See more
What plant did Mendel use in his garden?
garden peaMendel's Crosses Mendel's seminal work was accomplished using the garden pea, Pisum sativum, to study inheritance. This species naturally self-fertilizes, meaning that pollen encounters ova within the same flower.
Why did Mendel use pea plants 10?
Mendel choose pea plants for his experiments because of the following reasons: (i) The flowers of this plant are bisexual. (ii) They are self-pollinating, and thus, self and cross-pollination can easily be performed. (iii) The different physical characteristics were easy to recognize and study.
Did Mendel use hybrid pea plants?
Mendel and his assistants eventually developed 22 varieties of pea plants with combinations of these consistent characteristics. Mendel not only crossed pure-breeding parents, but he also crossed hybrid generations and crossed the hybrid progeny back to both parental lines.
What did Mendel use to pollinate peas?
pollenMendel was interested in the offspring of two different parent plants, so he had to prevent self-pollination. He removed the anthers from the flowers of some of the plants in his experiments. Then he pollinated them by hand with pollen from other parent plants of his choice.
Why did Mendel choose garden pea?
Solution: Pea plants were chosen for Mendel's experiments because they are easy to grow, have a short life period, and produce larger flowers. Pea plants are also self-pollinated.
What is the scientific name of pea plant?
Pisum sativumPea / Scientific namepea, (Pisum sativum), also called garden pea, herbaceous annual plant in the family Fabaceae, grown virtually worldwide for its edible seeds.
What plants did Mendel artificially fertilize?
Mendel's Pea Plants He had carried out artificial fertilization on plants many times in order to grow a plant with a new color or seed shape.
How did Mendel breed his peas?
Mendel followed the inheritance of 7 traits in pea plants, and each trait had 2 forms. He identified pure-breeding pea plants that consistently showed 1 form of a trait after generations of self-pollination. Mendel then crossed these pure-breeding lines of plants and recorded the traits of the hybrid progeny.
What type of pollination did Mendel performed on parenteral pea plants and f1 pea plants?
Mendel was interested in the offspring of two different parent plants, so he had to prevent self-pollination. He removed the anthers from the flowers of some of the plants in his experiments. Then he pollinated them by hand with pollen from other parent plants of his choice.
In what 2 ways did Mendel control how pea plants bred?
Mendel controlled breeding by separating the male and female parts of the flowers so they couldn't reproduce on their own. Next, he used a small brush to move pollen between plants. Lastly, pea plants had a number of visible traits, called phenotypes, that were easy to identify.
Why did Gregor Mendel use pea plants quizlet?
Mendel studied pea plants because they reproduced sexually and had traits that were easily observable.
What are the 7 pea plant traits?
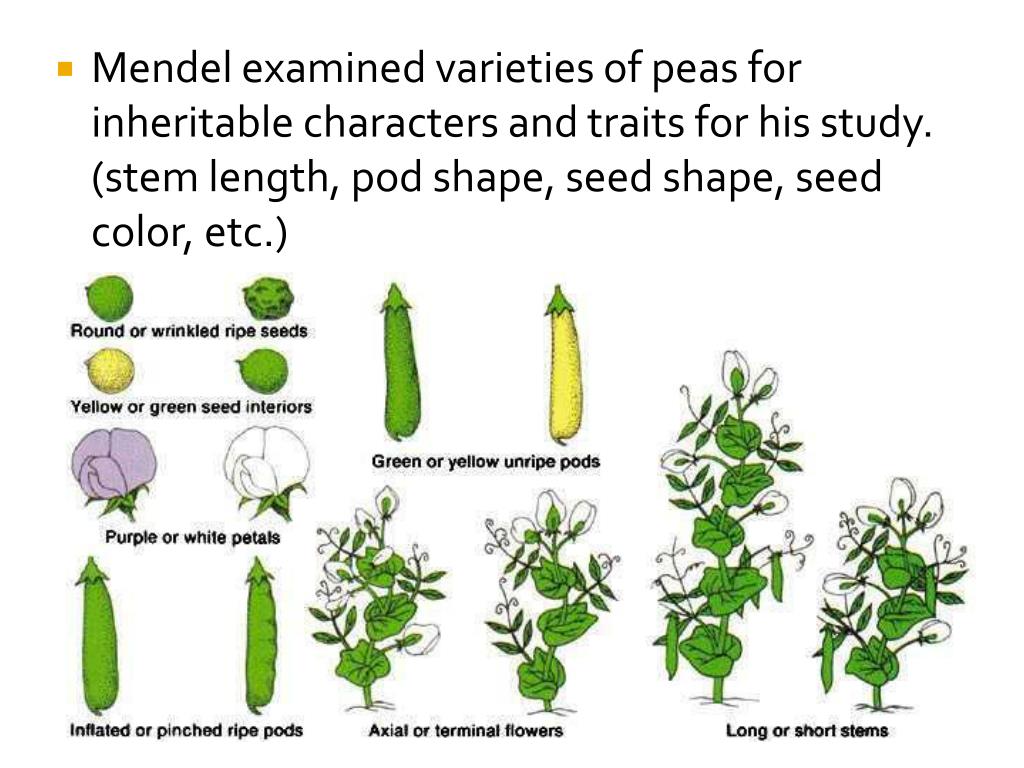
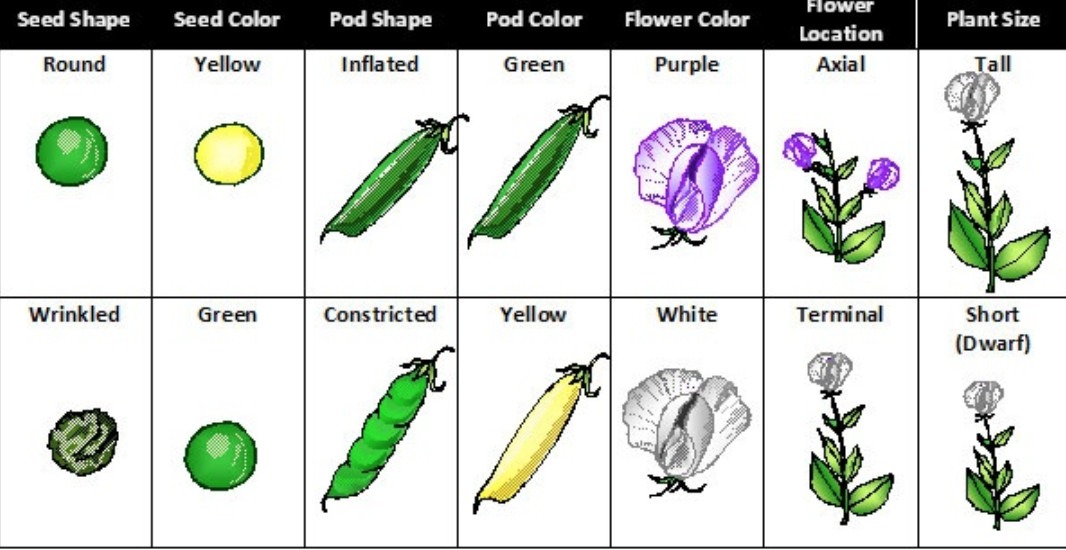
On the next screen, he reveals that there are seven different traits:Pea shape (round or wrinkled)Pea color (green or yellow)Pod shape (constricted or inflated)Pod color (green or yellow)Flower color (purple or white)Plant size (tall or dwarf)Position of flowers (axial or terminal)
Why did Mendel use peas?
Because peas were so easy to work with and prolific in seed production, Mendel could perform many crosses and examine many individual plants, making sure that his results were consistent (not just a fluke) and accurate (based on many data points).
How did Mendel investigate pea traits?
short height), he began to investigate how the traits were inherited by carrying out a series of crosses.
How do pea plants mate?
This is done by transferring pollen from the anthers (male parts) of a pea plant of one variety to the carpel (female part) of a mature pea plant of a different variety. To prevent the receiving plant from self-fertilizing, Mendel painstakingly removed all of the immature anthers from the plant’s flowers before the cross.
How many traits did Mendel study?
Mendel studied the inheritance of seven different features in peas, including height, flower color, seed color, and seed shape. To do so, he first established pea lines with two different forms of a feature, such as tall vs. short height. He grew these lines for generations until they were pure-breeding (always produced offspring identical to the parent), then bred them to each other and observed how the traits were inherited.
What did Mendel find about the features of plants?
Mendel also found that the features were inherited independently: one feature, such as plant height , did not influence inheritance of other features, such as flower color or seed shape.
What is the dominant trait of Mendel?
One form of a feature, such as tall, always concealed the other form, such as short, in the first generation after the cross. Mendel called the visible form the dominant trait and the hidden form the recessive trait.
Why did Mendel have difficulty paying for his education?
As a young man, Mendel had difficulty paying for his education due to his family's limited means , and he also suffered bouts of physical illness and depression; still, he persevered to graduate from high school and, later, university. After finishing university, he joined the Augustinian Abbey of St. Thomas in Brno, in what is now the Czech Republic. At the time, the monastery was the cultural and intellectual hub of the region, and Mendel was immediately exposed to new teachings and ideas.
Why did Mendel study pea plants?
To study genetics, Mendel chose to work with pea plants because they have easily identifiable traits (Figure below). For example, pea plants are either tall or short, which is an easy trait to observe. Mendel also used pea plants because they can either self-pollinate or be cross-pollinated.
What was Mendel's purpose in his experiments?
Likewise, what was the purpose of Mendel's experiments? Mendel planned to selectively cross pollinate the peas with one another to study the traits passed on and the results from each pollination. He acquired about 34 varieties of peas and chose 22 different types to conduct his experiments with which varied in color and size.
When Mendel measured two or more traits (eg, height and color) in an experiment, he found that?
When Mendel measured two or more traits (eg, height and color) in an experiment he found that each trait was transmitted independently. For example, tall or short plants can have smooth or wrinkled seeds. This is Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment (which strictly holds only if the genes are not too close).
Why did Mendel use peas?
Gregor Mendel chose pea plants for his experiments because they are easy to raise, have many offspring per mating, can fertilize themselves and have varieties in genotype and phenotype that are easily observable. These characteristics make pea plants ideal in the study of genetics and heredity.
What are the characteristics of a pea plant?
In general, pea plants grow well with minimal supervision and care .
Can peas self fertilize?
In general, pea plants grow well with minimal supervision and care. They can self-fertilize, so Mendel could pollinate the plants himself. The large number of offspring produced per mating gave Mendel a good number of plants to observe and work out the ratios of dominant and recessive alleles.
Why did Mendel select pea plants?
Mendel selected pea plants because they had easily observable traits. He found about 7 traits which he could use for his experiments. They had short life cycle which meant fast reproduction, so he could complete his experiment faster. Bisexual flowers which self pollinate.
What did Mendel discover about the garden pea plant?
In 1865, through his observations of the garden pea plants that grew there, Mendel developed three basic principles that—although ignored at the time by his scientific colleagues—would later become the foundation for the new science of genetics.
Why did Mendel choose a plant for his experiment?
There were many reasons of Mendel choosing the plant for his experiment on genetics…some of them are-. Pea plants are annual so experimenting was easy because after one year…you get rid of the parent plant and work on the daughter plants. Pea plants are bisexual and reproduce sexually.
Why is Mendel known as the father of modern genetics?
Mendel is known as father of modern genetics due to this genetic experiment with Pea (Pisum Sativum).
How many traits does a pea plant have?
Pea plant seven contrasting traits tall and dwarf yellow and green these constrasting character help ed a lot to Mendel and he also choose true breeding pea plant
What character traits did Mendel have in his garden pea?
Gregor Mendel and His Choice of Garden Pea. it exhibited characters that are constant and easily recognizable such as texture of seed, height or stature, color of specific plant organs, etc.
What is Gregor Mendel's contribution to genetics?
Gregor Mendel has big contributions to the field of genetics, for he has established a base for the study of inheritance and all the studies happening in the world of genetics is all developing because of this famous man's work.
Why is Mendel considered the father of modern genetics?
Mendel is known as the father of modern genetic because of genetic experiment with Pea or Pisum Sativum. Easy to grow in the garden. The flowers of pea plants are hermaphrodite, i.e flowers have bisexual characteristics. The generation time of pea plants is less.
What is the law of independent assortment?
(b) The law of independent assortment states that the alleles of different genes are inherited independently within the organisms that reproduce sexually.
