General
| Symbol | 60 Co |
| Names | cobalt-60, Co-60 |
| Protons (Z) | 27 |
| Neutrons (N) | 33 |
Is Cobalt 60 a radioactive isotope?
Cobalt-60. Cobalt-60 ( 60 Co), is a synthetic radioactive isotope of cobalt with a half-life of 5.2714 years. It is produced artificially in nuclear reactors. Deliberate industrial production depends on neutron activation of bulk samples of the monoisotopic and mononuclidic cobalt isotope 59 Co .
How does cobalt-60 decay?
Cobalt-60 decays by beta and gamma emission to non-radioactive nickel. Most of the radiation from the decay of cobalt- 60 is in the form of gamma emissions; some is in the form of beta particles. Beta particles are generally absorbed in the skin and do not pass through the entire body. Gamma radiation, however, can penetrate the body.
How is Cobalt 60 made from cobalt 59?
By bombarding cobalt 59 with neutrons, in a nuclear reactor, an additional neutron can be captured by the nucleus converting it into cobalt 60. Placing this non-radioactive, Cobalt 59 pellets into a nuclear reactor creates deliberately produced cobalt-60. Over time cobalt-59 absorbs a neutron to become cobalt-60.
Why is Cobalt 60 used as a gamma source?
Cobalt-60 is used as a gamma source because it decays to an excited state of the nickel-60 nucleus, which then cools by emitting a sequence, or a "cascade," of photons. The most common path seems to be.

What is the product of decay cobalt-60?
nickelCobalt-60 decays by beta and gamma emission to non-radioactive nickel. Most of the radiation from the decay of cobalt- 60 is in the form of gamma emissions; some is in the form of beta particles. Beta particles are generally absorbed in the skin and do not pass through the entire body.
What is the radioactive ray produced from the cobalt-60 decay?
γ-raysThe commonly used sources of radiation are cobalt-60, a radioactive element emitting γ-rays, or an accelerator producing a beam of electrons. Cobalt-60 is produced by neutron bombardment of stable cobalt in a nuclear reactor.
Is cobalt-60 an isotope?
Cobalt-60 is the longest-lived radioactive isotope of cobalt, with a half-life of 5.27 years. It is produced by irradiating the stable isotope cobalt-59 with neutrons in a nuclear reactor.
When cobalt-60 undergoes nuclear decay it emits what?
When cobalt 60 undergoes nuclear decay it emits beta particles. A beta particle is essentially an electron. It has no mass and a -1 electric charge....
Which particle is emitted as cobalt-60 decays to nickel-60?
0.32 MeV beta particleCobalt-60 decays, with a half-life of 5.3 years, to the element nickel-60 by the emission of a 0.32 MeV beta particle.
What is the isotope symbol for cobalt-60?
Isotopes of cobaltIsotopeabundancehalf-life (t1/2)58Cosyn70.86 d59Co100%stable60Cotrace5.2714 y2 more rows
Where is cobalt-60 produced?
nuclear reactorsWHERE DOES COBALT-60 COME FROM AND WHERE IS IT FOUND? Cobalt-60 is artificially produced by bombarding a target material, either cobalt-59 or nickel-60, with neutrons. This reaction is produced by nuclear weapons detonations and in nuclear reactors.
How is cobalt-60 disposed?
At the end of their useful life, typically 20 years, cobalt- 60 pencils are removed and generally returned to the supplier for re-use, recycling or disposal.
Why is cobalt-60 used?
What is it used for? Co-60 is used medically for radiation therapy as implants and as an external source of radiation exposure. It is used industrially in leveling gauges and to x-ray welding seams and other structural elements to detect flaws. Co-60 also is used for food irradiation, a sterilization process.
How many isotopes does cobalt have?
There are 30 isotopes and isomers of cobalt that are recognized.
How is carbon-14 produced in the atmosphere?
Carbon-14 is produced in the stratosphere by nuclear reactions of atmospheric nitrogen with thermal neutrons produced naturally by cosmic rays (with the highest production rate 10 to 13 miles above Earth's poles), as well as by atmospheric nuclear weapons testing in the 1950s and '60s.
What does nickel decay into?
Nickel-63 decays by emitting a beta particle and nickel-59 decays by electron capture, in which low-energy gamma radiation is emitted. While in the body, nickel presents a health hazard from the beta particles and gamma radiation; the main health concern is associated with the increased likelihood of inducing cancer.
How is Co-60 produced?
Radioactive Co-60 is produced commercially through linear acceleration for use in medicine and industry. Co-60 also is a byproduct of nuclear reactor operations, when metal structures, such as steel rods, are exposed to neutron radiation.
What is CO-60 used for?
Co-60 also is used for food irradiation, a sterilization process.
What happens if you eat Co-60?
Because it decays by gamma radiation, external exposure to large sources of Co-60 can cause skin burns, acute radiation sickness, or death. Most Co-60 that is ingested is excreted in the feces; however, a small amount is absorbed by the liver, kidneys, and bones.
Is Co-60 a solid or a powder?
Co-60 occurs as a solid material and might appear as small metal disks or in a tube, enclosed at both ends, that holds the small disks. Co-60 can occur as a powder if the solid sources have been ground or damaged.
How do calcium-40 and zirconium-90 decay?
The paper that you cite describes decays in calcium-40 and zirconium-90 by emission of two photons at once. Both of these nuclides have a first excited state with spin-parity 0 +, the same as their ground state. Since a single photon must carry away at least one unit of spin, these excitations cannot decay by one-photon emission. Mostly they decay by emitting a "virtual" photon, which produces a real positron-electron pair in the field of the nucleus. The paper you have linked measures a rare mode where two real photons are produced, and a surprising observation that in the double decay E -type photons are produced at the same rate as M -type photons. Usually, in nuclear decays, magnetic-dipole transitions are suppressed compared to electric-dipole transitions.
Is cobalt 60 a long-lived transition?
That photon must carry lots of orbital angular momentum, in addition to its spin, so the first excited state of cobalt is a relatively long-lived isomer (about ten minutes).
Is double photon decay paper rare?
These sorts of cascades are the bread and butter of nuclear physics; the double-photon decay paper you found is much rarer.
What is the half life of cobalt 60?
For other uses, see Cobalt-60 (disambiguation). Cobalt-60 ( 60 Co) is a synthetic radioactive isotope of cobalt with a half-life of 5.2713 years. It is produced artificially in nuclear reactors.
Which country has the most cobalt 60?
Argentina, Canada and Russia are the largest suppliers of cobalt-60 in the world.
How long does cobalt 60 last?
Cobalt-60 ( 60 Co) is a synthetic radioactive isotope of cobalt with a half-life of 5.2713 years. It is produced artificially in nuclear reactors. Deliberate industrial production depends on neutron activation of bulk samples of the monoisotopic and mononuclidic cobalt isotope 59. Co. .
What are the physical properties of cobalt?
The physical properties of cobalt such as resistance to bulk oxidation and low solubility in water give some advantages in safety in the case of a containment breach over some other gamma sources such as caesium-137 . The main uses for 60. Co. are: As a tracer for cobalt in chemical reactions.
When was the first irradiator invented?
Prototype irradiator for food irradiation to prevent spoilage, 1984. The 60
Which scientist discovered that the -decay process violated parity?
In 1957, Chien-Shiung Wu et al. discovered the β-decay process violated parity, implying nature has a handedness. nuclei by cooling the source to low temperatures in a magnetic field. Wu's observation was that more β-rays were emitted in the opposite direction to the nuclear spin.
Is cobalt a salting element?
As a radiation source for food irradiation and blood irradiation. Cobalt has been discussed as a " salting " element to add to nuclear weapons, to produce a cobalt bomb, an extremely "dirty" weapon which would contaminate large areas with 60. Co. nuclear fallout, rendering them uninhabitable.
What is Cobalt 60 used for?
One of the main uses of Cobalt 60 is in radiotherapy where cancer cells are exposed to a beam of high energy gamma radiation, effectively killing them. Its gamma rays are also used in the sterilisation of food and medical equipment and they can even be used in levelling devices and thickness gauges to detect structural errors.
Can Cobalt 60 be used in nuclear weapons?
Unfortunately, Cobalt 60 can also be used in weapons of mass destruction. Dirty nukes or salty nukes are nuclear weapons that contain Cobalt 59 but during nuclear fission, it turns into Cobalt 60 which contaminates the surrounding area for decades. Officially, there are no countries in possession of such weapons and let’s hope that even if there are, they will never use them.
Is Cobalt 60 a radioactive isotope?
Cobalt 60 is a radioactive isotope of Cobalt and it is produced by neutron activation of stable Cobalt 59 in nuclear reactors. Since it has a short half-life of only 5.3 years, it does not occur in nature and all samples that exist are synthetic. A single gram of Co-60 has an activity of 44TBq and it undergoes a beta decay into an excited state of Nickel 60 which emits two gamma rays at 1173 and 1332 keV before becoming stable.
When was cobalt 60 discovered?
Radioactive cobalt-60 was discovered by Glenn T. Seaborg and John Livingood at the University of California - Berkeley in the late 1930's. By bombarding cobalt 59 with neutrons, in a nuclear reactor, an additional neutron can be captured by the nucleus converting it into cobalt 60.
What is cobalt-60?
Over time cobalt-59 absorbs a neutron to become cobalt-60. After removal from the. reactor the cobalt-60 is double enclosed in stainless steel sealed sources . Cobalt-60 emits Beta and Gamma Rays.
Does Cobalt 60 emit gamma radiation?
Cobalt-60 emits Beta and Gamma Rays. Where Beta radiation is present, shielding may be required. Cobalt-60 is unstable and in trying to become stable it emits a beta-particle and two photons of gamma radiation. An isotope of nickel will remain.
What is the half life of Cobalt 60?
Cobalt-60 (half-life = 5.27 years) is the largest revenue-producing commercial radioisotope in the world. Most of its current use is in the sterilization industry, primarily for medical products intended for human consumption. (See Table VIII for a list of items that are sterilized.)
How to make cobalt-60?
The easiest way to produce cobalt-60 is by bombarding cobalt-59 with slow neutrons, as shown below.
Where are 60 Co irradiators made?
Cobalt-60 irradiators are produced and sold predominantly by MDS Nordion, headquartered in Kanata, Ontario, Canada. The 60 Co is produced in CANDU reactors, which are designed to use control rods made from 59 Co. Thus, the dual use of reactor control and radioisotope production enables the 60 Co production cost to be minimized. MDS Nordion purchases the control rods from Atomic Energy Limited of Canada, recovers the 60 Co, and fabricates 60 Co irradiation sources for sale.
How long does nickel-60 decay?
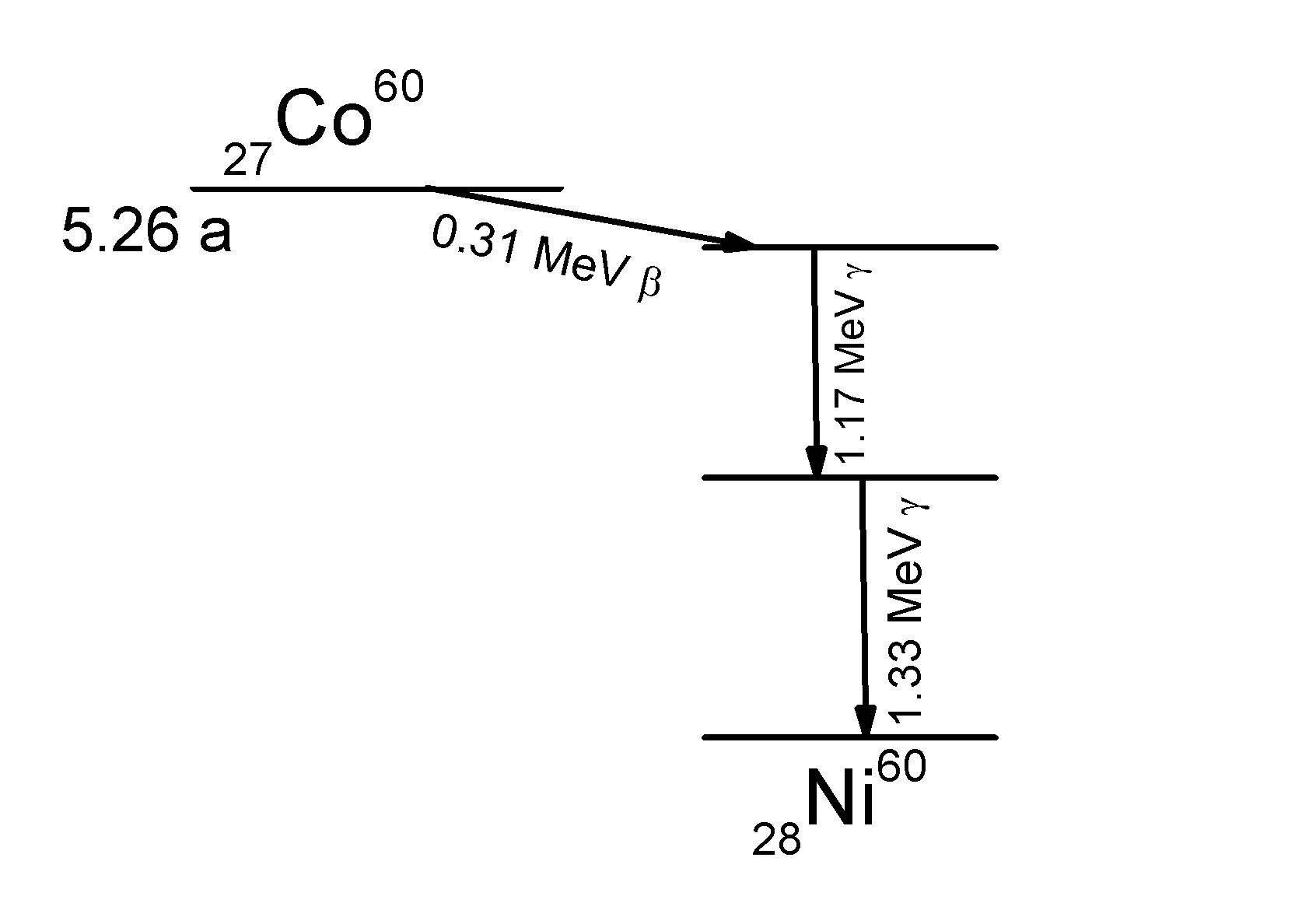
Cobalt-60 decays, with a half-life of 5.3 years, to the element nickel-60 by the emission of a 0.32 MeV beta particle. The nickel-60 daughter nuclide is formed at an excited energy state, and loses this energy immediately with the emission of two gamma rays of energies 1.17 and 1.33 MeV, settling at a stable nuclear state.
How is 60 Co irradiated?
The radiation source, 60 Co, in the form of cylindrical metal rods (“pencil” shaped), is encapsulated within sealed capsules. A number of capsules sufficient to provide the desired radiation source levels are placed in shielded containers for transportation to and from storage at shielded irradiation facilities. At the facility sites, the packaged products to be sterilized are placed on pallets and remotely conveyed inside the shielded radiation facility. The radiation source shield is then removed for the period of time necessary to irradiate and sterilize the packaged products. Finally, the pallet holding the sterilized packaged products is remotely conveyed out of the irradiation facility.
What is the dead time of a coincidence mixer?
A non-extendable dead time of 8.00 ± 0.04 μs was imposed on both channels using paralysis units. The coincidence - mixer resolving time was set at about 1 μs and subsequently measured to be 1.081 ± 0.010 μs.
When did low cobalt pins and rollers become standard on all replacement CRs?
Since 1983 , low cobalt pins and rollers have become standard on all replacement CR, as well as being installed as retrofits on original design CRBs. This change, eliminating the use of cobalt-base alloys, resulted in the single largest reduction in cobalt activity from CRs.
How many radioisotopes are in cobalt?
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Naturally occurring cobalt ( 27 Co) is composed of 1 stable isotope, 59 Co. 28 radioisotopes have been characterized with the most stable being 60 Co with a half-life of 5.2714 years, 57 Co with a half-life of 271.8 days, 56 Co with a half-life of 77.27 days, and 58 Co with a half-life of 70.86 days.
What is the primary decay mode of cobalt?
The primary decay mode for isotopes with atomic mass unit values less than that of the most abundant stable isotope, 59 Co, is electron capture and the primary mode of decay for those of greater than 59 atomic mass units is beta decay. The primary decay products before 59 Co are iron isotopes and the primary products after are nickel isotopes.
What is the use of cobalt in medicine?
Use of cobalt radioisotopes in medicine. Cobalt-57 ( 57 Co or Co-57) is a radioactive metal that is used in medical tests; it is used as a radiolabel for vitamin B 12 uptake. It is useful for the Schilling test. Cobalt-60 ( 60 Co or Co-60) is a radioactive metal that is used in radiotherapy.
How long does a radioactive isotope last?
All of the remaining radioactive isotopes have half-lives that are less than 18 hours and the majority of these have half-lives that are less than 1 second. This element also has 11 meta states, all of which have half-lives less than 15 minutes. The isotopes of cobalt range in atomic weight from 47 Co to 75 Co.
How are radioactive isotopes produced?
Radioactive isotopes can be produced by various nuclear reactions. For example, the isotope 57 Co is produced by cyclotron irradiation of iron. The principal reaction involved is the (d,n) reaction 56 Fe + 2 H → n + 57 Co.
What is the use of cobalt 60?
Cobalt-60 (Co-60 or 60 Co) is useful as a gamma ray source because it can be produced in predictable quantities, and for its high radioactive activity simply by exposing natural cobalt to neutrons in a reactor for a given time. The uses for industrial cobalt include: Sterilization of medical supplies and medical waste.
What is 60 Co?
Cobalt-60 ( 60 Co or Co-60) is a radioactive metal that is used in radiotherapy. It produces two gamma rays with energies of 1.17 MeV and 1.33 MeV. The 60 Co source is about 2 cm in diameter and as a result produces a geometric penumbra, making the edge of the radiation field fuzzy.
Overview
Cobalt-60 ( Co) is a synthetic radioactive isotope of cobalt with a half-life of 5.2713 years. It is produced artificially in nuclear reactors. Deliberate industrial production depends on neutron activation of bulk samples of the monoisotopic and mononuclidic cobalt isotope Co . Measurable quantities are also produced as a by-product of typical nuclear power plant operation and may be detected externally when leaks occur. In the latter case (in the absence of added cobalt) the inci…
Activity
Corresponding to its half-life, the radioactive activity of one gram of Co is 44 TBq (1,200 Ci). The absorbed dose constant is related to the decay energy and time. For Co it is equal to 0.35 mSv/(GBq h) at one meter from the source. This allows calculation of the equivalent dose, which depends on distance and activity.
For example, a Co source with an activity of 2.8 GBq, which is equivalent to 60 μg of pure Co , ge…
Decay
The diagram shows a (simplified) decay scheme of Co and Co . The main β-decay transitions are shown. The probability for population of the middle energy level of 2.1 MeV by β-decay is 0.0022%, with a maximum energy of 665.26 keV. Energy transfers between the three levels generate six different gamma-ray frequencies. In the diagram the two important ones are marked. Internal conversion energies are well below the main energy levels.
Applications
The main advantage of Co is that it is a high-intensity gamma-ray emitter with a relatively long half-life, 5.27 years, compared to other gamma ray sources of similar intensity. The β-decay energy is low and easily shielded; however, the gamma-ray emission lines have energies around 1.3 MeV, and are highly penetrating. The physical properties of cobalt such as resistance to bulk oxidation and low solubility in water give some advantages in safety in the case of a containmen…
Production
There is no natural Co in existence on earth; thus, synthetic Co is created by bombarding a Co target with a slow neutron source. Californium-252, moderated through water, can be used for this purpose, as can the neutron flux in a nuclear reactor. The CANDU reactors can be used to activate Co , by substituting the control rods with cobalt rods. In the United States, it is now being produced in a BWR at Hope Creek Nuclear Generating Station. The cobalt targets are substituted here for a …
Safety
After entering a living mammal (such as a human being), some of the Co is excreted in feces. The remainder is taken up by tissues, mainly the liver, kidneys, and bones, where the prolonged exposure to gamma radiation can cause cancer. Over time, the absorbed cobalt is eliminated in urine.
Cobalt is an element used to make steel. Uncontrolled disposal of Co in scrap metal is responsibl…
Parity
In 1957, Chien-Shiung Wu et al. discovered the β-decay process violated parity, implying nature has a handedness.
In the Wu experiment her group aligned radioactive Co nuclei by cooling the source to low temperatures in a magnetic field. Wu's observation was that more β-rays were emitted in the opposite direction to the nuclear spin. This asymmetry violates parity conservation.
Suppliers
Argentina, Canada and Russia are the largest suppliers of Co in the world. Both Argentina and Canada have (as of 2022) an all heavy water reactor fleet when it comes to nuclear power. Canada has the CANDU in numerous locations throughout Ontario as well as Point Lepreau Nuclear Generating Station in New Brunswick, while Argentina has two German supplied heavy water reactors at Atucha nuclear power plant and a Canadian-built CANDU at Embalse Nuclear Power St…