Ventilation, or breathing, is the movement of air through the conducting passages between the atmosphere and the lungs. The air moves through the passages because of pressure gradients that are produced by contraction of the diaphragm and thoracic muscles. What is ventilation quizlet respiratory system
Respiratory system
The respiratory system is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies greatly, depending on the size of the organism, the environment in which it lives and its evolutionary history. In land animals the respiratory surface is internalized as linings of the lungs. Gas exchange in the lu…
Full Answer
What is ventilation in the respiratory system?
Ventilation, or breathing, is the movement of air through the conducting passages between the atmosphere and the lungs. The air moves through the passages because of pressure gradients that are produced by contraction of the diaphragm and thoracic muscles. What is ventilation quizlet respiratory system? .Advertisements. CONTINUE READING BELOW
What is the primary function of the respiratory system Quizlet?
The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this through breathing. When we breathe, we inhale oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide.
What is the movement of air in the lungs?
Mechanics of Ventilation Ventilation, or breathing, is the movement of air through the conducting passages between the atmosphere and the lungs. The air moves through the passages because of pressure gradients that are produced by contraction of the diaphragm and thoracic muscles.
How does air flow through the respiratory system?
Air, like other gases, flows from a region with higher pressure to a region with lower pressure. Muscular breathing movements and recoil of elastic tissues create the changes in pressure that result in ventilation. Pulmonary ventilation involves three different pressures: Atmospheric pressure.

What is ventilation in the respiratory system?
Ventilation (V) refers to the flow of air into and out of the alveoli, while perfusion (Q) refers to the flow of blood to alveolar capillaries. Individual alveoli have variable degrees of ventilation and perfusion in different regions of the lungs.
What is ventilation quizlet respiratory system?
Ventilation. Act of Filling Up lungs with air and then breathing it out.
What is ventilation in the body quizlet?
Ventilation. process of moving air in and out of the chest in order to bring o2 into the lungs and remove CO2 from the body. Dead space. air containing spaces within the lungs like bronchi or alveoli that are not exposed to capillary blood and thus do not exchange gas.
What is ventilation what is its importance in respiration?
Ventilation: Exchange of air between the lungs and the air (ambient or delivered by a ventilator), in other words, it is the process of moving air in and out of the lungs. Its most important effect is the removal of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the body, not on increasing blood oxygen content.
What is the difference between ventilation and respiration quizlet?
Terms in this set (22) explain difference between ventilation and respiration? ventilation is the movement of air in and out of the lungs, respiration is the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
What is another word for pulmonary ventilation?
breathingThe correct answer is breathing. Another name for pulmonary ventilation is breathing. Pulmonary ventilation is the process of breathing.
What are the function of the respiratory system quizlet?
The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this through breathing. When we breathe, we inhale oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide.
What happens in the lungs quizlet?
Your lungs are organs in your chest that allow your body to take in oxygen from the air. They also help remove carbon dioxide. From your body. The respiratory system is a group of organs and tissues that help you breathe.
What happens when ventilation exceeds perfusion in the lungs quizlet?
What happens when ventilation exceeds perfusion in the lungs? The CO2 level in the alveolus and surrounding tissue increases.
What is ventilation and examples?
The bodily process of breathing; the inhalation of air to provide oxygen, and the exhalation of spent air to remove carbon dioxide. noun. Ventilation is a circulation of air, or an opening that lets air in. An example of ventilation is a window being open in a house.
What's the difference between breathing and ventilation?
Respiration vs Ventilation Respiration and ventilation are two different things. Ventilation is mechanical and involves the movement of air, Respiration is physiologic and involves the exchange of gases in the alveoli (external respiration) and in the cells (internal respiration).
What are the types of ventilation?
Therefore, it's a good idea to know some of the different types of ventilation systems before making an investment.NATURAL VENTILATION.MECHANISED FANS. ... EXHAUST VENTILATION. ... SUPPLY VENTILATION. ... BALANCED VENTILATION. ... SMOKE VENTILATION.
What happens when you breathe quizlet?
When you breathe in, or inhale, your diaphragm contracts (tightens) and moves downward. This increases the space in your chest cavity, into which your lungs expand. The intercostal muscles between your ribs also help enlarge the chest cavity. They contract to pull your rib cage both upward and outward when you inhale.
What happens in the lungs quizlet?
Your lungs are organs in your chest that allow your body to take in oxygen from the air. They also help remove carbon dioxide. From your body. The respiratory system is a group of organs and tissues that help you breathe.
What is the definition of vital capacity quizlet?
The vital capacity is the maximum amount of air that you can move into or out of your lungs in a single respiratory cycle. The vital capacity is the sum of the expiratory reserve volume.
What are the stages of the passage of air in pulmonary ventilation?
Breathing (or pulmonary ventilation) has two phases - inspiration (or inhalation) and expiration (or exhalation). It is a mechanical process that depends on volume changes in the chest cavity.
What is the process of letting air out of the lungs during the breathing cycle?
Expiration (exhalation) is the process of letting air out of the lungs during the breathing cycle. During expiration, the relaxation of the diaphragm and elastic recoil of tissue decreases the thoracic volume and increases the intraalveolar pressure. Expiration pushes air out of the lungs.
What is the difference between pulmonary ventilation and intraalveolar ventilation?
Pulmonary ventilation involves three different pressures: Atmospheric pressure is the pressure of the air outside the body. Intraalveolar pressure is the pressure inside the alveoli of the lungs. Intrapleural pressure is the pressure within the pleural cavity.
What is the process of air flow?
Air, like other gases, flows from a region with higher pressure to a region with lower pressure. Muscular breathing movements and recoil of elastic tissues create the changes in pressure that result in ventilation .
Why is inspiration the active phase of ventilation?
It is the active phase of ventilation because it is the result of muscle contraction. During inspiration, the diaphragm contracts and the thoracic cavity increases in volume. This decreases the intraalveolar pressure so that air flows into the lungs. Inspiration draws air into the lungs.
What is the mechanical process of air movement?
Mechanics of Ventilation. Ventilation, or breathing, is the movement of air through the conducting passages between the atmosphere and the lungs. The air moves through the passages because of pressure gradients that are produced by contraction of the diaphragm and thoracic muscles.
Why does air flow in and out of the lungs?
Air flows because of pressure differences between the atmosphere and the gases inside the lungs.
What is the difference between intraalveolar and intrapleural pressure?
Intraalveolar pressure is the pressure inside the alveoli of the lungs. Intrapleural pressure is the pressure within the pleural cavity. These three pressures are responsible for pulmonary ventilation.
What is the respiratory system?
Respiratory system (Systema respiratorum) The respiratory system, also called the pulmonary system, consists of several organs that function as a whole to oxygenate the body through the process of respiration (breathing).
What is the process of inhaling air and conducting it to the lungs?
This process involves inhaling air and conducting it to the lungs where gas exchange occurs, in which oxygen is extracted from the air, and carbon dioxide expelled from the body. The respiratory tract is divided into two sections at the level of the vocal cords; the upper and lower respiratory tract.
What is the upper respiratory tract?
The upper respiratory tract refers to the parts of the respiratory system that lie outside the thorax, more specifically above the cricoid cartilage and vocal cords. It includes the nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, pharynx and the superior portion of the larynx. Most of the upper respiratory tract is lined with the pseudostratified ciliated ...
How do the paranasal sinuses communicate with the nasal cavity?
The paranasal sinuses communicate with the nasal cavity via several openings, and thereby also receive the inhaled air and contribute to its humidifying and warming. In addition, the mucous membrane and respiratory epithelium that lines both the nasal cavity and the paranasal sinuses traps any harmful particles, dust or bacteria.
Which bronchus passes inferolaterally to enter the hilum of the right lung?
On its course, it passes inferior to the arch of the aorta and anterior to the esophagus and thoracic aorta. The right main bronchus passes inferolaterally to enter the hilum of the right lung. The right main bronchus has a more vertical course than its left counterpart and is also wider and shorter.
Which part of the pharynx is lined with the more protective non-keratinizing stratified?
Thus, the oropharynx is lined with the more protective non-keratinizing stratified squamous epithelium. The laryngopharynx (hypopharynx) is the most inferior part of the pharynx. It is the point at which the digestive and respiratory systems diverge.
Where is the oropharynx located?
The oropharynx is found posterior to the oral cavity and communicates with it through the oropharyngeal isthmus. The oropharynx is a pathway for both the air incoming from the nasopharynx and the food incoming from the oral cavity. Thus, the oropharynx is lined with the more protective non-keratinizing stratified squamous epithelium.
Which structure is responsible for pulmonary ventilation?
Combining the function of all these structures, the pulmonary ventilation mechanism establishes two gas pressure gradients.
How does ventilation work?
Simply put, ventilation is breathing – the physical movement of air between the outside environment and the lungs. Air travels through the mouth and nasal passages, then down the pharynx. Upon reaching the vocal cords, air flows into the trachea, transitioning from the upper airway into the lower airway. Here, it continues distally to the carina, then through the primary bronchi, various branches of bronchioles, and eventually arriving in the alveoli. This is inhalation. Air movement in a reverse pathway from alveoli to mouth and nose, is exhalation. Inhalation, followed by exhalation, equals one ventilation. This is what you observe (chest rise and fall) when determining the breathing rate.
How does the volume of the lungs change?
So, how does the lung volume change? Quite simply, it is a combination of muscle contractions stimulated by the central nervous system, and the movement of a serous membrane within the thorax called the pleura. The pleura is made of two layers: a parietal layer that lines the inside of the thorax and a visceral layer that covers the lungs and adjoining structures (blood vessels, bronchi, and nerves). Between the visceral and parietal layers is a small, fluid-filled space, called the pleural cavity.
Why are capillaries so large?
Capillaries are only large enough to accommodate one red blood cell at a time , and blood flow at this level is very slow. This maximizes the time for the release of oxygen and reabsorption of carbon dioxide. Cells require high concentration oxygen to function correctly.
What is the difference between inhalation and exhalation?
This is inhalation. Air movement in a reverse pathway from alveoli to mouth and nose, is exhalation. Inhalation, followed by exhalation, equals one ventilation. This is what you observe (chest rise and fall) when determining the breathing rate.
Why do we need to change the pressure in the alveoli?
These necessary changes in intrapulmonary pressure occur because of changes in lung volume.
Where does oxygen depleted blood go?
Oxygen-depleted blood, transported from the body’s cells and back to the right side of the heart, is pumped into the pulmonary trunk and through the pulmonary arteries. Eventually, the blood makes its way through the distal pulmonary capillaries surrounding the alveoli.
What are the components of the respiratory system?
The respiratory process consists of three components. Ventilation, diffusion and perfusion. Ventilation consists of two parts:
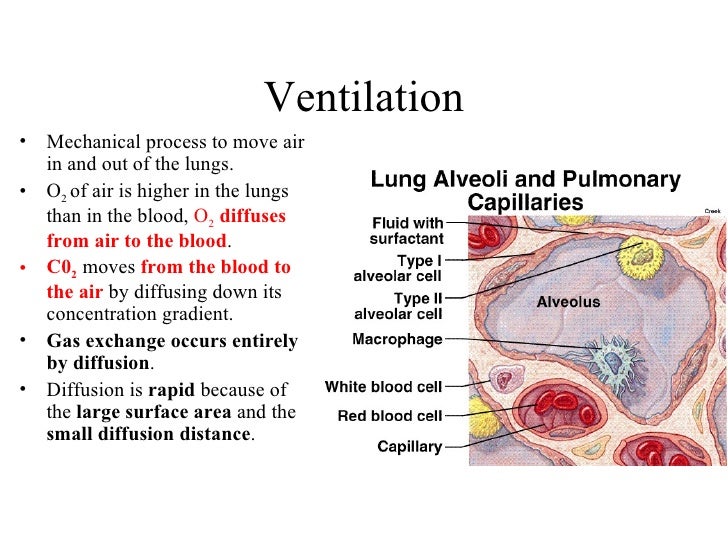
What is the process of gas exchange between the alveoli and lung capillaries?
Diffusion is the process whereby gases move from an area of high pressure to low pressure. This includes during - Internal respiration - this is the movement in the internal tissues between cells and capillaries, and - External respiration - when gas is exchanged between the alveoli and lung capillaries. Perfusion refers to the blood flow to tissues and organs. Alveoli are perfused by capillaries so the diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide can take place.