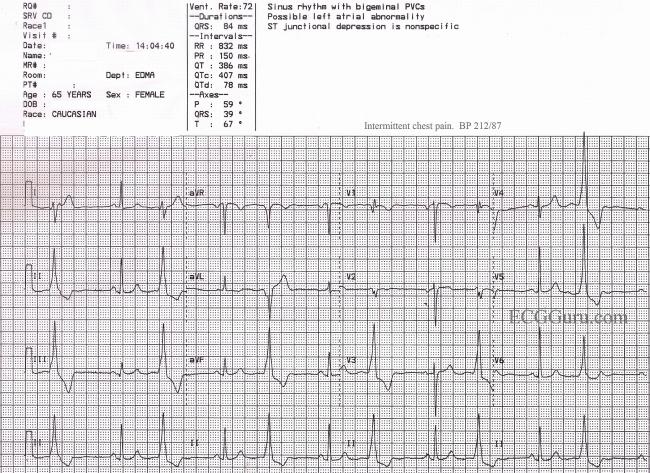
The Wenckebach phenomenon, or type I AV block, refers to a progressive lengthening of impulse conduction time, followed by a nonconducted impulse, or dropped beat. It can occur in a variety of pathologic settings, especially inferior myocardial infarction. Although a temporary pacemaker may be required, full spontaneous recovery is the rule.
What is a Wenckebach block?
Dr. Roach: Wenckebach is a heart-rhythm disturbance, called a heart block. There are three degrees of heart block. First-degree block is the mildest and rarely needs treatment, although it may (occasionally) predict more serious heart problems.
What causes Wenckebach phenomenon in a heart block?
Atropine or physical activity: these two increases heart rate which induces Wenckebach phenomenon in Mobitz type 1 block. Vagal stimulation: this causes increased block if the block is located in the AV node, which suggests Mobitz type 1 block. If the PR interval is prolonged, Mobitz type 1 block is more likely.
Is Wenckebach phenomenon the same as Mobitz type 1 block?
However, Wenckebach phenomenon may also occur in sinoatrial (SA) block which is why the term should not be used. Mobitz type 1 block is characterized by a gradual prolongation of the PR interval over a few heart cycles until an atrial impulse is completely blocked, which manifests on the ECG as a P-wave not followed by a QRS complex.
How common is Wenckebach syndrome?
For someone like you, a trained athlete with a slow heart rate, Wenckebach is common (about 10 percent of trained athletes). Since you have no symptoms, I agree with your cardiologist completely and can reassure you that the chance of developing worse heart block is low.
Is Wenckebach life threatening?
The prognosis for Mobitz type I (Wenckebach) is excellent. This is usually asymptomatic and requires no intervention in asymptomatic patients. The prognosis for Mobitz type II varies based on the cause of the rhythm.
What is the treatment for Wenckebach?
No specific therapy is required in the emergency department (ED) for Mobitz I (Wenckebach) second-degree AV block, unless the patient is symptomatic. Patients with suspected myocardial ischemia should be treated with an appropriate anti-ischemic regimen and worked up.
What causes a Wenckebach?
There are multiple causes of second-degree Mobitz type 1 (Wenckebach) AV block, including reversible ischemia, myocarditis, increased vagal tone, status post-cardiac surgery, or even medications that slow AV nodal conduction (e.g., beta-blockers, non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blocks, adenosine, digitalis, and ...
Can Wenckebach go away?
The P–R interval decreases and the Wenckebach block disappears with increased activity, and is considered normal vagal influence on the AV node. Acquired complete heart block is rarely seen in young adults without heart disease.
What are the symptoms of Wenckebach?
What are the signs and symptoms of Mobitz type I? Most people with Mobitz type I block do not present any symptoms. Some individuals may occasionally feel light-headedness, dizziness, or fatigue when exercising.
How common is Wenckebach?
For someone like you, a trained athlete with a slow heart rate, Wenckebach is common (about 10 percent of trained athletes). Since you have no symptoms, I agree with your cardiologist completely and can reassure you that the chance of developing worse heart block is low.
How long can you live with heart block?
The survival rate in the 68 cases of CHB was higher at one year (68%) as well as at 5 years (37%) than that reported by other investigators.
Which heart block is the most serious?
Third-degree heart block is the most severe. Electrical signals do not go from your atria to your ventricles at all with this type. There is a complete failure of electrical conduction. This can result in no pulse or a very slow pulse if a back up heart rate is present.
Which heart block is Wenckebach?
Wenckebach phenomenon, or type 1 second-degree atrioventricular (AV) block, is a common type of AV block in which there is a delay in transmission of impulses from the atria to the ventricles.
Is Wenckebach Type 1 or Type 2?
Second-degree AV block Mobitz type 1, also known as Wenckebach block.
What heart conditions require a pacemaker?
Pacemakers are used to treat heart rhythm disorders and related conditions such as: Slow heart rhythm (bradycardia) Fainting spells (syncope) Heart failure.
What medications cause heart block?
Common drugs that induce atrioventricular (AV) block include beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, antiarrhythmics, and digoxin. Withdrawal of the offending drugs is the first treatment for heart block.
Does Mobitz Type 1 require treatment?
Mobitz type 1 - this is the least serious type of second degree heart block - it may occasionally cause symptoms of mild dizziness and does not usually require treatment.
Which heart block is Wenckebach?
Wenckebach phenomenon, or type 1 second-degree atrioventricular (AV) block, is a common type of AV block in which there is a delay in transmission of impulses from the atria to the ventricles.
What medication is given for heart block?
Medications that may be used in the management of third-degree AV block (complete heart block) include sympathomimetic or vagolytic agents, catecholamines, and antidotes.
Is Wenckebach Type 1 or Type 2?
Second-degree AV block Mobitz type 1, also known as Wenckebach block.
What is a Wenckebach?
Dr. Roach: Wenckebach is a heart-rhythm disturbance, called a heart block. There are three degrees of heart block. First-degree block is the mildest and rarely needs treatment, although it may (occasionally) predict more serious heart problems. Second-degree block comes in two varieties: type I (Wenckebach), which you have, and type II, ...
Is Wenckebach a common condition?
For someone like you, a trained athlete with a slow heart rate, Wenckebach is common (about 10 percent of trained ath letes). Since you have no symptoms, I agree with your cardiologist completely and can reassure you that the chance of developing worse heart block is low.
What is a Second-Degree AV Block Type I?
An atrioventricular block, in general, occurs when there is a conduction delay between the atria and ventricles of the heart. A second-degree atrioventricular (AV) block type I is also known as Wenckebach or Mobitz type I. This rhythm occurs at the AV node, where conduction of an electrical impulse is impaired.
What Signs or Symptoms May be Present?
A patient with a second-degree AV block type I may have the following signs or symptoms:
What Causes a Second-Degree AV Block Type I?
This heart block is generally considered benign. Most commonly, there is little hemodynamic disruption, and patients are largely asymptomatic.
Treatment of Second-Degree AV Block Type I
It is essential to identify the difference between a second-degree AV block type I (Wenckebach or Mobitz type I) and type II (Mobitz type II) as the management approach to each is different. Patients with a second-degree AV block type I may be asymptomatic.
Next Steps & Considerations
A second-degree AV block type I bradyarrhythmia is often benign; many patients are asymptomatic. If this rhythm was induced by a medication, the rhythm disturbance often reverses after the medication’s cessation or a dosing modification - this would warrant management through expert consultation.
FAQs
Understanding the difference between second-degree AV blocks type I and type II is key to providing accurate and effective patient care. A second-degree AV block type I occurs at the AV node of the heart. On an ECG, the PR interval gradually lengthens until the QRS complex ‘drops’ (more P waves are present than QRS complexes).
How to Prepare for Your ACLS or PALS Exam
Achieving and maintaining these certifications ensures that you are a knowledgeable and skillful healthcare provider ready to respond and care for patients experiencing life-threatening cardiac emergencies. To earn this certification, you’ll need to master common ECG rhythms and the appropriate procedures to respond to each.
Which two increases heart rate which induces Wenckebach phenomenon in Mobitz type 1 block?
Atropine or physical activity: these two increases heart rate which induces Wenckebach phenomenon in Mobitz type 1 block.
Is Mobitz type 2 block a sporadically block?
Mobitz type 2 block implies that some atrial impulses are blocked sporadically. The PR interval is constant (although it may be prolonged). Mobitz type 2 is more serious, because it is usually chronic and tends to progress to third-degree AV block. Moreover, cardiac output may be reduced if many impulses are blocked.
What happens between pacing spikes?
The interval between the pacing spikes increases progressively until there is a non-conducted pacing spike.
Is Mobitz I a symptomatic or asymptomatic?
Mobitz I is usually a benign rhythm, causing minimal haemodynamic disturbance and with low risk of progression to third degree heart block. Asymptomatic patients do not require treatment. Symptomatic patients usually respond to atropine. Permanent pacing is rarely required.
Overview
Heart block is a problem with your heart's electrical system, which makes your heart beat and controls your heart rate and rhythm. The condition is also called atrioventricular (AV) block or a conduction disorder.
Symptoms and Causes
The most common cause of heart block is heart attack. Other causes include heart muscle disease, usually called a cardiomyopathy, heart valve diseases and problems with the heart’s structure. Heart block can also be caused by damage to the heart during open heart surgery, as a side effect of some medications or exposure to toxins.
Diagnosis and Tests
Your cardiologist will first review your medical history and family health history and ask questions about your overall health, your diet and activity level and your symptoms. You’ll also be asked about any medications you are taking (prescription or over-the-counter) and if you smoke or use illicit drugs.
Management and Treatment
Your cardiologist will determine how heart block (its type, location and severity) is affecting your heart’s ability to function and consider your symptoms to determine how to manage your condition. Symptoms and treatment vary from person to person.
Prevention
Some cases of heart block may be congenital (present at birth). But most heart block develops after birth. Some causes can’t be prevented. We also know that the risk of heart block increases with age and so does heart disease. Some causes of heart disease are preventable.
Living With
Avoid close contact with magnetic devices and any device that sends out an electrical field. This includes staying at least six inches from cell phones.
What is Achenbach syndrome?
Achenbach syndrome is a paroxysmal recurring painful bruising of the finger (s) or palm, not associated with serious underlying conditions.
What are the clinical features of Achenbach syndrome?
Achenbach syndrome characteristically follows minor trauma, although this is often not recalled.
How often does Achenbach syndrome recur?
Episodes can recur with minor trauma, with an average frequency of recurrences of 1.2 per year.
Is Achenbach syndrome a clotting disorder?
Achenbach syndrome is diagnosed clinically on the typical history and clinical presentation. Many patients have undergone exhaustive investigations for clotting disorders and ischaemic events, all of which are normal/negative.
What is it called when your heart beats slowly?
When that signal is slowed down or kept from sending its message, it causes a condition called heart block. This affects the rate and rhythm of your heart, or the number of times it beats and the pattern of those beats.
Is a pacemaker considered a minor surgery?
This is considered “minor” surgery and you’ll be sedated for it. Like a backup electrical system, it reminds the heart to beat at a normal rate if it slows or stops. Life After Heart Block. Just like your heart, your pacemaker needs to be treated right to work well.