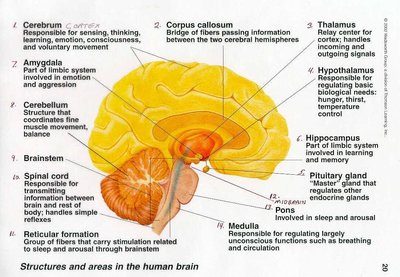
Your thalamus has many functions, including:
- Relaying sensory information. Taking in information, in the form of nerve signals, from all of your senses (taste, touch, hearing, seeing), except smell, into your brain. ...
- Relaying motor (movement) information. Similar to sensory information, motor pathways all pass through your thalamus.
- Prioritizing attention. ...
- Role in consciousness. ...
- Role in thinking (cognition) and memory. ...
What is the function of the thalamus?
Your thalamus serves as the main relay station for your brain. All motor and sensory signals (except smell) pass through this structure in the center of your brain. Your thalamus is arranged in regions, called nuclei, that each possesses specialization for dealing with that particular information.
Which sensory information is not relayed by the thalamus into the cortex?
The only sensory information that is not relayed by the thalamus into the cerebral cortex is information related to smell (olfaction). The thalamus is made up of three distinct groups of cells or nuclei and these include the following:
What is the involvement of the thalamic nuclei in sensory systems?
The involvement of thalamic nuclei in sensory systems. The thalamus is also important for touch - the ventral posterior nuclei relay information regarding touch and perception of bodily position to the primary somatosensory cortex in the cerebral cortex.
How does the thalamus modulate information transfer?
Detailed research has shown that specific thalamic neurons can modulate informational transfer by employing specific discharge modes. Furthermore, the thalamus is crucial for perception, with 98% of all sensory input being relayed by it.
See more

Do all senses go through the thalamus?
The thalamus is the major source of sensory information to the primary sensory cortex for all of the senses except olfaction.
What are the main functions of the thalamus?
The thalamus is composed of different nuclei that each serve a unique role, ranging from relaying sensory and motor signals, as well as regulation of consciousness and alertness.
What does the thalamus activate?
Central thalamus regulates forebrain arousal, influencing activity in distributed neural networks that give rise to organized actions during alert, wakeful states. Central thalamus has been implicated in working memory by the effects of lesions and microinjected drugs in this part of the brain.
What senses go through the thalamus on the way to the cortex?
Similarly, auditory and somatosensory (touch) information is routed through the thalamus before traveling to cortex for more complex processing.
What happens when thalamus is damaged?
While thalamus damage primarily causes sensory problems, it can also lead to behavioral and cognitive changes. For example, many patients with a thalamus injury have incorrect speech patterns and can struggle to find the right words. Others display apathy and memory problems.
Which special sense does not travel through the thalamus?
The thalamus (from the Greek thalamos or inner chamber) transmits 98 percent of sensory information to the cortex, including vision, taste, touch and balance; the only sense that doesn't pass through this brain region is smell.
What is the function of thalamus and hypothalamus?
Thalamus regulates sleep, alertness, and wakefulness, while the hypothalamus regulates body temperature, hunger, fatigue, and metabolic processes.
What is the thalamus in the brain?
thalamus, plural thalami, either of a pair of large ovoid organs that form most of the lateral walls of the third ventricle of the brain. The thalamus translates neural impulses from various receptors to the cerebral cortex.
How does the thalamus affect learning?
Researchers report the thalamus plays a far more active role in visual processing in the context of learning than previously thought. Source: Max Planck Institute. The cerebral cortex is where we learn and think, form impressions of our environment, control conscious behaviour, and store memories.
What is the relationship between the thalamus and our senses?
The thalamus relays sensory impulses from receptors in various parts of the body to the cerebral cortex. A sensory impulse travels from the body surface towards the thalamus, which receives it as a sensation. This sensation is then passed onto the cerebral cortex for interpretation as touch, pain or temperature.
Does thalamus affect vision?
HIGHER-ORDER THALAMIC NUCLEI The brain mechanisms that underlie this active vision depend on both visual inputs from the retina and information from within the brain. Both these inputs reach the cerebral cortical visual areas via nuclei in the thalamus.
What does the thalamus do quizlet?
Functions: The thalamus receives sensory information from other areas of the nervous system and sends this information to the cerebral cortex. The thalamus is also important for processing information related to movement.
What are the main functions of the thalamus and hypothalamus?
The thalamus regulates sleep, alertness and wakefulness, whereas the hypothalamus regulates body temperature, hunger, fatigue and metabolic processes in general.
What is the function of the thalamus quizlet?
Functions: The thalamus receives sensory information from other areas of the nervous system and sends this information to the cerebral cortex. The thalamus is also important for processing information related to movement.
What are the 7 functions of the hypothalamus?
While it's very small, the hypothalamus plays a crucial role in many important functions, including:releasing hormones.maintaining daily physiological cycles.controlling appetite.managing sexual behavior.regulating emotional responses.regulating body temperature.
What role does the thalamus play in memory?
Dr. Karel Svoboda's team at the Howard Hughes Medical Institute Janelia Research Campus, working with Dr. Charles Gerfen of NIMH, similarly showed that the thalamus plays a crucial role in sustaining short-term memory. To gather a reward, mice needed to remember where to move after a delay of seconds.
What is the role of the thalamus in wakefulness?
These form the thalamo-cortico-thalamic circuits which are thought to regulate consciousness and the thalamus plays a significant role in arousal, wakefulness and alertness. Damage to the thalamus is associated with a significant risk of coma.
Where does the thalamus receive input?
In the visual system, the thalamus receives input from the retina, which is relayed to the brain via the optic nerve. Signals are sent to the lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus which then forwards them onto the primary visual cortex (area V1) in the occipital lobe.
What are the three groups of cells in the thalamus?
The thalamus is made up of three distinct groups of cells or nuclei and these include the following: Sensory relay nuclei - These include the ventral posterior nucleus and the lateral and medial geniculate body.
How do thalamic neurons modulate informational transfer?
Detailed research has shown that specific thalamic neurons can modulate informational transfer by employing specific discharge modes. Furthermore, the thalamus is crucial for perception, with 98% of all sensory input being relayed by it.
What is the role of the thalamic nucleus in the brain?
Aside from olfaction, in all sensory processing , a sensory signal is received by a thalamic nucleus and then directed to the relevant cortical area.
Which part of the brain is responsible for touch?
The thalamus is also important for touch - the ventral posterior nuclei relay information regarding touch and perception of bodily position to the primary somatosensory cortex in the cerebral cortex. In addition, the thalamic nuclei are strongly and reciprocally linked with the cerebral cortex.
Which part of the brain relays information?
The thalamus not only relays the information but also processes it, as each of the primary sensory relay areas receives information back from the cerebral cortex (called back projections). On the other hand, the medial geniculate nuclei relay auditory information between the inferior colliculus of the midbrain and the primary auditory cortex.
What is the thalamus?
The thalamus translates neural impulses from various receptors to the cerebral cortex. While the thalamus is classically known for its roles as a sensory relay in visual, auditory, ...
Where is the thalamus located?
Anatomically, the thalamus lies deep within the brain, adjacent to the midline third ventricle. The paired thalami (one per hemisphere) are connected by the massa intermedia (interthalamic adhesion). The arterial supply to the thalami is predominantly by branches of the posterior cerebral arteries, as well as by the posterior communicating artery.
What are the nuclei of the thalamus?
The major nuclei of the thalamus include the relay nuclei, association nuclei, midline/intralaminar nuclei, and the reticular nucleus. With the exception of the reticular nucleus, these nuclear groups are divided regionally (i.e., anterior, medial, and lateral) by sheets of myelinated neural fibres known as the internal medullary lamina. The reticular nucleus is separated from the remainder of the thalamic nuclei by the external medullary lamina.
What are the two domains of the thalamus?
The thalamus is derived from the embryonic diencephalon and early in development becomes divided into two progenitor domains, the caudal domain and the rostral domain . The patterning of these domains is driven by the mid-diencephalic organizer (MDO), which sets a gradient of transcription factors to form distinct thalamic regions. Differential transcription of genes leads to neuronal differentiation. The caudal progenitor domain leads to the development of excitatory glutamatergic neurons (those that modulate glutamate and aspartate signaling), which contribute to the formation of the functionally and spatially distinct groups of neurons known as the thalamic nuclei. The rostral progenitor domain leads to the development of inhibitory gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) neurons that form the thalamic reticular nucleus.
Which part of the brain receives strong reciprocal connections from the cortex back to the thalamus?
Most thalamic nuclei project to the cortex, and all thalamic nuclei receive strong reciprocal connections from the cortex back to the thalamus. Each nucleus is discussed in the following sections in relation to its inputs (afferents) and outputs (efferents) in the context of the function of the thalamic nucleus.
What is the thalamic cell pattern?
The physiology of thalamic cells is unique in that they show either a tonic pattern (regularly spaced, continuous action potentials) or a bursting pattern (intermittent groupings of action potentials, such as doublets or triplets), depending on physiological state and activity.
Where do thalamic neurons project?
While there are numerous morphologies(shapes) to the neurons that compose the thalamic nuclei, thalamic neurons usually either project within the thalamus (interneurons) or project to the cerebral cortex. The physiology of thalamic cells is unique in that they show either a tonic pattern (regularly spaced, continuous action potentials) or a bursting pattern (intermittent groupings of action potentials, such as doublets or triplets), depending on physiological state and activity.
What is the role of the thalamus in the brain?
Besides signals from sensory systems, other information travels within the brain itself, which the thalamus also plays a role in. At times, the thalamus even assists with cognitive processes as well, such as memory and emotion. One of the main processes that the thalamus controls is the regulation of consciousness and sleep.
How to help a damaged thalamus?
The following are some treatments that can help you overcome the effects of damage to the thalamus: 1. Physical Therapy . If your brain injury damaged your thalamus, you might experience problems coordinating movements — a condition called apraxia.
How does DBS work?
DBS uses surgically implanted electrodes to send high-frequency signals to the thalamus. That signal can eliminate tremors. There is also evidence that thalamic stimulation can enhance cognitive performance after brain injury. This makes it even more helpful for patients with thalamus damage.
What happens when the thalamus is damaged?
Damage to the Thalamus: Understanding the Side Effects and Recovery Process. When a brain injury affects the thalamus, it can lead to sensory and/or cognitive side effects. This article will share symptoms and treatment to help you understand the ways in which thalamus damage can affect your everyday life.
What are the side effects of thalamic damage?
Some of the most common side effects of thalamic damage include: Sensory issues such as tingling, numbness, hypersensitivity, Chronic pain. Vision loss or light sensitivity. Motor impairments. Tremors.
What is sensory reeducation?
Sensory reeducation, also known as sensory retraining, is a form of cognitive-behavioral therapy that teaches the brain how to process sensation again. Some examples of sensory exercises include:
Why is it important to work with your doctor about thalamus injuries?
Because the thalamus has so many different roles though, every injury is different. Therefore, it’s crucial to work with your doctors to find the treatments that best fit your unique needs. We hope this article helps you better understand thalamus injuries and achieve a full recovery from TBI.
What is the function of the thalamus?
The thalamus has multiple functions. Generally, it acts as a relay station, exchanging and modulating information between the body and the brain. In addition, the thalamus plays a role in regulating consciousness and alertness.
What is the thalamus?
Gross anatomy. The thalamus is an egg shaped, bilateral, symmetrical mass of grey matter which forms a major part of the diencephalon , along with the hypothalamus and epithalamus. There are two thalami in total, one situated on each side of the third ventricle.
What do the anterior thalamic nuclei receive?
Specifically, the anterior thalamic nuclei receive afferent fibers input from the mammillary bodies via the mammillothalamic tract.
What are the ventral tiers of the thalamic nucleus?
These are the largest division of the thalamic nuclei, divided into dorsal and ventral tiers of nuclei. The ventral tier nuclei are the ventral anterior (VA), ventral lateral (VL) and ventral posterior (VP) nuclei.
Where are the thalamic nuclei located?
The thalamus is an ovoid, paired gray matter structure, found in the center of the brain , just superior to the brainstem .
Which part of the brain is responsible for synapse?
Basically, almost all ascending neural pathways first synapse within a thalamic nucleus, where the information is sorted, integrated, and analysed by the thalami before they are sent further to the cerebral cortex. This fact makes the thalamus a so-called “ gateway ” to the cerebral cortex for limbic, motor, and all sensory modalities besides olfaction, including vision, hearing, taste, and somatic sensation.
What is the dorsomedial nucleus?
Through all these connections, the dorsomedial nucleus is responsible for integrating sensory, motor, visceral and olfactory information and subsequently relating it to the individual’s emotional state. Its overall functions are similar to those of the prefrontal cortex.