What is vital few in Pareto analysis?
Juran has also coined the terms “vital few” and “useful many” or “trivial many” to refer to those few contributions, which account for the bulk of the effect and to those many others which account for a smaller proportion of the effect.
What is vital few?
The term is derived from the 80-20 rule, also known as the Pareto principle, which asserts that the vast majority — about 80% — of all outcomes or outputs are the direct result of only 20% of all possible causes or inputs.
What is vital few and trivial many associated with Pareto Principle?
This was also known as "the vital few and the trivial many." 1. In later years, Juran recoined the Pareto Principle as the 80/20 Rule. The 80/20 Rule means that in anything a few (20%) are vital and many (80%) are trivial.
What is vital view?
Vital View is a startup spinning out of the University of Notre Dame based on the proprietary technology coming out of Dr. Thomas Pratt's lab. The mission of Vital View is to help people make more intelligent health decisions through its non-contact, non-wearable vital sign monitoring technology.
How do you identify vital few?
To determine the vital few, look at the list of your initiatives on the right side of your alignment map and pick the top set of initiatives that will deliver 80 percent impact on your vision. Focus on those initiatives.
Who said the vital few and the trivial many?
Joseph JuranThe 80/20 principle was further refined by another deep thinker, Joseph Juran, who recognized a universal principle that he called “The Vital Few and The Trivial Many,” basically stating that 20% of something is always responsible for 80% of the results.
Which technique is used to separate the vital few from the useful many?
Pareto Analysis is used to separate Vital few from Trivial Many parameters. Vital few contributing to 20% and trivial many 80%. This principle is otherwise called as 80-20 Rule.
Which technique is used for segregating the vital few from trivial many?
Pareto Principle is also called the law of “The Vital Few and Trivial Many”. It is a prioritization tool that helps to find “VITAL FEW” and “TRIVIAL MANY” causes. Vital Few means many problems come from a relatively small number of causes.
How do you read a Pareto analysis?
How to Create and Read a Pareto Chart ?Step 1: Find the Causes. The process starts with finding the underlying causes. ... Step 2: Prepare a Frequency Table. ... Step 3: Convert it into Percentages. ... Step 4: Arrange in Descending Order. ... Read The Bar Charts For Individual Values. ... Read The Line For Cumulative Value.
How is Pareto principle calculated?
To build the Pareto, they followed these steps:Step 1: Total the data on effect of each contributor, and sum these to determine the grand total. ... Step 2: Re-order the contributors from the largest to the smallest. ... Step 3: Determine the cumulative-percent of total. ... Step 4: Draw and label the left vertical axis.More items...•
Why Pareto analysis is used?
The Pareto analysis, also known as the 80/20 rule, is useful when many decisions need to be made. A Pareto analysis is a tool to help business leaders improve their companies by identifying key problems and opportunities. The technique is named after Italian economist Vilfredo Pareto.
Which technique is used to separate the vital few from the useful many?
Pareto Analysis is used to separate Vital few from Trivial Many parameters. Vital few contributing to 20% and trivial many 80%. This principle is otherwise called as 80-20 Rule.
What do you know about Six Sigma?
The Six Sigma method is focused on limiting fluctuation within business processes and quality management of process output by implementing problem-solving statistical methods. Conversely, the primary focus of Lean Six Sigma is to eliminate waste and improve existing processes.
Which methodology uses the Dmaic steps?
Lean Six Sigma programDMAIC methodology is typically used as a part of a larger Lean Six Sigma program to create 'breakthroughs' in an organization. Each project is assigned to a Lean or Six Sigma leader called a Black or Green Belt and a team of subject matter experts.
What is Pareto chart?
A Pareto Chart is a type of Bar Chart in which a series of bars which signifies contributing factors are arranged based on the magnitude of the effect. This relatively means that the tall bars on the left are more significant than on the right. Also known as 80/20 rule, where it states that roughly 80% of the effects come from 20% of the causes.
What does it mean when you look at a Pareto chart?
When you look at a Pareto Chart, you can see break points in the heights of the bars which indicates the most important categories. This information is useful when you are establishing priorities.
What is Pareto chart analysis?
Pareto Chart Analysis is one of the seven statistical quality control tool. It helps project team or the decision maker to identify key contributing issues and to take corrective measures on time, ensuring continuous improvement in the desired outcome in order to maximize the output for the system.
Why is Pareto Chart Analysis important?
Pareto Chart Analysis should be practiced in a continuous manner at regular intervals for better monitoring and control .E.g. Analysis at the end of a project, or at the end of a release , or at the end of each sprint cycle. Depending on the logical end of any particular project phase. It helps in taking the remedial actions for the vital issues at the right time based on the analysis performed to ensure the Quality runs within the project in controlled environment.
Who created the Pareto concept?
The concept was founded by management Guru Joseph M Juran and named it after Italian economist Mr. Vilfredo Pareto, who at first observed that 80% of the income of Italy is from 20% of the population.
What is Pareto chart?
The Pareto chart plots the frequencies and corresponding percentages of a categorical variable. It helps you identify the vital few—the “20%" that really matters. It helps you prioritize and shows you where to focus your efforts and resources.
What is the Pareto principle?
The Pareto principle states that about 80% of outcomes come from 20% of the causes. And whether you’re assessing a population’s wealth, a company's profits, a product's defects, a store's customer complaints, or some other outcome, the Pareto chart is a must-have in any analyst’s toolbox.
What is Pareto diagram?
A Pareto diagram displays the relative impact each contributing factor has on the overall problem. It ranks the sources from largest to smallest and shows the total cumulative impact for the two largest, three largest, etc.
What is Pareto analysis?
Pareto analysis is a ranked comparison of factors related to a quality problem and is a statistical decision-making technique used for the selection of a limited number of tasks that produce a significant overall effect. It helps to identify and focus on the vital few factors.
What is the Pareto Principle (80/20 Rule)?
The Pareto Principle, also known as the 80/20 Rule, The Law of the Vital Few and The Principle of Factor Sparsity, illustrates that 80% of effects arise from 20% of the causes – or in lamens terms – 20% of your actions/activities will account for 80% of your results/outcomes.
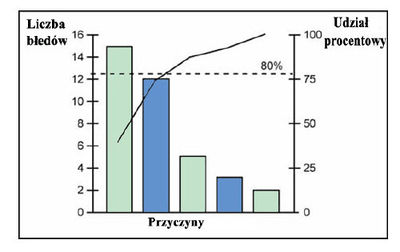
What percentage of the total is flattening out after the first four contributors?
Note how the slope of the line graph begins to flatten out after the first four contributors (the vital few), accounting for 86 percent of the total. Sometimes there is not a clear break point between the vital few and the useful many. Dr. Juran referred to this as the Awkward Zone.
Where are the 18 product codes on the Juran Pareto diagram?
On the Juran Pareto diagram, the 18 product codes are listed on the horizontal axis in the order of their contribution to the total. The height of each bar relates to the left vertical axis, and shows the number of product returns on that item. The line graph corresponds to the right vertical axis, and shows the cumulative-percent of total.
Why do we use the 80/20 rule?
Today, organizations need to use the Pareto Principle to help them separate the “vital few” problems from the “useful many.” The premise behind this rule is that improvement efforts will be more effective if the vital few are addressed first.
How many items of information must be filled in on an order form?
Of the 18 items of information that must be filled in on an order form, four of the items generate 86 percent of the errors found on these forms
Why use Pareto chart?
Pareto charts are used to display the Pareto principle in action, arranging data so that the few vital factors that are causing most of the problems reveal themselves. Concentrating improvement efforts on these few will have a greater impact and be more cost-effective than undirected efforts.
Who is Vilfredo Pareto?
Vilfredo Pareto, a turn-of-the-century Italian economist , studied the distributions of wealth in different countries, concluding that a fairly consistent minority – about 20% – of people controlled the large majority – about 80% – of a society's wealth.
What is a Pareto Chart?
The Pareto Chart is a mix of a bar graph and a line chart. It’s used for demonstrating the 80-20 principle. Individual problems (or data points) are represented using bars, and these bars are arranged in descending order — from the largest to the smallest. A curved line is used to represent the cumulative total of the data set.
Why are Pareto charts so effective?
Pareto Charts are most effective when you are facing conflicting problems. In PPC advertising, you may have a lot of competing keywords, making it hard to decide on how best to allocate your marketing budget.
What is the characteristics of Pareto analysis?
In case of Pareto Column Chart, the Y-axis contains the number of events. It is reverse in case of Pareto Bar Chart.
What is the cumulative percentage in the Pareto Chart?
The cumulative percentage in the Pareto Chart shows the percentage of the defect that can be removed if you want to solve the most important defect types. It also shows what percent contributes the most to the overall data set.
How to do Pareto Analysis?
Here are some things you need to understand before performing a Pareto analysis.
Why a Pareto Chart is useful compared to other types of graphs?
But the Pareto Chart is the only chart that is used to find defects in a data set . It can also be used to identify the 20% effort that generates 80% of the results.
How does Pareto work?
Pareto chart works on the idea that 80% of a project’s benefit can be achieved by doing 20% of the work or , conversely, 80% of problems can be traced to 20% of the causes and can help you to assess and prioritize different problems or tasks by comparing the benefit that solving each one will provide.
How to use Pareto chart?
When to Use a Pareto Chart 1 When analyzing data about the frequency of problems or causes in a process 2 When there are many problems or causes and you want to focus on the most significant 3 When analyzing broad causes by looking at their specific components 4 When communicating with others about your data
What does the length of the bars on a Pareto chart represent?
The lengths of the bars represent frequency or cost (time or money), and are arranged with longest bars on the left and the shortest to the right. In this way the chart visually depicts which situations are more significant. This cause analysis tool is considered one of the seven basic quality tools. When to use a Pareto chart.
How to draw cumulative sums?
Calculate and draw cumulative sums: add the subtotals for the first and second categories, and place a dot above the second bar indicating that sum. To that sum add the subtotal for the third category, and place a dot above the third bar for that new sum. Continue the process for all the bars. Connect the dots, starting at the top of the first bar. The last dot should reach 100% on the right scale.
What are the basic quality control tools?
Jack ReVelle provides a brief description and example of each of the seven basic quality control tools: data tables, Pareto charts, scatter analysis, cause and effect analysis, trend analysis, histograms, and control charts.
How to find percentage of a category?
Calculate the percentage for each category: the subtotal for that category divided by the total for all categories. Draw a right vertical axis and label it with percentages. Be sure the two scales match. For example, the left measurement that corresponds to one-half should be exactly opposite 50% on the right scale.
