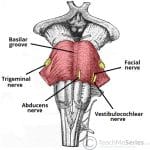
The following structures pass through the tendinous ring (superior to inferior):
- Superior division of the oculomotor nerve (CNIII)
- Nasociliary nerve (branch of ophthalmic nerve)
- Inferior division of the oculomotor nerve (CNIII)
- Abducens nerve (CNVI)
- Optic nerve
What nerve passes through common tendinous ring?
Optic nerveOptic nerve (B) containing within dural sheath and coursing through the common tendinous ring. Superior Rectus (A), Lateral Rectus (D), Levator Palpebrae Superioris, Medial Rectus (F), Inferior Rectus (G). Intra-orbital vessels (C).
What passes through ring of Zinn?
The optic, oculomotor, and abducens nerves all pass through the annulus of Zinn, while the trochlear nerve travels just medial to the annulus of Zinn. The nasociliary nerve is the sole portion of the ophthalmic division of cranial nerve V which passes through the annulus of Zinn.
What muscles originate from common tendinous ring?
The four rectus muscles have their origin on the common tendinous ring (annulus of Zinn). This oval band of connective tissue is continuous with the periorbita and is located at the apex of the orbit anterior to the optic foramen and the medial part of the superior orbital fissure.
Which of the following passes through the superior orbital fissure but not through the common tendinous ring?
Correct Answer: Ophthalmic artery.
Which of the following muscles does not take its origin from the common tendinous ring?
Unlike most of the other extraocular muscles (recti and superior oblique), the inferior oblique muscle does not originate from the common tendinous ring (annulus of Zinn).
What goes through superior orbital fissure?
Numerous structures pass through the SOF: the oculomotor (III) and trochlear nerves (IV), the ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve (VI) with its frontal, lacrimal, and nasociliary branch, the abducens nerve (VI), and both the ophthalmic veins, superior and inferior.
What muscles attach to the common tendon?
The common extensor tendon serves as the upper attachment (in part) for the superficial muscles that are located on the posterior aspect of the forearm:Extensor carpi radialis brevis.Extensor digitorum.Extensor digiti minimi.Extensor carpi ulnaris.
What is the origin of the 4 Recti muscles?
The four recti muscles all arise from a connective tissue ring called the common tendinous ring (annulus of Zin). This is located at the apex of orbit, surrounding the optic canal. Respectively, the recti muscles insert onto the superior, inferior, medial and lateral sides of the eyeball.
What is the common origin of the four rectus muscles called?
The annulus of Zinn is the common origin point for the rectus muscles and spans the superior orbital fissure and orbital apex. It consists of superior and inferior tendons. The superior tendon is involved with the entire superior rectus muscle as well as portions of the medial rectus and lateral rectus muscles.
Which nerve passes through the superior orbital fissure quizlet?
Motor fibers. REMINDER: the trochlear nerve comes from the Mesencephalon, aka the Midbrain, and goes through the superior orbital fissure, which is between the lesser and greater wings of the sphenoid.
What travels through the inferior orbital fissure?
The IOF is formed by a cleft between the greater wing of the sphenoid and the body of the maxilla at the orbital floor and transmits the infraorbital artery, vein, and nerve (from V2).
Does optic nerve pass through superior orbital fissure?
The optic foramen, through which the optic nerve and ophthalmic artery run, lies just superior and medial to the superior orbital fissure in the lesser wing of the sphenoid.
What passes through the inferior orbital fissure and Infraorbital groove?
The IOF is formed by a cleft between the greater wing of the sphenoid and the body of the maxilla at the orbital floor and transmits the infraorbital artery, vein, and nerve (from V2).
Where is the upper orbital fissure and what passes through it?
It lies between the lesser and greater wings of the sphenoid bone. It allows for many structures to pass, including the oculomotor nerve, the trochlear nerve, the ophthalmic nerve, the abducens nerve, the ophthalmic vein, and sympathetic fibres from the cavernous plexus.
What is the tendinous ring?
Definition. Any anomaly of the ring of fibrous tissue that surrounds the optic nerve at its entrance at the apex of the orbit. The common tendinous ring, also known as the annulus of Zinn or annular tendon, is the origin for five of the seven extraocular muscles. [
Which muscle forms a ring around your eyes and allows you to squint?
The Orbicularis Oculi The Orbicularis Oculi muscle opens and closes the eyelids thus allowing us to blink, wink or squint in bright sunlight.
What is the annulus of Zinn?
Tendinous ring. The tendinous ring, also known as the annulus of Zinn, is the common origin of the four rectus muscles ( extrao cular muscles ). The tendinous ring straddles the lower, medial part of the superior orbital fissure. It attaches to a tubercle on the greater wing of the sphenoid bone (at the margin of the superior orbital fissure).
What is the medial portion of the ring?
The medial portion of the ring also encompasses the optic foramen through which the optic nerve and ophthalmic artery pass. A memory aid for the specific nerves in the structure is the mnemonic for the contents of the annulus of Zinn.
What is the ISBN for FRCS CSS?
1. FRCS CSS. Last's Anatomy. Churchill Livingstone. (1999) ISBN:0443056110. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
Which portion of the ring encompasses the optic foramen through which the optic nerve and ophthalmic?
Through it (from superior to inferior) pass: The medial portion of the ring also encompasses the optic foramen through which the optic nerve and ophthalmic artery pass. A memory aid for the specific nerves in the structure is the mnemonic for the contents of the annulus of Zinn.
Which part of the ring encompasses the optic nerve?
The medial portion of the ring also encompasses the optic foramen through which the optic nerve and ophthalmic artery pass.
What are the three nerves that connect the rectus muscles?
The three nerves are: the nasocilliary nerve, which branches from the optic nerve, the abducens or sixth cranial nerve, and the oculomotor or third cranial nerve. The one artery that passes through the ring, the opthalmic artery, supplies the eye with the necessary blood supply.
What is the annulus of the eye?
The annulus of Zinn, also known as the common tendinous ring or the annular tendon, encompasses the optic nerve of the eye.
What is the action of the levator palpebrae superioris?
Actions: Elevates the upper eyelid. Innervation: The levator palpebrae superioris is innervated by the oculomotor nerve (CN III). The superior tarsal muscle (located within the LPS) is innervated by the sympathetic nervous system. There are six muscles involved in the control of the eyeball itself.
What are the extraocular muscles?
There are seven extraocular muscles - the levator palpebrae superioris, superior rectus, inferior rectus, medial rectus, lateral rectus, inferior oblique and superior oblique.
What muscles are involved in the eyeball?
The extraocular muscles are located within the orbit, but are extrinsic and separate from the eyeball itself. They act to control the movements of the eyeball and the superior eyelid. There are seven extraocular muscles – the levator palpebrae superioris, superior rectus, inferior rectus, medial rectus, lateral rectus, ...
What is partial ptosis?
Partial ptosis (drooping of the upper eyelid) – Due to denervation of the superior tarsal muscle.
How many muscles are involved in the control of the eyeball?
There are six muscles involved in the control of the eyeball itself. They can be divided into two groups; the four recti muscles, and the two oblique muscles. Recti Muscles. There are four recti muscles; superior rectus, inferior rectus, medial rectus and lateral rectus.
Which cranial nerve is affected by the extraocular muscle?
Thus, a lesion of each cranial nerve has its own characteristic appearance: Oculomotor nerve ( CN III) – A lesion of the oculomotor nerve affects most of the extraocular muscles. The affected eye is displaced laterally by the lateral rectus and inferiorly by the superior oblique.
Which nerve innervates the superior tarsal muscle?
Innervation: The levator palpebrae superioris is innervated by the oculomotor nerve (CN III). The superior tarsal muscle (located within the LPS) is innervated by the sympathetic nervous system.
What is the superior rectus?
The superior rectus has fascial attachments to the superior oblique tendon and the levator palpebrae muscle. If the attachments to the levator palpebrae are not severed during recession or resection of the superior rectus, eyelid fissure changes may occur. Connective tissue attachments between the inferior rectus and the inferior oblique may assist the surgeon in locating a “lost” inferior rectus muscle.
How many rectus muscles are there?
Rectus muscles. There are four striated rectus muscles arising from the annulus of Zinn in the apex of the orbit. Each is 40 mm in length and inserts on the sclera anterior to the equator of the globe.
What is the annulus of Zinn?
Muscle Cone and Annulus of Zinn. The annulus of Zinn serves as the origin of six of the seven extraocular muscles (Fig. 50-2 ). Superiorly, the superior rectus arises from the annulus, which at this point is fused with the dura of the optic nerve. The levator palpebrae arises medial and superior to the superior rectus muscle ...
How many extraocular muscles are there?
Extraocular muscles. The six extraocular muscles are striated with unique properties. 16 The four rectus muscles (each about 3–4 cm long) originate from the annulus of Zinn at the orbital apex, which is contiguous with the dura surrounding the optic nerve and the periorbita.
How to correct mild ptosis?
Cases of mild ptosis can be corrected with a external levator resection and advancement, or Müllerectomy. For patients with severe ptosis with maintained levator excursion, levator advancement is the procedure of choice. Severe ptosis with absent levator function will usually require a frontalis sling procedure. Secondary correction of severe injuries should be delayed until the scar has remodeled 6–12 months post injury. 55,56
What muscle is anteriorly and laterally attached to the sclera?
The inferior rectus muscle courses anteriorly, laterally, and inferiorly to insert on the sclera. The inferior rectus forms a 23° angle with the visual axis when the globe in the primary gaze position. It has fascial attachments to the inferior oblique muscle and the lower eyelid retractors ( Fig. 85.5 ).
Where are the rectus muscles located?
This oval band of connective tissue is continuous with the periorbita and is located at the apex of the orbit anterior to the optic foramen and the medial part of the superior orbital fissure.