
What are the 5 main functions of the endocrine system?
the major functions it coordinates are • homeostasis – maintains the internal body environment • storage and utilization of energy substrates (carbohydrates, proteins and fats); • regulation of growth and reproduction • control of the body’s responses to external stimuli (particularly stress) made up of a collection of small organs that are …
What is the endocrine system and what are its functions?
What is the endocrine system?
- Functions of stability and growth of the organism. ...
- Reproductive functions in men. ...
- Reproductive functions in women. ...
- Thyroid gland. ...
- Kidney glands. ...
- Types of Hormone Communication. ...
- Classification of the functions of hormones. ...
- Relationship with the nervous system. ...
- Types of glands. ...
- Diseases of the endocrine system. ...
What is the main function of endocrine system?
What are the 3 main functions of endocrine system?
- Metabolism (the burning of fuels by the body)
- Growth and development.
- Sexual function and reproduction.
- Blood pressure.
- Appetite (satiety and hunger)
- Sleeping and waking cycles.
What system does the endocrine system rely on?
Your endocrine system works closely with your brain and central nervous system to control the creation of specific hormones and enzymes. Your digestive and excretory systems work with the nervous system in both conscious and unconscious ways. Why is the nervous system the most important body system?

What are 3 types of endocrine?
Endocrine glands include: Adrenal glands: Two glands that sit on top of the kidneys that release the hormone cortisol. Hypothalamus: A part of the lower middle brain that tells the pituitary gland when to release hormones. Ovaries: The female reproductive organs that release eggs and produce sex hormones.
What are the 4 main functions of the endocrine system?
What does the endocrine system do?metabolism.growth and development.sexual function and reproduction.heart rate.blood pressure.appetite.sleeping and waking cycles.body temperature.
What are the 3 main functions of the endocrine system?
Below are the 3 vital functions of your endocrine system.Makes Hormones for Mood, Development, and Growth. Many different vital hormones are created and controlled within the endocrine system. ... Sends Hormones into Your Bloodstream. ... Regulates the Release of Hormones.
What 3 diseases can affect the endocrine system?
Endocrine Disease TopicsAcromegaly.Adrenal Insufficiency & Addison's Disease.Cushing's Syndrome.Cystic Fibrosis link.Graves' Disease.Hashimoto's Disease.
Which brain is endocrine?
Pituitary. The pituitary gland is located below the brain. Usually no larger than a pea, the gland controls many functions of the other endocrine glands.
What are the 7 hormones?
The following types of hormones are key players in how your body functions and can affect your health in multiple ways.Estrogen. Estrogen is one of the key female sex hormones, but men have estrogen too. ... Progesterone. ... Testosterone. ... Insulin. ... Cortisol. ... Growth Hormone. ... Adrenaline. ... Thyroid Hormones.
How do you keep your endocrine system healthy?
How Can I Help Keep My Endocrine System Healthy?Get plenty of exercise.Eat a nutritious diet.Go for regular medical checkups.Talk to the doctor before taking any supplements or herbal treatments.Let the doctor know about any family history of endocrine problems, such as diabetes or thyroid problems.
Why endocrine system is important?
The endocrine system controls growth and development during childhood, regulation of bodily functions in adulthood, and the reproductive process. The endocrine system is important for the control and regulation of all the major functions and processes of the body: Energy control.
What are the functions of endocrine?
Endocrine glands release hormones into the bloodstream. This lets the hormones travel to cells in other parts of the body. The endocrine hormones help control mood, growth and development, the way our organs work, metabolism , and reproduction. The endocrine system regulates how much of each hormone is released.
What are 5 functions of hormones?
Hormones control many different bodily processes, including:Metabolism.Homeostasis (constant internal balance), such as blood pressure and blood sugar regulation, fluid (water) and electrolyte balance and body temperature.Growth and development.Sexual function.Reproduction.Sleep-wake cycle.Mood.
What is the main function of the endocrine system quizlet?
The endocrine system's main function is to regulate short-term and long-term activities by sending hormones throughout the body. The relationship between homeostasis and the endocrine system is that the glands in the body produce specific hormones that help the body maintain a balance.
What is important about the endocrine system?
The endocrine system controls growth and development during childhood, regulation of bodily functions in adulthood, and the reproductive process. The endocrine system is important for the control and regulation of all the major functions and processes of the body: Energy control.
Why Are Hormones Important?
Hormones act as chemical messengers that are released into the blood stream to act on an organ in another part of the body. Although hormones reach...
Where Are Endocrine Glands Located in The Human body?
Hypothalamus - The hypothalamus links our endocrine and nervous systems together. The hypothalamus drives the endocrine system.Pituitary gland - Th...
How Can Chemicals Affect The Endocrine System?
Scientific research on human epidemiology, laboratory animals, and fish and wildlife suggests that environmental contaminants can disrupt the endoc...
What are the functions of the endocrine system?
The hormones created and released by the glands in your body’s endocrine system control nearly all the processes in your body. These chemicals help coordinate your body’s functions, from metabolism to growth and development, emotions, mood, sexual function and even sleep.
How do hormones coordinate different functions in the body?
Hormones are chemicals that coordinate different functions in your body by carrying messages through your blood to your organs, skin, muscles and other tissues. These signals tell your body what to do and when to do it.
What glands release hormones?
The pituitary gland senses when your hormone levels rise, and tells other glands to stop producing and releasing hormones. When hormone levels dip below a certain point, the pituitary gland can instruct other glands to produce and release more.
What are the glands in the body?
Glands produce and release different hormones that target specific things in the body. You have glands all over your body, including in your neck, brain and reproductive organs. Some glands are tiny, about the size of a grain of rice or a pea. The largest gland is the pancreas, which is about 6 inches long. The main glands that produce hormones ...
Where is the pituitary gland located?
The pituitary gland is in charge of many different functions, including how your body grows. It’s located at the base of your brain.
Which gland produces hormones?
The main glands that produce hormones include: Hypothalamus: This gland is located in your brain and controls your endocrine system. It uses information from your nervous system to determine when to tell other glands, including the pituitary gland, to produce hormones. The hypothalamus controls many processes in your body, including your mood, ...
How do hormones affect your body?
Hormones affect nearly every process in your body, including: Metabolism (the way you break down food and get energy from nutrients). Growth and development. Emotions and mood. Fertility and sexual function. Sleep.
What is the endocrine system?
Conditions. The endocrine system is a network of glands and organs located throughout the body. It’s similar to the nervous system in that it plays a vital role in controlling and regulating many of the body’s functions. However, while the nervous system uses nerve impulses and neurotransmitters for communication, ...
What are some examples of bodily functions that are controlled by the endocrine system?
Some examples of bodily functions that are controlled by the endocrine system include: metabolism. growth and development. sexual function and reproduction. heart rate. blood pressure. appetite. sleeping and waking cycles. body temperature.
What are some examples of hormones produced by the endocrine system?
Below are some examples of hormones that are produced by the endocrine system. Hormone. Secreting gland (s) Function. adrenaline. adrenal. increases blood pressure, heart rate, and metabolism in reaction to stress.
What is the endocrine function of the ovaries?
Its endocrine function involves controlling blood sugar levels. Some endocrine glands also have non-endocrine functions. For example, the ovaries and testes produce hormones, but they also have the non-endocrine function of producing eggs and sperm, respectively.
What is the function of hormones in the body?
Hormones are the chemicals the endocrine system uses to send messages to organs and tissue throughout the body. Once released into the bloodstream, they travel to their target organ or tissue, which has receptors that recognize and react to the hormone.
Which gland controls appetite?
Hypothalamus. While some people don’t consider it a gland, the hypothalamus produces multiple hormones that control the pituitary gland. It’s also involved in regulating many functions, including sleep-wake cycles, body temperature, and appetite. It can also regulate the function of other endocrine glands. Pituitary.
What hormones are involved in the production of body hair during puberty?
ovary. works to regulate menstrual cycle, maintain pregnancy, and develop female sex characteristics; aids in sperm production. follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) pituitary. controls the production of eggs and sperm. glucagon. pancreas.
What is the endocrine system?
The endocrine system is a collection of ductless glands that produce hormones and secrete them into the circulatory system. Endocrine glands work without ducts for carrying secretions towards target organs. Instead, hormones can act as chemical messengers for a large number of cells and tissues simultaneously.
How does the endocrine system work?
The endocrine system consists of many glands, which work by secreting hormones into the bloodstream to be carried to a target cell. Endocrine system hormones work even if the target cells are distant from the endocrine glands. Through these actions, the endocrine system regulates nearly every metabolic activity of the body to produce an integrated response. The endocrine system can release hormones to induce the stress response, regulate the heartbeat or blood pressure, and generally directs how your cells grow and develop.
Why is the endocrine system not responding to messenger signals?
Endocrine system diseases primarily arise from two causes – either a change in the level of hormone secreted by a gland , or a change in the sensitivity of the receptors in various cells of the body. Therefore, the body fails to respond in an appropriate manner to messenger signals. Among the most common endocrine diseases is diabetes, which hampers the metabolism of glucose. This has an enormous impact on the quality of life since adequate glucose is not only important for fueling the body, but it is also important in maintaining glucose at an appropriate level to discourages the growth of microorganisms or cancerous cells.
How does the endocrine system affect the body?
The endocrine system is involved in every process of the human body. Starting from the motility of the digestive system, to the absorption and metabolism of glucose and other minerals, hormones can affect a variety of organs in different ways. Some hormones affect the retention of calcium in bones or their usage to power muscle contraction.
Why are endocrine glands important?
These glands can help to coordinate the overall actions of the system and the body as a whole. A release of hormones from these glands can create a cascade of effects from the release of a single hormone. This makes the endocrine system one of the most complexly structured body systems.
What are the effects of hormones on the reproductive system?
Imbalances of hormones from the reproductive system are also significant since they can influence fertility, mood, and wellbeing. Another important endocrine gland is the thyroid, with both high and low levels of secretion affecting a person’s capacity to function optimally, even affecting fertility in women. The thyroid also needs a crucial micronutrient, iodine, in order to produce its hormone. Dietary deficiency of this mineral can lead to an enlargement of the thyroid gland as the body tries to compensate for low levels of thyroid hormones.
What are the functions of gonads?
The gonads also have important endocrine functions that influence the proper development of reproductive organs, the onset of puberty, and maintenance of fertility. Other organs such as the heart, kidney, and liver also act as secondary endocrine organs, secreting hormones like erythropoietin that can affect red blood cell production.
What are the learning objectives of the endocrine system?
Learning Objectives. The endocrine system consists of a series of glands that produce chemical substances known as hormones ( [link] ). Like neurotransmitters, hormones are chemical messengers that must bind to a receptor in order to send their signal. However, unlike neurotransmitters, which are released in close proximity to cells ...
Which system controls hormones?
Also, hormones are slower to take effect, and tend to be longer lasting. The major glands of the endocrine system are shown. Hormones are involved in regulating all sorts of bodily functions, and they are ultimately controlled through interactions between the hypothalamus (in the central nervous system) and the pituitary gland ...
What is the master gland of the brain?
The pituitary gland descends from the hypothalamus at the base of the brain, and acts in close association with it. The pituitary is often referred to as the “master gland” because its messenger hormones control all the other glands in the endocrine system, although it mostly carries out instructions from the hypothalamus. In addition to messenger hormones, the pituitary also secretes growth hormone, endorphins for pain relief, and a number of key hormones that regulate fluid levels in the body.
How is hormone secretion regulated?
Hormone secretion is often regulated through a negative feedback mechanism, which means that once a hormone is secreted it will cause the hypothalamus and pituitary to shut down the production of signals necessary to secrete the hormone in the first place. Most oral contraceptives are made of small doses of estrogen and/or progesterone. Why would this be an effective means of contraception?
What is the effect of the introduction of relatively low, yet constant, levels of gonadal hormones?
The introduction of relatively low, yet constant, levels of gonadal hormones places the hypothalamus and pituitary under inhibition via negative feedback mechanisms. This prevents the alterations in both estrogen and progesterone concentrations that are necessary for successful ovulation and implantation. Chemical messengers are used in both the ...
What hormones do gonads secrete?
The gonads secrete sexual hormones, which are important in reproduction, and mediate both sexual motivation and behavior. The female gonads are the ovaries; the male gonads are the testes. Ovaries secrete estrogens and progesterone, and the testes secrete androgens, such as testosterone. Athletes and Anabolic Steroids.
Which gland releases hormones that regulate appetite and metabolism?
Located in the neck, the thyroid gland releases hormones that regulate growth, metabolism, and appetite.
What are the endocrine systems?
The endocrine system is a chemical messenger system consisting of hormones, the group of glands of an organism that secrete those hormones directly into the circulatory system to regulate the function of distant target organs, and the feedback loops which modulate hormone release so that homeostasis is maintained . In humans, the major endocrine glands are the thyroid gland and the adrenal glands. In vertebrates, the hypothalamus is the neural control center for all endocrine systems. The field of study dealing with the endocrine system and its disorders is endocrinology, a branch of internal medicine.Special features of endocrine glands are, in general, their ductless nature, their vascularity, and commonly the presence of intracellular vacuoles or granules that store their hormones. In contrast, exocrine glands, such as salivary glands, sweat glands, and glands within the gastrointestinal tract, tend to be much less vascular and have ducts or a hollow lumen. A number of glands that signal each other in sequence are usually referred to as an axis, for example, the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. In addition to the specialized endocrine organs mentioned above, many other organs that are part of other body systems, such as bone, kidney, liver, heart and gonads, have secondary endocrine functions. For example, the kidney secretes endocrine hormones such as erythropoietin and renin. Hormones can consist of either amino acid complexes, steroids, eicosanoids, leukotrienes, or prostaglandins.The endocrine system is in contrast to the exocrine system, which secretes its hormones to the outside of the body using ducts. As opposed to endocrine factors that travel considerably longer distances via the circulatory system, other signaling molecules, such as paracrine factors involved in paracrine signalling diffuse over a relatively short distance. The word endocrine derives via New Latin from the Greek words ἔνδον, endon, "inside, within," and "exocrine" from the κρίνω, krīnō, "to separate, distinguish".
What is the numerical value of the endocrine system in Pythagorean numerology?
The numerical value of endocrine system in Pythagorean Numerology is: 8
What is a system?
system(a group of physiologically or anatomically related organs or parts)
What is the definition of organic structure?
body; organic structure(the entire physical structure of an organism (an animal, plant, or human being))
Where are pituitary hormones produced?
Pituitary hormones are produced by the pituitary gland, the master gland of the endocrine systemwhich is located at the base of the brain.
Is "endocrine system" a noun?
Familiarity information: ENDOCRINE SYSTEMused as a noun is very rare.
What is the endocrine system?
The endocrine system is a network of glands that produce and release hormones that help control many important body functions, including the body's ability to change calories into energy that powers cells and organs . The endocrine system influences how your heart beats, how your bones and tissues grow, ...
Why is endocrine disease important?
Endocrine disease due to the development of lesions (such as nodules or tumors) in the endocrine system , which may or may not affect hormone levels. The endocrine's feedback system helps control the balance of hormones in the bloodstream.
What is a problem with the endocrine feedback system?
A problem with the endocrine feedback system. Disease. Failure of a gland to stimulate another gland to release hormones (for example, a problem with the hypothalamus can disrupt hormone production in the pituitary gland) A genetic disorder, such as multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) or congenital hypothyroidism.
What glands are responsible for sperm production?
Problems with the pituitary gland can affect bone growth, a woman's menstrual cycles, and the release of breast milk. Testes: The male reproductive glands that produce sperm and sex hormones. Thymus: A gland in the upper chest that helps develop the body's immune system early in life.
Why does hormone imbalance occur?
A hormone imbalance may occur if this feedback system has trouble keeping the right level of hormones in the bloodstream, or if your body doesn't clear them out of the bloodstream properly. Increased or decreased levels of endocrine hormone may be caused by: A problem with the endocrine feedback system. Disease.
What are the different types of endocrine disorders?
Endocrine disorders are typically grouped into two categories: 1 Endocrine disease that results when a gland produces too much or too little of an endocrine hormone, called a hormone imbalance. 2 Endocrine disease due to the development of lesions (such as nodules or tumors) in the endocrine system, which may or may not affect hormone levels.
How do you know if you have an endocrine disorder?
However, most people with endocrine disease complain of fatigue and weakness. Blood and urine tests to check your hormone levels can help your doctors determine if you have an endocrine disorder.
What is the endocrine system?
The endocrine system is made up of a collection of glands. Each gland has a specific function in the body, and all these glands work together to regulate vital functions of our body.
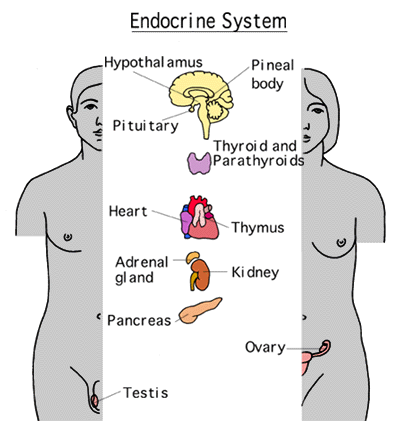
Which organs are involved in the endocrine system?
These glands include the hypothalamus, pineal body, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroids, adrenals, pancreas, testes and ovaries.
How do the four parathyroid glands work?
Each the size of a grain of rice, the body’s four parathyroid glands monitor the calcium level in our bodies. Parathyroid glands control the calcium levels in our blood, in our bones and throughout our body. Parathyroid glands regulate the calcium by producing a hormone called parathyroid hormone (PTH).
Why is the pituitary called the master gland?
No larger than the size of a pea, the pituitary is often referred to as the “master” gland because it releases hormones that regulate the function of endocrine glands such as the thyroid, adrenals and reproductive glands.
What are the functions of hormones?
When a hormone reaches its target, it tells that part of your body what work to do, when to do it and for how long. Hormones are often referred to as the “messengers” because they help different parts of the body communicate. Overall, they are involved in many different processes in the body, including: 1 Blood sugar control 2 Growth and development 3 Metabolism (the process of getting and maintaining energy in the body) 4 Regulation of heart rate and blood pressure 5 Sexual development and function 6 Reproduction 7 Mood
How many hormones are in the blood?
The hormones in your body all have specific jobs to complete. There are up to 40 different hormones circulating in your blood at any time. Once released into the bloodstream, a hormone travels throughout the body until it reaches its specific destination (s) to perform its function.
What is an endocrinologist?
An endocrinologist is a physician who specializes in the field of endocrinology. Endocrinologists diagnose and treat a wide range of conditions affecting the endocrine system, including diabetes mellitus, thyroid disorders, osteoporosis, growth hormone deficiency, infertility, cholesterol problems, hypertension (high blood pressure), ...
Function
Mechanism
- Endocrine glands are usually heavily vascularized, containing a dense network of blood vessels. Cells within these organs produce and contain hormones in intracellular granules or vesicles that fuse with the plasma membrane in response to the appropriate signal. This action releases the hormones into the extracellular space, or into the bloodstream. The endocrine system can be ac…
Causes
- As an example, the long-term secretion of growth hormone in the body influences the development of bones and muscles to increase height and also induces the growth of every internal organ. This happens over the course of many years. Hormones like cortisol, produced during times of stress, can change appetite, and metabolic pathways in skeletal and smooth mu…
Structure
- The neck contains the thyroid and parathyroid glands. The thyroid gland consists of two symmetric lobes connected by a narrow strip of tissue called the isthmus glandularis, forming a butterfly-like structure. Each lobe is about 5cm in height, and the isthmus is approximately 1.25 cm in length. The gland is situated in the front of the neck, behind the thyroid cartilage. Each lob…
Overview
- Diabetes, or diabetes mellitus, refers to a metabolic disease where the blood consistently carries a high concentration of glucose. This is traced back to the lack of effective insulin hormone, produced by the pancreas, or a lack of functioning hormone receptors. Diabetes mellitus could either arise from a low level of insulin production from the pancreas or an insensitivity of insulin …
Pathophysiology
- Hypothyroidism is a condition where the body has an insufficient supply of thyroid hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). Both these hormones contain iodine and are derived from a single amino acid tyrosine. Iodine deficiency is a common cause for hypothyroidism since the gland is unable to synthesize adequate amounts of hormone. This can arise due to damage to t…
Definition
- Hypogonadism refers to a spectrum of disorders where there is an insufficiency of sex hormones. These are usually secreted by the primary gonads (testes and ovaries) and affect the development, maturation, and functioning of sex organs and the appearance of secondary sexual characteristics. It can arise due to a low level of sex hormone production by the gonads itself, o…
Signs and symptoms
- Depending on the period of onset, hypogonadism can result in different characteristics. Hypogonadism during development can cause ambiguous genitalia. During puberty, it can affect the onset of menstruation, breast development and ovulation in females, delay the growth of the penis and testicles, and affect the development of secondary sexual characteristics. It can also i…