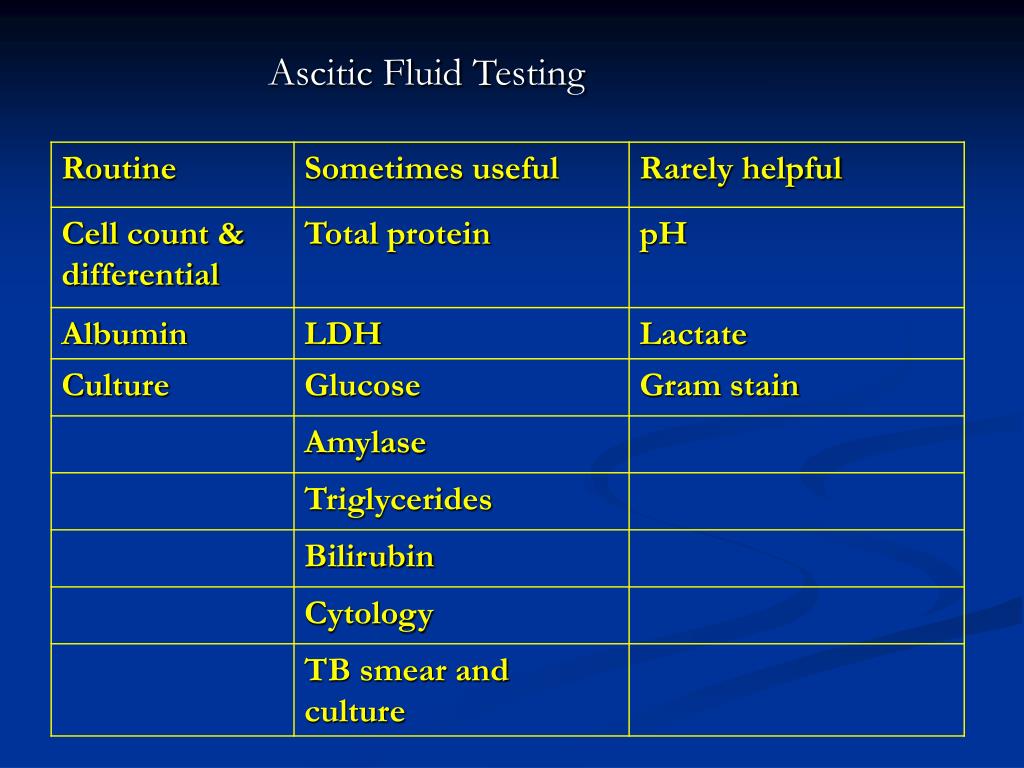
These tests typically include:
- Fluid albumin level—the serum-ascites albumin gradient (SAAG) calculation ( serum albumin level minus the fluid albumin level) may be used to differentiate between transudates and exudates. A SAAG level of 1.1 g/dL or greater suggests the presence of a transudate and less than 1.1 g/dL, an exudate.
- Cell count and differential
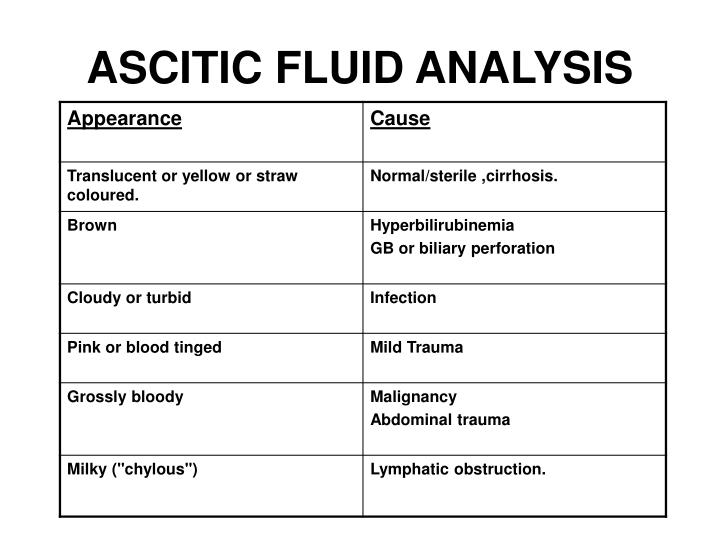
- Appearance
Full Answer
What is an ascitic fluid sample?
A sample of fluid is typically obtained using a needle and syringe (known as an “ascitic tap” or “paracentesis”) and sent for analysis.
What is biochemical analysis of ascitic fluid?
Biochemical analysis of ascitic fluid can provide useful insights which can help narrow the differential diagnosis. The table below summarises the typical patterns of biochemical findings which are associated with specific underlying disease processes.
What is ascites?
Ascites is the accumulation of ascitic fluid in the peritoneal cavity.
What is the purpose of ascitic fluid microscopy?
Ascitic fluid microscopy provides valuable information about the number and type of red and white cells within the fluid which can help narrow the differential diagnosis. Ascitic fluid microscopy.
How many OSCE checklists are there?
If you'd like to support us and get something great in return, check out our OSCE Checklist Booklet containing over 150 OSCE checklists in PDF format. You might also be interested in our Clinical Skills App and our OSCE Flashcard Collection which contains over 1800 cards.
Why are ascites samples analyzed?
Because many diseases can cause ascites, in particular cirrhosis, samples of ascitic fluid are commonly analyzed in order to develop a differential diagnosis. The concept of transudate versus exudate, as determined by total protein measurements, is outdated and the use of serum-ascites albumin gradient as an indicator of portal hypertension is more ...
What is ascitic fluid viscosity?
Ascitic fluid viscosity is a newly proposed indicator in differentiating ascites. A recent study by Gokturk et al. evaluated the role of ascitic fluid viscosity in discriminating between ascites due to portal hypertension-related and non-portal hypertension-related causes, and compared the results with SAAG.37In that study, ascitic fluid viscosity was determined in a programmable rotational viscometer using 0.5 mL ascitic samples from 142 patients with newly diagnosed ascites due to various causes.37The mean ascitic fluid viscosities were 0.86±0.12 cP and 1.22±0.25 cP in patients with an SAAG greater than 11 g/L and an SAAG of 11g/L or less, respectively, indicating a close correlation between viscosity and SAAG. Moreover, with a cut-off value of 1.03 cP, ascitic fluid viscosity measurement exhibited high sensitivity (98%), specificity (80%), and positive and negative predictive values (79% and 94%, respectively) for the etiological discrimination of ascites.37Although there are only a few studies evaluating the viscosity of ascites,70, 71the speed, simplicity, inexpensiveness, and necessity of only a small sample volume make it a useful, and likely more popular, diagnostic tool for the differential diagnosis of ascites in clinical research and practice.
How long does ascites last?
Ascites is one of the most frequent complications of cirrhosis.1, 4, 8, 9Up to 60% of patients with compensated cirrhosis will develop ascites within 10 years of the disease course.10, 11, 53, 93After the development of ascites, survival rate is only 50% at two to five years.93Therefore, differential diagnosis is essential for better management of cirrhosis, and ascitic fluid analysis plays an important role in this purpose. Table 2outlines the typical characteristics of the ascites in patients with cirrhosis relative to other diseases.
What is high amylase in ascites?
Amylase-rich ascitic fluid commonly occurs in cases of pancreatic duct damage or obstruction due to pancreatitis or pancreatic trauma.44Elevation of amylase levels above the serum reference range in ascitic fluid was found in up to 90% of patients with acute pancreatitis and pancreatic pseudocyst.2When pancreatic ascite s needs to be distinguished from ascites secondary to alcoholic cirrhosis, it can be accomplished by detecting high amylase levels in the ascitic fluid.45During the course of severe acute pancreatitis, the level of ascitic amylase can be 100 times higher than serum. However, increased amylase in ascites can also been found in patients with malignancy,46perforated peptic ulcer, upper abdominal surgery, mechanical intestinal obstruction, mesenteric vascular disease, biliary obstruction, and acute cholecystitis. Therefore, hyperamylasemia is not a specific marker for pancreatic damage.47
What is ascites in medicine?
Ascites is defined as pathological fluid accumulation within the abdominal cavity.1The word ascites is derived from the Greek word ‘askos’, which means a bag or sack.1–3Clinically, ascites is a consequence or complication of a number of diseases, including hepatic, cardiac, and renal diseases, infection, and malignancy.
What is milky ascites?
Milky ascites, also called chylous ascites, is characterized by the presence of chylomicrons, which are lipoprotein particles that consist of large amounts of triglycerides.2 , 17, 18There are many known causes of chylous ascites, including cirrhosis, infections (parasitic and tuberculosis), malignancy, congenital defects, traumatism, inflammatory processes, nephropathies, and cardiopathies.2, 19, 20Abdominal malignancy is a major cause of chylous ascites in adults, whereas congenital lymphatic abnormalities are more likely causes in children.21However, it should be noted that pseudochylous ascites or cloudy/turbid ascites is associated with bacterial infection, peritonitis, pancreatitis, or perforated bowel.22Therefore, the presence of both chylomicrons and a high concentration of triglycerides is necessary to distinguish chylous ascites from pseudochylous ascites. This is important since the frequency of malignancy is as high as 80% in adults with chylous ascites.2
What are non-biochemical tests?
Non-biochemical tests. Cell counts, bacterial culture, and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) . Non-biochemical tests of ascitic fluid, including cell counts, bacterial culture, and PCR, play an important role in diagnosing the cause of ascites, especially in infectious ascites.
What do ascitic fluid test results mean?
Presence of ascitic fluid is an indication of an underlying condition and is usually associated with a poor prognosis. Assessment of the levels of various substances in the fluid will help the doctor evaluate the primary cause of fluid accumulation and order other tests as needed. The table given below relates the conditions associated with a change in the level of particular substances in ascitic fluid.
What is the best test to confirm ascites?
An ultrasound exam may be done to confirm ascites. Once ascites is confirmed, it is important for the doctor to diagnose the underlying cause since the chances of survival in ascites that requires hospitalisation drop to around 85% at 1 year. Ascitic fluid test is one of the ways to diagnose the cause of accumulation of fluid.
What is ascites fluid?
Ascites is a condition characterised by accumulation of water in the abdomen. Ascitic fluid test checks this water for its characteristics and presence of various cells and proteins. Ascites commonly presents itself in individuals with cirrhosis, but can also be seen in various other non-liver-related conditions.
Why is ascites important?
Ascites could be of different types and is caused due to dysfunction of various organs like liver, kidney, heart, pancreas and ovaries. Some cancers or infections are also responsible for the accumulation of fluid in the abdomen. Therefore, it becomes essential for the doctor to identify the exact cause of fluid accumulation. The levels of various substances in the fluid reflect the underlying condition. Therefore, ascitic fluid test is an essential part of ascites diagnosis.
How to take a fluid sample?
The doctor will ask the person to lie down on their back or side and will assess the abdomen to know the correct place from where the fluid should be taken. The point of insertion is in the line of the belly button, either on the left or on the right. Then the doctor will clean the area of puncture with a sterile solution and apply a numbing cream on it. They will aspirate about 50 mL of fluid from the abdomen using a sterile needle. The sample fluid is then sent to a laboratory for testing.
Is a clinically correlated diagnosis a substitute for medical advice?
The above information is provided from a purely educational point of view and is in no way a substitute for medical advice by a qualified doctor.
Do you need a special preparation for an ascites fluid test?
Ascitic fluid test does not need any special preparations. Individual undergoing this test must inform the doctor about any medical conditions they might have or any medications or herbal supplements that they are on. It is important to let the doctor know if women undergoing the test are pregnant. The doctor should also be given an accurate and detailed history of past medical conditions, as they may be the cause of ascites.
How do you know if you have ascites?
The main symptoms of ascites are a large belly and rapid weight gain. Other symptoms include: Swelling in your ankles. Shortness of breath. Digestive issues, such as bloating, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, indigestion and constipation. Back pain.
What is ascites in a doctor?
Ascites. Ascites is a buildup of fluid in your abdomen. It often occurs as a result of cirrhosis, a liver disease. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have cirrhosis and notice you’re gaining weight very quickly. Your provider will talk to you about treatments, which often include a low-salt diet. Appointments 216.444.7000.
What is it called when you have a lot of fluid in your abdomen?
Ascites (ay-SITE-eez) is when too much fluid builds up in your abdomen (belly). This condition often happens in people who have cirrhosis (scarring) of the liver.
What causes ascites in the heart?
Cirrhosis is the most common cause of ascites. Other conditions that can cause it include heart failure, kidney failure, infection or cancer.
How to reduce ascites risk?
Limit alcohol: It’s best to avoid alcoholic beverages entirely to reduce your ascites risk.
How to treat ascites in the abdomen?
You may need other treatments, including: Paracentesis: Your provider inserts a needle into your abdomen to remove the fluid. This procedure can remove a large amount of excess fluid.
What are the symptoms of ascites?
The main symptoms of ascites are a large belly and rapid weight gain .
How is ascites diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will do a physical exam and ask about your symptoms. You may also have tests such as:
How do you know if you have ascites?
These are symptoms of ascites: Swelling in the abdomen. Weight gain. Sense of fullness. Bloating. Sense of heaviness. Nausea or indigestion. Vomiting. Swelling in the lower legs.
What causes ascites?
The most common cause of ascites is cirrhosis of the liver. Drinking too much alcohol is one of the most common causes of cirrhosis of the liver.
What is the condition where fluid collects in spaces within the abdomen?
Ascites is a condition in which fluid collects in spaces within your abdomen. As fluid collects in the abdomen, it can affect your lungs, kidneys, and other organs. Ascites causes abdominal pain, swelling, nausea, vomiting, and other difficulties.
What is ascites in a patient?
What is ascites? Ascites is a condition in which fluid collects in spaces within your abdomen. If severe, ascites may be painful. The problem may keep you from moving around comfortably. Ascites can set the stage for an infection in your abdomen.
How to reduce potassium levels in ascites?
Cut back on your salt intake. Your healthcare provider or a dietitian can show you how to follow a low-sodium diet. Avoid salt substitutes that contain potassium. This is because some medicines used in treating ascites can cause your potassium levels to rise.
How to prevent ascites?
Stopping all alcohol intake, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising, not smoking, and limiting salt intake can help prevent cirrhosis or cancer that may lead to ascites. Ascites can’t be cured but lifestyle changes and treatments may decrease complications.
How is a fluid test performed?
How the Test is Performed. The sample of fluid is removed from the peritoneal space using a needle and syringe. Ultrasound is often used to direct the needle to the fluid. Your health care provider will clean and numb a small area of your belly area (abdomen).
What is peritoneal fluid analysis?
Peritoneal fluid analysis is a lab test. It is done to look at fluid that has built up in the space in the abdomen around the internal organs. This area is called the peritoneal space. The condition is called ascites.
What is the purpose of removing fluid from the peritoneal space?
Remove large amounts of fluid from the peritoneal space in people who have liver disease. (This is done to make breathing comfortable. )
Where is fluid collected?
The fluid is collected into a tube (syringe) attached to the end of the needle. The fluid is sent to a lab where it is examined. Tests will be done on the fluid to measure: Tests will also check for bacteria and other types of infection.
What happens if you take fluid out?
If a large amount of fluid is taken out, you may feel dizzy or lightheaded. Tell the provider if you feel dizzy.