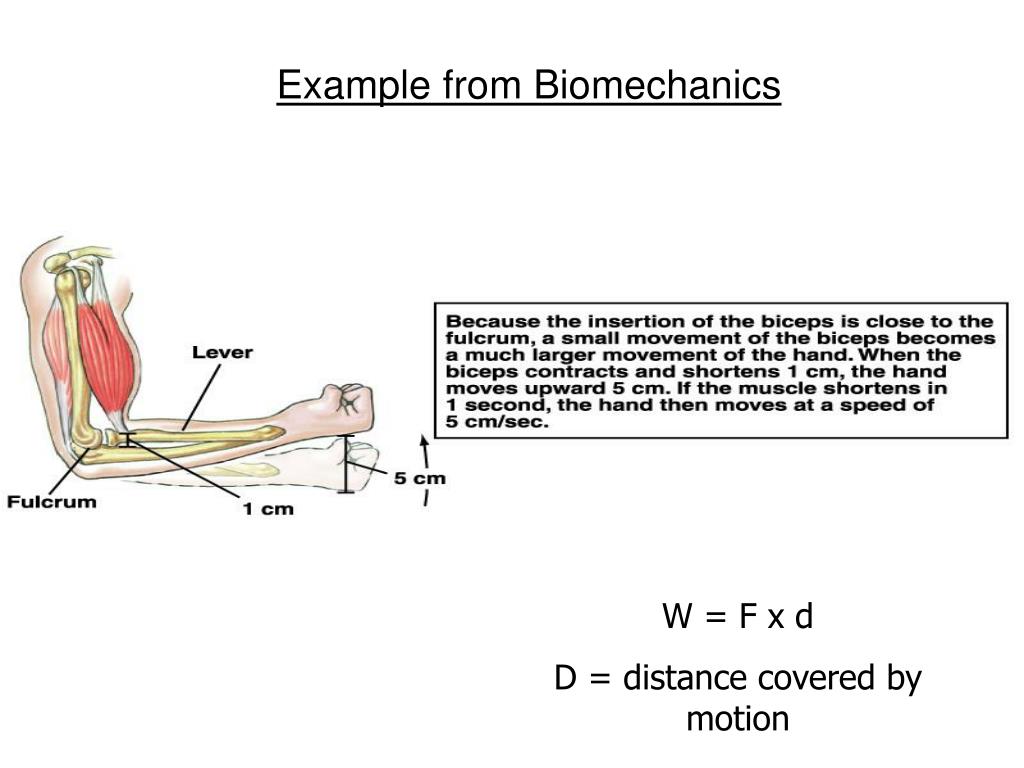
Introduction In everyday life, the terms speed and velocity are often used interchangeably but in biomechanical terms, there is a difference. Velocity is defined as the rate of change of position of an object with respect to time.
What is the relationship between velocity and speed?
Velocity is the speed of a body in a specific direction and is the rate of change of displacement. Unlike speed, velocity is a vector quantity which means it has a direction as well as a magnitude. So if the direction of the moving body changes then the velocity changes, even though the speed might stay the same.
How is angular velocity used in biomechanics?
Angular velocity is used in two ways in biomechanics. We are either interests in the average angular velocityor the instantaneous angular velocity. Average angular velocity tells us how long it takes for something to rotate through a certain angular displacement.
What is a change in the velocity of a body?
A change in the velocity of a body can depict a variance in its speed, movement direction or indeed both. The SI unit is the modern metric system of measurement. All systems of weights and measures, metric and non-metric are linked through a network of international agreements supporting the SI units.
How do you find the average speed and average velocity?
Average speed of a body is obtained by dividing the distance by the time and average velocity is obtained by dividing the displacement by the time e.g. a swimmer in a 50m race in a 25m length pool who completes the race in 71 seconds - distance is 50m and displacement is 0m (swimmer is back where they started)...
What is the main definition of velocity?
Velocity defines the direction of the movement of the body or the object. Speed is primarily a scalar quantity. Velocity is essentially a vector quantity. It is the rate of change of distance. It is the rate of change of displacement.
What is speed and velocity in biomechanics?
Velocity is the displacement of an object over time and includes direction. So an athlete might have a velocity of 17 Km/h in a southeast direction. Velocity is different to speed, which does not have a direction attached to it, and is the distance covered by the athlete in a specified time.
What is the velocity in simple words?
Velocity is quickness of motion or action. A synonym is celerity; a simpler word is speed. In physics, velocity specifically refers to the measurement of the rate and direction of change in position of an object.
What is acceleration in biomechanics?
Acceleration & Biomechanics September 15, 2022. Acceleration is the rate at which a body changes its velocity and, similarly to velocity, it is a vector quantity which means it has a direction as well as a magnitude. We measure it in m/s/s or metres per second per second (metres per second squared – ms-2).
What is difference between speed and velocity?
Speed is the time rate at which an object is moving along a path, while velocity is the rate and direction of an object's movement. Put another way, speed is a scalar value, while velocity is a vector.
What is the difference between speed and velocity and acceleration?
The speed of an object is the rate of change of its position, and the object's velocity includes its speed as well as its direction of motion. The rate of change of the object's velocity gives the acceleration.
What is velocity explain with example?
Velocity is defined as the vector measure of level and direction of movement. Simply put, velocity is the speed at which an object moves in one direction. The speed of the car heading north on the main highway and the speed of the rocket exploding in space can both be measured using speed.
What are the 3 types of velocity?
The Types of VelocityConstant Velocity. An object with a constant velocity does not change in speed or direction. ... Changing Velocity. Objects with changing velocity exhibit a change in speed or direction over a period of time. ... Mathematics of Acceleration. ... Instant Velocity. ... Terminal Velocity.
What are three examples of velocity?
Loved by our communityExamples:1) Revolution of Earth around the sun.2) Revolution of moon around the earth.3) Velocity of a satellite around the earth.4) Velocity of a car while driving.5) Velocity of a ball when hitted with a bat.6). Velocity of water coming from a tap.7). Velocity of the train .More items...•
What is velocity of release in sport?
Velocity at release. The speed of projection determines the length of trajectory (range). A higher velocity at release will increase the maximum distance and flight time of the projectile.
What is deceleration in biomechanics?
Deceleration always refers to acceleration in the direction opposite to the direction of the velocity. Deceleration always reduces speed. Negative acceleration, however, is acceleration in the negative direction in the chosen coordinate system.
What is momentum in biomechanics?
In biomechanics momentum p is the product of mass of a human body m (or mass of any object) and its velocity v: p = mv 33. Momentum allows us to use a single value to express the measure of both motion and inertia of the given body. In sport and physical exercise most bodies have constant mass.
Why is speed important in biomechanics?
This brings into focus the importance of the direction of the application of force as well as its quantity. Force needs to be applied in a direction opposite to the intended direction of motion. Speed, therefore, is maximized when both the quantity and direction of the force are optimal.
What is speed in terms of sport?
Speed. Definition: The ability to move all or part of the body as quickly as possible. Examples: Speed is important in sprinting, speed skating, sprint cycling and sports such as tennis when a player has to move forward quickly from the baseline to reach a drop shot close to the net.
How important is the concept of speed velocity and acceleration in sports?
In terms of running, anytime the body starts, speeds up, or changes direction, it is accelerating. Given the number of direction changes in most sports, together with the number of times the rate of velocity needs to change, then clearly acceleration plays a crucial role in speed performance in sport.
What is the importance of speed in sport?
Athletes who can move faster than their opponents have an advantage. For example, a faster athlete may be able to get to a ball more quickly than a competitor or may even outrun a pursuer. For this reason, athletes in most sports value speed highly.
What are the variables used to determine the velocity of a walk?
Three variables –walking, speed walking , and jogging – were used to test if the Intended Velocity formula truly represented the velocity of an individual’s walk, or more closely represented an individual’s speed walk. I hypothesized that the formula would better represent a speed walk because the Velocity Intended formula was created from a pendulum formula meaning that the straighter the leg the more accurate the formula. Jogging was included as a control group for the experiment. When humans jog, they bend their knees allowing them greater mobility thus ignoring the straight leg motion the Velocity Intended formula was emphasizing.
Why is the velocity intended formula revised?
With the data collected from these three tests I now know the Velocity Intended formula would have to be revised in order for prosthetic leg manufactures to better fit prosthetic legs to humans that have above-the-knee amputations. A revised formula could give amputees as easier transition to their new leg.
How much standard deviation is needed to determine if there is a correlation between the velocity measured and the velocity intended?
In order to determine if there was a correlation between the Velocity Measured (field data) and the Velocity Intended data, I took one standard deviation, 68.2%, of the collected data to determine if there was any overlap between the Velocity Intended formula and any of the Velocity Measured values.
Does speed walking fit velocity?
An analysis using one standard deviation showed an overlap between the speed walking and the Velocity Intended data values. In addition, it was noted that the R 2 values were slightly higher for the speed walk than for the walking and jogging values. The analysis proved my hypothesis that speed walking velocities best fit the Velocity Intended formula velocities.
What is instantaneous velocity?
Instantaneous velocity v is the velocity at a specific instant or the average velocity for an infinitesimal interval.
How does time relate to motion?
How does time relate to motion? We are usually interested in elapsed time for a particular motion, such as how long it takes an airplane passenger to get from his seat to the back of the plane. To find elapsed time, we note the time at the beginning and end of the motion and subtract the two. For example, a lecture may start at 11:00 A.M. and end at 11:50 A.M., so that the elapsed time would be 50 min. Elapsed time Δt is the difference between the ending time and beginning time,
What does the minus sign mean in a plane?
The minus sign indicates the average velocity is also toward the rear of the plane.
How to find the elapsed time?
Time is measured in terms of change, and its SI unit is the second (s). Elapsed time for an event is Δt = tf – ti where tf is the final time and ti is the initial time. The initial time is often taken to be zero, as if measured with a stopwatch; the elapsed time is then just t.
What is Figure 2?
Figure 2. A more detailed record of an airplane passenger heading toward the back of the plane, showing smaller segments of his trip. Note: this figure uses the symbols x instead of px to denote position. Both conventions can be used.
What is the definition of time?
In biomechanics, the definition of time is simple— time is change, or the interval over which change occurs. It is impossible to know that time has passed unless something changes.
How to visualize motion?
Another way of visualizing the motion of an object is to use a graph. A plot of position or of velocity as a function of time can be very useful.
What is velocity in sports?
Velocity: velocity is the rate of change of position of the athlete. It’s just like the term speed, but with a direction associated with it. It is usually measured in meters per. second, but can also be expressed in miles per hour or kilometers per hour. Vector: vectors contain both magnitudes and directions.
What are active and passive forces in biomechanics?
Active: in biomechanics, active muscle forces are generated by muscle contractions, namely the sarcomeres. Passive: in biomechanics, passive muscle forces are generated by the elastic properties of materials such as those found in muscles (collagen, titin, etc.), ligaments, bones, tendons, and fascia.
What is muscle force?
Muscle Force: when muscles contract or are stretched, they create muscle force. This muscle force pulls on bones which creates joint torque. In general, force, including muscle force, is measured in Newtons.
What is the force that is projected forward during sprinting?
However, in sprinting, you have vertical forces as well as horizontal forces. When the foot strikes the ground during maximum speed sprinting, at first the force is projected forward which is called braking forces, and once the COM passes over the foot, the force is projected rearward which is called propulsive forces.
How to plot force velocity curve?
Force-Velocity Curve: you can plot the force-velocity curve on a graph by plotng force on the y-axis and velocity on the x-axis. In strength & conditioning, the goal is to shift the curve upward and to the right so that the athlete can exhibit more force and power at every possible load.
What is force in math?
Force: force equals mass times acceleration and is a vector quantity, meaning that it’s displayed in a particular direction. Force is usually measured in Newtons.
How are resultant vectors formed?
Resultant: in biomechanics, often resultant vectors are calculated, in which case a single vector is formed by combining (or summing) two or more other vectors. For example, combining horizontal and vertical forces into a resultant force.
What is the angular velocity in biomechanics?from lambdageeks.com
Angular velocity can be divided into two parts in biomechanics: angular velocity or instantaneous angular velocity.
What is the amount of change of angular displacement of a particle at a given period of time called?from byjus.com
The amount of change of angular displacement of the particle at a given period of time is called angular velocity. The track of the angular velocity vector is vertical to the plane of rotation, in a direction which is usually indicated by the right-hand rule. It is articulated as.
Why can't old people move their necks?from lambdageeks.com
3. Movement in the neck: the neck joints enable us to move our hands both laterally and vertically. This movement also takes place due to the angular motion of the muscles present in our neck. In Old age these muscles get weekend and I am not able to cover a large range of angles for rotation. For this reason, old people are not able to move their necks freely. Certain organisms like parrots and rabbits are able to rotate their head up to 180 degrees i.e. take and rotate their head backward.
What is angular velocity?from byjus.com
The amount of change of angular displacement of the particle at a given period of time is called angular velocity. The track of the angular velocity vector is vertical to the plane of rotation, in a direction which is usually indicated by the right-hand rule.
What is the role of the knee joint in animal movement?from lambdageeks.com
For example, when animals walk, their knee joint helps to undergo a rotatory motion in the lower limbs enabling the person or the animal to move . The joint here acts as an axis of rotation for the angular motion of the lower limb bones.
What is the role of the wings in birds?from lambdageeks.com
4. Movement of wings: The wings enable birds to fly. Angular motion plays a very important role in the movement of wings. Wings act like a lever that is attached to a hinge i.e. the joint. The joint acts like a pivot point or axis of rotation for the wings. The angular range of a bird’s wing depends on the species of the bird. Certain birds have a larger angular range than others. Usually larger birds have a limited range of angular movement.
What is glenohumeral abduction?from sciencedirect.com
The degree of glenohumeral joint abduction during cocking and acceleration is of prime importance in executing a proper mechanical serve. Increases in glenohumeral joint abduction can lead to placement of the shoulder in a position of subacromial impingement. Initial observation of a highly skilled player's service motion shows an apparent vertical orientation of the arm to contact the ball overhead. Closer observation reveals that highly skilled players have significant contributions from lateral flexion of the contralateral trunk and abduction of the scapula. These components allow a mid range of glenohumeral joint abduction throughout the four phases of the tennis serve.
Why is the velocity intended formula revised?from sciencebuzz.com
With the data collected from these three tests I now know the Velocity Intended formula would have to be revised in order for prosthetic leg manufactures to better fit prosthetic legs to humans that have above-the-knee amputations. A revised formula could give amputees as easier transition to their new leg.
What are some examples of displacement?from teachpe.com
More examples of distance and displacement: 1 A marathon runner has run a distance of approximately 26 miles 352 metres. Is displacement the same? Probably not unless the course is one very straight line. 2 A 400m sprinter? The distance travelled by the sprinter is 400m, but the displacement is practically zero as they finish in the same place they started.
What are the variables used to determine the velocity of a walk?from sciencebuzz.com
Three variables –walking, speed walking , and jogging – were used to test if the Intended Velocity formula truly represented the velocity of an individual’s walk, or more closely represented an individual’s speed walk. I hypothesized that the formula would better represent a speed walk because the Velocity Intended formula was created from a pendulum formula meaning that the straighter the leg the more accurate the formula. Jogging was included as a control group for the experiment. When humans jog, they bend their knees allowing them greater mobility thus ignoring the straight leg motion the Velocity Intended formula was emphasizing.
Why is it so hard to adjust to an above knee prosthetic leg?from sciencebuzz.com
Adjusting to an above-knee prosthetic leg is especially hard because an individual is missing both knee and ankle joints, which restricts their range of mobility. This Velocity Intended formula was created to help people who had gone through a dramatic change adjust to their new lives by providing a way for them to potentially customize the prosthetic leg to each person’s specific gait.
How much standard deviation is needed to determine if there is a correlation between the velocity measured and the velocity intended?from sciencebuzz.com
In order to determine if there was a correlation between the Velocity Measured (field data) and the Velocity Intended data, I took one standard deviation, 68.2%, of the collected data to determine if there was any overlap between the Velocity Intended formula and any of the Velocity Measured values.
What is the difference between displacement and distance?from teachpe.com
What is the difference between distance and displacement? Displacement is how far away a body has moved from its starting point. It is the shortest distance between the starting point and the finishing point.
How far can a marathon runner run?from teachpe.com
A marathon runner has run a distance of approximately 26 miles 352 metres. Is displacement the same? Probably not unless the course is one very straight line.
What is the difference between kinetics and biomechanics?
Biomechanics. Biomechanics is the science concerned with the internal and external forces acting on the human body and the effects produced by these forces. Kinetics is a study of the cause of motion , namely forces and torques, e.g. forces between the feet and the ground when jumping and Kinematics is the study of movement regarding the amount ...
How to find the average velocity and speed?
Speed and velocity describe the rate at which a body moves from one location to another. The average speed of a body is obtained by dividing the distance by the time, and average velocity is obtained by dividing the displacement by the time , e.g. a swimmer in a 50m race in a 25m long pool who completes the race in 71 seconds - distance is 50m, and displacement is 0m (swimmer is back where they started), so the speed is 50/71= 0.70m/s and velocity is 0/71=0 m/s
What is acceleration in science?
Acceleration is defined as the rate at which velocity changes with respect to time.
How to calculate time of flight?
Time of flight = Distance (D) ÷ velocity (Vh)
What is displacement in physics?
Distance (length of the path a body follows) and displacement (length of a straight line joining the start and finish points) are quantities used to describe a body's motion. e.g. in a 400m race on a 400m track, the distance is 400 metres, but their displacement will be zero metres (start and finish at the same point).
How much acceleration does a body have in the air?
While a body is in the air, it is subject to a downward acceleration, due to gravity, of approximately 9.81m/s²
What is the angle of release of a medicine ball?
Figure 2 indicates the angle of release of the medicine ball is 35° and the velocity at release as 12 metres/second.
What is the highest linear velocity?
Graph 1 shows the linear velocities of the different sports. The greatest linear velocity occurred in the long jump, 11.79ms‾¹, followed by the swimmer with a velocity of 6.26 ms‾¹. The other two values had lower maximum linear velocity values, 1.2ms‾¹ and 1.42ms‾¹ for the barbell and golf club respectively. The reason for this can be seen when the velocity is broken down into the two components of horizontal and vertical velocity.
What happens to the barbell as you extend your arms?
As the arms are being extended, the barbell is returning to its initial position. The horizontal velocity is increasing again but this time in a negative direction as the barbell is travelling in the opposite direction. Towards the end of the exercise, the horizontal velocity is returning to zero.
What happens to the velocity of a golf club when the arms are extended?
When the arms are being extended, the velocity increases positively as it is travelling in the opposite direction. The golf club has negligible vertical velocity, 0.35ms‾¹, due to only a slight vertical movement of the golf club during the swing.
Why does my golf club have a negative horizontal velocity?
This velocity returns to zero when the golf club reaches the top of the back swing.
Why is velocity important in coaching?
The ability to calculate velocity is a very useful tool for coaches to have as it will allow them to have a deeper analysis of a performance and improve it. As for teachers, being able to apply the laws of kinematics to such videos as shown above will give students a clearer demonstration of the velocity mechanism. Being able to associate the laws of velocity with a visual aid ( Quintic Video anlaysis software) will give students a better understanding in seeing how it applies to everyday life thus promoting better learning.
Which sport has the highest horizontal velocity?
The second graph shows just the horizontal velocities of the skills. Again as expected the long jump has the highest horizontal velocity in the shortest period of time, 11.78ms‾¹, due to the fact that the long jumper is mainly travelling horizontally. When looking at the other sports we see that the barbell has minimal horizontal velocity reaching a maximum value of 0.26ms‾¹. This is because the bench press is virtually a ‘straight up-straight down’ exercise with little movement forward and back. The golf club has a negative horizontal velocity for a short period due to the initial direction of the swing. During the back swing the golf club is travelling in a negative direction creating a negative horizontal velocity. This velocity returns to zero when the golf club reaches the top of the back swing. From then on, the club is travelling in a positive direction thus has a positive velocity.
Why does velocity increase when an object goes past the point of release?
Firstly, it will result in a negative velocity as the object goes past the point of release and secondly it will lead to an increased velocity because the speed of the object progressively increases due to the force of gravity. Hence, in this case the final velocity is not equal to the initial velocity.