
Bacteria have four broad classes of organelles: membrane bound (for example, chromatophores, anammoxosomes and magnetosomes; green shading), protein bound (for example, carboxysomes, metabolosomes and iron nanocompartments; blue shading), lipid monolayer (for example, chlorosomes and lipid bodies; orange shading) and phase-defined (for example, nucleolus-like compartment; orange shading, far right).
What organelles are found in bacteria cells?
What Organelles Are Found In Bacterial Cells? A number of membrane-bound organelles – lysosomal organisms, mitochondrial organisms, golgi bodies, reticulums, and nucleus as well. Large ribosome bodies in cytoplasm, and ater and on rough ER. Genetic information that exists inside the cells. DNA is composed primarily of bacterial cells and also ...
What are the 12 organelles in a cell?
Word List:
- Cell Wall
- Chloroplasts
- Chromosomes
- Cytoskeleton
- Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Golgi Apparatus
- Lysosomes
- Microfilaments
- Microtubules
- Mitochondrion (ia)
What are cell organelles and their functions?
Types of organelles and their functions
- Cell Membrane. Cell membrane is also called plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane. ...
- Cell Wall. Cell wall is a non-living structure forming the outer covering for the plasma membrane of fungi and plants.
- Cytoplasm. ...
- Nucleus. ...
- Endoplasmic reticulum. ...
- Mitochondria. ...
- Plastids. ...
- Ribosomes. ...
- Cytoskeleton. ...
- Golgi apparatus. ...
What do organelles do for the cell?
Things to remember
- Organelles are the cellular components responsible for the normal functioning of the cell.
- Organelles are classified into three types i.e., organelles without membrane, single membrane bound organelle and double membrane bound organelle.
- Fluidity is the measure of the movement of the proteins within the membrane.
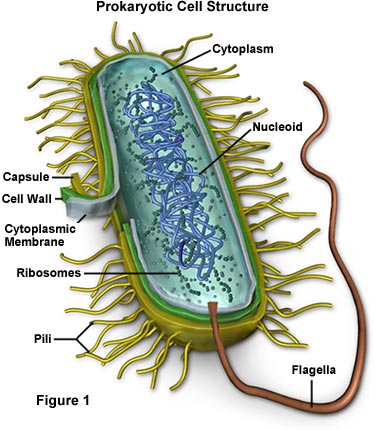
What organelles are in bacteria?
The organelles that bacteria have include:Capsule.Cell wall.Cell membrane.Cytoplasm.Ribosomes.Genetic material.Cilia.Flagella.
Do bacterial cells contain organelles?
Bacteria do not contain membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria or chloroplasts, as eukaryotes do. However, photosynthetic bacteria, such as cyanobacteria, may be filled with tightly packed folds of their outer membrane.
What do bacterial cells contain?
Bacterial cell contains two outer layers: cell wall and cell membrane. The outer layer of the bacterial cell is called cell wall, which is composed of a polymer matrix named peptidoglycan.
What organelles are unique to bacteria cells?
Unique Features They also lack membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria or chloroplasts. The DNA of a bacterial cell is also different from a eukaryotic cell.
What organelle is not found in bacteria?
Answer. Membrane bound cell organelles are absent in Bacteria. » Mitochondria, Plastids, Endoplasmic Reticulum (both smooth and rough), lysosome, golgi apparatus etc are absent In Bacteria. » Nuclear membrane is absent in bacteria.
What are the 7 parts of a bacterial cell?
Bacterial Structure Structure of a typical bacterium. The numbered parts are: (1) pilus, (2) plasmid, (3) ribosome, (4) cytoplasm, (5) cytoplasmic membrane, (6) cell wall, (7) capsule, (8) nucleoid, and (9) flagellum (Source: LadyofHats [Public domain] via Wikimedia Commons).
Do bacterial cells have ribosomes?
Like other organisms, bacteria need ribosomes in order to make proteins. Ribosomes are found mainly bound to the endoplasmic reticulum and the nuclear envelope. As well as the cells are freely dispersed throughout the cytoplasm, depending on whether they are plants, animals, or bacteria.
Do bacteria have ribosomes?
Looking at all the different forms of life on the Earth, we find that all living organisms have ribosomes and that they come in two basic sizes. Bacteria and archaebacteria have smaller ribosomes, termed 70S ribosomes, which are composed of a small 30S subunit and large 50S subunit.
Do bacteria have lysosomes?
The cells of bacteria have no organelles that have membrane covering them. Thus they have their digestion extracellular. The bacteria do keep a breakdown for the molecules inside the media covering the bacteria and then get to absorb the materials. As they do not have membrane bound organs they also have no lysosomes.
What organelle is most like a bacterial cell?
The eukaryotic cell organelle that most resembles a bacterial cell is the C. mitochondria. Both bacteria and mitochondria have their own cell membrane, and their own DNA, and they both reproduce by pinching in half. The nucleus of a cell stores the genetic material of the cell and directs the cellular processes.
Do bacterial cells have a nucleus?
Bacterial cells are considered to be unicellular prokaryotic cells. This means that they do not have a nucleus or any membrane-bound organelles.
Which organelle is closely related to bacteria?
This indicates that chloroplasts and mitochondria are more closely related to bacteria than they are to the nucleus of the cells in which they live.
What are bacteria made of?
Bacteria are microbes with a cell structure simpler than that of many other organisms. Their control centre, containing the genetic information, is contained in a single loop of DNA. Some bacteria have an extra circle of genetic material called a plasmid rather than a nucleus.
What contains DNA in a bacterial cell?
The DNA of most bacteria is contained in a single circular molecule, called the bacterial chromosome. The chromosome, along with several proteins and RNA molecules, forms an irregularly shaped structure called the nucleoid. This sits in the cytoplasm of the bacterial cell.
Which organelle protects bacteria from phagocytocis?
The presence of glycocslyx or capsule, protect the bacteria from phagocytocis and hence such bacteria are more pathogenic. Cell Wall: It is one of the most important organelle for maintaining the viability of bacterial cell.
What is the structure of bacteria?
Structure of Bacteria & it’s Organelles. Bacteria belongs to prokaryotes and hence it lacks nucleus and membrane bound organelle. But it has sufficient organelles that maintains and regulated important physiological, biochemical and molecular process. Invention of Electron microscope allowed us to explore the structure of bacteria.
What is the name of the organelle that swims in liquid media?
Flagella: Flagella known as motility or locomotor organelle also look like hair like appendage. They are longer than pilli and fimbriae. Their structure is rigid and slender. The bacteria are able to swim in liquid media is due to the rotating movement of flagella. Please read to more about Flagella and chemotaxis here.
Why is the cell wall important?
Understanding its role, it’s obvious that if we want to kill the bacteria we would make use of such synthetic or biological chemical which attacks on cell wall. We also use the knowledge of cell wall in distinguishing the bacteria. Please read Bacterial Cell wall composition and its difference for detailed learning. You can also read the method used for distinguishing gram positive and gram negative bacteria.
What are the nutrients that bacteria use in a catastrophe?
In catastrophe situation bacteria utilise the stored nutrients. The bacteria store carbon in the form of glycogen, protein in the form of cyanophycin and other such essential nutrients in inclusion bodies. The inclusion bodies have not only involed in storing food but have found to have multiple functions.
Why do bacteria need inclusion bodies?
Bacteria need such store house because they may not always get nutrient rich environment. In catastrophe situation bacteria utilise the stored nutrients. The bacteria store carbon in the form of glycogen, protein in the form of cyanophycin and other such essential nutrients in inclusion bodies. The inclusion bodies have not only involed in storing food but have found to have multiple functions. The bacteria accumulates gas and stores in the form of gas vacoules. The stored gas allows bacteria to float and maintain bouyancy. Bacteria stores phosphate in the form of polyphosphate chains called as volutin. Phosphate is required for ATP synthesis and DNA or RNA. One more interesting form of inclusion bodies are magnetosome consisting of magnetite (mineral ore with iron). It acts like compass needle to directing the bacteria in the earth’s magnetic field.
What is the cell envelope?
Lets learn and explore them one by one. Cell Envelope – It consist of capsule, cell wall and Cell membrane. The cell envelop: Glycocalyx, cell wall and cell membrane. Glycocalyx: It is a sticky coating produced by many bacteria covering the surface of cell.
How are bacteria different from eukaryotic cells?
They have some interesting organelle-like structures that are reminiscent of eukaryotic organelles and other structures that seem to be unique. Some bacteria have structures that other ones lack.
Which cell has a gas vacuole?
Eukaryotic cells contain vacuoles and vesicles. Vacuoles are larger. These membranous sacs store substances and are the site of certain chemical reactions. Bacteria have gas vacuoles that have a wall made of protein molecules instead of membrane. They store air. They are found in aquatic bacteria and enable the microbes to adjust their buoyancy in the water.
How do bacteria perform photosynthesis?
It involves the capture of light energy by a pigment and its conversion into chemical energy in the reaction center. Researchers who are exploring the chlorosome say that it's an impressive light-harvesting structure.
Why can an illustrator create a picture that represents all animal cells or all plant cells?
Illustrators can create a picture that represents all animal cells or all plant cells because each group has organelles and structures in common. Though some animal and plant cells are specialized and have differences from other ones, their basic structure is the same. This doesn't seem to be true for bacteria because of the apparent variation in their structure.
What is the Golgi body?
The Golgi body can be thought of as a packaging and secretion plant. It's composed of membranous sacs. It accepts substances from the endoplasmic reticulum and changes them into their final form. It then secretes them for use within the cell or outside it. At the moment, highly membranous structures such as the ER and Golgi body haven't been found in bacteria.
Why is it important to study bacteria?
For a long time, bacteria were thought to have comparatively primitive cells. Researchers now know that the organisms are more complex than they realized. Studying the structure and behavior of bacteria is important for advancing scientific knowledge. It’s also important because it might indirectly benefit us.
Where is chlorophyll found?
Chlorophyll is located in the membrane of the thylakoids. The substance traps light energy. Other processes involved in photosynthesis occur in the stroma. Some bacteria contain chlorosomes that contain the bacterial version of chlorophyll and enable them to perform photosynthesis.
When did bacteria first appear on Earth?
This is before plants and animals. From a study of fossils scientists estimate the earliest bacteria to have evolved around 3.5 billion years ago .
Do bacteria have organelles?
Bacterial cells do not have any organelles that are bound by membranes except ribosome which contain granules of RNA and where protein synthesis takes place.
Where are all the cell organelles and inclusions found?
All the cell organelles and inclusions are found floating in cytoplasmic fluid.
Why are ribosomes considered universal organelles?
Ribosomes are known as universal cell organelle because it is found in both bacterial cell and eukaryotic cell.
What is the function of the cell wall?
Function: Helps in attachment to solid surface. 7. Cell wall: It is an important structure of a bacteria. It give shape to the organism. On the basis of cell wall composition, bacteria are classified into two major group ie. Gram Positive and gram negative.
What is the hollow tube that holds the chain of bacteria?
Some bacteria forming chain or trichome are enclosed by a hollow tube like structure known as Sheath.
Which layer of the cell wall is present in both Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria?
Peptidoglycan layer is present in cell wall of both gram positive as well as gram negative bacteria. However, gram positive have thick layer of peptidoglycan.
What is the most important part of the cell?
Nucleus is the most important part of the cell. It controls and directs all the cellular activities and stores hereditary information of cell. Bacterial nucleus is known as nucleoid; it lacks nuclear membrane, nuceloplasm and nucleolus.
Which bacteria are semi-rigid extension of cell wall and cell membrane?
One bacteria may contains one or many prosthecae. Some prosthecae develop bud at the tip and hence helps in reproduction. Some prosthecate bacteria are: Caulibacter , Stella, Prosthecobacter, Hyphomicrobium.
Which organelle separates carbon dioxide from the rest of the cell?
Many species of photosynthetic bacteria (the precursor to the chloroplast organelle that makes plants photosynthetic) have protein-bound compartments that separate the carbon dioxide capturing machinery from the rest of the cell, called carboxysomes.
What are animal cells made of?
Animal cells are made up of many smaller membrane-bound compartments called organelles that perform highly specialized functions necessary for life. Incredibly, several of these organelles have been shown to be evolutionarily related to free-living bacteria, captured and incorporated inside a larger cell billions of years ago in a complex mutually ...
Which enzyme captures carbon dioxide and turns its carbon atoms into chemical forms that the cell can use?
The enzyme that captures the carbon dioxide and turns its carbon atoms into chemical forms that the cell can use is called RuBisCO and it kind of sucks. Every carbon atom in a photosynthetic cell comes from this enzyme's function, but the reaction happens much much slower than most enzymatic reactions and if there's too much oxygen ...
Do bacteria have compartments?
Bacteria themselves are much smaller and much simpler cells, performing many of the same cellular functions without the spatial organization of organelles, all the cell's enzymes and genetic material are instead floating freely in the cell. Some types of bacteria, however, do have compartments that have specialized functions, ...
Do bacteria have organelles?
These compartments are surrounded by a protein shell, not a membrane, so they aren't technically organelles, but they're still pretty amazing. Many species of photosynthetic bacteria (the ...
Plasma Membrane
The plasma membrane is also termed as a Cell Membrane or Cytoplasmic Membrane. It is a selectively permeable membrane of the cell, which is composed of a lipid bilayer and proteins.
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is present both in plant and animal cells. They are jelly-like substances, found between the cell membrane and nucleus. They are mainly composed of water, organic and inorganic compounds. The cytoplasm is one of the essential components of the cell, where all the cell organelles are embedded.
Nucleus
The nucleus is a double-membraned organelle found in all eukaryotic cells. It is the largest organelle, which functions as the control centre of the cellular activities and is the storehouse of the cell’s DNA. By structure, the nucleus is dark, round, surrounded by a nuclear membrane.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The Endoplasmic Reticulum is a network of membranous canals filled with fluid. They are the transport system of the cell, involved in transporting materials throughout the cell. There are two different types of Endoplasmic Reticulum:
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are called the powerhouses of the cell as they produce energy-rich molecules for the cell. The mitochondrial genome is inherited maternally in several organisms. It is a double membrane-bound, sausage-shaped organelle, found in almost all eukaryotic cells.
Plastids
Plastids are large, membrane-bound organelles which contain pigments. Based on the type of pigments, plastids are of three types:
Ribosomes
Ribosomes are nonmembrane-bound and important cytoplasmic organelles found in close association with the endoplasmic reticulum. Ribosomes are found in the form of tiny particles in a large number of cells and are mainly composed of 2/3rd of RNA and 1/3rd of protein.
