Explore
Phantom pain typically occurs soon after limb loss. It can take three to six months for a wound to heal after amputation. Rarely, the pain comes on months or years later. Experts believe phantom pain results from a mix-up in nervous system signals, specifically between the spinal cord and brain.
What is Phantom Pain and will it go away?
This is known as phantom limb pain. For some people, the pain will go away on its own. For others, it can be long-lasting and severe. It can last from seconds to minutes, to hours, to days.
Does Phantom Pain ever go away?
On gamepad press the left d-pad button again, on keyboard I don't know, but probably the same key you pressed to initiate it. Press 4. It stops any active effect (invisibility, cigar, infrared erm infrayellow, etc). Note: This is ONLY to be used to report spam, advertising, and problematic (harassment, fighting, or rude) posts.
How to stop Phantom Pain?
Using mirror therapy for phantom pain allows you to receive visual feedback that the phantom limb is relaxing and moving and therefore offers phantom pain relief. The visual information received by the brain overpowers the proprioceptive information and thus allows the brain to think the limb is moving.
How does mirror therapy relieve Phantom Pain?

What causes the phantom limb experience?
This phantom limb phenomenon has been found to be caused by the changes occurring in the cortex of the brain following amputation of a limb. Moreover, it appears that the brain continues to receive signals from the nerve endings that originally supplied signals to and from the missing limb.
How do you calm phantom pain?
These include:Acupuncture.Massage of the residual limb.Use of a shrinker.Repositioning of the residual limb by propping on a pillow or cushion.Mirror box therapy.Biofeedback.TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation)Virtual reality therapy.More items...
What does phantom pain feel like?
Phantom pain is the term used to describe sensations felt by amputees, which may include tingling, itching, twisting, cramping, pins-and-needles, stabbing pains, pressure, a sense of fullness (as if the limb was still there, but slightly swollen), and so on.
Can you create phantom pain?
0:032:46Scientists create phantom sensations in non-amputees - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipExperienced the phenomenon of a phantom limb which is a vivid sensation of that a missing limb isMoreExperienced the phenomenon of a phantom limb which is a vivid sensation of that a missing limb is still present. Over time these phantom limbs can become very painful. And it's difficult to treat.
Is phantom pain psychological?
Phantom pain is pain that feels like it's coming from a body part that's no longer there. Doctors once believed this post-amputation phenomenon was a psychological problem, but experts now recognize that these real sensations originate in the spinal cord and brain.
Will phantom pain ever go away?
Phantom pain does eventually go away with time. Many people find their pain has decreased by about 75 percent or more within two years after amputation surgery. If it does return, talk to your doctor. There may be an underlying problem — such as a neuroma (nerve overgrowth) — triggering the sensation.
Is phantom pain neurological?
Phantom limb pain is considered a neuropathic pain, and most treatment recommendations are based on recommendations for neuropathic pain syndromes. Mirror therapy, a relatively recently proposed therapy for phantom limb pain, has mixed results in randomized controlled trials.
Can you have phantom pain without amputation?
Almost everyone who has had an arm or leg amputated experiences a phantom limb: a vivid sensation that the missing limb is still present. A new study by neuroscientists at the Karolinska Institutet in Sweden shows that it is possible to evoke the illusion of having a phantom hand in non-amputated individuals.
How long is phantom pain?
When focusing on the main objectives, Metal Gear Solid V: The Phantom Pain is about 45½ Hours in length. If you're a gamer that strives to see all aspects of the game, you are likely to spend around 162 Hours to obtain 100% completion.
What happens in the brain during phantom limb pain?
A popular theory of the cause of phantom limb pain is faulty 'wiring' of the sensorimotor cortex, the part of the brain that is responsible for processing sensory inputs and executing movements. In other words, there is a mismatch between a movement and the perception of that movement.
How painful is losing a limb?
Losing a limb can deliver a one-two punch. First there's the physical and mental trauma of an amputation. Then, for more than 80 percent of amputees, comes the chronic pain that can be nearly as debilitating as their original injury. For some, the painful feelings radiate from the limb that has been removed.
Can CBD help phantom pain?
Research shows that CBD has the following physical benefits, all of which may help an individual with phantom pain.
Does phantom pain ever vanish?
Phantom pain eventually goes away with time. Several patients find that their pain has reduced by about 75% or more within a period of 2 years afte...
Why do amputated patients feel phantom pain?
Several experts believe that phantom pain may be explained partly as a response to mixed signals from the brain
Do dogs feel phantom pain too?
They too experience discomfort and pain after a limb is lost
What tests are needed for phantom pain?
These tests may include blood tests and imaging scans like ultrasounds. If your provider can’t identify a cause, your provider may diagnose phantom pain based on your symptoms.
How long does phantom pain last after amputation?
Still, as many as 8 in 10 people continue to have phantom pain two years after amputation. The phantom pain may feel like:
What is the pain of an amputation?
After an amputation, some people experience pain in the part of the limb that’s no longer there. This sensation is phantom limb pain. The pain is real. The phantom part refers to the location of the pain: the missing limb or part of the limb (such as fingers or toes).
How long does a phantom limb last?
Phantom limb pain ranges from mild to severe and can last for seconds, hours, days or longer. It may occur after a medical amputation (removing part of a limb with surgery). It can also happen after accidental amputation, when you lose a finger, toe or other body part. Phantom pain can be managed.
How long does it take for a phantom to heal?
Phantom pain typically occurs soon after limb loss. It can take three to six months for a wound to heal after amputation. Rarely, the pain comes on months or years later. Experts believe phantom pain results from a mix-up in nervous system signals, specifically between the spinal cord and brain.
Can amputations cause phantom pain?
If you’ve had an amputation (limb loss), you may develop phantom pain. The pain is real, but it feels like it’s happening in the missing body part. This condition may gradually go away. Some people have residual limb pain in the remaining part of the limb. Pain relievers and a treatment called mirror therapy can ease phantom pain.
Does Phantom limb pain go away?
Phantom limb pain often improves over time. Eventually, it may go away completely. Chronic pain can affect your ability to enjoy life, but a combination of medications and other therapies can ease the pain.
How to relieve phantom pain?
Newer approaches to relieve phantom pain include virtual reality goggles. The computer program for the goggles mirrors the person's intact limb, so it looks like there's been no amputation. The person then moves his or her virtual limb around to accomplish various tasks, such as batting away a ball hanging in midair.
What is the best medicine for phantom pain?
Acetaminophen (Tylenol, others), ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) or naproxen sodium (Aleve) might relieve phantom pain. Take these medications only as directed by your doctor. Overuse can cause serious side effects, such as stomach bleeding. Antidepressants.
What is the best medication for nerve pain?
Epilepsy drugs — such as gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) — may be used to treat nerve pain. Side effects may include dizziness, sedation and mood changes. Narcotics. Opioid medications, such as codeine and morphine, may be an option for some people.
Can a doctor diagnose phantom pain?
Although there's no medical test to diagnose phantom pain, doctor s identify the condition based on your symptoms and the circumstances, such as trauma or surgery, which occurred before the pain started.
Can you have phantom pain after surgery?
You may not have control over whether you develop phantom pain after surgery, but you can reduce your discomfort and improve your quality of life. One or more of these approaches may help you get through a flare-up of phantom pain:
Can short pulses cause phantom pain?
Research suggests that this therapy may be helpful for phantom pain, though it isn't yet specifically approved for this condition.
Can you have phantom pain and residual pain at the same time?
Even though it's common to have phantom pain and residual limb pain at the same time, treatments for these two problems may differ — so an accurate diagnosis is important.
What are the Types of Phantom pain?
Residual Limb pain: Also called stump pain, residual limb pain is a type of phantom pain. Great research suggests that stump pain occurs in approximately half the number of people who have undergone an amputation.
What are the Causes of Phantom Pain?
The main cause of phantom pain is still unknown. However, some experts tend to believe that phantom pain is psychological. Similarly, it is thought to arise due to mixed signals from your brain or spinal cord. This occurs when the nerves in the part of your spinal cord and brain lose signals due to the detachment.
What are the Risk Factors of Phantom Pain?
It is not always that phantom pain will develop after amputation. However, some of the risk factors which may expose you to phantom pain include:
What are the Treatment Options?
Finding the right treatment for phantom pain can be a daunting task. However, physicians will undertake a multi pronged approach. This takes the form of medications coupled with noninvasive therapies. Also, surgery may be used as a last resort.
Medications
This involves the use of certain drugs to alleviate the pain. Some medications you may be subjected to include:
Medical Therapies
This involves treatment techniques designed to help alleviate the pain where medication is not enough. Such treatment includes:
Surgery
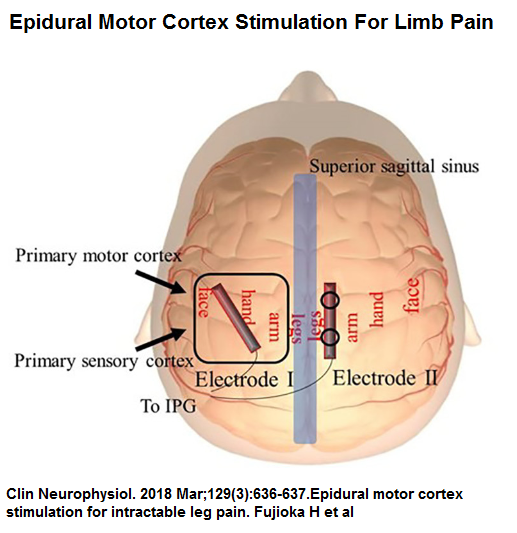
Brain stimulation: This procedure is similar to spinal cord stimulation. However, in this case, a surgeon places electrodes in the right spot in your brain using magnetic resonance imaging. Although it is yet to be treated as a definite approach, brain stimulation has been found to alleviate pain in selected individuals.
What is the best medicine for a phantom limb?
Each of them is thought to work on different kinds of pain sensations. The categories of some of the medications you might be given include: Acetaminophen and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
What is PLP pain?
Unlike pain that is caused by trauma directly to a limb, PLP is thought to be caused by mixed signals from your brain or spinal cord. This is an important concept to consider, because the treatment for this pain has differences from the treatment you would receive for other kinds of pain. New therapies for PLP all involve trying to change ...
What is the goal of pain management?
The goal of pain management is to reduce pain levels to allow you to get you back to living and enjoying life again. Work closely with your healthcare team to create and maintain the pain management plan that works for you. When possible, avoid things that trigger your phantom limb pain/sensation.
Can amputation cause phantom limb pain?
Phantom limb pain/sensation is common for most people after amputation surgery. Symptoms generally improve over time. Your phantom limb pain/sensation can be managed so that it does not overwhelm your life.
What happens to the nerves during amputation?
During amputation, peripheral nerves are severed. This results in massive tissue and neuronal injury causing disruption of the normal pattern of afferent nerve input to the spinal cord. This is followed by a process called deafferentation and the proximal portion of the severed nerve sprouts to form neuromas [18].
Is phantom limb pain a neuropathic pain?
Phantom limb pain is considered a neuropathic pain, and most treatment recommendations are based on recommendations for neuropathic pain syndromes. Mirror therapy, a relatively recently proposed therapy for phantom limb pain, has mixed results in randomized controlled trials.
