What does prolactin stimulate and what gland produces it?
Prolactin is a hormone produced by the pituitary, the gland at the base of the brain. Prolactin stimulates the production of breast milk after childbirth; it also has the task of regulating the menstrual cycle in women.
What causes high prolactin?
Why Do You Have High Prolactin Levels?
- Prolactinoma A prolactinoma is a tumor in the pituitary gland that secretes prolactin. ...
- Prescription Drugs Certain prescription drugs can increase prolactin levels. Drugs that block dopamine, for example, will cause a rise in prolactin levels. ...
- Other Causes
What are the dangers of high prolactin levels?
What are the side effects of high prolactin levels in men?
- Headaches
- Visual impairment
- Reduced libido
- Fertility issues
- Erectile dysfunction
- Abnormal lack of body and facial hair
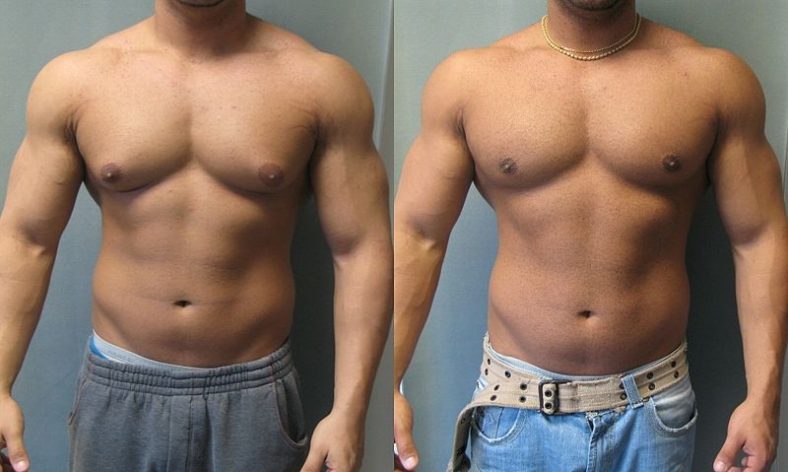
- Gynecomastia (commonly known as man-boobs)
What is antidiuretic hormone produced by?
The anti-diuretic hormone is secreted by the neurohypophysis of the pituitary gland. Since it stimulates the constriction of blood vessels and results in an increase in blood pressure, therefore it is called vasopressin.

What type of cells produce prolactin?
Prolactin is a polypeptide hormone that is synthesized in and secreted from specialized cells of the anterior pituitary gland, the lactotrophs.
What produces prolactin and growth hormones?
Prolactin is a single-chain protein hormone closely related to growth hormone. It is secreted by so-called lactotrophs in the anterior pituitary. It is also synthesized and secreted by a broad range of other cells in the body, most prominently various immune cells, the brain and the decidua of the pregnant uterus.
What hormone does prolactin?
Prolactin is a hormone released by the pituitary gland. The pituitary is a small gland at the base of the brain. It regulates the body's balance of many hormones. Prolactin stimulates breast development and milk production in women.
When does your body produce prolactin?
You will need to take your test about three to four hours after waking up. Prolactin levels change throughout the day, but are usually the highest in early morning.
Does high prolactin cause low estrogen?
Endocrine Condition Therefore, high prolactin causes low estrogen in women and low testosterone in men and decreases fertility in both women and men. Low estrogen and testosterone also can result in bone loss and osteoporosis.
Is prolactin a stress hormone?
Prolactin (PRL) is one of the most versatile hormones known. It is considered an adaptive hormone due to the key roles it plays in the modulation of the stress response and during pregnancy and lactation.
What happens if prolactin is high?
Too much prolactin reduces the production of the hormones estrogen and testosterone. Too much prolactin also can prevent the release of an egg during the menstrual cycle (anovulation) in females. In males, too much prolactin also can lead to decreased sperm production. Bone loss (osteoporosis).
Can stress cause high prolactin levels?
Stress is also an important physiologic cause of hyperprolactinemia, and its clinical significance is still being explored. This review will provide an overview of prolactin physiology, the role of stress in prolactin secretion, as well as the general clinical approach to hyperprolactinemia.
Where is growth hormone produced?
the pituitary glandGH is produced in the pituitary gland. In the periphery, GH acts directly and indirectly through stimulation of IGF-I production.
Which hormone is produced in the hypothalamus?
The thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH), corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), somatostatin, and dopamine are released from the hypothalamus into the blood and travel to the anterior pituitary.
What type of hormone is growth hormone?
peptide hormoneGrowth hormone is a peptide hormone that stimulates growth, development and regeneration. This peptide hormone is made up of 191 amino acids that form a long, single-chain polypeptide. Growth hormone is synthesized in the somatotropic cells, which are found in the anterior pituitary gland.
Where is the pituitary gland?
the brainThe pituitary gland is no larger than a pea, and is located at the base of the brain. The gland is attached to the hypothalamus (a part of the brain that affects the pituitary gland) by nerve fibers and blood vessels.
What is prolactin in biology?
PubMed search. n/a. n/a. Wikidata. View/Edit Human. Prolactin, also known as lactotropin, is a protein best known for its role in enabling mammals (and birds), usually females, to produce milk. It is influential in over 300 separate processes in various vertebrates, including humans.
Where is prolactin secreted?
Prolactin is secreted from the pituitary gland in response to eating, mating, estrogen treatment, ovulation and nursing. It is secreted heavily in pulses in between these events. Prolactin plays an essential role in metabolism, regulation of the immune system and pancreatic development.
What is the key regulator of prolactin production?
A key regulator of prolactin production is estrogens that enhance growth of prolactin-producing cells and stimulate prolactin production directly, as well as suppressing dopamine . In decidual cells and in lymphocytes the distal promoter and thus prolactin expression is stimulated by cAMP.
What are the two types of prolactins in fish?
Many fish have variants prolactin A and prolactin B. Most vertebrates, including humans, also have the closely related somatolactin. In humans, three smaller (4, 16, and 22 kDa) and several larger (so-called big and big-big) variants exist.
How long does prolactin stay in your system?
It is used to stimulate lactation in animals. The biological half-life of prolactin in humans is around 15–20 minutes. The D 2 receptor is involved in the regulation of prolactin secretion, and agonists of the receptor such as bromocriptine and cabergoline decrease prolactin levels while antagonists of the receptor such as domperidone, metoclopramide, haloperidol, risperidone, and sulpiride increase prolactin levels. D 2 receptor antagonists like domperidone, metoclopramide, and sulpiride are used as galactogogues to increase prolactin secretion in pituitary gland and induce lactation in humans.
Why does prolactin rise after surgery?
Levels can rise after exercise, high-protein meals, minor surgical procedures, following epileptic seizures or due to physical or emotional stress. In a study on female volunteers under hypnosis, prolactin surges resulted from the evocation, with rage, of humiliating experiences, but not from the fantasy of nursing.
When was the first IRP for human prolactin?
Previous standards use other ratios. The first International Reference Preparation (or IRP) of human Prolactin for Immunoassay was established in 1978 (75/504 1st IRP for human prolactin) at a time when purified human prolactin was in short supply. Previous standards relied on prolactin from animal sources.
Where is prolactin produced?
In humans, prolactin is produced both in the front portion of the pituitary gland ( anterior pituitary gland) and in a range of sites elsewhere in the body. Lactotroph cells in the pituitary gland produce prolactin, where it is stored and then released into the bloodstream. Human prolactin is also produced in the uterus, immune cells, brain, ...
What is the name of the hormone that makes prolactin?
Alternative names for prolactin. In everyday language, prolactin is referred to as the ‘milk hormone’; PRL; luteotropic hormone; LTH.
How is prolactin controlled?
One of the main regulators of the production of prolactin from the pituitary gland is the hormone called dopamine, which is produced by the hypothalamus, the part of the brain directly above the pituitary gland. Dopamine restrains prolactin production, so the more dopamine there is, the less prolactin is released. Prolactin itself enhances the secretion of dopamine, so this creates a negative feedback loop.
What happens if I have too much prolactin?
The condition of having too much prolactin circulating in the blood is called hyperprolactinaemia. The most common causes of hyperprolactinaemia include pregnancy, medications that reduce dopamine action in the body, thyroid underactivity and benign pituitary tumours (known as prolactinomas). Symptoms can include the unwanted production of milk, disturbances to the menstrual cycle and symptoms due to oestrogen deficiency (in women) or testosterone deficiency (in men). The vast majority of patients with a prolactinoma can be treated successfully using drugs which mimic the action of dopamine. The most commonly used is cabergoline.
What hormones increase prolactin production?
Oestrogen is another key regulator of prolactin and has been shown to increase the production and secretion of prolactin from the pituitary gland. Studies have shown small increases in prolactin in the blood circulation of women during stages of their reproductive cycle where oestrogen levels are at their highest.
Which hormones decrease prolactin?
In addition to dopamine and oestrogen, a whole range of other hormones can both increase and decrease the amount of prolactin released in the body, with some examples being thyrotropin-releasing hormone, oxytocin and anti-diuretic hormone.
Can low prolactin cause insufficient milk production?
A decrease in the amount of prolactin secreted can lead to insufficient milk being produced after giving birth . Most people with low prolactin levels do not have any specific medical problems, although preliminary evidence suggests they might have reduced immune responses to some infections.
What is prolactin in physiology?
Prolactin is a polypeptide hormone that is responsible for lactation, breast development, and hundreds of other actions needed to maintain homeostasis. The chemical structures prolactin is similar to the structure of growth hormone and placental lactogen hormone.
What is the family of prolactin?
Together, they form the "prolactin/growth hormone/placental lactogen" family, which is characterized by a conserved helix bundle protein composition. All hormones in this family derive from a common ancestral gene. Prolactin is a polypeptide hormone that is responsible for lactation, breast development, and hundreds of other actions needed ...
What is the role of prolactin in breast development?
Prolactin is a polypeptide hormone that is responsible for lactation, breast development, and hundreds of other actions needed to maintain homeostasis. The chemical structures prolactin is similar to the structure of growth hormone and placental lactogen hormone.
How long does it take for prolactin to drop after breastfeeding?
If the mother does not nurse her baby, prolactin levels fall to non-pregnant levels after 1 to 2 weeks.
How much prolactin is in a male?
In males, serum prolactin levels range from 2 to 18 ng/ml, in females 2 to 30 ng/ml, and during the third trimester of pregnancy, 10 to 210 ng/ml. In cases of prolactinomas, the serum prolactin level is typically greater than 200 mg/mL.
Why do lactotrophs increase during pregnancy?
The number of lactotrophs will increase during pregnancy in response to the physiological need to develop breast tissues and to prepare for milk production. It should be noted that the increase in lactotrophs cells is not accompanied by an increase in angiogenesis.
Which hormones are released by the hypothalamus and have activity in modulating lactotophic activity?
Factors that stimulate production, upregulate prolactin gene transcription while factors that inhibit secretion downregulate prolactin gene transcription. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) and dopamine are both released by the hypothalamus and have activity in modulating lactotophic activity.
What is prolactin hormone?
Prolactin is a protein hormone of the anterior pituitary gland that was originally named for its ability to promote lactation in response to the suckling stimulus of hungry young mammals . We now know that prolactin is not as simple as originally described. Indeed, chemically, prolactin appears in a multiplicity of posttranslational forms ranging from size variants to chemical modifications such as phosphorylation or glycosylation. It is not only synthesized in the pituitary gland, as originally described, but also within the central nervous system, the immune system, the uterus and its associated tissues of conception, and even the mammary gland itself. Moreover, its biological actions are not limited solely to reproduction because it has been shown to control a variety of behaviors and even play a role in homeostasis. Prolactin-releasing stimuli not only include the nursing stimulus, but light, audition, olfaction, and stress can serve a stimulatory role. Finally, although it is well known that dopamine of hypothalamic origin provides inhibitory control over the secretion of prolactin, other factors within the brain, pituitary gland, and peripheral organs have been shown to inhibit or stimulate prolactin secretion as well. It is the purpose of this review to provide a comprehensive survey of our current understanding of prolactin's function and its regulation and to expose some of the controversies still existing.
What is the function of prolactin?
Prolactin: structure, function, and regulation of secretion. Prolactin is a protein hormone of the anterior pituitary gland that was originally named for its ability to promote lactation in response to the suckling stimulus of hungry young mammals. We now know that prolactin is not as simple as originally described.
Does dopamine inhibit prolactin?
Finally, although it is well known that dopamine of hypothalamic origin provides inhibi tory control over the secretion of prolactin, other factors within the brain, pituitary gland, and peripheral organs have been shown to inhibit or stimulate prolactin secretion as well.
Is prolactin a simple hormone?
We now know that prolactin is not as simple as originally described. Indeed, chemically, prolactin appears in a …. Prolactin is a protein hormone of the anterior pituitary gland that was originally named for its ability to promote lactation in response to the suckling stimulus of hungry young mammals. We now know that prolactin is not as simple as ...
What is Prolactin?
Prolactin is a hormone that mammals secrete from their pituitary gland (the part of the brain where all of our hormones come from) and promotes lactation and mammary gland development ( 1 ). Lactation is the ability to produce milk to feed our babies, and mammary glands are the milk production sites within breast tissues. Prolactin levels increase during pregnancy and breastfeeding, then decrease after delivery and weaning ( 2 ). This is an interesting evolutionary advantage because breast milk contains so many different beneficial ingredients beyond nutrition, including vital immune-system boosters, molecules needed for organ growth and development, and microbes to colonize our gut, forming the gut microbiome ( 3 ). Several types of milk exist, but “What Is The Healthiest Milk?”
Why is prolactin important?
We’ve now seen why prolactin is essential for good health and what happens when this misunderstood hormone is too much or too little. Beyond pregnancy and breastfeeding (which are extremely important on their own), this hormone may have a variety of other functions in mental health (interacting with serotonin and dopamine), metabolic disorders (seeming to have some interactions with our gut microbiome and diabetes development), and a number of other body functions. Prolactin remains a topic of debate and research, as scientists continue to try to determine all of the applications and functions of this mysterious hormone.
How does prolactin help with pregnancy?
Prolactin plays a significant role in the stimulation of pregnancy, fertilization of eggs in the ovaries, ovulation, and mammary gland development and maintenance during and shortly after pregnancy ( 5 ). Studies in mice have even found that prolactin has a role to play in maternal behavior. When prolactin was not present, mice did not develop normal maternal behavior such as feeding, grooming, and care of their pups. During pregnancy and lactation, the mice developed new neurons in the forebrain, which migrated to the olfactory bulb (the part of our brain right at the front, near the nose). Researchers suggest that the addition of these new neurons likely helped the new mother adapt to the needs of her pups, increasing the likelihood of their survival, though details on this are still being worked out ( 5 ).
What is the best food to digest beta glucan?
Oats, brown rice, and barley are all high in beta-glucan, a form of fiber found in the outer shell (called the kernel). To learn more about beta-glucan, take a look at the “World’s Healthiest Rice Varieties.” This fiber helps with digestion and has many health benefits. Among the lesser-known benefits is a recent study performed in cells that showed beta-glucan stimulated prolactin secretion. Of course, further studies in animal and human models are needed, but this fiber may hold the key to maintaining healthy prolactin levels.
Does asparagus increase prolactin?
Asparagus. Asparagus seems to increase prolactin, thus increasing lactation and milk production, in some studies ( 12 ). However, how this occurs and why remains a mystery under investigation. In rats, those given asparagus extract had a higher prolactin level than those that did not receive the extract.
Does prolactin work?
When Prolactin Does Work. Prolactin has been tested as a treatment for lactation insufficiency before in women who cannot produce enough milk. Breastfeeding is encouraged for newborns where it is a feasible option (some women cannot breastfeed due to medical conditions or treatments such as radiation).
Is prolactin a lactation aid?
So, we can see that prolactin isn’t as simple as “a lactation aid” and has many roles. The majority of research so far on prolactin has been on its effect during conception, pregnancy, and early stages of post-birth infant development.
How does prolactin affect fertility?
A person’s fertility can be affected by how much of the hormone prolactin they have in their blood. A doctor can suggest possible treatments after a prolactin level test has measured the amount that is in a blood sample. Prolactin is the hormone that tells the body to make breast milk when a person is pregnant or breast-feeding.
How high is prolactin?
Prolactin levels of between 30 ng/mL and 200 ng/mL are considered moderately high. This level of prolactin in the blood can have many causes.
What tests show high prolactin levels?
liver disease. anorexia nervosa. If test results show high levels of prolactin, further tests may be needed. If a doctor suspects that a prolactinoma is causing high levels, they may recommend a CT or MRI scan. The scan can look at the pituitary gland and show if there is a growth and how large it has become.
What does it mean to test prolactin levels?
A doctor may recommend a prolactin level test if someone: produces breast milk when not pregnant or breast-feeding. has symptoms of a growth on the pituitary gland called a prolactinoma. has another pituitary disorder. experiences infertility or irregular periods.
What is the prolactin level test?
Doctors measure the hormone levels in nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL). A prolactin level test is simple and measures the amount of the hormone in the blood. It can check to see if levels are too low or too high.
How much does a prolactin level test cost?
The cost of the test varies widely, depending on the test provider. The price can range from $20 to $32 with health insurance, to $140 or more without.
Why do doctors measure prolactin levels?
Doctors will measure prolactin levels to obtain more information about someone’s health.
What foods increase prolactin?
Increase oats, quinoa, and sesame in your diet. Whole grain oats contain a protein that may increase prolactin, so incorporate them into your meals regularly. The same goes for quinoa and seeds, especially sesame seeds.
What hormones are produced by the pituitary gland?
The pituitary gland regulates many hormones, including prolactin – if your pituitary isn’t working well it may cause low prolactin. If you’re worried about your prolactin level, visit your doctor so they can check your pituitary gland.
How to increase milk supply?
Try taking fenugreek. Some mothers find that the herb fenugreek may increase milk supply, likely by increasing prolactin. Get capsules at your drug store or health food store, or by ordering them online in 610mg capsules. Try taking 2 capsules 3 times daily with food. If you have no side effects, you can gradually increase the dose to 4 capsules 3 times daily. A normal side effect is that your urine and sweat may start to smell like maple syrup.
What hormone stimulates breasts to make milk during pregnancy?
Prolactin is the hormone that stimulates your breasts to make milk during and after pregnancy. [1] X Trustworthy Source Mayo Clinic Educational website from one of the world's leading hospitals Go to source.
Does metoclopramide increase milk supply?
Try metoclopramide to boost milk supply, if approved by your doctor. Metoclopramide (Reglan, Maxolon) indirectly increases your prolactin. It requires a prescription, so visit your doctor to discuss whether this medication is safe for you to take. [9]
Can you stop taking prolactin?
Limit the prolactin-decreasing drugs you take. Some medications decrease prolactin as a side effect. Never stop taking your medications without talking to your doctor first, but if you’re taking any of the following then discuss your concerns with your doctor.
Can you breastfeed with low prolactin?
Not being able to breastfeed due to low milk supply is often the biggest problem with having low prolactin, and is why many mothers seek remedies to increase their prolactin level. You can increase your prolactin by stimulating your breasts with regular feedings and pumping, and if needed, with prescription medications. Steps.
Why is prolactin overproduced?
Other possible causes of prolactin overproduction include medications, other types of pituitary tumors, an underactive thyroid gland, ongoing irritation to the chest, pregnancy and breast-feeding.
How to treat prolactin?
Doctors can often treat prolactinoma with medications to restore your prolactin level to normal. Surgery to remove the pituitary tumor also might be an option.
What is the cause of pituitary tumors?
The cause of these tumors is unknown. The pituitary gland is a small bean-shaped gland situated at the base of your brain. Despite its small size, the pituitary gland influences nearly every part of your body. Its hormones help regulate important functions such as growth, metabolism, blood pressure and reproduction.
What is the effect of prolactinoma on the pituitary?
This tumor causes the pituitary to make too much of a hormone called prolactin. The major effect of prolactinoma is decreased levels of some sex hormones — estrogen in women and testosterone in men. Although prolactinoma isn't life-threatening, it can cause vision difficulties, infertility and other problems.
What is a prolactinoma?
Open pop-up dialog box. Close. Prolactinoma. Prolactinoma. A prolactinoma is a type of tumor that develops in the pituitary gland at the base of your brain. Prolactinoma is a noncancerous tumor of the pituitary gland. This tumor causes the pituitary to make too much of a hormone called prolactin.
What causes facial hair to grow?
Acne and excessive body and facial hair growth. In males, prolactinoma can cause: Erectile dysfunction. Decreased body and facial hair. Enlarged breasts, uncommonly. In both sexes, prolactinoma can cause: Low bone density. Reduction of other hormone production by the pituitary gland as a result of tumor pressure.
What are the complications of prolactin?
Complications. Complications of prolactinoma may include: Bone loss (osteoporosis). Too much prolactin can reduce production of the hormones estrogen and testosterone, resulting in decreased bone density and an increased risk of osteoporosis. Pregnancy complications.
Overview
Lactation is the process of producing and releasing milk from the mammary glands in your breasts. Lactation begins in pregnancy when hormonal changes signal the mammary glands to make milk in preparation for the birth of your baby.
Function
A series of hormonal events, which begin when you’re pregnant, trigger the lactation process. That process is called lactogenesis.
Anatomy
Mammary glands are commonly called breasts and both genders have them. They are located on your chest and are composed of connective tissue, fat and special glandular tissue that makes milk. A woman’s glandular tissue is slightly different because it contains the alveoli and lobules necessary for producing milk.
Conditions and Disorders
The ability to lactate and the length of time you’re able to produce milk varies. Some can produce milk for years, while others have trouble producing enough milk for their baby.
Care
Maintaining lactation is mostly based on supply and demand. The more your baby breastfeeds or the more milk you express with a breast pump, the more your body will make. There are ways to suppress lactation with hormones or oral contraceptives. If you wish to maintain lactation, some things you should do are:
Frequently Asked Questions
Lactation describes the process of making and secreting milk from your breast. Colostrum is the first milk your breasts create during lactation and the first milk your baby drinks. It’s thick, yellow and commonly called “liquid gold.” Colostrum is high in protein, minerals, vitamins and antibodies.

Overview
Regulation
In humans, prolactin is produced at least in the anterior pituitary, decidua, myometrium, breast, lymphocytes, leukocytes and prostate.
Pituitary prolactin is controlled by the Pit-1 transcription factor that binds to the prolactin gene at several sites. Ultimately dopamine, extrapituitary prolactin is controlled by a superdistal promoter and apparently unaffected by dopamine. The thyrotropin-releasing hormone and the vasoactive in…
Functions
Prolactin has a wide variety of effects. It stimulates the mammary glands to produce milk (lactation): increased serum concentrations of prolactin during pregnancy cause enlargement of the mammary glands and prepare for milk production, which normally starts when levels of progesterone fall by the end of pregnancy and a suckling stimulus is present. Prolactin plays an important role in maternal behavior.
Structure and isoforms
The structure of prolactin is similar to that of growth hormone and placental lactogen. The molecule is folded due to the activity of three disulfide bonds. Significant heterogeneity of the molecule has been described, thus bioassays and immunoassays can give different results due to differing glycosylation, phosphorylation and sulfation, as well as degradation. The non-glycosylated form of prolactin is the dominant form that is secreted by the pituitary gland.
Prolactin receptor
Prolactin receptors are present in the mammillary glands, ovaries, pituitary glands, heart, lung, thymus, spleen, liver, pancreas, kidney, adrenal gland, uterus, skeletal muscle, skin and areas of the central nervous system. When prolactin binds to the receptor, it causes it to dimerize with another prolactin receptor. This results in the activation of Janus kinase 2, a tyrosine kinase that initiates the JAK-STAT pathway. Activation also results in the activation of mitogen-activated protein kin…
Diagnostic use
Prolactin levels may be checked as part of a sex hormone workup, as elevated prolactin secretion can suppress the secretion of follicle stimulating hormone and gonadotropin-releasing hormone, leading to hypogonadism and sometimes causing erectile dysfunction.
Prolactin levels may be of some use in distinguishing epileptic seizures from psychogenic non-epileptic seizures. The serum prolactin level usually rises following an epileptic seizure.
Units and unit conversions
The serum concentration of prolactin can be given in mass concentration (µg/L or ng/mL), molar concentration (nmol/L or pmol/L), or international units (typically mIU/L). The current IU is calibrated against the third International Standard for Prolactin, IS 84/500. Reference ampoules of IS 84/500 contain 2.5 µg of lyophilized human prolactin and have been assigned an activity of .053 International Units. Measurements that are calibrated against the current international standard …
Reference ranges
General guidelines for diagnosing prolactin excess (hyperprolactinemia) define the upper threshold of normal prolactin at 25 µg/L for women and 20 µg/L for men. Similarly, guidelines for diagnosing prolactin deficiency (hypoprolactinemia) are defined as prolactin levels below 3 µg/L in women and 5 µg/L in men. However, different assays and methods for measuring prolactin are employed by different laboratories and as such the serum reference range for prolactin is often d…