
Why is the electron transport chain so important?
Why is the electron transport chain so important? The ETC is the most important stage of cellular respiration from an energy point of view because it produces the most ATP. When a cell needs energy, it breaks the third phosphate group bond and uses the resulting energy.
What is the end result of the electron transport chain?
What is the end result of the electron transport chain? The end products of the electron transport chain are water and ATP. A number of intermediate compounds of the citric acid cycle can be diverted into the anabolism of other biochemical molecules, such as nonessential amino acids, sugars, and lipids.
Where does the electron transport chain take place?
Summary of Mitochondrial Electron Transport Chain
- The electron transport chain as indicated by its name “transport means transfer”, is a membrane-embedded protein labelled as complex I-IV.
- Electron transport chain also known as ETC complexes.
- Electron transport chain is located on the inner mitochondrial membrane known as cristae.
What happens in the electron transport chain?
- The iron-sulfur (FeS) proteins exist in the oxidized (Fe 3+ ) or reduced (Fe 2+)
- These are non-heme iron-sulfur proteins.
- The simplest iron-sulfur protein is FeS in which iron is tetrahedrally coordinated by four cysteines.
- About half a dozen FeS proteins connected with respiratory chain have been identified which participates in electron transport.
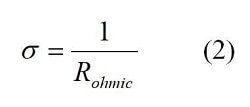
What are the 3 main steps in the electron transport chain?
Step 1: Generating a Proton Motive Force.Step Two: ATP Synthesis via Chemiosmosis.Step Three: Reduction of Oxygen.Summary: Oxidative Phosphorylation.
What are the 5 steps of the electron transport chain?
Summarized steps of the ETC: The transfer of electrons by NADH and FADH2 to complex I and II, respectively. The establishment of an electrochemical gradient by proton pumping and movement of electrons through the chain. Splitting of oxygen molecule to form water. Generation of ATP molecules by ATP synthase.
What events take place in the electron transport chain?
The events of the electron transport chain involve NADH and FADH, which act as electron transporters as they flow through the inner membrane space. In complex I, electrons are passed from NADH to the electron transport chain, where they flow through the remaining complexes. NADH is oxidized to NAD in this process.
What is the electron transport chain in simple terms?
The electron transport chain is a series of four protein complexes that couple redox reactions, creating an electrochemical gradient that leads to the creation of ATP in a complete system named oxidative phosphorylation. It occurs in mitochondria in both cellular respiration and photosynthesis.
What is the main product of electron transport chain?
The electron transport chain produces the most ATP out of all the steps, producing 28 molecules of ATP. This results in a total of 32 ATP molecules for the entire process of cellular respiration.
What happens during the electron transport stage of cellular respiration?
The Electron Transport Chain is the final stage of cellular respiration. In this stage, energy being transported by NADH and FADH2 is transferred to ATP. In addition, oxygen acts as the final proton acceptor for the hydrogens released from all the NADH and FADH2, forming water.
Which of the following is true about electron transport chain?
all of the above. In the electron transport chain, most of the enzymes are part of the inner mitochondrial membrane, oxygen is the terminal electron acceptor, electrons are passed from donor to recipient carrier molecules in a series of redox reactions, and electrons are received from NADH and FADH2.
What does the electron transport chain do in cellular respiration?
The primary task of the last stage of cellular respiration, the electron transport chain, is to transfer energy from the electron carriers to even more ATP molecules, the "batteries" which power work within the cell.
What is the first step of the electron transport chain?
We first consider the use of in the electron transport chain. During the first step, a pair of electrons from are transferred to the electron carrier coenzyme Q by NADH dehydrogenase (site 1 and Q in Figure 8.26), and using the energy released, a pair of hydrogen ions are pumped into the intermembrane space.
What is the correct order for respiration?
Thus the correct order of the stages in cellular respiration is: Glycolysis - Oxidative decarboxylation - Krebs cycle - Electron transport chain - Oxidative phosphorylation.
What is complex 4 in the electron transport chain?
Complex-IV is a cytochrome c oxidase enzyme. It consists of cytochrome-a, cytochrome-a3, haem, and copper ions as prosthetic groups. Complex IV, also known as cytochrome c oxidase, catalyzes the final step in the mitochondrial electron transport chain and is one of the key regulators of oxidative phosphorylation.
What are the members of the chain in the electron transport system?
The electron transport chain is a mitochondrial pathway in which electrons move across a redox span of 1.1 V from NAD+/NADH to O2/H2O. Three complexes are involved in this chain, namely, complex I, complex III, and complex IV.
Q.1. How many protons are required to form 1 ATP molecule?
Ans: When 2 protons get a release from the F0-F1 complex present in the inner mitochondrial membrane, 1 ATP is formed.
Q.2. How many complexes are there in an electron transport system in mitochondria?
Ans: There are five complexes in an Electron transport system embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Q.3. What is Light Reaction?
Ans: The light reaction is the first reaction in which light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll molecules present in the reaction centre of the phot...
Q.4. In which layer of mitochondria, the Electron Transport System takes place?
Ans: The electron transport system takes place in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
What is the electron transport system?
Definition of Electron Transport System. It refers to the mechanism of cellular respiration that occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane. It is the third and last stage of cellular respiration. Electron transport chain or Respiratory chain is the alternative terms of the electron transport system. ETS follows an aerobic pathway.
What is the mechanism of electron transport?
The electron transport chain sometimes refers to the “ Respiratory chain ”, which is the third or final stage of cellular respiration. It requires the presence of oxygen to carry out cellular respiration. The energy is produced during the transfer of electrons from one carrier to the other.
How do electrons pass from one complex to the other?
Electrons pass from one complex to the other by redox reactions. The free energy during electron transfer is captured as a proton gradient and used up by the ATP synthase to derive ATP. The electron carrier Co-Q receives the electrons formed by the reduction of FADH 2 and NADH.
How does ETS work?
ETS involves electron transfer through a series of protein complexes from higher (NADH +) to lower energy state (O 2) by releasing protons into the cytosol. A movement of proton or H + from a matrix to cytosol generates a proton motive force and creates an electrochemical gradient.
How is energy produced in a cell?
The energy is produced during the transfer of electrons from one carrier to the other. A cell harnesses the energy loss during electron transport to pump protons into the cytosol. It creates a chemiosmotic gradient. A chemiosmotic gradient becomes charged by the potential energy of the electrons.
What are the steps of the electron transport chain?
The electron transport system can be summarized into the following steps: Step 1: Generation of proton motive force. In the first step of the electron transport chain, the NADH + and FADH 2 molecule of glycolysis and Kreb’s cycle is oxidized into NAD + and FAD, respectively, along with the release of high energy electrons and protons.
How do H+ ions diffuse?
H + ions tend to diffuse back into the mitochondrial matrix through the channel proteins via a transmembrane enzyme (ATP synthase), and thereby producing ATP. For the continuation of the electron transport system, the de-energized electrons must be release out via an electron acceptor O2 molecule.
Where does the electron transport system occur?
Electron Transport System. The electron transport system occurs in the cristae of the mitochondria, where a series of cytochromes (enzymes) and coenzymes exist. These cytochromes and coenzymes act as carrier molecules and transfer molecules. They accept high-energy electrons and pass the electrons to the next molecule in the system.
What is the final electron acceptor in cellular respiration?
In cellular respiration, the final electron acceptor is an oxygen atom. In their energy-depleted condition, the electrons unite with an oxygen atom. The electron-oxygen combination then reacts with two hydrogen ions (protons) to form a water molecule (H 2 O). The role of oxygen in cellular respiration is substantial.
How many protons are transported by NADH?
Each NADH molecule is highly energetic, which accounts for the transfer of six protons into the outer compartment of the mitochondrion.
What is the role of oxygen in cellular respiration?
The role of oxygen in cellular respiration is substantial. As a final electron acceptor, it is responsible for removing electrons from the electron transport system. If oxygen were not available, electrons could not be passed among the coenzymes, the energy in electrons could not be released, the proton pump could not be established, ...
Where Does the Electron Transport Chain Occur?
During the process, a proton gradient is created when the protons are pumped from the mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane space of the cell, which also helps in driving ATP production. Often, the use of a proton gradient is referred to as the chemiosmotic mechanism that drives ATP synthesis since it relies on a higher concentration of protons to generate “proton motive force”. The amount of ATP created is directly proportional to the number of protons that are pumped across the inner mitochondrial membrane.
How do electrons move in the electron transfer chain?
In the electron transfer chain, electrons move along a series of proteins to generate an expulsion type force to move hydrogen ions, or protons, across the mitochondrial membrane. The electrons begin their reactions in Complex I, continuing onto Complex II, traversed to Complex III and cytochrome c via coenzyme Q, and then finally to Complex IV. The complexes themselves are complex-structured proteins embedded in the phospholipid membrane. They are combined with a metal ion, such as iron, to help with proton expulsion into the intermembrane space as well as other functions. The complexes also undergo conformational changes to allow openings for the transmembrane movement of protons.
How many electrons does NADH have?
The NADH now has two electrons passing them onto a more mobile molecule, ubiquinone (Q), in the first protein complex (Complex I). Complex I, also known as NADH dehydrogenase, pumps four hydrogen ions from the matrix into the intermembrane space, establishing the proton gradient.
How is ATP generated in an exothermic reaction?
energy is released in an exothermic reaction when electrons are passed through the complexes ; three molecules of ATP are created. Phosphate located in the matrix is imported via the proton gradient, which is used to create more ATP. The process of generating more ATP via the phosphorylation of ADP is referred to oxidative phosphorylation since the energy of hydrogen oxygenation is used throughout the electron transport chain. The ATP generated from this reaction go on to power most cellular reactions necessary for life.
What is the mechanism that drives ATP synthesis?
Often, the use of a proton gradient is referred to as the chemiosmotic mechanism that drives ATP synthesis since it relies on a higher concentration of protons to generate “proton motive force”. The amount of ATP created is directly proportional to the number of protons that are pumped across the inner mitochondrial membrane. ...
Which protein transfers electrons to the last complex?
ISP and cytochrome b are proteins that are located in the matrix that then transfers the electron it received from ubiquinol to cytochrome c1. Cytochrome c1 then transfers it to cytochrome c, which moves the electrons to the last complex. (Note: Unlike ubiquinone (Q), cytochrome c can only carry one electron at a time).
What is the process of generating more ATP?
The process of generating more ATP via the phosphorylation of ADP is referred to oxidative phosphorylation since the energy of hydrogen oxygenation is used throughout the electron transport chain. The ATP generated from this reaction go on to power most cellular reactions necessary for life.
