws each day, groundwater is estimated to be 79.6 billion gallons, or 26 percent. 2
How much groundwater does California use?
California pumps 17.4 billion gallons per day of groundwater for all purposes, 2.4 times as much as the second-ranked state — Texas (7.2 bgd). 9. Groundwater is tapped through wells placed in water-bearing soils and rocks beneath the surface of the earth.
How long does it take for groundwater to refill?
Scientists estimate it could take 6,000 years to refill naturally if it were ever to be fully withdrawn. 17. Texas leads the nation in the number of irrigation wells with 81,511. 18.
Why is adequate time needed to replenish groundwater reservoirs?
Adequate time is needed to allow replenishment of underlying groundwater reservoirs (aquifers); also such areas must be properly managed in order to prevent water-soluble waste products stored in these areas from infiltrating and polluting the underground supply.