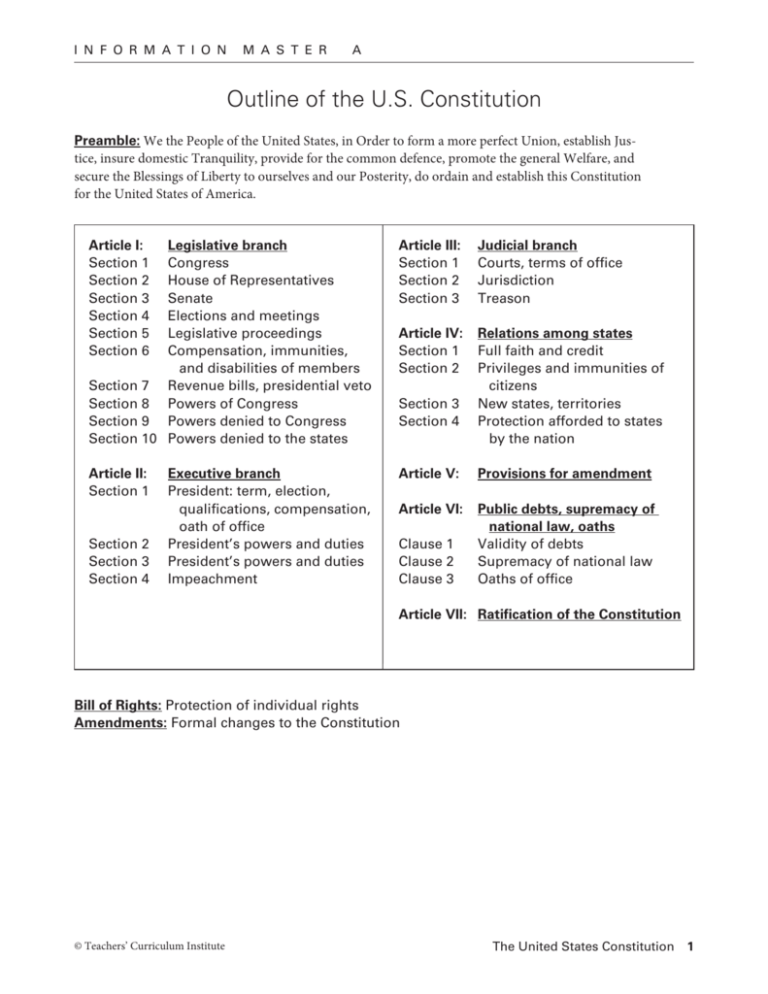
What powers are denied to Congress in Article 1?
The powers denied to Congress are enumerated in Article 1, Section 9 of the Constitution of the United States. A key provision necessary for passing the original Constitution was a compromise between the free and slave states. In that section of the Constitution, Congress was prevented from interfering with the slave trade until at least 1808.
What does Article 1 Section 9 of the constitution say about immigration?
Article I Section 9 Clause 1 The Migration or Importation of such Persons as any of the States now existing shall think proper to admit, shall not be prohibited by the Congress prior to the Year one thousand eight hundred and eight, but a Tax or duty may be imposed on such Importation, not exceeding ten dollars for each Person.
Does the Constitution limit the powers of Congress?
Robert Longley is a U.S. government and history expert with over 30 years of experience in municipal government. He has written for ThoughtCo since 1997. Article 1, Section 9 of the U.S. Constitution places limits on the powers of Congress, the Legislative Branch.
What are the constitutional restrictions on the legislative branch?
Constitutional Restrictions on the Legislative Branch. Article 1, Section 9 of the U.S. Constitution places limits on the powers of Congress, the Legislative Branch. These restrictions include those on limiting the slave trade, suspending civil and legal protections of citizens, apportionment of direct taxes, and granting titles of nobility.

How are the powers of Congress limited in Article 1 Section 9 of the Constitution?
Article I, Section 9 specifically prohibits Congress from legislating in certain areas. In the first clause, the Constitution bars Congress from banning the importation of slaves before 1808. In the second and third clauses, the Constitution specifically guarantees rights to those accused of crimes.
Where are the powers denied to Congress?
"The powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the states, are reserved to the states respectively, or to the people."
What does Article I Section 9 Clause 1 mean?
Article 1, Section 9, Clause 1, is one of a handful of provisions in the original Constitution related to slavery, though it does not use the word “slave.” This Clause prohibited the federal government from limiting the importation of “persons” (understood at the time to mean primarily enslaved African persons) where ...
What are some denied powers?
Grant titles of nobility. Permit slavery (13th Amendment) Deny citizens the right to vote due to race, color, or previous servitude (15th Amendment) Deny citizens the right to vote because of gender (19th Amendment)
Which of the following is a power denied to Congress by the Constitution?
Today, there are four remaining relevant powers denied to Congress in the U.S. Constitution: the Writ of Habeas Corpus, Bills of Attainder and Ex Post Facto Laws, Export Taxes and the Port Preference Clause.
What are the powers in section 9 called?
Article 1, Section 9 of the U.S. Constitution places limits on the powers of Congress, the Legislative Branch. These restrictions include those on limiting the slave trade, suspending civil and legal protections of citizens, apportionment of direct taxes, and granting titles of nobility.
What does Section 9 of the Constitution say?
9. (1) Everyone is equal before the law and has the right to equal protection and benefit of the law. (2) Equality includes the full and equal enjoyment of all rights and freedoms.
What Congress Cannot do?
Congress could not raise funds, regulate trade, or conduct foreign policy without the voluntary agreement of the states.
What powers are denied to Congress by the Constitution quizlet?
No titles of nobility or accept foreign titles without Congressional approval (if someone comes in the U.S. saying they are the King of Italy it does not mean anything to the U.S.
What are some limits on the powers of Congress?
Other limits on are that it cannot tax products from a state, it cannot give preference to any states seaport, government money can only be spent by passing a law and finally Congress cannot issue titles of nobility. That means the Senate or House cannot make people knights, lords or duchesses.
What is the meaning of Article 4 section 2?
The Meaning Article IV, Section 2 guarantees that states cannot discriminate against citizens of other states. States must give people from other states the same fundamental rights it gives its own citizens.
What are 3 powers denied to states?
No State shall enter into any Treaty, Alliance, or Confederation; grant Letters of Marque and Reprisal; coin Money; emit Bills of Credit; make any Thing but gold and silver Coin a Tender in Payment of Debts; pass any Bill of Attainder, ex post facto Law, or Law impairing the Obligation of Contracts, or grant any Title ...
What is Section 9?
Section 9. The Migration or Importation of such Persons as any of the States now existing shall think proper to admit, shall not be prohibited by the Congress prior to the Year one thousand eight hundred and eight, but a Tax or duty may be imposed on such Importation, not exceeding ten dollars for each Person.
What is the meaning of Clause 2 of the Habeas Corpus?
Clause 2. The Privilege of the Writ of Habeas Corpus shall not be suspended, unless when in Cases of Rebellion or Invasion the public Safety may require it. ArtI.S9.C2.1 Writ of Habeas Corpus and the Suspension Clause. Clause 3. No Bill of Attainder or ex post facto Law shall be passed. ArtI.S9.C3.1 Bills of Attainder.
Can the United States grant a title of noble?
No Title of Nobility shall be granted by the United States: And no Person holding any Office of Profit or Trust under them, shall, without the Consent of the Congress, accept of any present, Emolument, Office, or Title, of any kind whatever, from any King, Prince, or foreign State. ArtI.S9.C8.1 Foreign Emoluments Clause.
What is the meaning of Clause 1 of the Constitution?
Clause 1, Importation of Enslaved People. "Clause 1: The Migration or Importation of such Persons as any of the States now existing shall think proper to admit, shall not be prohibited by the Congress prior to the Year one thousand eight hundred and eight, but a Tax or duty may be imposed on such Importation, not exceeding ten dollars ...
What is the meaning of clause 8?
Clause 8, Titles of Nobility and Emoluments . "Clause 8: No Title of Nobility shall be granted by the United States: And no Person holding any Office of Profit or Trust under them, shall, without the Consent of the Congress, accept of any present, Emolument, Office, or Title, of any kind whatever, from any King, Prince, or foreign State.".
What are some examples of violations of the Emoluments Clause?
Past examples of violations of the Emoluments Clause by some of America’s Founding Fathers include Benjamin Franklin’s acceptance of diamond-covered snuffbox from the King of France and John Jay’s acceptance of a purebred stallion from the King of Spain.
What are the restrictions on the slave trade?
These restrictions include those on limiting the slave trade, suspending civil and legal protections of citizens, apportionment of direct taxes, and granting titles of nobility. It also prevents government employees and officials from accepting foreign gifts and titles, known as emoluments.
When did the Supreme Court dismiss the Saudi Arabia arms deal?
The payments had come just a few months before Trump had authorized one of the largest arms deals to Saudi Arabia in US history. On January 25, 2021, the U.S. Supreme Court dismissed the suit, unanimously finding that no case or controversy remained because Trump was no longer in office. Cite this Article. Format.
Which amendment allowed income tax to be levied on trade between states?
Explanation: These clauses set limits on how taxes can be levied. Originally, an income tax would not have been allowed, but this was authorized by the 16th Amendment in 1913. These clauses prevent taxes from being levied on trade between states.
Can a civil servant accept a foreign gift?
If you are a civil servant or elected official, you can't accept anything from a foreign government or official, including an honorary title or an office. This clause prevents any government official from receiving foreign gifts without the permission of Congress.
What are the 4 powers denied to Congress?
What Are the Four Powers Denied to Congress? Article I Section 9 of the United States Constitution prohibits Congress from six specific areas of legislation. However, the first limit placed on congressional power was a limit on regulating the slave trade which did not extend beyond the year 1808. Article I Section 9 also prohibited Congress ...
Which clause of Article I Section 9 limits Congress' power?
The second and third clauses of Article I Section 9 limit congressional powers in ways designed specifically to protect the rights of citizens accused of crimes. The second clause prohibits Congress from suspending the Privilege of the Writ of Habeas Corpus.
What powers did Congress deny Congress?
Constitution: the Writ of Habeas Corpus, Bills of Attainder and Ex Post Facto Laws, Export Taxes and the Port Preference Clause.
What does the 5th clause mean?
The fifth clause reads very simply, "No Tax or Duty shall be laid on Articles exported from any State.". This means that Congress is prohibited from imposing export taxes on goods transported across state lines and also across international borders.
What is an ex post facto law?
Ex post facto laws are laws that make an action illegal after that action has been committed. By prohibiting ex post facto laws, the framers ensured that all citizens would have the ability to know an action was illegal before committing it.
Who has suspended Habeas Corpus?
While Congress does not generally have the power to suspend the Writ of Habeas Corpus, presidents like Abraham Lincoln and Franklin D. Roosevelt have suspended the Writ during war times, the Civil War and World War II respectively. In more recent times, George W. Bush tried to suspend Habeas Corpus after the 9/11 attacks and was overturned by ...
What is the purpose of the Port Preference Clause?
The sixth clause, also called the Port Preference Clause, was also written with the aim of preventing Congress from discriminating against certain states or regions. This clause prohibits Congress from passing any commercial or trade regulations that favor the ports of one state over the ports of another state.
Main Idea
Congress has implied powers, but there are limits to them. Section 9 of Article 1 of the Constitution lists the powers that are denied to Congress. These limits protect the citizens of the United States of America from unjust treatment.
Illegal Punishment
No preference can be given to a certain port of a certain state where goods can be dropped off or shipped and where ships can come and go.
