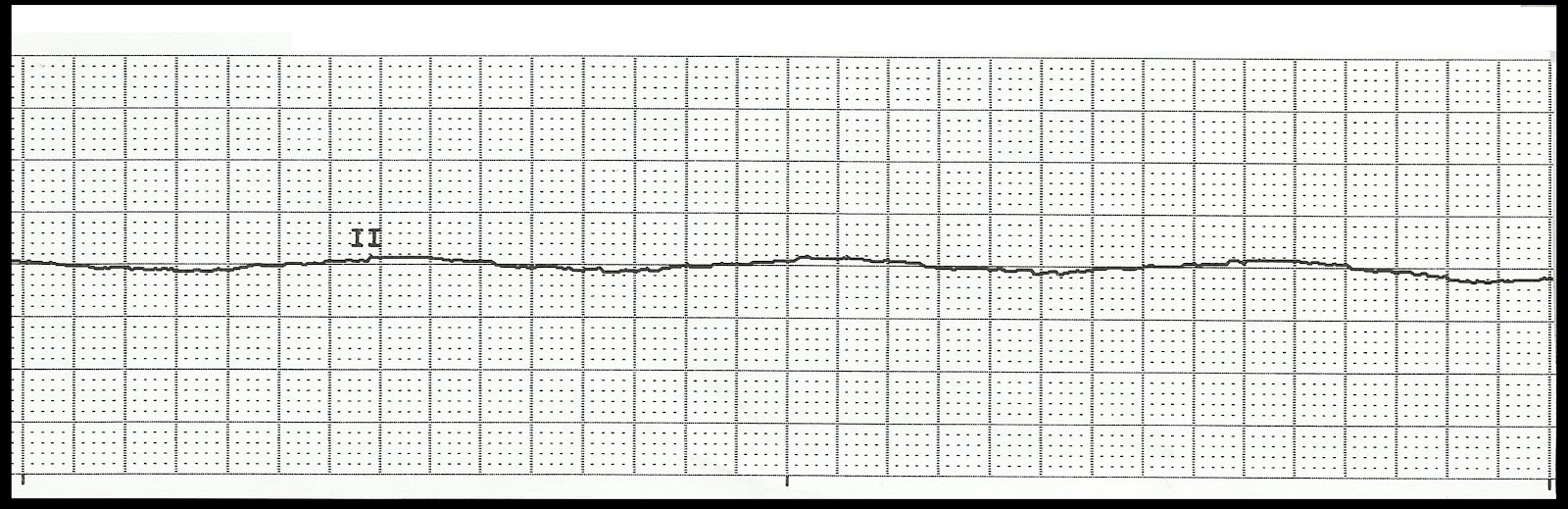
Ventricular standstill is the absence of any ventricular activity for more than a few seconds.
What is the time interval of ventricular contraction?
the time interval of ventricular contraction 0.3 seconds if an individual's heart rate is 80 beats/min, what is the length of the cardiac cycle? What portion of the cardiac cycle decreases with a more rapid heart rate?
What is true regarding ventricular systole?
The ventricles begin to contract (ventricular systole), raising pressure within the ventricles. When ventricular pressure rises above the pressure in the atria, blood flows toward the atria, producing the first heart sound, S 1 or lub. As pressure in the ventricles rises above two major arteries, blood pushes open the two semilunar valves and moves into the pulmonary trunk and aorta in the ventricular ejection phase.
What does ventricular repolarization result in?
Ventricular repolarization. It is the restoring of the resting state. In the ECG, repolarization includes the J point, ST segment, and T and U waves. The transthoracically measured PQRS portion of an electrocardiogram is chiefly influenced by the sympathetic nervous system.
What are the risks of ventricular shunting?
- infection in the shunt or brain
- blood clots
- bleeding in the brain
- damage to brain tissue
- swelling of the brain

Is ventricular standstill a heart block?
Ventricular standstill (also called ventricular asystole) is a potentially lethal arrhythmia if not treated promptly. It occurs when there is cessation of supraventricular impulse formation or blockage in the transmission of these impulses from the atria to the ventricles resulting in asystolic cardiac arrest.
What can cause ventricular standstill?
Ventricular standstill is most common in people who are older and have structural heart disease, such as weakening or scar of the heart muscle. Structural heart disease may be congenital, something you are born with, or the result of illness, trauma, high blood pressure, or a heart attack.
What is the treatment for ventricular standstill?
Ventricular standstill often occurs in relation to conduction blocks though it can occur without them. Once discovered, ventricular standstill requires immediate treatment. Treatment usually requires temporary pacing wires and eventually permanent pacemaker insertion.
Is P wave asystole the same as ventricular standstill?
Introduction. Unstable emergency patients might experience different cardiac arrhythmias. A rarely seen arrhythmia is the p-wave asystole also mentioned ventricular asystole, ventricular standstill or third-degree atrioventricular block with no ventricular escape rhythm.
Can a heart block go away?
Heart block occurs when the electrical signal is slowed down or does not reach the bottom chambers of the heart. Your heart may beat slowly, or it may skip beats. Heart block may resolve on its own, or it may be permanent and require treatment.
How long is a sinus pause?
Sinus pause or arrest where there are pauses of 3 seconds or more without atrial activity. This is often rescued by an escape rhythm which can be atrial, junctional and ventricular in origin. It usually reflects a failure of P cells to generate the action potential.
How can you tell if you have a complete heart block?
Complete Heart Block:Atrial rate is ~ 85 bpm.Ventricular rate is ~ 38 bpm.None of the atrial impulses appear to be conducted to the ventricles.Rhythm is maintained by a junctional escape rhythm.Marked inferior ST elevation indicates that the cause is an inferior STEMI.
What is a 3rd degree heart block?
Third-degree AV block indicates a complete loss of communication between the atria and the ventricles. Without appropriate conduction through the AV node, the SA node cannot act to control the heart rate, and cardiac output can diminish secondary to loss of coordination of the atria and the ventricles.
Why do doctors hit the chest before CPR?
Procedure. In a precordial thump, a provider strikes at the middle of a person's sternum with the ulnar aspect of the fist. The intent is to interrupt a potentially life-threatening rhythm. The thump is thought to produce an electrical depolarization of 2 to 5 joules.
Can you do CPR on asystole?
Asystole is a non-shockable rhythm. Therefore, if asystole is noted on the cardiac monitor, no attempt at defibrillation should be made. High-quality CPR should be continued with minimal (less than five seconds) interruption.
Can asystole have P waves?
Ventricular asystole is characterized by a complete absence of a ventricular rhythm. P waves may be present if AV block exists, but no QRS complexes are observed. Primary asystole occurs when the Purkinje fibers intrinsically fail to generate a ventricular depolarization.
What is asystole ECG?
What is asystole? Asystole is when your heart's electrical system fails entirely, which causes your heart to stop pumping. It is also known as “flat-line” or “flat-lining” because of how your heart's electrical activity appears as a flat line on an electrocardiogram.
How do you identify pea rhythm?
0:124:52EKG l Pulseless Electrical Activity (PEA) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWell using our five steps let's interpret this EKG. Step number one the rate can be Brady. Normal orMoreWell using our five steps let's interpret this EKG. Step number one the rate can be Brady. Normal or tachy. The rhythms gonna be regular. The P wave will be present and normal same with PR interval.
How do you identify a junctional escape rhythm?
The terminology used to identify the type junctional rhythm depends on its rate and is as follows: Junctional bradycardia: rate below 40 beats per minute. Junction escape rhythm: rate 40 to 60 beats per minute. Accelerated junctional rhythm: rate of 60 to 100 beats per minute.
What does torsades de pointes look like on ECG?
Torsades de Pointes is actually ventricular tachycardia that happens in the setting of Long QT interval. During Torsades de Pointes, your provider can see a specific pattern of ventricular tachycardia that looks like twisting points or peaks (which is what the name means in French) on an electrocardiogram (EKG).
What is ventricular standstill?
Ventricular Standstill. Ventricular standstill is an uncommon yet potentially fatal arrhythmia, which requires urgent . recognition and treatment. As the name suggests, the ventricles come to a standstill with an . almost immediate cessation of cardiac output. The SA node continues to conduct without any .
What happens when a pacemaker goes into a run of ventricular standstill?
It goes into a run of ventricular standstill, Then the pacemaker starts to pace again (AV pacing).
What is Ventricular Standstill?
Ventricular standstill in cats describes when the ventricles within the heart cease to function in pumping blood throughout the body. A cat’s heart is made up of four sections, or chambers, which work together to efficiently pump blood throughout the circulatory system. The upper chambers are called atria and the lower chambers are called ventricles.
What is the heart of a cat?
A cat’s heart is made up of four sections, or chambers, which work together to efficiently pump blood throughout the circulatory system. The upper chambers are called atria and the lower chambers are called ventricles. During an episode of ventricular standstill in cats an ECG, or electrocardiogram, will show the absence of any ventricular activity.
Why does my cat stand still?
Ventricular standstill in cats is an underlying symptom caused by a variety of diseases and conditions related to heart disease or degeneration. While many illnesses or conditions may cause ventricular standstill, a few of the most common are listed below.
Can a cat have a heart rate of ventricular standstill?
Cats suffering from ventricular standstill will have no apparent heart rate and will not display any reading on an ECG. Your veterinarian will perform an emergency examination if they believe your cat is suffering from ventricular standstill. Once your cat has been stabilized, the focus will switch to diagnosis of the underlying condition which may ...
Do ventricular standstill medications work?
These medications typically will only work in instances where minor, prolonged conditions are present. In acute cases of ventricular standstill, special electrical or manual stimulation will be required to restore normal function to the heart.
What is Ventricular Standstill?
With ventricular standstill, the heart appears to function normally but has episodes of stopping for a few seconds at a time, at irregular intervals. Also called pulseless electrical activity and asystole, this loss of cardiac output takes place in the bottom chambers of the heart. The bottom two chambers are called the ventricles. The top two chambers are known as the atria; atrial standstill is another condition of the heart altogether.
How to tell if my dog has ventricular standstill?
The most obvious sign you will see your dog display if he has ventricular standstill is episodic fainting. This symptom should be taken as a serious event, and it is imperative that you get your canine companion to the veterinary clinic without delay.
What is the absence of activity in the ventricle chambers of the heart?
The asystole, or absence of activity in the ventricle chambers of the heart, results in the blood not being pumped rhythmically as it should into the lungs and the body.
What Is Ventricular Standstill in Dogs?
Ventricular standstill is also known as asystole. It occurs when parts of the heart, called the ventricles, stop working properly and emit no electrical signal on a machine designed to read these signals called an electrocardiogram. This signal on the electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) is referred to as a QRS complex and is the visual representation of the electrical impulse going through the ventricles. It is seen as the main spike on an ECG tracing line or is often thought of as the visual heartbeat on the ECG monitor screen. When ventricular standstill occurs, a flat line is seen on an ECG because there are no electrical impulses occurring in the heart ventricles. It may also commonly be referred to as a type of cardiac arrest but a heart attack is something different.
What happens if a dog has ventricular standstill?
This is of course an emergency situation in which cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is often started but an ECG is often also connected to a dog at this time to gather insight into whether or not there is electrical activity in the heart. Ventricular standstill will be seen at this time on the ECG monitor screen as a flat line.
What is ventricular standstill?
Ventricular standstill is an uncommon yet potentially fatal arrhythmia, which requires urgent recognition and treatment. As the name suggests, the ventricles come to a standstill with an almost immediate cessation of cardiac output. If this persists for more than a few seconds the patient will lose consciousness and no pulse will be palpable.
What is the best treatment for a patient with a pulse that is palpable?
Recommended treatment includes prompt initiation of cardiopulmonary resuscitation, and if return of circulation is achieved, pacemaker insertion is usually required.
Can a young child have ventricular standstill?
We present four cases of ventricular standstill, which occurred in patients of very different ages; a young child, a young female, a middle-aged female and an elderly male. These cases highlight the fact that ventricular standstill can occur at any age.
Can a ventricular standstill be seen at any age?
Conclusion. Ventricular standstill can occur at any age. It can be difficult to diagnose with many cases only evident on pre-hospital ECG recordings. It may present as recurring episodes of loss of consciousness yet the patient may be well in the intervening period.
Is asystole a poor prognosis?
The prognosis from asystole is extremely poor with only 2–5% of patients, in one study, who suffered an out of hospital asystolic cardiac arrest surviving to hospital discharge. 6 Therefore prompt diagnosis is required and treatment commenced without delay.
Is ventricular standstill a structural heart disease?
Ventricular standstill usually occurs in patients with structural heart disease ( Table 1) but it has also been reported in patients with normal heart structure. 10, 11 Ventricular standstill should be considered amongst the differential diagnoses of recurrent episodes of collapse.

What Is Ventricular Standstill?
- The ventricles are the bottom chambers of the heart. The left ventricle is in charge of pumping blood to the body. When this ventricle is not moving then the heart is not pumping blood to the rest of the body. Ventricular standstill occurs during a cardiac arrest. It is a medical emergency. Ventricular standstill is sometimes referred to as ventric...
How Common Is Ventricular Standstill?
- Ventricular standstill is very uncommon. Even among all people suffering a cardiac arrest, ventricular standstill only occurs some of the time. When a person is not able to be resuscitated successfully, observing ventricular standstill on an ultrasound of the chest will confirm that they have died.
Signs and Symptoms
- Ventricular standstill refers to no movement of the heart. Regardless of the rhythm causing this problem, if the heart is not moving, the person will lose consciousness as is common in other forms of cardiac arrest. This will occur suddenly and without warning.
Causes and Risk Factors
- Ventricular standstill is most common in people who are older and have structural heart disease, such as weakening or scar of the heart muscle. Structural heart disease may be congenital, something you are born with, or the result of illness, trauma, high blood pressure, or a heart attack. Some specific cases of structural heart disease include: 1. Myocardial infarction, or a he…
How Is It Diagnosed?
- Ventricular standstill will be diagnosed when it is noticed that the heart of a patient suffering from a cardiac arrestis not moving. This is typically done by using an ultrasound. A doctor can evaluate for signs of structural heart disease in several ways. Measuring blood pressure is an important risk for structural heart disease. Tests such as cardiac ultrasound, or echocardiogram, stress te…
Treatment Options
- Ventricular standstill is an ominous finding during a cardiac arrest. This typically means that the person's heart is not responding to attempts to revive them. Continued resuscitation measures such as CPR, medications, and electric shocks may be required to save the person.