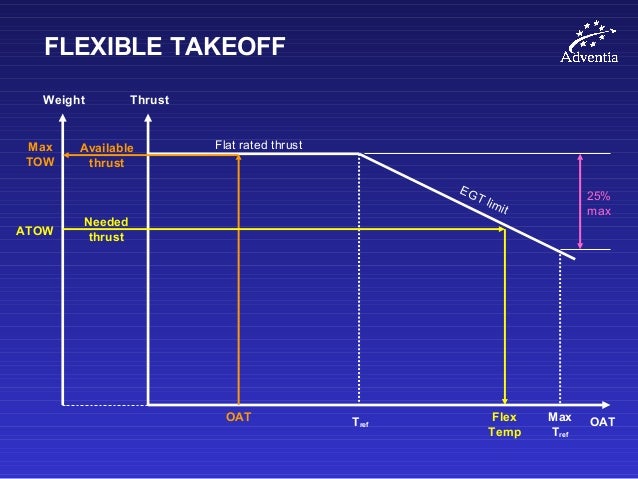
What is a V1 takeoff speed in aviation?
V1 means the maximum takeoff speed at which the pilot must take the first action (e.g., apply brakes, reduce thrust, deploy speed brakes) to stop the aircraft at an accelerate-stop distance.
What is the difference between V1 and V2 in aviation?
V1 also means the minimum speed at takeoff, following the vital engine’s failure at VEF, at which the pilot can continue to take off and reach the necessary height above the takeoff surface within the takeoff distance. It is also called decision speed. V2 is the safe speed of takeoff.
What do'V1'and'V2'mean during takeoff?
OK, just trying to clarify, V1 means the aircraft is committed to take off. "The point of no return". V2 is the minimum speed needed with an engine failure to avoid any obstacles that might interfere with take off?" Originally Answered: What do "V1" and "V2" mean during takeoff? During takeoff roll pilots call out 3 checks.
What does V2 mean during take off?
What does v2 mean during take off? Take off safety speed which comes just after rotation: the speed at which the aircraft will comply with normal flying characteristics in the event of one engine failing. Why do the pilots call out "100 knots … Checked " during a takeoff roll?
What does V1 mean in cockpit?
A: V1 is the speed by which time the decision to continue flight if an engine fails has been made. It can be said that V1 is the "commit to fly" speed. V2 is the speed at which the airplane will climb in the event of an engine failure. It is known as the takeoff safety speed.
Why do pilots say V1 rotate?
Long story short, pilots say rotate as a verbal queue that the aircraft has reached its predetermined Vr and hence appropriate inputs can be applied to safely pitch the aircraft in a nose-up attitude to gain lift.
What is V1 and Vr in aviation?
0:287:18TAKE-OFF Speeds V1, Vr, V2! Explained by "CAPTAIN" JoeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipOk first to know this again is a basic introduction about takeoff speeds the speeds we're talkingMoreOk first to know this again is a basic introduction about takeoff speeds the speeds we're talking about today will always follow in that order v1 VR or rotate and v2. And these speeds apply no matter
What is V2 on takeoff?
V2: Takeoff Safety Speed. V2 is the minimum speed that needs to be maintained up to acceleration altitude, in the event of an engine failure after V1. Flight at V2 ensures that the minimum required climb gradient is achieved, and that the aircraft is controllable.
Can a pilot abort takeoff after V1?
Above V1, the takeoff must be continued unless there is reason to believe that the aircraft will not fly. An engine failure identified before V1 should always result in a rejected takeoff. If the decision is made to reject, the aircraft can be brought to a stop within the Accelerate Stop Distance Available (ASDA).
Can you abort takeoff at V1?
V1 - decision speed V1 is arguably the most important speed when taking off. It is known as the decision speed, as beyond it a takeoff should not be aborted if anything goes wrong.
What do pilots say when taking off V1?
Why Do Pilots Say Rotate on Take Off? (V1, Vr, & V2)Pilots say rotate because it is a verbal queue that an airplane has reached its predetermined rotation speed (frequently abbreviated to Vr). ... Not all airlines have in their standard operating procedures the requirement to call out V2.More items...
Is V1 greater than Vr?
Rotation speed (Vr) cannot be less than V1. If it is greater than V1 and it is found that, at Vr, rotation cannot be achieved, a subsequent rejected take off may not be possible within the remaining runway length and is likely to result in a Runway Excursion.
What is the V1 speed for a 747?
V1, approximately 159 KIAS, is decision speed. Above V1, you probably won't be able to stop the airplane on the runway after an engine failure or other problem. At Vr, approximately 177 KIAS, smoothly pull the stick (or yoke) back to raise the nose to 10 degrees above the horizon.
What does V1 VR and V2 mean?
For every aircraft type, V1, VR and V2 are computed by Airbus on the basis of design speeds and evidence collected during the certification testing of the airplane. (fig.1) V1: Decision speed. VR: Rotation speed. V2: Take-off safety speed.
How fast is V1 speed?
What is the normal V1 speed for a commercial jet? For commercial aircraft such as the B737, A320 and even the large ones like the Boeing 747 Jumbo Jet or Airbus 380, a typical range for the V1 speed is between 120 – 140 knots.
What is a V1 cut?
0:239:38V1 Cut explained! - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSee if the engine fails right at v1 remember v1 is the decision speed the go no-go decision you'reMoreSee if the engine fails right at v1 remember v1 is the decision speed the go no-go decision you're still on the runway. And the benefit of that is you still have visual reference to the centreline.
What does squawk 7777 mean?
military interceptionSome squawk codes are reserved, such as 7700 (emergency), 7600 (communication failure), 7500 (hijacking), 1202 (glider), 1200 (VFR), etc. One of these, 7777, is apparently used for "military interception." What does this mean in the United States?
Could a Spitfire keep up with a V1?
Spitfires reached speeds of about 369mph which meant that pilots had to target a V1 by diving from higher altitudes, about 5000ft, to build up enough speed to allow them to close in on their target at ranges as close as several hundred yards.
Why do pilots say Niner?
Aviators often speak “pilot English” to avoid miscommunications over radio transmission. “Tree” for instance, means three, “fife” is the number five and “niner” means nine, says Tom Zecha, a manager at AOPA. The variations stemmed from a desire to avoid confusion between similar-sounding numbers, he says.
What is V1 speed in aviation?
What is the normal V1 speed for a commercial jet? For commercial aircraft such as the B737, A320 and even the large ones like the Boeing 747 Jumbo Jet or Airbus 380, a typical range for the V1 speed is between 120 – 140 knots.
What does V NO mean on an aircraft?
V NO: Maximum Structural Cruising Speed.
Where is the V FE on a flap?
Maximum Flap Extended Speed is specific to each flap setting. On an airspeed indicator, V FE is sometimes marked at the top of the white arc.
What is the V speed?
To fully understand the capacities, safe performance operation, and limitations of any aircraft, it’s important to have a good grasp of “velocity speeds”, known as V-speeds. For the most part, V-speeds correspond to green, yellow, red, and white markings on an aircraft’s speed indicator. These assist the pilot in ensuring safe operation by ...
Why do engineers take V A into consideration when designing airplanes intended for aerobatics?
Weight is taken into consideration when V A is calculated: As the airplane burns fuel and becomes lighter, its V A drops as well.
What does V1 mean in airplanes?
Photo source: lakako.com. V1 is defined as the speed beyond which the take-off should no longer be aborted. Meaning that in case you experience any trouble with your plane before reaching V1 you would immediately abort your take-off and would apply all the necessary means to bring the aircraft to a halt.
What happens if a pilot fails to take off after V1?
If pilots experience any serious aircraft malfunction after V1, otherwise they have to continue the take-off, a take-off board will lead to a runway overrun and could severely damage the plane. Vr or Rotate is defined as the speed at which the pilot begins to apply control inputs to make the aircraft nose to pitch up, ...
What is V2 speed?
Photo source: airlines.net. V2 is the speed at which the aircraft may safely be climbed with one engine inoperative. This speed is nicknamed a “take-off safety speed”; it is the speed an aircraft with one engine inoperative must be able to attain in order to leave the runway and get 35 feet off the ground at the end of the runway, ...
What is V1 in aviation?
V1 also means the minimum speed at takeoff, following the vital engine’s failure at VEF, at which the pilot can continue to take off and reach the necessary height above the takeoff surface within the takeoff distance. It is also called decision speed.
What is V2 in airplanes?
V2 is the safe speed of takeoff. It is the minimum speed that must be sustained up to the acceleration altitude in the event of engine failure after V1. Flight at V2 ensures that the minimum climb gradient needed is achieved and that the aircraft is controllable.
What is V speed?
In aviation, V-speeds are standard terms used to describe airspeeds necessary or useful for all aircraft operations. These speeds are derived from aircraft designers’ and manufacturers’ data during flight tests for aircraft type-certification tests.
What is the primary safety element for takeoff?
Takeoff speeds are the primary safety element for takeoff and allow pilot situations sight and decision-making in a very complicated situation. The use of incorrect takeoff speeds can lead to tail strikes, rejected high-speed takeoffs, or degraded initial climbs.
What do you know about take off speed?
What do you know about take-off speed? V1, Vr, and V2. Takeoff is the flight phase in which an aircraft leaves the ground and gets airborne. This usually includes beginning the transition from the ground on a runway for horizontal takeoffs. Some VTOL aircraft do the vertical take-off and do not require horizontal takeoff.
What happens when an aircraft is on the runway?
When the aircraft is on the runway, the aircraft engine produces a significant amount of thrust. This drives the aircraft when the aircraft reaches the particular speed of the aircraft takeoff. The takeoff speed of aircraft depends open the types of aircraft.
What happens when an airplane fails at V EF?
The most critical engine is failed at V EF and the airplane continues to accelerate on one engine while the pilot recognizes that the engine has failed and makes the decision to abort. Once the test pilot initiates the abort, that speed is noted and becomes V 1.
What percentage of RTO accidents are avoidable?
Unfortunately, many rejected takeoff (RTO) accidents have been caused by such a set of circumstances. One industry study found that 80 percent of RTO accidents were avoidable, and the accident airplanes would have been able to safely continue the takeoff with the problem in effect.
What happens if an airplane reaches a peak speed of 10 knots?
If the airplane reaches a peak speed of only 10 knots beyond V 1, the brakes must now dissipate 20 percent more energy than had the abort been initiated at V 1.
How much does an oxygen hood cost on an Essex?
You pull on the hood, yank on an oxygen cord, and the oxygen flow begins. This hood, also fitted with a neck seal, sells for $850, and must also be replaced at 10-year intervals.
What is a pilot protective hood?
The pilot protective hood is meant for use with the cockpit’s emergency oxygen masks. It is essentially a Teflon-treated transparent bag that can be slid into place in approximately two seconds, says Essex PB&R (Protective Breathing and Rescue—a St. Louis firm with a major presence in this market). A silicon neck seal keeps the smoke out. Each pilot protective hood sells for $300, and is good for 10 years. After that time, the unit must be replaced.
What happens if runway is less than runway required?
Above this speed and before V 1, if the runway available is less than the runway required plus a defined safety margin (often 50 percent), the takeoff will only be aborted for an engine failure, engine fire, or the perception that the aircraft is unable to fly.
Is smoke hood good for jets?
Whether you choose an Essex model, an Aeromedix, or a Parat-C, smoke hoods are good investments. The FAA may not mandate them for use in private or corporate turboprops or jets, but if all hell breaks loose you’ll be glad to have them aboard. —TAH.
What is V1 in airplanes?
V1 is the speed at which the pilot decides whether to go ahead (if everything is okay) or to reduce thrust or abort takeoff.
What is the difference between V1 and V2?
while V2 is the speed at which the plane can still take off, even of one engine. clear?
What is the reference speed used during landing?
The one reference speed that is always used during landing is Vref (or Vapp according to some manufacturers). This is the Reference Landing Speed and it's defined by the aircraft manufacturer and listed in the AOM or FCOM. Normally you would add corrections to this speed to get the Final Approach Speed (which doesn't have a V-speed identifier). These speeds are not used during callout, except when the Pilot Flying asks the Pilot Monitoring to help him set this speed as a reference during landing.
What is the V2min?
V2min is the take off safety speed with critical engine inoperative. This speed should be greater than 1.13 Vsr (Stall reference speed) for 2 and 3 engined turboprops and 1.08 Vsr for 4 engined turboprops and all turbojets. The difference comes because turboprops rely heavily on propellers to create lift over the wings. Losing an engine in 2 or 3 engined turboprop can result in loss of considerable lift. While in four engined airplanes this effect is lower and turbojets have other lift augmentation devices fitted to the wings. This speed is also not to be lower than 1.1 Vmc.
How fast can you pull flaps 1?
For example: Don't select flaps 1 any faster than 240 knots, but make sure you have them out prior to slowing below 180 knots. On retraction, as long as you're accelerating you can often raise them a set number of knots prior to the lower number, but still want to have them up prior to reaching the higher number.
How do you determine the maneuver speed for landing?
For landing, we use the maneuver speeds based on flap configuration (and weight). Each flap setting has a speed on the high end defined by how much air pressure the flaps can take and then a low end, where you need to have selected them.
What is V2 in aviation?
V2 is actually the "takeoff safety speed ;" it's the speed an aircraft with one engine inoperative must be able to attain in order to leave the runway and be 35 feet off the ground at the end of the runway, and then maintain a 200 ft/min climb thereafter. When the FAA designs obstacle avoidance procedures, they assume your aircraft is at least capable of that -- if you can do at least that, you get guaranteed obstacle collision protection. So, V2 assumes that you lose an engine at exactly the wrong time, and tells you how fast you need to fly in order to continue being protected from obstacle collision. Once the aircraft in distress accelerates beyond V2 to the flap retraction speed, flaps are retracted and the pilots deal with the engine failure.
Why is V1 lower on a runway?
Runway altitude, length, and surface condition: If a runway has a displaced threshold and is shorter than normal, or is wet, V1 (the speed beyond which takeoff should not be aborted )will be lower because it will take longer to slow down on a wet runway and there is less runway available for slowing down. Additionally, this has been discussed before in our article on why runways aren’t flat
What Is Rotation Speed? Is It the Only Significant Part of Takeoff?
There are three critical speeds as an aircraft accelerates during take-off. In sequential order, they are:
What happens if you rotate before reaching Vr?
Rotation before reaching Vr can result in a tailstrike, meaning that the tail of the airplane hits the ground and gets damaged.
What is the Vr in airplanes?
Vr (rotation speed), which is defined as the speed at which the pilot begins to apply control inputs to cause the aircraft nose to pitch up, after which it will leave the ground. The act of rotating the airplane and pulling the nose up is to achieve lift-off earlier, by increasing the angle of attack of the wing through the air.
Do all airlines have to call out V2?
Not all airlines have in their standard operating procedures the requirement to call out V2. It must also be said this only applies to multi-engine airplanes!
Is it necessary to use 100% thrust?
The heavier an aircraft, the higher Vr. Thrust and flap settings: It is not always necessary, nor possible, to use 100% of the available thrust when departing, and it is avoided where possible to limit engine wear.
What are the effects of V1?
Airport elevation, the existence of any slope on the runway, and the presence of precipitation or ice also play a role. Temperature and wind speed are also factors, as are configuration of the airplane. The bigger the airplane, the higher V 1 will be, since the airspeed depends on weight.
What is V2 aviation?
V2: Takeoff Safety Speed. V2 is the minimum speed that needs to be maintained up to acceleration altitude, in the event of an engine failure after V1. Flight at V2 ensures that the minimum required climb gradient is achieved, and that the aircraft is controllable.
Why do pilots say V1 rotate?
Pilots say rotate because it is a verbal queue that an airplane has reached its predetermined rotation speed (frequently abbreviated to Vr). This is the speed at which control inputs can be applied to lift the nose off the runway and make the airplane fly away.
What is the V1 speed for a 747?
A fully loaded Boeing 747 ‘Jumbo Jet’ on a normal long haul flight would take off at a speed of around 160 knots which is 184 mph. The calculated take-off speeds vary depending on environmental conditions, runway length and weight.
What speed is VMC?
Familiar to pilots of multi-engine aircraft, Vmc is the speed below which aircraft control cannot be maintained if the critical engine fails under a specific set of circumstances (see 14 CFR part 23). It is marked as a red radial line on most airspeed indicators.
Why do pilots say heavy?
When a pilot uses the phrase “ heavy,” he is reminding ATC that his aircraft is large and requires more separation between it and the aircraft following.