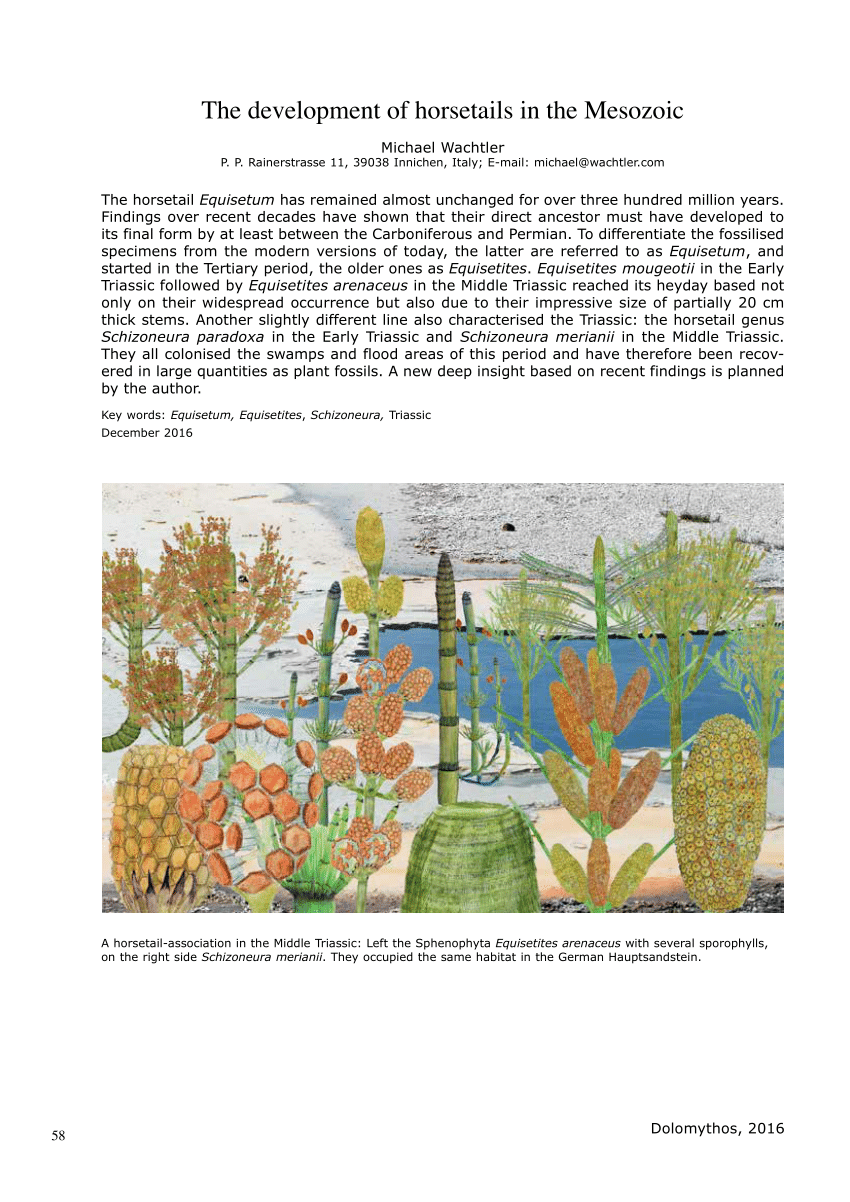
Full Answer
What lived in the Tertiary period?
What lived in the Tertiary Period? Some examples are marsupials, insectivores, bears, hyenas, dogs, cats, seals, walruses, whales, dolphins, early mastodons, hoofed mammals, horses, rhinoceroses, hippopotamuses, oreodonts, rodents, rabbits, monkeys, lemurs, apes, and humans (Australopithecus).
How did the Tertiary period end?
The tertiary time period began about 66 million years ago with a mass extinction that noticed the dinosaur and ended when the ice ages of the Quaternary Period began, about 2.6 million years ago. The Paleocene Epoch (first epoch of the tertiary period) lasted from 65 to 55.8 million years ago.
What was the Tertiary period?
The Tertiary is a system of rocks, above the Cretaceous and below the Quaternary, that defines the Tertiary Period of geologic time. The Tertiary Period began about 66 million years ago with a mass extinction that ‘clocked’ the dinosaurs and ended when the ice ages of the Quaternary Period began, about 2.6 million years ago.
What is Tertiary period?
The Tertiary Period Is the old name given to the first period of the Cenozoic Era. It is no longer an official term and has been replaced by the Paleogene Period for the first 3 Epochs while the next 2 now belong to the Neogene Period. Did humans appear in the Tertiary Period? During the tertiary period, mammals diversified rapidly.
See more

Why did the Tertiary Period start?
The Tertiary Period began abruptly when a meteorite slammed into the earth, leading to a mass extinction that wiped out about 75 percent of all species on Earth, ending the reptile-dominant Cretaceous Period and Mesozoic Era. This event formed the Cretaceous-Tertiary, or K-T, boundary.
What was in the Tertiary Period?
The Tertiary was made up of five subdivisions: (from oldest to youngest) the Paleocene, Eocene, Oligocene, Miocene, and Pliocene epochs. During most of the Tertiary the spatial distribution of the major continents was largely similar to that of today.
What era was the Tertiary Period in?
In geologic time , the Tertiary Period (also sometimes referred to in terms of a Paleogene Period and a Neogene Period), represents the first geologic period in the Cenozoic Era . The Tertiary Period spans the time between roughly 65 million years ago (mya) and 2.6 mya.
Why is it called the Tertiary Period?
The Age Of Mammals Begins. The Tertiary Period Is the old name given to the first period of the Cenozoic Era. It is no longer an official term and has been replaced by the Paleogene Period for the first 3 Epochs while the next 2 now belong to the Neogene Period.
When did the Tertiary Period start and end?
65 million years ago - 2.588 million years agoTertiary / Occurred
Why was the Tertiary Period important?
This period began 65 million years ago and ended roughly 1.8 million years ago and bore witness to some major geological, biological and climatological events. This included the current configuration of the continents, the cooling of global temperatures, and the rise of mammals as the planet's dominant vertebrates.
What caused the Tertiary Period to end?
The end of the Tertiary is characterized by the growth of glaciers in the Northern Hemisphere and the emergence of primates that later gave rise to modern humans (Homo sapiens), chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes), and other living great apes. The stratigraphic chart of geologic time.
When did the Tertiary Period End?
2.588 million years agoTertiary / Ended
How are Tertiary landforms formed?
The tertiary landforms refer to a period that was two hundred million years ago formed by the Gondwana deposits with the extinction of dinosaurs which was an integration of period of Paleogene and Neogene also known as the Lower Tertiary and the Upper Tertiary.
What fossils were in the Tertiary Period?
Fossils of the TertiaryFossil Amber Centipede and > 200 insects Pliocene Andes Mountains, ColombiaUrsus speleaus (Cave Bear) Pleistocene Ural Mountains, RussiaProcyon lotor (Raccoon) Holocene to Pleistocene Bonner Springs, KansasSparnodus sp. Fossil Fish Eocene Monte Bolca Quarry, Italy8 more rows
When did the Quaternary Period start?
2.58 million years agoQuaternary / BeganIntroduction. The Quaternary Period is the third and last of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era. You and I are living in this period, which began only 2.58 million years ago.
When did the Cretaceous period start?
145.5 million years agoCretaceous / Began
What fossils were in the Tertiary Period?
Fossils of the TertiaryFossil Amber Centipede and > 200 insects Pliocene Andes Mountains, ColombiaUrsus speleaus (Cave Bear) Pleistocene Ural Mountains, RussiaProcyon lotor (Raccoon) Holocene to Pleistocene Bonner Springs, KansasSparnodus sp. Fossil Fish Eocene Monte Bolca Quarry, Italy8 more rows
What animals lived in the Tertiary Period?
During this time mammals diversified quickly. Some examples are marsupials, insectivores, bears, hyenas, dogs, cats, seals, walruses, whales, dolphins, early mastodons, hoofed mammals, horses, rhinoceroses, hippopotamuses, oreodonts, rodents, rabbits, monkeys, lemurs, apes, and humans (Australopithecus).
What animals were in the Quaternary Period?
These steppes supported enormous herbivores such as mammoth, mastodon, giant bison and woolly rhinoceros, which were well adapted to the cold. These animals were preyed upon by equally large carnivores such as saber toothed cats, cave bears and dire wolves.
What organisms lived in the Cretaceous period?
Tyrannosa...VelociraptorMosasaurusTarbosaurusDromaeos...Luanchua...Cretaceous/Organisms
1. Which Mammals were Widely Observed during the Tertiary Period?
Ans: The tertiary period is divided into 5 epochs namely palaeocene, Eocene, Oligocene, Miocene, Pliocene. During the tertiary period, mammals dive...
2. What was The Earth’s Average Temperature at the Time of the Tertiary Period?
Ans: The tertiary period lasted 63 million years. During this period, Earth's average temperature steadily increased from Cretaceous greenhouse tem...
3. How did the Tertiary Period End?
Ans: The cooling climate of the tertiary period led to the huge glaciers at the poles. The mountains along with the newly formed Himalayas and alps...
Tertiary Time Period
The tertiary time period began about 66 million years ago with a mass extinction that noticed the dinosaur and ended when the ice ages of the Quaternary Period began, about 2.6 million years ago.
Tertiary Period Epochs
The Paleocene Epoch (first epoch of the tertiary period) lasted from 65 to 55.8 million years ago. This epoch marks the beginning of the Cenozoic era and the tertiary period.
Tertiary Plants
The tertiary plants closely resemble the plants that we have at present. The warmer climate of the tertiary period, in the beginning, favored dense forests. As the climate cooled, it opened woodland and grassland became abundant. The grasses played an important role during the tertiary period as they supported a large herd of grazing animals.
Tertiary Period Climate
The tertiary period climate during the beginning was very warm and moist compared to today's climate. Much of the Earth was tropical or subtropical. Plant trees grew as far North as Grasslands. The climate began to cool by the middle of the tertiary i.e. during the Oligocene epoch.
Tertiary Period Animals
During the start of the tertiary era, the first large mammals and primitive primates were largely seen. Soon, at the start of the second epoch of the tertiary period i.e. Eocene epoch, the first modern mammals began to appear, and within a short span, most modern mammals were observed.
Tertiary Period Major Events
In terms of tertiary period major events, the tertiary era covers the major demise of dinosaurs and the beginning of the most recent ice age. At the start of the tertiary period, reptiles were replaced by mammals as dominant vertebrates. Furthermore, all the non-avian dinosaurs also became extinct.
What is the Tertiary Period?
In geologic time , the Tertiary Period (also sometimes referred to in terms of a Paleogene Period and a Neogene Period), represents the first geologic period in the Cenozoic Era . The Tertiary Period spans the time between roughly 65 million years ago (mya) and 2.6 mya. When referred to in terms of a Paleogene Period ...
What is the last epoch of the Tertiary Period?
The last epoch of the Tertiary Period is the Pliocene Epoch . The Pliocene Epoch is further subdivided into Zanclian and Placenzian stages. The onset of the Tertiary Period is marked by the K-T boundary or K-T event — a large mass extinction.
How many geologic epochs are there in the Tertiary Period?
The Tertiary Period contains five geologic epochs. The earliest epoch, the Paleocene Epoch , ranges from approximately 65 mya to 55 mya.
How many epochs are there in the Tertiary era?
Tertiary. The Tertiary era, from 65 to 2 million years ago, consists of six epochs: the Paleocene, Eocene, Oligocene, Miocene, and Pliocene, which represent chapters in the story of the mammal's rise to dominance of land and oceans.
What is the earliest epoch?
The earliest epoch, the Paleocene Epoch , ranges from approximately 65 mya to 55 mya. The Paleocene Epoch is further subdivided into (from earliest to most recent) Danian and Thanetian stages. The second epoch, the Eocene E poch ranges from approximately 55 mya to 34 mya.
Which continent had begun a southward migration toward the south polar region?
The Antarctic continent had begun a southward migration toward the south polar region. At the outset of the Tertiary Period, the Indian subcontinent remained far south of the Euro-Asiatic continent. By the middle of the Tertiary Period (approximately 30 mya), the modern continental arrangement was easily recognizable.
When did Pangaea break apart?
By the Eocene, also known as the "dawn of early life" (55-39 million years ago), Pangaea had begun to break apart. Australia had split off, carrying a load of marsupials, mammals who give birth to immature young who then crawl into a pouch (marsupium) in which they suckle and grow.
How long ago was the Tertiary?
For much of the time during which the term 'Tertiary' was in formal use, it referred to the span of time between 65 and 1.8 million years ago . The end date of the Cretaceous and the start date of the Quaternary were subsequently redefined at c. 66 and 2.6 million years ago respectively.
Who first used the term "tertiary"?
The term Tertiary was first used by Giovanni Arduino during the mid-18th century. He classified geologic time into primitive (or primary), secondary, and tertiary periods based on observations of geology in northern Italy. Later a fourth period, the Quaternary, was applied. In the early development of the study of geology, ...
Who categorized the Tertiary Period into four epochs?
In 1828, Charles Lyell incorporated a Tertiary Period into his own, far more detailed system of classification. He subdivided the Tertiary Period into four epochs according to the percentage of fossil mollusks resembling modern species found in those strata.
What was the tertiary era?
In terms of major events, the Tertiary period began with the demise of the non-avian dinosaurs in the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction event, at the start of the Cenozoic era, and lasted to the beginning of the most recent Ice Age at the end of the Pliocene epoch.
What is the Hadean period?
There’s the Hadean period, which began with the creation of the Earth and was marked by the formations of the oceans and atmosphere.
What was the dominant vertebrate in the early dinosaurs?
By the beginning of the period, mammals replaced reptiles as the dominant vertebrates on the planet. In addition, all non-avian dinosaurs (referring to terrestrial dinosaurs and not their avian descendants) had all become extinct by the beginning of this period.
What is the most important period in mammals?
But when it comes to us mammals, perhaps the most important period was the one known as the Tertiary Period . This period began 65 million years ago and ended roughly 1.8 million years ago and bore witness to some major geological, biological and climatological events.
Which continent was formed by the separation of South America from West Africa?
This led to the formation of the Himalayas, the gradual creation of the continent of Australia (a haven for the non-placental, marsupial mammals), the separation South America from West Africa and its connection to North America, and Antarctica taking its current position below the South Pole.
What was the climate during the Paleocene?
In terms of climate, the period was marked by widespread cooling, beginning in the Paleocene with tropical-to-moderate worldwide temperatures and ending before the first extensive glaciation at the start of the Quaternary. In terms of species evolution, this period was of extreme importance to modern life.
What is the Eocene era?
The Eocene epoch/series is the oldest of the four original subdivisions of the Tertiary period/system proposed in 1833 by Sir Charles Lyell in his Principles of Geology. The name derives from the Greek ‘ eos ’, meaning dawn, and ‘ kainos ’, meaning recent. This is “… because the very small proportion of living species contained in those strata indicates what may be considered the first commencement, or dawn, of the existing state of the animate creation” (vol. 3, p. 55). The time covered by Lyell's ‘existing state’ is what we now understand to be the Cenozoic era/erathem, which itself is broadly divided into either Tertiary and Quaternary or Paleogene and Neogene periods. Lyell subdivided the Tertiary into four epochs based on the proportions of living and extinct species of shelled organisms (molluscs and foraminifera) encountered as fossils in different strata. He recognized 1238 Eocene species, of which he considered only 42 (or 3.5%) remain alive today. Lyell's species are about equivalent to what modern marine biologists would rank as genera or even subfamilies. For this reason, no modern species of mollusc or foraminifer is currently recognized as occurring as far back as the Eocene.
How was the PRD formed?
The PRD was formed as a result of the Tibetan Plateau uplift during the Tertiary and Quaternary Periods. Quaternary deposits cover the central and southern parts of the PRD and compose the PRD plain. Deposits in the PRD plain mainly consist of four stratigraphic units, including two marine units and two terrestrial units ( Fig. 18.1 ). The younger marine unit has an elevation above −20 m and was formed during the Holocene, while the other three units were formed during the Pleistocene. The younger terrestrial unit can be sandy fluvial deposits or clayey silt and becomes a local aquifer, while the older terrestrial unit is dominated by sand and gravel and becomes the basal aquifer. Groundwater in porous aquifer is mainly recharged by vertical infiltration of precipitation and agricultural irrigation, and the lateral flow of rivers. In addition, porous aquifers in coastal areas are often intruded by seawater ( Huang et al., 2018b ). The PRD plain is surrounded by hills on east, west, and north, and the maximum elevation of hilly areas is 1210 m. Fissured aquifer is distributed in hilly areas where bedrocks (e.g., limestone, mudstone, sandstone, shale, dolomite, granite, and gneiss) ranging in age from Cambrian to Tertiary crop out. Karst aquifer is less than 10% of the total area. The regional groundwater flow in the PRD is from northeast and northwest to the coast ( Zhang et al., 2019 ).
How long did the Paleocene last?
The Paleocene succeeds the Cretaceous Period/System and precedes the Eocene Epoch. The Paleocene lasted nearly 10 million years, from 65.5 till 55.8 Ma, and is divided approximately equally into three ages/stages (in order of decreasing age): the Danian, the Selandian, and the Thanetian (Figure 1).
When did salmonids first appear?
Salmonids appear to have developed during the Mesozoic Era and were probably already distributed over the Northern Hemisphere land masses by the early Tertiary Period. A fossil find from British Columbia indicates that a salmon-like fish (Eosalmon driftwoodensis) existed nearly 50 million years ago ( Wilson 1977 ). The oldest Salvelinus fossil was found in northern Nevada and is at least 10 million years old ( Cavender 1986 ). By that time divergence and spread of the major evolutionary groups of charrs had apparently already taken place. Divergence of an ancient Salmo - type ancestor into an Atlantic Ocean group ( Salmo) and a Pacific Ocean group ( Oncorhynchus) may have occurred about 15 million years ago by mid-Miocene times ( Behnke 1992). Thus, the basic pattern of the present geographic distribution of salmonids may have taken place millions of years ago, before the first ice age. This distribution has been influenced and modified by the glacial events during the Pleistocene.
When was the Holocene epoch established?
The only other GSSP currently ratified for the Quaternary defines the base of the Holocene Epoch/Series. It was established in 2008, and is defined in the North Greenland Ice Core Project’s NGRIP2 ice core, with an age of 11,700 calendar years before 2000 ( Walker et al., 2009 ).
What is the geology of the Thetis Ocean?
For most of the Mesozoic period, the Thetis Ocean covered this area, whereas during the Tertiary period, its central part was exposed to the Alpine orogenesis, when the majority of today's mountains were uplifted and folded. In flat areas in the south (Puglia) and in marginal parts in the northern (Pannonian basin) and eastern (Black Sea basin) regions, the sedimentation continued until the Quaternary period or is still ongoing.
Disuse of the term
The decision to replace the term “Tertiary” by Paleogene and Neogene was made at the beginning of the 20th century , leaving the initial term as a “sub-era” of the Cenozoic.
Cenozoic Era Division
The Quaternary period encompasses two eras, the Pleistocene and the Holocene.
Climate of the Tertiary period
In the periods of the Tertiary , an important climatic transition occurred between the warm, humid and regular world of past eras, to a colder and drier world, characteristic of the ice ages. There were much steeper steps in climate and temperature depending on the latitudes.
Fauna of the Tertiary period
During the Tertiary period, large flightless birds such as the gastornis appeared.
Massive ocean extinctions
Tertiary climatic changes particularly affected marine life : between 30 and 50% of marine species became extinct as ocean temperatures increased. However, they then descended again, and new marine extinctions occurred between the Eocene and Oligocene.
Prelude to humanity
The first apes or primate-like species emerged in the Tertiary , in the Eocene period. Diverse families appeared in Europe and North Africa ( Tarsiidae ), in North America and Europe ( Adapidae ) and North America, Europe, Egypt and Asia ( Omomyidae ).

Overview
Tertiary is a widely used but obsolete term for the geologic period from 66 million to 2.6 million years ago. The period began with the demise of the non-avian dinosaurs in the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, at the start of the Cenozoic Era, and extended to the beginning of the Quaternary glaciation at the end of the Pliocene Epoch. The time span covered by the Tertiary has no exact equivalent in the current geologic time system, but it is essentially the …
Historical use of the term
The term Tertiary was first used by Giovanni Arduino during the mid-18th century. He classified geologic time into primitive (or primary), secondary, and tertiary periods based on observations of geology in Northern Italy. Later a fourth period, the Quaternary, was applied.
In the early development of the study of geology, the periods were thought by scriptural geologists to correspond to the Biblical narrative, the rocks of the Tertiary being thought to be associated w…
Modern equivalents
The Tertiary's time span lies between the Mesozoic and the Quaternary, although no longer recognized as a formal unit by the International Commission on Stratigraphy.
The span of the Tertiary is subdivided into the Paleocene (66–56 million years BP), the Eocene (56–33.9 million years BP), the Oligocene (33–23.9 million years BP), the Miocene (23–5.3 million years BP) and the Pliocene (5.3–2.6 million years BP), extending to the first stage of the Pleistoce…
External links
• "Tertiary" . Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). 1911.