The hilum of the lung is the wedge-shaped area on the central portion of each lung, located on the medial (middle) aspect of each lung. The hilar region is where the bronchi, arteries, veins, and nerves enter and exit the lungs.
What structures enter and exit the lungs in the chest?
The major bronchi, pulmonary arteries, pulmonary veins, and nerves are the structures which enter and exit the lungs in this region. Lymph nodes, called hilar lymph nodes, are also present in this region. Both hilum are similar in size, with the left hilum usually found slightly higher in the chest than the right hilum.
Where is the hilum of the lung located in lung cancer?
More in Lung Cancer. The hilum of the lung is the wedge-shaped area on the central portion of each lung, located on the medial (middle) aspect of each lung. The hilum is where the bronchi, the arteries, veins, and nerves enter and exit the lungs.
What is the anatomy of the hilus region?
Anatomy of the Hilum. Each lung may be visualized as having an apex (the top) a base (the bottom) a root and a hilus. The major bronchi, pulmonary arteries, pulmonary veins, and nerves are the structures which enter and exit the lungs in this region. Lymph nodes, called hilar lymph nodes, are also present in this region.
What is the hilar region of the lung?
The hilum of the lung is the wedge-shaped area on the central portion of each lung, located on the medial (middle) aspect of each lung. The hilar region is where the bronchi , arteries, veins, and nerves enter and exit the lungs.
What structures enter and exit the hilum of the lung?
Anatomy of the Hilum The major bronchi, pulmonary arteries, pulmonary veins, and nerves are the structures which enter and exit the lungs in this region.
What runs through the hilum?
Lung hilum diagram The hilum is visible as a triangular section at the inner midpoint of each lung. It is the space where vessels and nerves pass from your bronchus to your lungs.
What are the hilar structures of the lung?
The lung roots, or hila (singular – hilum), are complicated anatomical structures containing the pulmonary vessels and the major bronchi, arranged asymmetrically. Although the hilar lymph nodes are not visible on a normal chest X-ray, they are of particular importance clinically.
What are the three structures that pass through the hilum?
Medial view and hilum of cadaveric lungs: The lung hilum contains the main bronchus, pulmonary artery and pulmonary veins. The main bronchus is located posterior to the vessels, while the pulmonary artery is superior to the vein.
What is the hilum which three structures enter and exit the kidney at the hilum?
The hilum of the kidney is the site of entry and exit for renal artery, renal vein, and ureter.
What is the hilum which three structures enter and exit the kidney at the hilum quizlet?
What structures enter and leave the kidney at this location? Renal Hilum - Medial indentation of the kidney. Ureters, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves enter and leave the renal hilum.
Where is the hilum of the lung found quizlet?
Where is the hilum of the lung located? The mediastinal surface.
Where is the hilar in the lung?
The hilum (root) is a depressed surface at the center of the medial surface of the lung and lies anteriorly to fifth through seventh thoracic vertebrae. It is the point at which various structures enter and exit the lung. The hilum is surrounded by pleura, which extends inferiorly and forms a pulmonary ligament.
Which vessel passes directly behind the right hilum?
The root of the right lung lies behind the superior vena cava and part of the right atrium (beneath the azygos vein). The root of the left lung passes beneath the aortic arch and in front of the descending aorta.
What is the correct order of structures through which air flows into the respiratory tract?
When you inhale through your nose or mouth, air travels down your pharynx (back of your throat), passes through your larynx (voice box) and into your trachea (windpipe). Your trachea is divided into two air passages called bronchial tubes. One bronchial tube leads to your left lung, the other to your right lung.
Which is a correct arrangement of the structures that passes inside the renal hilum from anterior to posterior?
So the arrangement of the structures in the hilum of left kidney from anterior to posterior aspect was anterior division of the renal vein-anterior division of renal artery-renal pelvis-posterior division of renal vein-posterior division of renal artery (A-V-P-V-A).
What is the function of the hilum quizlet?
Renal blood vessels and nerves enter and exit the hilum. The hilum is on the most superior surface of the kidney. The hilum is where the ureter exits the kidney.
Where are the hilar nodes located?
Hilar-interlobar 10 Hilar nodes are the proximal lobar nodes, which are outside the mediastinal pleura and adjacent to the bronchus intermedius and mainstem bronchi. They are inferior to the upper aspect of the upper lobe bronchi.
What does the medical term hilar mean?
Medical Definition of hilar : of, relating to, affecting, or located near a hilum hilar lymph nodes of the lung.
How many hilar lymph nodes are there?
The mediastinal and hilar lymph nodes are divided into the following 11 stations: anterior carina lymph nodes (station 1), posterior carina lymph nodes (station 2), right paratracheal lymph nodes (station 3), left paratracheal lymph nodes (station 4), right main bronchus lymph nodes (station 5), left main bronchus ...
What is the right hilar?
Right hilum The arteries lie in front of their respective bronchi. The two pulmonary veins are similar to that of the left side, one in front and one below the right main bronchus. The structures of the lung hilum are enclosed in a sleeve of pleura continuous below with the pulmonary ligament.
Which lung has a hilum?
Both the right and the left lung have a hilum which lies roughly midway down the lungs, and slightly towards the back (closer to the vertebrae than to the front of the chest). Each lung may be visualized as having an apex (the top), a base (the bottom), a root, and a hilum.
Why is the hilum of one or both lungs enlarged?
There are four main reasons why the hilum of one or both lungs may appear enlarged on an X-ray. These include: 1 . Tumors and lymphadenopathy: Cancers such as lung cancers and lymphomas, as well as cancer that has spread to this region from other parts of the body (metastatic cancer) can cause masses in this region.
Why is the hilum enlarged?
Enlargement of the hilum may occur due to tumors (such as lung cancer), pulmonary hypertension, or enlarged hilar lymph nodes due to conditions such as infections (especially tuberculosis and fungal infections), cancer (either local or metastatic), sarcoidosis, and more. 1 . An Overview of Pulmonary Hypertension. Theresa Chiechi / Verywell.
What is the hilum on a chest X-ray?
The hilar region is where the bronchi, arteries, veins, and nerves enter and exit the lungs. This area can be difficult to visualize on a chest X-ray, and further tests such as computerized tomography (CT) scan with contrast are often needed to determine if a problem exists. Enlargement of the hilum may occur due to tumors (such as lung cancer), ...
What causes hilar masses?
Tumors, both primary and metastatic, are a far too common cause of both hilar masses and lymphadenopathy. The most common causes overall include tuberculosis worldwide, and conditions such as histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis, and sarcoidosis in the United States. 10 .
Why is my hilum abnormal?
Some apparent abnormalities of the hilum may simply be due to positioning, and further views may rule out problems. If a mass or enlargement is noted, possible causes can vary depending on the appearance:
What is the name of the test that shows abnormalities in the hilar region?
In addition to imaging tests, abnormalities in the hilar region may be identified with tests such as a bronchoscopy, a test in which a tube is inserted through the mouth and down into the major airways (bronchi).
Anatomy of the Hilum
Both the right and the left lung have a hilum which lies roughly midway down the lungs, and slightly towards the back (closer to the vertebrae than to the front of the chest). Each lung may be visualized as having an apex (the top), a base (the bottom), a root, and a hilum.
Tests to Evaluate the Hilum
Abnormalities in the hilum are usually noted on imaging studies, but further tests and procedures are often needed to determine if a problem is present, and where.
Hilar Lymphadenopathy
Enlarged lymph nodes in the hilum may occur in both the right and left hilum (bilateral lymphadenopathy) or on one side alone (asymmetric lymphadenopathy.) Causes may include:
A Word From Get Meds Info
There are a number of conditions that can cause an abnormal appearance of the hilum on imaging studies, many of which are serious.
What is called hilum?
In anatomy, hilum refers to the part of an organ or gland where structures such as blood vessels, nerves, ducts, etc. enter or emerge from an anatomic part. Word origin: Latin hilum (a trifle; a spot on a seed)
Is sarcoidosis a lung disease?
Sarcoidosis is a rare disease caused by inflammation. It usually occurs in the lungs and lymph nodes, but it can occur in almost any organ. Sarcoidosis in the lungs is called pulmonary sarcoidosis. It causes small lumps of inflammatory cells in the lungs.
When should I worry about lung nodules?
Are lung nodules cancerous? Most lung nodules are benign, or non-cancerous. In fact, only 3 or 4 out of 100 lung nodules end up being cancerous, or less than five percent. But, lung nodules should always be further evaluated for cancer, even if they’re small.
What is a hilum in medical terms?
In human anatomy, the hilum (/ˈhaɪləm/; plural hila), sometimes formerly called a hilus (/ˈhaɪləs/; plural hili), is a depression or fissure where structures such as blood vessels and nerves enter an organ. Examples include: … Hilum of lymph node, the portion of a lymph node where the efferent vessels exit.
What is a pleural effusion in the lung?
Pleural effusion, sometimes referred to as “water on the lungs,” is the build-up of excess fluid between the layers of the pleura outside the lungs. The pleura are thin membranes that line the lungs and the inside of the chest cavity and act to lubricate and facilitate breathing.
Why do lungs have lobes?
Each lung is separated into lobes branching off the main bronchus; the right lung has three lobes, while the left has only two lobes. As the bronchi branch out, the total area of the two new branches is larger than its parent bronchus, making it extremely easy for the air to rush into the lungs.
What lobe is the hilum in?
In the right hilum the bronchus of the upper lobe and the branch of the right pulmonary artery to the upper lobe originate prior to entering the hilum. Thus, the upper lobe bronchus and artery are found above the level of the right main bronchus and right pulmonary artery.
Where are the lungs located?
The lungs are located within the thorax and extend from their apex, just above the first rib superiorly, level with T1, to the diaphragm inferiorly, level with T12 at their most inferior point in the posterior thorax on inspiration.
Which notch indents the anteroinferior aspect of the superior lobe of the left lung?
The cardiac notch indents the anteroinferior aspect of the superior lobe of the left lung.
What is the visceral pleura?
The visceral pleura covers the lungs and is adherent to all its surfaces, including the horizontal and oblique fissures; it cannot be separated from the lungs.
What covers the internal surfaces of the thoracic wall?
The costal pleura covers the internal surfaces of the thoracic wall.
What are the lungs of a healthy person?
In the healthy living person the lungs are light, soft and spongy.
Where does blood flow to the intercostal muscles?
The blood supply to the intercostal muscles is provided by the intercostal arteries and drains via the intercostal veins.
Which respiratory system conditions inspired air to match the environment in the lungs?
The upper respiratory tract conditions inspired air to match the environment in the lungs.
What are the C-shaped rings that support the trachea composed of?
The C-shaped rings that support the trachea are composed of Blank 1 of 1 cartilage tissue.
Which plate supports the secondary and tertiary bronchi but not the trachea?
Overlapping plates of cartilage support the secondary and tertiary bronchi but not the trachea.
What is the inferior portion of the larynx formed by?
The inferior portion of the larynx is formed by the Blank 1 of 1 cartilage.
Where is the nasal vestibule located?
The nasal vestibule is located in the Blank 1 of 1 portion of the nasal cavity.
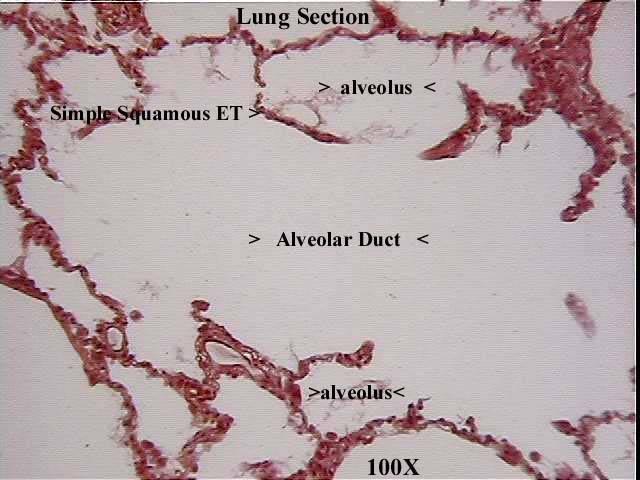
How many bronchus are there in each lung?
Each lung has one main or primary bronchus.
Which epithelium lines the majority of the digestive tract?
Recall that simple columnar epithelium lines the majority of the digestive tract, not the respiratory tract.
Where are the sphenoid bones?
The sphenoid bones are posterior to the bridge of the nose.
Introduction
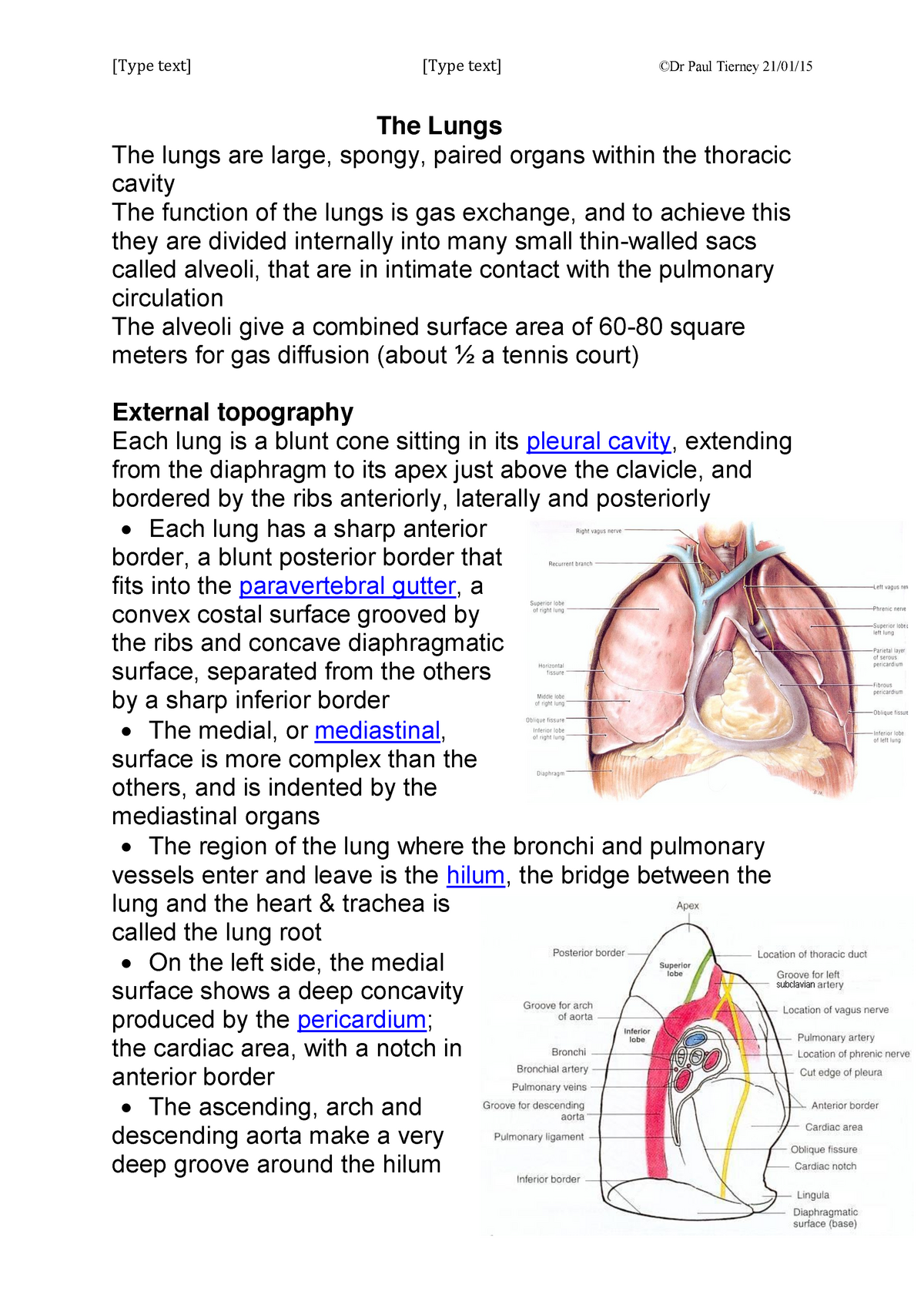
The hilum is located on the medial aspect of each lung and provides the only route via which other structures enter and exit the lung. The hilum also serves as the point of attachment for the lung root and is the point at which the visceral and parietal pleura connect.
Location of the Hilum
The hilum is a large triangular depression located superior to the centre of the lung’s mediastinal surface and posterior to the cardiac impression. Anteriorly, the hilum corresponds to the 4-5th costal cartilages and posteriorly to T5-T7.
The Root of the Lung
The root of the lung is located at the hilum of each lung, just above the middle of the mediastinal surface and behind the cardiac impression.