
What languages are spoken in Bantu?
- Beti (1.7 million: 900,000 Bulu, 600,000 Ewondo, 120,000 Fang, 60,000 Eton, 30,000 Bebele)
- Basaa (230,000)
- Duala (350,000)
- Manenguba languages (230,000)
Who are the Bantu speaking people?
South African Bantu-speaking peoples are the majority of Black South Africans. Occasionally grouped as Bantu, the term itself is derived from the word for "people" common to many of the Bantu languages.
What languages are spoken by Saan people?
What Languages Are Spoken in San Marino?
- Linguistic Affiliation in San Marino. There are two official languages spoken in San Marino: standard Italian and a Sammarinese dialect. ...
- Italian. The primary and the national language of San Marino is Italian, and the country ranks 19th in terms of the number of native Romance language speakers.
- Sammarinese. ...
What languages do the Nubians speak?
- Nobiin, the largest Nubian language with 545,000 speakers in Egypt, Sudan, and the Nubian diaspora. ...
- Kenzi ( endonym: Mattokki) with 100,000 speakers in Egypt and Dongolawi ( endonym: Andaandi) with 180,000 speakers in Sudan. ...
- Midob (Meidob) with 30,000 speakers. ...
What language is spoken in Bantu?
SwahiliBantu languages such as Swahili, Zulu, Chichewa or Bemba are spoken by an estimated 240 million speakers in 27 African countries, and are one of the most important language groups in Africa in terms of geographical and demographic distribution.
What are 3 major Bantu languages?
Twelve Bantu languages are spoken by more than five million people, including Rundi, Rwanda, Shona, Xhosa, and Zulu.
How many languages did the Bantu speak?
The Bantu languages are a large family of languages spoken primarily in the Southern part of Africa. Over 500 languages are classified in this family, including Swahili, Xhosa, and Zulu.
What was the first Bantu language?
Proto-Bantu is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Bantu languages, a subgroup of the Southern Bantoid languages. It is thought to have originally been spoken in West/Central Africa in the area of what is now Cameroon.
What race are Bantu?
They are Black African speakers of Bantu languages of several hundred indigenous ethnic groups. The Bantu live in sub-Saharan Africa, spread over a vast area from Central Africa across the African Great Lakes to Southern Africa.
Is Bantu a Swahili?
Swahili is characteristically Bantu in its grammar, and it has a large vocabulary of word roots traceable to a common Bantu stock.
Why is Bantu called so?
The name was said to be coined to represent the word for "people" in loosely reconstructed Proto-Bantu, from the plural noun class prefix *ba- categorizing "people", and the root *ntʊ̀ - "some (entity), any" (e.g. Zulu umuntu "person", abantu "people", into "thing", izinto "things").
Is Zulu a Bantu language?
IsiZulu is part of the Nguni sub group of the Bantu languages which are part of the Niger-Congo language family. As one of the Nguni languages, IsiZulu is mostly closely related to other major languages such as isiXhosa, isiSwati (in Swaziland) and isiNdebele (in Zimbabwe) and some parts of South Africa.
Does Bantu mean black?
Usage notes. Black South Africans were at times officially called "Bantus" by the Apartheid regime. New legislation and documents from the South African government have replaced "Bantu" with "Black" due to the former word's derogatory connotations.
What is the oldest language in Africa?
Egyptian1. Egyptian – 2690 BC (circa. 4700 years old) The first known language ever was a proto-language on the African continent, and the first known proto-writing system was created in Nigeria. So, it is perhaps no surprise that the oldest language on this list is also from and used in Africa – Egyptian.
What language did African slaves speak?
In the English colonies Africans spoke an English-based Atlantic Creole, generally called plantation creole. Low Country Africans spoke an English-based creole that came to be called Gullah. Gullah is a language closely related to Krio a creole spoken in Sierra Leone.
What are the 3 major languages in Africa?
The most widely spoken languages of Africa, Swahili (200 million), Yoruba (45 million), Igbo (30 million), and Fula (35 million) all belong to the Niger-Congo family. Learn more about the Niger-Congo language family on Ethnologue.
What are the top 3 most spoken languages in Africa?
The List of 10 Most Spoken Languages in AfricaSwahili: Swahili, known as Kiswahili in the native tongue, is a Bantu language spoken by some 150 million Africans in the African Great Lakes region in Central and Southern Africa. ... Arabic: ... French: ... Hausa: ... Yoruba: ... Oromo: ... Igbo: ... Amharic:More items...•
What are the top 4 languages spoken in South Africa?
IsiZulu is South Africa's biggest language, spoken by almost a quarter (23%) of the population. Our other official languages are isiXhosa (spoken by 16%), Afrikaans (13.5%), English (10%), Sesotho sa Leboa (9%), Setswana and Sesotho (both 8%), Xitsonga (4.5%), siSwati and Tshivenda (both 2.5%), and isiNdebele (2%).
What are the 5 major language families in Africa?
African Languages are categorized into five major language families including Afroasiatic, Austronesian, Indo-European, Niger–Congo (Bantu and non-Bantu) and Nilo-Saharan languages.
What is the Bantu language?
Predominantly Christianity, traditional faiths; minority. Bantu peoples are the speakers of Bantu languages, comprising several hundred indigenous ethnic groups in Africa, spread over a vast area from Central Africa across the African Great Lakes to Southern Africa.
What brought the Bantu to Madagascar?
The Bantu migrations, and centuries later, the Indian ocean slave trade, brought Bantu influence to Madagascar, the Malagasy people showing Bantu admixture, and their Malagasy language Bantu loans.
What are some examples of Bantu states?
examples of such Bantu states include: the Kingdom of Kongo, Anziku Kingdom, Kingdom of Ndongo, the Kingdom of Matamba the Kuba Kingdom, the Lunda Empire, the Luba Empire, Mbunda Kingdom, Yeke Kingdom, Kasanje Kingdom, Empire of Kitara, Butooro, Bunyoro, Buganda, Busoga, Rwanda, Burundi, Ankole, the Kingdom of Mpororo, the Kingdom of Igara, the Kingdom of Kooki, the Kingdom of Karagwe, Swahili city states, the Mutapa Empire, the Zulu Kingdom, the Ndebele Kingdom, Mthethwa Empire, Tswana city states, Mapungubwe, Kingdom of Eswatini, the Kingdom of Butua, Maravi, Danamombe, Khami, Naletale, Kingdom of Zimbabwe and the Rozwi Empire.
What is the cognate of Nguni abantu?
In the Sotho–Tswana languages of southern Africa, batho is the cognate term to Nguni abantu, illustrating that such cognates need not actually look like the -ntu root exactly. The early African National Congress of South Africa had a newspaper called Abantu-Batho from 1912 to 1933, which carried columns in English, Zulu, Sotho, and Xhosa.
How many people are in the Congo?
About 60 million speakers (2015), divided into some 200 ethnic or tribal groups, are found in the Democratic Republic of Congo alone. The larger of the individual Bantu groups have populations of several million, e.g. the Hutu of Rwanda and Burundi (25 millions) the Shona of Zimbabwe, (15 million as of 2018.
How many languages are there in Africa?
The total number of languages ranges in the hundreds, depending on the definition of "language" or "dialect", estimated at between 440 and 680 distinct languages. The total number of speakers is in the hundreds of millions, ranging at roughly 350 million in the mid-2010s (roughly 30% of the population of Africa, ...
What did the term "Bantu" mean in South Africa?
In the 1920s, relatively liberal South Africans, missionaries, and the small black intelligentsia began to use the term "Bantu" in preference to "Native". After World War II, the National Party governments adopted that usage officially, while the growing African nationalist movement and its liberal allies turned to the term "African" instead, so that "Bantu" became identified with the policies of apartheid. By the 1970s this so discredited "Bantu" as an ethno-racial designation that the apartheid government switched to the term "Black" in its official racial categorizations, restricting it to Bantu-speaking Africans, at about the same time that the Black Consciousness Movement led by Steve Biko and others were defining "Black" to mean all non-European South Africans (Bantus, Khoisan, Coloureds, and Indians ). In modern South Africa due to its connection to apartheid the noun has become so discredited that it is only used in its original linguistic meaning.
What language do Bantu speak?
Swahili is the language Bantu people speak. I’m native speaker of Swahili language from Tanzania
What was the name of the Bantu homeland?
The word Bantu sounded less offensive so the homelands for Bantus were also called Bantustans (Transkei, Vandaland etc.). The Apartheid ideology insisted on all non-white groups being different nasies or nations. They would have residence and voting rights only in these “homelands”, even if they had been born, had lived and worked in the townships in subsections reserved for Xhosa, Basotho, Zulus, Coloureds etc., or in the compounds, barracks attached to the mines. Apartheid or separate development had a complex tribal ideology that supposedly would allow the “natives” or “naturals” stay inside their culture without outside intervention and with, supposed, forms of self-determination under their “customary laws” and “traditional leaders”.
What is the Bantu language called?
There is no single language called Bantu same as there is no language called European. The “Bantu” tribes or nations speak Zulu, Xhosa, Swazi, Herero … and plenty more.
What is a bantu?
First off what is a Bantu? A Bantu is someone who speaks one of the major subdivisions of the Bantu language family which was brought somewhere from central western Africa around 4000 years ago which was accompanied by iron working and agriculture which led to states or kingdoms being formed. This spread happened slowly over time as more and more people move out from their original homeland or traded with each other, but also as people realized how useful the bantu lifestyle was compared to previous ones prompting them to fuse with the bantu and/or learn their language. You see, Bantu became a useful language to learn in Africa because it allowed you access to the Bantu world. If you can speak a bantu language you can become a part of the bantu trading network and have access to what they have to offer. It is no different how latin or Greek became a common language to learn in Europe as it gave you access to the goods or world of the Mediterranean. The Bantu people compared to many of the contemporaries had more durable and flexible tools made of iron which allowed whatever labor they had to produce more. They were also agriculturalist which gave them access to surpluses of food compared to the lifestyle relying solely on foraging, fishing and hunter gathering. This ties into my next point.
Why are Bantu people different?
Bantu people are different depending on where you are talking about and this is precisely because they purposefully fused with the populations they ran into. Why is it, that Eastern bantu speakers can process milk in a way western ones can not? It is because they fused with the Cushitic and Nilotic populations of Eastern Africa. Why is it, that western Bantu have immunities to rainforest diseases that other bantu do not?
Which languages have z?
Plenty of Bantu languages have the z consonant. For example Swahili, Zulu, Kinyarwanda. In fact, the Zulu language has the consonant z in the beginning of the word Zulu. Proto-Bantu is believed not to have had the consonant z. So Bantu languages which have z, developed this consonant later in their history. Some Bantu languages have never developed z, for example Basaa, Kikuyu, Tswana, or use them only in borrowings from foreign languages like English. There are languages like Bemba, which used to have z, but lost it later during their history. An ancestor of Bemba used to have z, but during the history of Bemba, every z changed to s. So this way z was lost, and s became considerably more common, since before this change happened, the language already had s, but now every z became s, so s became more common.
Which languages have the Z consonant?
Plenty of Bantu languages have the z consonant. For example Swahili, Zulu, Kinyarwanda. In fact, the Zulu language has the consonant z in the beginning of the word Zulu. Proto-Bantu is believed not to have had the consonant z. So Bantu languages which have z, developed this consonant later in their history. Some Bantu languages have never developed z, for example Basaa, Kikuyu, Tswana, or use them only in borrowings from foreign languages like English. There are languages like Bemba, which used to have z, but lost it later during their history. An ancestor of Bemba used to have z, but during t
What language do people in Zimbabwe speak?
Several thousand people in Zimbabwe and Botswana speak the Tshwa or the Tsoa, a Khoe language.
How many people speak Kgalagadi?
The Bantu language of Kgalagadi, also known as Kalahari, is spoken by about 40,000 people in Botswana and Namibia. In Botswana, Kgalagadi speakers account for about 3.4% of the total population and the language is mainly spoken along the country's border with South Africa.
Where is Setswana spoken?
The Setswana language, also known as Tswana, is spoken widely in Botswana and other parts of Southern Africa. The Bantu language is a member of the Niger–Congo language family. Tswana serves as the lingua franca in Botswana. It is spoken by most of the population of the nation.
What language do people speak in Botswana?
What Languages are Spoken in Botswana? A street sign in Botswana. English is the official language of Botswana, while Setswana is the most widely spoken language in the country. Several other minority languages, especially Bantu languages, are also spoken in Botswana.
What is the native language of Botswana?
Shona. About 2% of the population of Botswana speak Shona, the native language of the Shona people. The language is also spoken in Zimbabwe, South Africa, and Mozambique.

Overview
The Bantu languages are a large family of languages spoken by the Bantu people of Central, Southern, and Southeast Africa. They form the largest branch of the Southern Bantoid languages.
The total number of Bantu languages ranges in the hundreds, depending on the definition of "language" versus "dialect", and is estimated at between 440 and 6…
Name
The similarity among dispersed Bantu languages had been observed as early as the 17th century. The term Bantu as a name for the group was coined (as Bâ-ntu) by Wilhelm Bleek in 1857 or 1858, and popularised in his Comparative Grammar of 1862. He coined the term to represent the word for "people" in loosely reconstructed Proto-Bantu, from the plural noun class prefix *ba- categorizing "people", and the root *ntʊ̀- "some (entity), any" (e.g. Zulu umuntu "person", abantu "people").
Origin
The Bantu languages descend from a common Proto-Bantu language, which is believed to have been spoken in what is now Cameroon in Central Africa. An estimated 2,500–3,000 years ago (1000 BC to 500 BC), speakers of the Proto-Bantu language began a series of migrations eastward and southward, carrying agriculture with them. This Bantu expansion came to dominate Sub-Saharan Africa east of Cameroon, an area where Bantu peoples now constitute nearly the en…
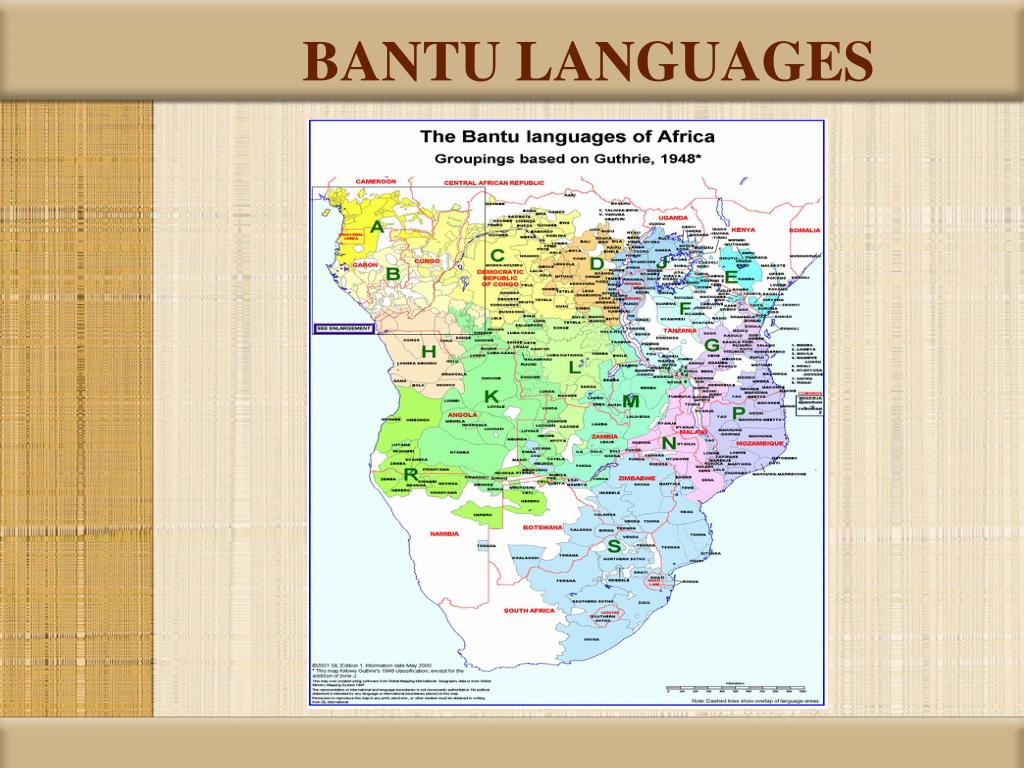
Classification
The most widely used classification is an alphanumeric coding system developed by Malcolm Guthrie in his 1948 classification of the Bantu languages. It is mainly geographic. The term "narrow Bantu" was coined by the Benue–Congo Working Group to distinguish Bantu as recognized by Guthrie, from the Bantoid languages not recognized as Bantu by Guthrie.
Language structure
Guthrie reconstructed both the phonemic inventory and the vocabulary of Proto-Bantu.
The most prominent grammatical characteristic of Bantu languages is the extensive use of affixes (see Sotho grammar and Ganda noun classes for detailed discussions of these affixes). Each noun belongs to a class, and each language may have several numbered classes, somewhat like grammatical gender in European languages. The class is indicated by a prefix that is part of the …
By country
Following is an incomplete list of the principal Bantu languages of each country. Included are those languages that constitute at least 1% of the population and have at least 10% the number of speakers of the largest Bantu language in the country.
Most languages are referred to in English without the class prefix (Swahili, Tswana, Ndebele), but are sometimes seen with the (language-specific) prefix (Kiswahili, Setswana, Sindebele). In a fe…
Geographic areas
Map 1 shows Bantu languages in Africa and map 2 a magnification of the Benin, Nigeria and Cameroon area, as of July 2017.
Bantu words popularised in western cultures
A case has been made out for borrowings of many place-names and even misremembered rhymes – chiefly from one of the Luba varieties – in the USA.
Some words from various Bantu languages have been borrowed into western languages. These include:
• Boma