| Type | Name | Originated by | Distance | Description |
| 4 | ASBR Summary | ABR (Area Border Router) | Within the network | Contain information about the ASBR where ... |
| 5 | AS-external LSA | ASBR (Autonomous System Boundary Router) | Within the network | Contain information about routes importe ... |
| 6 | Group Membership LSA | It was defined for multicast extensions. ... | ||
| 7 | NSSA External LSA | ASBR (Autonomous System Boundary Router) | Intra-area | Identical to type-5 but are flooded with ... |
What is OSPF LSA?
OSPF LSA Types Explained. OSPF uses a LSDB (link state database) and fills this with LSAs (link state advertisement). Instead of using 1 LSA packet OSPF has many different types of LSAs and in this tutorial I’m going to show all of them to you. Let’s start with an overview:
What is the difference between Type 1 router LSA and OSPF?
Type 1 router LSAs always stay within the area. OSPF however works with multiple areas and you probably want full connectivity within all of the areas. R1 is flooding a router LSA within the area so R2 will store this in its LSDB. R3 and R4 also need to know about the networks in Area 2.
What is an LSA Type 5 packet?
LSA Type 5 ( ASBR External LSA) packets are generated by the ASBR to advertise external redistributed routes into the OSPF’s AS. A typical example of an LSA Type 5 would be an external prefix e.g 192.168.10.0/24 or default route (internet) as shown below: Figure 6. LSA Type 5 packets advertise the default route to all OSPF routers
Is R1 Type 5 LSA allowed in NSSA?
NSSA areas do not allow type 5 external LSAs. In my picture R1 is still our ASBR redistributing information from RIP into OSPF. Since type 5 is not allowed we have to think of something else. That’s why we have a type 7 external LSA that carries the exact same information but is not blocked within the NSSA area.
What is the difference between OSPF LSA type 4 and 5?
Is there really a difference between Type 4 & 5 LSA? LSA type 4 is a summary LSA ( ASBR location) and a type 5 LSA is a external LSA which is sent from an ASBR into and ospf area depending on what type of area you setup.
What are OSPF LSA types?
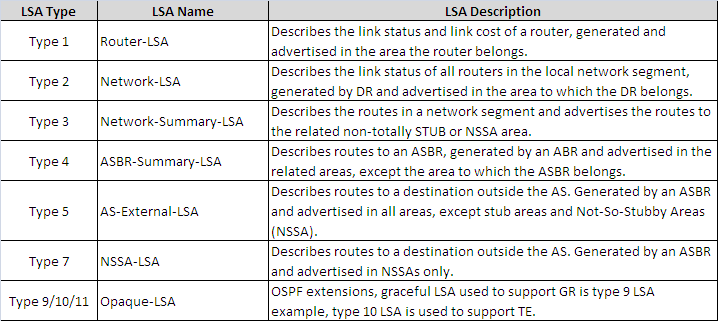
6 Types of OSPF LSAType1 is a Router LSA.Type2 is a Network LSA.Type3 is a Network summary LSA.Type4 is the ASBR summary.Type5 is an external summary.Type7 is therefore written to the OSPF standard.Learn More:
What are five types of LSA packets in OSPF?
OSPF LSA Types ExplainedLSA Type 1: Router LSA.LSA Type 2: Network LSA.LSA Type 3: Summary LSA.LSA Type 4: Summary ASBR LSA.LSA Type 5: Autonomous system external LSA.LSA Type 6: Multicast OSPF LSA.LSA Type 7: Not-so-stubby area LSA.LSA Type 8: External attribute LSA for BGP.
What is Type 6 LSA OSPF?
Type 6 LSAs are Group-Membership-LSAs used to identify multicast group membership in the Multicast Open Shortest Path First (MOSPF) protocol. Type 6 LSAs are not supported on the switch.
What is Type 4 LSA OSPF?
OSPF Type 4 ASBR Summary LSA A type 4 LSA identifies the ASBR and provides a route to the ASBR. The link-state ID is set to the ASBR router ID. All traffic that is destined to an external autonomous system requires routing table knowledge of the ASBR that originated the external routes.
Why is type 4 LSA required?
LSA 4 is generated by the ABR. Link ID in that is the router ID of ASBR and Adv. Router is the ASBR itself. LSA 4 is required to tell the routers in other areas how to reach the ASBR to get to external network eventually.
What is Type 3 LSA OSPF?
The Summary (Type 3) LSA is used for advertising prefixes learned from the Type 1 and Type 2 LSAs into a different area. The Area Border Router (ABR) is the OSPF device that separates areas and it is this device that advertises the Type 3 LSA. Examine the OSPF topology shown in Figure 1 below.
What is ABR and ASBR in OSPF?
Area border router (ABR) A router that connects one or more areas to the OSPF backbone. Autonomous system border router (ASBR) A router that is connected to one or more logical entities (AS), usually through an exterior routing protocol such as BGP.
What are the six OSPF route types?
This is the prefered path list that OSPF uses:Intra-Area (O)Inter-Area (O IA)External Type 1 (E1)NSSA Type 1 (N1)External Type 2 (E2)NSSA Type 2 (N2)
What is LSA 7 and how it can be used?
LSA Type 7 (NSSA External LSA) packets are used for some special area types that do not allow external distributed routes to go through and thus block LSA Type 5 packets from flooding through them, LSA Type 7 packets act as a mask for LSA Type 5 packets to allow them to move through these special areas and reach the ...
What is E1 and E2 in OSPF?
E1 includes – the internal cost to ASBR added to the external cost, E2 does not include – internal cost. it is same as external cost. Below Diagram will help in understanding how OSPF E1 and E2 external routes are calculated external routes within the OSPF domain – Related – OSPF Cost Calculation.
What is DR and BDR in OSPF?
In an OSPF broadcast network, OSPF elects one router to serve as the designated router (DR) and another router on the segment to act as the backup designated router (BDR). This minimizes the amount of repetitive information that is forwarded on the network. OSPF forwards all messages to the designated router.
LSA Types - Quick Overview
Before we begin, let’s take a quick look at the different type of OSPF LSA packets we’ll cover:
LSA Type 1 – OSPF Router LSA
LSA Type 1 ( Router LSA) packets are sent between routers within the same area of origin and do not leave the area. An OSPF router uses LSA Type 1 packets to describe its own interfaces but also carries information about its neighbors to adjacent routers in the same area.
LSA Type 2 – OSPF Network LSA
LSA Type 2 ( Network LSA) packets are generated by the Designated Router ( DR) to describe all routers connected to its segment directly. LSA Type 2 packets are flooded between neighbors in the same area of origin and remain within that area.
LSA Type 3 – OSPF Summary LSA
LSA Type 3 ( Summary LSA) packets are generated by Area Border Routers ( ABR) to summarize its directly connected area, and advertise inter-area router information to other areas the ABR is connected to, with the use of a summary prefix (e.g 192.168.0.0/22).
LSA Type 4 – OSPF ASBR Summary LSA
LSA Type 4 ( ASBR Summary LSA) packets are the LSAs that advertise the presence of an Autonomous System Border Router ( ASBR) to other areas.
LSA Type 5 – OSPF ASBR External LSA
LSA Type 5 ( ASBR External LSA) packets are generated by the ASBR to advertise external redistributed routes into the OSPF’s AS. A typical example of an LSA Type 5 would be an external prefix e.g 192.168.10.0/24 or default route (internet) as shown below:
LSA Type 6 – OSPF Group Membership LSA
LSA Type 6 ( Group Membership LSA) packets were designed for Multicast OSPF (MOSPF), a protocol that supports multicast routing through OSPF. MOSPF is not supported by Cisco and is not widely used and is expected to be retired soon.
What is OSPF LSA?
OSPF creates a type 5 LSA for a subnet that is injected into OSPF from an external source. To inject the route, the autonomous System Border Router (ASBR), which is by definition a router that connects to a non-OSPF routing domain, uses the redistribute command.
What is type 5 LSA?
Type 5 LSAs come in 2 types, or metric types: External type 1 and type 2 (default). I'll touch on the simpler type 2 today. LSA type 5, metric type 2 (often called external 2 or external type 2 to avoid confusion with the LSA types) is: Created by the ASBR. LSA contains the metric as dictated by the ASBR.
Does R2 see LSAs?
R2 sees both LSAs, then floods both LSAs into area 1, so R3 sees both type 5 LSAs. Given the comments before the figure, R2's route for 11.0.0.0/8 will use R1 as the next-hop, with a metric of 10 - the metric of the Type 5 LSA flooded by R1.
Does LSA change metric?
LSA contains the metric as dictated by the ASBR. Flooded by ABR's to other normal (non-stubby) OSPF areas. The flooding process does not change the metric in the type 5 LSA. Routers choose "best" route based on the metric in the ASBR; the OSPF cost calculation ignores the costs inside the OSPF domain, instead using only the cost listed in ...
What is a LSA type 2?
Network LSA (Type 2) is advertised only from DR and contains all the routers that is its adjacent on the segment. Network LSA (Type 2) also can not pass throught the ABR and can not go to the other areas.
How many different LSA types are there?
There are eleven different LSA types and each of them has a special purpose. Some of the LSA types are the main LSA types that are used in OSPF operations often. Let’s see all the LSA types: Now, let’s talk about these OSPF LSA types detailly.
What is LSA router?
Router LSA (Type 1) is used for only Internal Routers in a Standard Area. Router LSA (Type 1) list router neighbors and their costs. This LSA type can not pass throught the ABR (Area Border Router) and can not go to the other areas.
LSA Sequences
OSPF uses the sequence number to overcome problems caused by delays in LSA propagation in a network.
LSA Age and Flooding
Every OSPF LSA includes an age that is entered into the local LSDB and that will increment by 1 every second.
How metric is calculated?
The advertising router for Type 3 LSAs is the last ABR that advertises the prefix. The metric in the Type 3 LSA uses the following logic:
Summary LSA Example
The Link State ID field is the network 9.9.9.0, and the network mask is /24.
Metric's logic to reach ASBR
When the Type 5 LSA crosses the first ABR, the ABR creates a Type 4 LSA with a metric set to the total path metric to the ASBR.
NSSA LSA Example
The P bit is used to tell the NSSA ABR whether to translate Type 7 LSAs into Type 5 LSAs. No Type 7/5 translation means P bit = 0 Type 7/5 translation means P bit = 1