
What are the characteristics of a Paramecium?
What are characteristics of paramecium?
- Shape and Size. P.
- Pellicle. Its whole body is covered with a flexible, thin and firm membrane called pellicles.
- Cilia. Cilia refers to the multiple, small hair-like projections that cover the whole body.
- Cytostome. It contains the following parts:
- Nucleus.
- Vacuole.
What is the genus and species of Paramecium?
Genus: Paramecium Species: Paramecium Bursaria. Paramecium bursaria is a protozoan that has a symbiotic relationship with green algae called Zoochlorellae, because the algae lives in its cytoplasm. The algae provides the paramecium with food, and the paramecium provides the algae with movement. Paramecium are more often found in stagnant warm ...
What is the common name for Paramecium?
- The cell size varies from 50 µ to 300 µ. ...
- The cellular cytoplasm is enclosed in a pellicle. ...
- Cilia project from the depressions in the pellicle and cover the entire body surface. ...
- Protoplasm is divided into outer ectoplasm and inner endoplasm, which is granular
- Trichocysts are present and embedded in the ectoplasm. ...
- The endoplasmic granules reserve food. ...
What is the Kingdom of Paramecium?
Paramecium is a unicellular, eukaryotic organism belonging to the kingdom Protista. Its size varies between 50 to 300um, depending on the species. There are a total of 10 species of Paramecium; Aurelia and Caudatum are two of them. These ciliate protozoa are found mainly in freshwater as well as brackish and marine water.
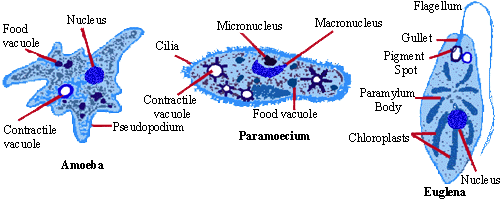
What type of protist is Paramecium?
Paramecium are unicellular protozoans classified in the Genus Paramecium, and the Kingdom Protista. The Paramecium is commonly found throughout the world in fresh and marine water containing bacteria and decaying organic matter.
Is Paramecium a bacteria or protozoa?
So, the correct answer is 'Protozoan'
What kingdom is Paramecium belong to?
ChromistaParamecium / KingdomAmoeba and Paramecium belong to Kingdom Protista. Amoeba belongs to phylum Protozoa while Paramecium is a ciliate or belongs to phylum Ciliophora.
Is Paramecium a protist?
Paramecium or paramecia are single-celled protists that are naturally found in aquatic habitats. They are typically oblong or slipper-shaped and are covered with short hairy structures called cilia.
What is the family of Paramecium?
ParameciidaeParamecium / FamilyParameciidae is a family of ciliates in the order Peniculida. Members of this family have differentiated anterior and posterior regions and are bounded by a hard but elastic pellicle. The family contains the genera Paramecium and Physanter. Wikipedia
How many daughter cells does the paramecium have?
Half of the nuclei will start to behave like, and become, macronuclei and the other half will behave like, and become, micronuclei. Then the two paramecium divide into four daughter cells and then again to form a total of eight daughter cells each with a micronucleus and a macronucleus.
What is the contractile vacuole?
It is constantly working to regulate this balance. There are two different types of contractile vacuoles. One type is a canal-fed vacuole and a vesicle-fed vacuole. The other is called a canal-fed vacuole. Pellicle – The pellicle is what helps the paramecium keep their shape although it is capable of deformations.
How does the paramecium work?
The paramecium uses these receptors to track down the bacteria. Once the bacteria are near enough it uses the cilia to push these organisms, along with some water, into the vestibulum. They then move along the buccal cavity until it reaches the mouth (cytostome). From there the bacteria will be acidified and killed.
How does the vacuole work?
The vacuole is used to transport waste liquid out of the cell. The vacuoles work by collapsing in an alternating fashion which empties the liquid out through pores. In short, if there is too much water in the cell, it will rupture, so the contractile vacuole is crucial to the survival of the paramecium.
What is the function of the cilia during mating?
During the mating process cilia are used to initiate the mating process also known as conjugation. Contractile vacuole – There are typically two contractile vacuoles on a paramecium. One located at each end of the cell opposite from the cytostome. The vacuole is used to transport waste liquid out of the cell.
What are the functions of the cilia?
The two main functions of the cilia are for movement and for ingesting food. The cilia responsible for ingesting food are located in a funnel shaped depressed region of the cell called the gullet. All other cilia on the paramecium are thought to be used for movement except for the caudal cilia which are longer cilia.
What is the classification of paramecium?
Paramecium are officially classified in the following way: Kingdom: Protista. Subkingdom: Protozoa. Phylum: Ciliophora. Class: Oligohymenophorea. Subclass: Hymenostomatia. Order: Hymenostomatida. Suborder: Peniculina.
What is the groove in the paramecia?
In all species, there is a deep oral groove running from the anterior of the cell to its midpoint. This is lined with inconspicuous cilia which beat continuously, drawing food inside the cell. Paramecia live mainly by heterotrophy, feeding on bacteria and other small organisms.
What happens during conjugation?
During conjugation, two Paramecia of a compatible mating type come together and a bridge forms between their cytoplasms. Their respective micronuclei undergo meiosis, and haploid micronuclei are exchanged over the bridge. Following conjugation, the cells separate. The old macronuclei are destroyed, and both post-conjugants form new macronuclei, by amplification of DNA in their micronuclei. Conjugation is followed by one or more "exconjugant divisions".
What is the function of the paramecium?
The macronucleus controls non-reproductive cell functions, expressing the genes needed for daily functioning. The micronucleus is the generative, or germline nucleus, containing the genetic material that is passed along from one generation to the next.
What is the relationship between Paramecium and other organisms?
Symbiosis. Some species of Paramecium form mutualistic relationships with other organisms. Paramecium bursaria and Paramecium chlorelligerum harbour endosymbiotic green algae, from which they derive nutrients and a degree of protection from predators such as Didinium nasutum.
How does the paramecium propel itself?
A Paramecium propels itself by whiplash movements of the cilia, which are arranged in tightly spaced rows around the outside of the body. The beat of each cilium has two phases: a fast "effective stroke", during which the cilium is relatively stiff, followed by a slow "recovery stroke", during which the cilium curls loosely to one side and sweeps forward in a counter-clockwise fashion. The densely arrayed cilia move in a coordinated fashion, with waves of activity moving across the "ciliary carpet", creating an effect sometimes likened to that of the wind blowing across a field of grain.
What does Paramecium feed on?
Paramecium feeding on Bacteria. Paramecia feed on microorganisms like bacteria, algae, and yeasts. To gather food, the Paramecium makes movements with cilia to sweep prey organisms, along with some water, through the oral groove (vestibulum, or vestibule), and into the cell.
How big is a paramecium?
Description. Species of Paramecium range in size from 50 to 330 micrometres (0.0020 to 0.0130 in) in length. Cells are typically ovoid, elongate, foot- or cigar-shaped. The body of the cell is enclosed by a stiff but elastic structure called the pellicle. This consists of the outer cell membrane (plasma membrane), ...
How long is a paramecium?
Paramecium vary in length from about 0.05 to 0.32 mm ( 0.002 to 0.013 inch).
What are the two types of nuclei in Paramecia?
Paramecia have two kinds of nuclei: a large ellipsoidal nucleus called a macronucleusand at least one small nucleus called a micronucleus. Both types of nuclei contain the full complement of genesthat bear the hereditary information of the organism.
What is the function of contractile vacuoles?
Contractile vacuoles function in regulating the water content within the cell and may also be considered excretory structures, since the expelled water contains metabolic wastes. Get a Britannica Premium subscription and gain access to exclusive content. Subscribe Now.
How do cilia move?
Cilia occur in large numbers and move in a coordinated way. Ciliated cells within the vertebrate body propel fluid and mucus along interior passages, such as the lining…. nervous system: Organelle systems. In a ciliate such as Paramecium, the beating of the cilia—which propels it along—is not random, but coordinated.
What is the genus of Paramecium?
Paramecium, genus of microscopic, single-celled, and free-living protozoans. Most species can be cultivatedeasily in the laboratory, making them ideal model organisms, well suited for biological study. Parameciumvary in length from about 0.05 to 0.32 mm (0.002 to 0.013 inch).
What is an encyclopedia editor?
Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree. ...
Where does the beating of the cilia begin?
Beating of the cilia begins at one end of the organism and moves in regularly spaced waves to the other end, suggesting that coordinating influences are conducted longitudinally. A system of fibrils…. chemoreception: Single-celled organisms.
How many nuclei are in Paramecia?
Paramecia contain at least two nuclei, micronuclei (one or more) and one macronucleus. Micronuclei have diploid chromosomes and take part in the reproduction. Macronuclei regulate all vital metabolic activities and growth. The macronucleus has multiple copies of the genome, i.e. polyploid.
How many times does an individual have to multiply before reproducing?
An individual has to multiply asexually 50 times before reproducing by conjugation. In the process of conjugation, the conjugation bridge is formed and united paramecia are known as conjugants. Macronuclei of both the cells disappear. The micronucleus of each conjugant forms 4 haploid nuclei by meiosis.
How does paramecium reproduce?
Paramecium Reproduction. Asexual Reproduction in paramecium is by binary fission. The mature cell divides into two cells and each grows rapidly and develops into a new organism. Under favourable conditions, Paramecium multiplies rapidly up to three times a day .
What kingdom is Paramecium in?
Paramecium Classification. Paramecium is unicellular and eukaryotic, so they are kept in the kingdom Protista. They are ciliated protozoan and come under phylum Ciliophora. The common species of Paramecium include: Paramecium aurelia. Paramecium caudatum. Paramecium woodruffi. Paramecium trichium. Domain.
What do holozoic worms eat?
They are mostly heterotrophic. They feed on bacteria, algae, yeast and other microorganisms. They are holozoic. The food-laden water is drawn inside by the movement of cilia and it goes to the cytostome and to the gullet (cytopharynx).
Where is the oral groove located?
The oral groove opens in the mouth known as cytostome and to the gullet or pharynx. There are numerous food vacuoles present for digesting food. There is an anal pore present on the ventral surface in the posterior half of the cell known as cytoproct or cytopyge, which helps in egesting undigested food.
How is food acted upon?
The food is acted upon by digestive enzymes present in the food vacuoles. The undigested residue is egested through the temporary anal pore (cytopyge). Some of the Paramecium species, e.g. Paramecium bursaria, etc. form a symbiotic relationship with green algae.
What is the role of macronucleus in a cell?
The macronucleus plays a role in non-reproductive cell functions including the expression of genes needed for the everyday functioning of the cell. Paramecium reproduces asexually through binary fission. The micronuclei during reproduction undergo mitosis while the macronuclei divide through amitosis.
What are the two types of vacuoles in the paramecium?
Paramecium consists of two types of vacuoles: contractile vacuole and food vacuole. Contractile vacuole: There are two contractile vacuoles present close to the dorsal side, one on each end of the body. They are filled with fluids and are present at fixed positions between the endoplasm and ectoplasm.
What are the functions of a contractile vacuole?
Some of the main functions of contractile vacuoles include osmoregulation, excretion, and respiration. Food vacuole: Food vacuole is non-contractile and is roughly spherical in shape. In the endoplasm, the size of food vacuole varies and digest food particles, enzymes alongside a small amount of fluid and bacteria.
What does Paramecium eat?
Paramecium also feeds on other microorganisms like yeasts and bacteria. To gather the food it makes use of its cilia, making quick movements with cilia to draw the water along with its prey organisms inside the mouth opening through its oral groove. The food further passes into the gullet through the mouth.
What is the name of the cell that controls the vegetative function of paramecium?
It's densely packed within the DNA (chromatin granules). The macronucleus controls all the vegetative functions of paramecium hence called the vegetative nucleus. Micro Nucleus: The micronucleus is found close to the macronucleus. It is a small and compact structure, spherical in shape.
Which canals pour liquid from the paramecium into the contractile vacuole?
These radical canals consist of a long ampulla, a terminal part and an injector canal which is short in size and opens directly into the contractile vacuole. These canals pour all the liquid collected from the whole body of paramecium into the contractile vacuole which makes the vacuole increase in size.
What is the structure of cadatum?
Structure and Function. 1. Shape and Size. P. cadatum is a microscopic, unicellular protozoan. Its size ranges from 170 to 290um or up to 300 to 350um. Surprisingly, paramecium is visible to the naked eye and has an elongated slipper like shape, that’s the reason it’s also referred to as a slipper animalcule.

Other uses
- Cilia also aid in feeding by pushing food into a rudimentary mouth opening known as the oral groove. Paramecia feed primarily on bacteria, but are known to eat yeast, unicellular algae and even some non-living substances such as milk powder, starch and powdered charcoal, accordin…
Types
- The two types of nuclei are the micronucleus and macronucleus. The micronucleus is diploid; that is, it contains two copies of each paramecium chromosome. Forney notes that the micronucleus contains all of the DNA that is present in the organism. \"It's the DNA that is passed from one generation to the another during sexual reproduction,\" he said. On the other hand, the macronuc…
Purpose
- Why the presence of two distinct nuclei? One evolutionary reason is that it is a mechanism by which paramecia and other ciliates can stave off genetic intruders: pieces of DNA that embed themselves into the genome. \"In the case of ciliates, there's a mechanism in which, if a piece of DNA is in the micronucleus but it's not in the macronucleus, it will be removed from the next ma…
Reproduction
- Paramecia can reproduce either asexually or sexually, depending on their environmental conditions. Asexual reproduction takes place when ample nutrients are available, while sexual reproduction takes place under conditions of starvation. In addition, paramecia can also undergo \"autogamy\" or self-fertilization under conditions of prolonged starvation, according to de Onda…
Cause
- During binary fission, one paramecium cell divides into two genetically identical offspring, or daughter cells. According to Forney, the micronucleus undergoes mitosis, but the macronucleus divides another way, called an amitotic, or non-mitotic, mechanism. \"It is not based on mitosis but it [macronucleus] divides between the two cells and somehow is able to keep approximately …
Mechanism
- \"Autogamy is essentially the same thing as conjugation, but it is only happening with a single cell,\" Forney said. During this process, the micronucleus replicates multiple times. One of these new micronuclei undergo rearrangement of their genetic content. Some DNA is fragmented and some DNA sequences, known as \"Internal Eliminated Sequences,\" are removed, according to d…
Classification
- The methods of classifying paramecia have changed over the years. The earliest methods were through visual observation and were based on morphology, ultimately describing all paramecia as either aurelia or bursaria. More recently, classification has combined morphological observation with molecular and genetic information. This has helped to develop a family tree, known as a ph…
Discovery
- Strüder-Kypke said that a method of identifying species known as \"DNA barcoding\" has been used for Paramecium. \"Identification of species based on the sequence of a particular fragment of DNA has been referred to as DNA barcoding,\" she explained. \"Just like a barcode in the stores identifies each product, a short DNA sequence that is sufficiently divergent, can identify each sp…
Taxonomy
- New insights into Paramecium taxonomy and the existence of new species continue to be described even today. The 19th morphospecies,Paramecium buetschlii, was discovered in a freshwater pool in Norway and described in a 2015 research paper, published in the journal Organisms Diversity & Evolution. The same paper also described three new \"cryptic species\" fo…
Overview
Paramecium is a genus of eukaryotic, unicellular ciliates, commonly studied as a representative of the ciliate group. Paramecia are widespread in freshwater, brackish, and marine environments and are often very abundant in stagnant basins and ponds. Because some species are readily cultivated and easily induced to conjugate and divide, it has been widely used in classrooms and lab…
Historical background
Paramecia were among the first ciliates to be seen by microscopists, in the late 17th century. They were probably known to the Dutch pioneer of protozoology, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, and were clearly described by his contemporary Christiaan Huygens in a letter of 1678. The earliest known illustration of a Paramecium was published anonymously in Philosophical Transactions of the …
Description
Species of Paramecium range in size from 50 to 330 micrometres (0.0020 to 0.0130 in) in length. Cells are typically ovoid, elongate, foot- or cigar-shaped.
The body of the cell is enclosed by a stiff but elastic structure called the pellicle. This consists of the outer cell membrane (plasma membrane), a layer of flattened membrane-bound sacs called alveoli, and an inner membrane called …
Movement
A Paramecium propels itself by whiplash movements of the cilia, which are arranged in tightly spaced rows around the outside of the body. The beat of each cilium has two phases: a fast "effective stroke", during which the cilium is relatively stiff, followed by a slow "recovery stroke", during which the cilium curls loosely to one side and sweeps forward in a counter-clockwise fashion. The densely arrayed cilia move in a coordinated fashion, with waves of activity moving …
Gathering food
Paramecia feed on microorganisms like bacteria, algae, and yeasts. To gather food, the Paramecium makes movements with cilia to sweep prey organisms, along with some water, through the oral groove (vestibulum, or vestibule), and into the cell. The food passes from the cilia-lined oral groove into a narrower structure known as the buccal cavity (gullet). From there, food particles pass through a small opening called the cytostome, or cell mouth, and move into t…
Symbiosis
Some species of Paramecium form mutualistic relationships with other organisms. Paramecium bursaria and Paramecium chlorelligerum harbour endosymbiotic green algae, from which they derive nutrients and a degree of protection from predators such as Didinium nasutum. Numerous bacterial endosymbionts have been identified in species of Paramecium. Some intracellular bacteria, known as Kappa particles, give Paramecia that have them the ability to kill other strain…
Genome
The genome of the species Paramecium tetraurelia has been sequenced, providing evidence for three whole-genome duplications.
In some ciliates, like Stylonychia and Paramecium, only UGA is decoded as a stop codon, while UAG and UAA are reassigned as sense codons (that is, codons that code for standard amino acids), coding for the amino acid glutamic acid.
Learning
The question of whether Paramecia exhibit learning has been the object of a great deal of experimentation, yielding equivocal results. However, a study published in 2006 seems to show that Paramecium caudatum may be trained, through the application of a 6.5 volt electric current, to discriminate between brightness levels. This experiment has been cited as a possible instance of cell memory, or epigenetic learning in organisms with no nervous system.