
Where is the azygos vein located?
The azygos vein is present only on the right side in the upper part of the posterior abdominal wall and the posterior mediastinum. It attaches the inferior vena cava together with the superior vena cava.
Is the hemiazygos vein on the left or right side?
While there is the hemiazygos vein and its accessory on the left side of the body, they are considered tributaries of the azygos vein rather than its left-side equivalent. This terminology is only accurate in some species, such as the human, dog, and cat. Ruminants (such as sheep and cows) have paired azygos veins.
What is azygos continuation of the inferior vena cava?
This is referred to as azygos continuation of the inferior vena cava or absence of the hepatic segment of the inferior vena cava with azygos continuation. To compensate for this congenital abnormality, the azygos vein dilates in order to accommodate for the increase in blood flow.
What are the structures that are located posterior to the azygos vein?
Which vein joins the azygos vein anterior to the body of T12?
What causes azygos vein rupture?
How many tributaries does the Azygos vein have?
Why does the azygos vein dilate?
Which nerve is in close proximity to the azygos vein?
Which venous system drains into the superior vena cava?
See 4 more
About this website
/images/library/587/vena_cava_inferior_4_large_6IkFTwzOYPPXzhTo1d8T2Q.png)
Where are azygos veins located?
The azygos vein originates at the junction of the right ascending lumbar and subcostal veins, entering the chest through the aortic hiatus. It ascends along the anterolateral surface of the thoracic vertebrae and arches ventrally to the right main bronchus at T5–T6, draining into the SVC.
What is unusual about the azygos vein?
Azygos vein is the vein that drains the venous blood from the upper part of the posterior abdominal wall and the thoracic wall. It is very important for the reason that it connects the superior vena cava with the inferior vena cava, and it has very few to no valves.
What happens if the azygos vein is blocked?
Blockages at the level of the azygos If the SVC blockage is at the level of the azygos vein, then there is no physiological pathway for blood to reenter the SVC. Blood must reverse flow in the azygos system into the lower venous system and the inferior vena cava (IVC) (Fig.
Where is the azygos and hemiazygos veins located?
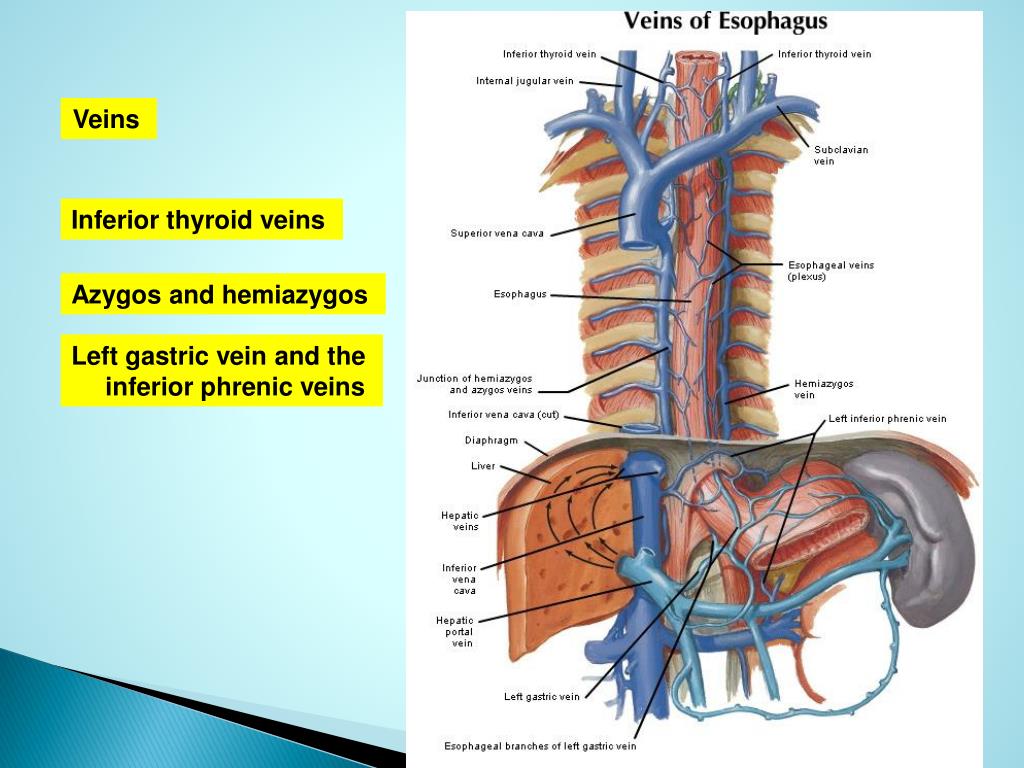
Accessory hemiazygos vein It arises from the 4th to 8th left posterior intercostal veins and lies longitudinally on the left side of the vertebral bodies. It also drains the left bronchial vein and some veins from the esophagus. It joins the azygos vein behind the esophagus at the level of T8.
What is the function of azygos vein?
The azygos vein's function is to drain deoxygenated blood into one of your body's largest veins (superior vena cava). The superior vena cava carries blood to your heart's right upper chamber (atrium) so it can reoxygenate blood.
What is the meaning of azygos?
Azygos (impar), from the Greek άζυξ, refers to an anatomical structure that is unpaired. This is relatively unusual, as most elements of anatomy reflect bilateral symmetry. Azygos may refer to: Azygos anterior cerebral artery.
Does everyone have an azygos vein?
Usually, there is a singular azygos vein on the right side of the body. However, the azygos vein is occasionally located in the midline or two independent veins may be present like in early embryonic development. The azygos vein usually originates at the level of the lumbar vertebrae, but may originate further up.
What is the largest vein in the body?
inferior vena cavaYour inferior vena cava, your body's largest vein, carries oxygen-depleted blood back to your heart from the lower part of your body (below your diaphragm).
What are the symptoms of inferior vena cava syndrome?
Inferior vena cava syndrome (IVCS) is characterized by tachycardia, hypotension, tachypnea, hypoxemia, and shortness of breath. The differential diagnosis of IVCS is broad, mainly because it is rarely ever diagnosed as a primary disease process. The differential diagnosis of IVCS are: Chronic venous insufficiency.
Which vein drains the left side of the lower thoracic wall?
The posterior intercostal veins drain into the azygos (right side) and hemiazygos and accessory hemiazygos vein (left side).
What is the name of the large vein that drains blood from the body from above the diaphragm?
The superior vena cava (SVC) drains all venous blood from above the diaphragm except that from the heart and lungs. It lies anterolateral to the trachea and posterolateral to the ascending aorta, and enters the right atrium at the level of the third costal cartilage.
What are the azygos and hemiazygos veins?
0:185:43Azygos and Hemiazygos veins - Gross anatomy of Abdomen and pelvisYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSystem of veins. The azygous system vanes consists of the azygous hemizygous ant accessoryMoreSystem of veins. The azygous system vanes consists of the azygous hemizygous ant accessory hemizygous veins these veins lie anterior to the thoracic part of the vertebral column and play an important
Where is the azygos vein located and what area does it drain?
The azygos vein originates at the junction of the right ascending lumbar and subcostal veins, entering the chest through the aortic hiatus. It ascends along the anterolateral surface of the thoracic vertebrae and arches ventrally to the right main bronchus at T5–T6, draining into the SVC.
Which veins are part of the azygos system quizlet?
What does the azygos system include? Azygos vein, hemiazygos vein and the accessory hemiazygos vein.
What are the functions of the Azygous the hemiazygos and the accessory hemiazygos veins?
That is, the azygos vein serves to drain most of the posterior intercostal veins on the right side of the body, and the hemiazygos vein and the accessory hemiazygos vein drain most of the posterior intercostal veins on the left side of the body.
Where does azygos vein pass through diaphragm?
aortic hiatusAzygos vein It enters the thorax via the aortic hiatus in the diaphragm and ascends posteriorly alongside the vertebral bodies, arching over the right main bronchus at T5-T6 and enters the superior vena cava (SVC) at T4 2.
Azygos Vein - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
Susan Standring MBE, PhD, DSc, FKC, Hon FAS, Hon FRCS, in Gray's Anatomy, 2021. Azygos vein. The azygos vein has a variable origin at or below the level of the renal veins (Figs 56.2 – 56.3; see Fig. 56.14B).When present, the azygos lumbar vein ascends anterior to the bodies of the upper lumbar vertebrae and passes either posterior to, or through, the right diaphragmatic crus or traverses ...
Azygos and Hemiazygos Veins – Earth's Lab
Azygos is a term which means single that means without a companion. Azygos, hemiazygos, and accessory hemiazygos veins together compose the azygos system. The front of thoracic part of vertebral column is where these veins are located and play a significant role in the venous drainage of the thorax.
What are the structures that are located posterior to the azygos vein?
The following structures are located posterior to the azygos vein: the anterior longitudinal ligament. right posterior intercostal arteries. the bodies of T4-T12.
Which vein joins the azygos vein anterior to the body of T12?
The common trunk of the right ascending lumbar vein and the right subcostal vein joins the azygos vein anterior to the body of T12. However, if the lumbar segment is absent, this trunk may form the azygos vein.
What causes azygos vein rupture?
Laceration, or ruptures of the azygos vein may occur in blunt trauma to the thorax as a result of a motor vehicle accident or a fall from a height . Rupture of the vein usually occurs at its arch, just proximal to where it joins the superior vena cava.
How many tributaries does the Azygos vein have?
The azygos vein has two tributaries, which are referred to as the hemiazygos vein and the accessory hemiazygos vein .
Why does the azygos vein dilate?
To compensate for this congenital abnormality, the azygos vein dilates in order to accommodate for the increase in blood flow. It occurs in 0.3% of the population and is associated with congenital heart disease or asplenia syndromes (syndromes with an absence of normal spleen function).
Which nerve is in close proximity to the azygos vein?
the right greater splanchnic nerve. lung. pleura. The azygos vein is also in close proximity to the right posterolateral aspect of the descending thoracic aorta. Pulsations within the aorta may aid venous return in the azygos vein, as well as the hemiazygous vein.
Which venous system drains into the superior vena cava?
It passes through the diaphragm, reaches the mediastinum and finally drains into the superior vena cava. The azygos venous system has many anastomoses with inferior vena cava and vertebral venous plexuses.
Where is the Azygos vein?
The azygos vein is a singular blood vessel of the torso that ascends on a course just to the right of the spine. It’s part of the system that drains blood from the mediastinum (the tissues between your lungs), as well as parts of the back and abdominal walls. Arising in the mid-low back, it bends around the hilum of the lungs and passes through the diaphragm before piercing the pericardium of the heart. 1
Which veins form a trunk before joining the Azygos vein?
The hemiazygos and accessory hemiazygos veins form a common trunk before joining the azygos vein.
What causes azygos vein to bleed?
Laceration (deep cut or tear) and bleeding of this internal vein is a clinical concern, and it can be affected by obstructions of surrounding veins, among other conditions. In very rare cases, congenital abnormalities affect the development of the azygos vein, something associated with some types of heart disease or asplenia (absence of the spleen). 1
What happens when the inferior vena cava is obstructed?
As a result, lesions can form in the vein, and an insufficient amount of blood is able to return to the heart. 3 Breathing problems, swelling, cognitive issues, and heart arrhythmia are among the symptoms.
How many tributaries does the Azygos vein have?
The azygos vein also has two tributaries (branches of the main vein): 1
What happens when blood flow from the superior vena cava to the right atrium of the heart is obst?
When blood flow from the superior vena cava to the right atrium of the heart is obstructed, an insufficient amount from the head and neck is drained. This can cause blood flow to reverse—to move away from the heart—leading to breathing problems, lightheadedness, and swelling. 3
Where is the accessory hemiazygos vein?
Accessory hemiazygos vein: Draining the superior left hemithorax as well as veins of the esophagus, the accessory hemiazygos vein descends to the left of the spinal column. It crosses over to join the azygos vein, or sometimes the hemiazygos vein, at the seventh vertebra.
Where is the Azygos vein?
The azygos vein is a vein running up the right side of the thoracic vertebral column draining itself towards the superior vena cava. It connects the systems of superior vena cava and inferior vena cava and can provide an alternative path for blood to the right atrium when either of the venae cavae is blocked.
Where does the Azygos vein originate?
The azygos vein generally begins at the level of the lumbar verte brae but may originate above the point in some cases. The lumbar aspect of the azygos vein can ascend anteriorly to the lumbar vertebrae and pass behind the right crus of the diaphragm or cross the aortic hiatus (where the aorta pierces the diaphragm) to the right of the cisterna chyli, a dilated lymph sac. The common trunk of the right ascending lumbar vein and the right subcostal vein join the azygos vein anterior to the body of T12. However, if the lumbar segment is absent, this trunk may form the azygos vein.
What veins form when the lumbar segment is absent?
However, if the lumbar segment is absent, this trunk may form the azygos vein. Structure and location of Azygos vein. It has been proposed that the azygos vein develops by originally draining to the posterior cardinal vein and then to the longitudinal venous channel.
How to diagnose azygos vein?
Azygos and hemiazygos continuation of the inferior vena cava (IVC) was not common in daily life. It is very hard to observe, particularly when it is not associated with congenital heart disease or deep venous thrombosis. Thus, it is crucial to diagnose the enlarged azygos vein at the confluence with the superior vena cava and in the retrocrural space to prevent misdiagnosis as a right-sided paratracheal mass. The loss of the intrahepatic segment of IVC with azygous and hemiazygos continuation happens in 0.6% of patients diagnosed for congenital heart disease and usually occurs simultaneously with situs inversus, asplenia, or polysplenia, persistent left superior vena cava (SVC), and congenital pulmonary venolobar syndrome. Azygos and hemiazygos continuation of the IVC is rare especially when it is not associated with congenital heart disease.
What is the name of the vein that drains the bronchial veins?
The azygos vein transports deoxygenated blood from the posterior walls of the thorax and abdomen into the superior vena cava vein. The anatomy of this blood vessel can be quite variable. In some rare variations, for example, it also drains thoracic veins, bronchial veins, and even gonadal veins. The vein is so named because it has no symmetrically equivalent vein on the left side of the body.
Why is the Azygos vein so named?
The vein is so named because it has no symmetrically equivalent vein on the left side of the body. The azygos system is considered to be the azygos vein located from rib number 2 to rib number 4, while on the left part of the body, the hemiazygos vein and the accessory hemiazygos vein together form the analogous venous system.
Which veins are left sided?
The azygos system of veins is considered to be the azygos vein, along with its left-sided counterparts, the hemiazygos vein and the accessory hemiazygos vein. It also creates a cavo-caval anastomosis by offering an alternative, collateral blood flow from the lower half of the body to the superior vena cava, bypassing the inferior vena cava. This can have clinical significance in any blood flow restriction of the inferior vena cava.
What is an azygos vein?
The azygos vein makes from the joint of the right subcostal veins and the ascending lumbar veins. Azygos vein is a unilateral vessel rise in the right posterior mediastinum by the right edge of the inferior eight thoracic vertebrae. In some cases, the azygos vein can proceed in the midline with the head of the thoracic vertebrae. It carries deoxygenated blood forming a collateral pathway between the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava.
Where does the azygos vein rise?
It then rises in the posterior mediastinum dorsally at the origin of the right lung (at the level of T5-T6), it connects the superior vena cava just before it enters the pericardium. Although there is a considerable irregularity that the azygos vein takes the accessory hemiazygos vein and the hemiazygos vein at the level of T8 and T9 distributively.
What is the fusion of the ascending lumbar veins and right subcostal veins?
The azygos vein is made by the fusion of the ascending lumbar veins and right subcostal veins at about the T12-L2 vertebral level.
Where does the accessory hemiazygos vein drain?
The accessory hemiazygos vein empties the superior left hemithorax. It originates from the 4th to 8th left posterior intercostal veins and places longitudinally on the left side of the vertebral bodies. It also drains the left bronchial vein. The accessory hemiazygos veins connect azygos veins at the T8 level.
Which veins drain the back, esophageal, and mediastinal?
The azygos vein receiving the right posterior intercostal veins and communicates with the vertebral venous plexus that drain the back, vertebrae, and structures in the vertebral canal. The azygos vein also takes the mediastinal, esophageal, bronchial veins, hemiazygos, and accessory hemiazygos veins. The main function of the azygos vein is;
Do medical students know about the Azygos vein?
We agree that medical students have known about azygos vein. It might be difficult for the layman to understand more rapidly than medical students but it’s not unlikely for you. If you are interested in the anatomy of your body then this article is for you. Before going toward the azygos vein let’s have a glimpse of the azygos venous system. The azygos (venous) system is a combined term set to the H-shaped arrangements of the azygos, hemiazygos, accessory hemiazygos veins, and left superior intercostal vein.
What is azygos vein stenosis?
The azygos vein is a vein running up the right side of the spinal column in the thoracic (chest) area that transports deoxygenated blood from the posterior walls of the thorax and abdomen into the superior vena cava vein. Stenosis is an abnormal narrowing in a blood vessel.
Common symptoms reported by people with azygos vein stenosis
Reports may be affected by other conditions and/or medication side effects. We ask about general symptoms (anxious mood, depressed mood, fatigue, pain, and stress) regardless of condition.
Treatments taken by people for azygos vein stenosis
Let’s build this page together! When you share what it’s like to have azygos vein stenosis through your profile, those stories and data appear here too.
Compare treatments taken by people with azygos vein stenosis
Let’s build this page together! When you share what it’s like to have azygos vein stenosis through your profile, those stories and data appear here too.
Who has azygos vein stenosis on PatientsLikeMe?
Let’s build this page together! When you share what it’s like to have azygos vein stenosis through your profile, those stories and data appear here too.
Where is the Azygos vein located?
Azygos Vein. The azygos vein is present only on the right side in the upper part of the posterior abdominal wall and the posterior mediastinum. It attaches the inferior vena cava together with the superior vena cava.
What is the function of the Azygos vein?
The functions of azygos vein are as follows: It drains venous blood from the thoracic wall and upper lumbar region. It creates an essential collateral channel attaching the superior vena cava and inferior vena cava.
What are the tributaries of the Azygos vein?
The tributaries of the azygos vein are as follows: Lower 7th right posterior intercostal veins with the exception of first. Right superior intercostal vein (created by union of 2nd, 3rd, and 4 th right posterior intercostal veins). Hemiazygos vein (at the level of T7 or T8 vertebra). Accessory hemiazygos vein (at the level of T8 or T9 vertebra).
What is the meaning of the word "azygos"?
Contents. Azygos is a term which means single that means without a companion. Azygos, hemiazygos, and accessory hemiazygos veins together compose the azygos system. The front of thoracic part of vertebral column is where these veins are located and play a significant role in the venous drainage of the thorax.
What level is the Hemiazygos vein?
Hemiazygos vein (at the level of T7 or T8 vertebra).
Where does the accessory hemiazygos vein end?
The accessory hemiazygos vein begins at the medial end of left 4th or 5th intercostal space and descends to the left side of the vertebral column. At the level of T8 vertebra, it turns to the right enters in front of the vertebral column posterior to the aorta, esophagus and thoracic duct to terminate in the azygos vein.
Which veins join together to form a trunk?
Sometimes the terminal parts of hemiazygos and accessory hemiazygos veins join together to create a common trunk which crosses across the vertebral column to open into the azygos vein.
What are the structures that are located posterior to the azygos vein?
The following structures are located posterior to the azygos vein: the anterior longitudinal ligament. right posterior intercostal arteries. the bodies of T4-T12.
Which vein joins the azygos vein anterior to the body of T12?
The common trunk of the right ascending lumbar vein and the right subcostal vein joins the azygos vein anterior to the body of T12. However, if the lumbar segment is absent, this trunk may form the azygos vein.
What causes azygos vein rupture?
Laceration, or ruptures of the azygos vein may occur in blunt trauma to the thorax as a result of a motor vehicle accident or a fall from a height . Rupture of the vein usually occurs at its arch, just proximal to where it joins the superior vena cava.
How many tributaries does the Azygos vein have?
The azygos vein has two tributaries, which are referred to as the hemiazygos vein and the accessory hemiazygos vein .
Why does the azygos vein dilate?
To compensate for this congenital abnormality, the azygos vein dilates in order to accommodate for the increase in blood flow. It occurs in 0.3% of the population and is associated with congenital heart disease or asplenia syndromes (syndromes with an absence of normal spleen function).
Which nerve is in close proximity to the azygos vein?
the right greater splanchnic nerve. lung. pleura. The azygos vein is also in close proximity to the right posterolateral aspect of the descending thoracic aorta. Pulsations within the aorta may aid venous return in the azygos vein, as well as the hemiazygous vein.
Which venous system drains into the superior vena cava?
It passes through the diaphragm, reaches the mediastinum and finally drains into the superior vena cava. The azygos venous system has many anastomoses with inferior vena cava and vertebral venous plexuses.
Overview
- Structure and Location
A larger vein, the azygos is about 0.9 centimeters in diameter. It most commonly arises at the junction of the right ascending lumbar and the right subcostal veins, in the lower back, though it can also emerge directly from the inferior vena cava (IVC)vein. It then enters the abdomen (or th… - Anatomical Variations
Congenital abnormalities of the azygos vein are relatively common, and they’re usually asymptomatic. Among the most commonly seen such variations are the following:1 1. The azygos vein runs up the midline instead of to the right of the spinal column. 2. The origin of the a…
Structure
Function
Clinical significance
The azygos vein is a vein running up the right side of the thoracic vertebral column draining itself towards the superior vena cava. It connects the systems of superior vena cava and inferior vena cava and can provide an alternative path for blood to the right atrium when either of the venae cavae is blocked.
History
The azygos vein transports deoxygenated blood from the posterior walls of the thorax and abdomen into the superior vena cava vein.
It is formed by the union of the ascending lumbar veins with the right subcostal veins at the level of the 12th thoracic vertebra, ascending to the right of the descending aorta and thoracic duct, passing behind the right crus of diaphragm, anterior to the vertebral bodies of T12 to T5 and righ…
Additional images
The azygos system of veins is considered to be the azygos vein, along with its left-sided counterparts, the hemiazygos vein and the accessory hemiazygos vein. It also creates a cavo-caval anastomosis by offering an alternative, collateral blood flow from the lower half of the body to the superior vena cava, bypassing the inferior vena cava. This can have clinical significance in any blood flow restriction of the inferior vena cava.
See also
Azygos vein abnormalities can be suggested on chest radiograph by enlargement of the azygos shadow to greater than 1 cm. False positives can occur in heart failure causing increased pressures on the right side of the heart, or adjacent lymphadenopathy. Azygos and hemiazygos continuation of the inferior vena cava (IVC) was not common in daily life. It is very hard to observe, particularly when it is not associated with congenital heart disease or deep venous thro…
External links
The Greek root zyg refers to a pair. 'A-' means not. Thus, azygos means unpaired. The azygos vein is unpaired in that there is only one in the body, mostly on the right side. While there is the hemiazygos vein and its accessory on the left side of the body, they are considered tributaries of the azygos vein rather than its left-side equivalent.
This terminology is only accurate in some species, such as the human, dog, and cat. Ruminants …