
What do you mean by water of crystallization class 10th? The water of crystallization means having a fií number of molecules present in one formula of a unit of salt. Crystal salts with water of crystallization are known as hydrates.
What is water of crystallisation?
Water Of crystallisation The water molecules which form part of the structure of a crystal are called water of crystallisation. The salts which contain water of crystallisation are called hydrated salts.
Which of the following salts contains water of crystallisation?
The salts which contain water of crystallisation are called hydrated salts. 1) Copper Sulphate crystals contain 5 molecules of water of crystallisation (CuSO4.5H2O) It is blue in colour. 2) Sodium carbonate crystals contains 10 molecules of water of crystallisation (Na2CO3.10H2O)
How many molecules of water of crystallisation are in calcium sulphate crystals?
3) Calcium sulphate crystals contains 2 molecules of water of crystallisation (CaSO4.2H20) The water of crystallisation gives the crystals of the salts their shape and colour. When hydrated salts are heated strongly, they lose their water of crystallisation.
How many molecules of water of crystallisation are there in Na2CO3?
2) Sodium carbonate crystals contains 10 molecules of water of crystallisation (Na2CO3.10H2O) 3) Calcium sulphate crystals contains 2 molecules of water of crystallisation (CaSO4.2H20) The water of crystallisation gives the crystals of the salts their shape and colour.
What do you mean by water of crystallisation?
Classically, "water of crystallization" refers to water that is found in the crystalline framework of a metal complex or a salt, which is not directly bonded to the metal cation. Upon crystallization from water, or water-containing solvents, many compounds incorporate water molecules in their crystalline frameworks.
What is removing water of crystallization Class 10?
When hydrated salts are heated strongly, they lose their water of crystallisation. By losing water of crystallisation, the hydrated salts lose their regular shape and colour and become colourless powdery substances. The salts which have lost their water of crystallisation are called anhydrous salts.
What is water of crystallization and give examples?
Water of crystallization is defined as water that comes from a crystal substance after heat is applied. An example of water of crystallization is the water that drips off of a water crystal hanging from the eaves of the house as it warms up after a freezing rain.
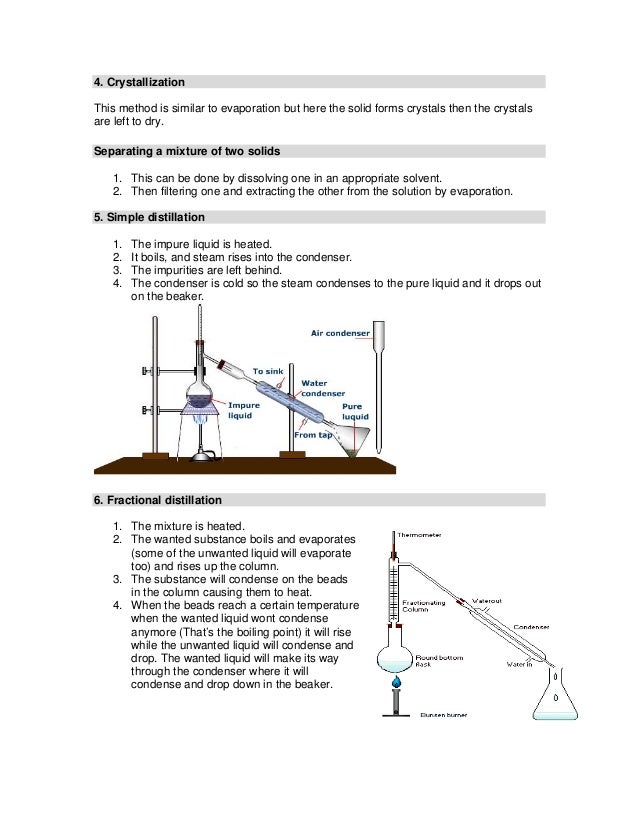
What is the process of crystallization Class 10?
Crystallization can be defined as the process through which the atoms/molecules of a substance arrange themselves in a well-defined three-dimensional lattice and consequently, minimize the overall energy of the system.
What is water of crystallization name and formula?
The water associated with the crystal (or molecule) of any salt is called water of crystallisation . The hydrated salt is known as washing soda which is sodium carbonate containing 10 molecules of water of crystallization , i.e ., it is sodium carbonate decahydrate . Its molecular formula is `Na_(2)CO_(3). 10H_(2)O`.
Why is water of crystallization important?
The production of crystals frequently requires the use of water. A fixed number of molecules in one formula of a unit of salt is referred to as water of crystallization. Hydrates are crystal salts that contain water during the crystallization process.
What is water of crystallization write the common name?
Text Solution. Solution : Water of crystallisation is the fixed number of water molecules present in one formula unit of the compound. The compound having ten water molecules as water of crystallisation in `Na_2CO_3. 10H_2O` Its name is washing soda.
What is crystallisation in chemistry?
Crystallization is a method for transforming a solution into a solid, where a supersaturated solution nucleates the solute by a chemical equilibrium controlled process. Uniform particles with well-defined morphology are formed, and these readily re-dissolve. Crystals tend to be brittle.
What happens when water is removed from crystallization?
The tendency of some crystals to melt in their Water of crystallization when exposed to heat decreases after a part of the water of crystallization is removed from them until the tendency to meltat any temperature whatsoever ceases when a sufficient percentage has been removed.
What is dilution in chemistry class 10?
Dilution is the process of decreasing the concentration of a solute in a solution, usually simply by mixing with more solvent. To dilute a solution means to add more solvent without the addition of more solute. ... If one adds 1 litre of water to thissolution the salt concentration is reduced.
What is the water of crystallization of washing soda?
The correct option is C. 10. Washing soda has formula Na2CO3. 10 H2O. Hence, it has 10 molecules of water of crystallization.
What is water of crystallization?
The water of crystallization means having a fixed number of molecules present in one formula of a unit of salt. Crystal salts with water of crystallization are known as hydrates. The other names of water crystallization are crystallization water or water of hydration. The water of crystallization is caused by forming purified crystals ...
What causes water to crystallize?
The water of crystallization is caused by forming purified crystals from an aqueous solution. These crystals do not include contaminants. These crystals are easily affected by the heat.
What is water of crystallization?
water of crystallization or water of hydration are water molecules that are present inside crystals. ... Classically, "water of crystallization" refers to water that is found in the crystalline framework of a metal complex or a salt, which is not directly bonded to the metal cation.
What is the fixed amount of water molecules attached with unit of a salt called?
The fixed amount of water molecules attached with unit of a salt is known as water of crystallisation.
