
Why is cellulose bad for You?
Cellulose has no calories, vitamins or minerals, and no protein, carbohydrates or fat. Cellulose is a type of insoluble fiber, which means the body can't digest it. When you eat a piece of celery, the other components of the vegetable are digested, but the cellulose moves through your digestive tract unchanged.
What is cellulose and is it safe to eat?
Cellulose is prized for its inherent dryness. That property allows it absorb moisture in certain kinds of foods, like baked goods, and thus reduce spoilage. In other cases, it makes for a less "slimy" texture than you might get with other common additives like agar or pectin. So cellulose is completely safe to eat.
What are the three classes of carbohydrates?
What Are the 3 Types of Carbohydrates?
- BY SANDI BUSCH | LIVESTRONG
- Carbohydrates often get clumped together in two extreme categories: good and bad. Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy. ...
- Often referred to as simple and complex carbohydrates, the three types of carbs — sugar, starch, and fiber — all have a place in your diet. ...
Does cellulose contain carbohydrates?
Cellulose is found in varying amounts in all the plant foods you eat, and it's even present in your clothing and the walls of your home. Cellulose has no calories, vitamins or minerals, and no protein, carbohydrates or fat. Cellulose is a type of insoluble fiber, which means the body can't digest it.
See more

Is cellulose monosaccharide or polysaccharide?
Cellulose is a linear polysaccharide polymer with many glucose monosaccharide units. The acetal linkage is beta which makes it different from starch.
Why is cellulose called a carbohydrate?
Cellulose is classified as a complex carbohydrate since it has more than two units of sugar linked together. Cellulose is a polysaccharide. This suggests it's made up of smaller, interconnected units. Monomers are the little units in question.
Is cellulose a polysaccharide?
, a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall of green plants, many forms of algae and the oomycetes. Some species of bacteria secrete it to form biofilms.
Why is cellulose a polysaccharide?
Cellulose is the most important structural polysaccharide present in plants. It is made up of unbranched chains of glucose molecules linked via beta 1-4 glycosidic bonds. Every alternate glucose molecule in cellulose chains is inverted. These chains are arranged parallel to each other to form microfibrils.
Is cellulose a simple sugar or complex carbohydrate?
complex carbohydratecellulose, a complex carbohydrate, or polysaccharide, consisting of 3,000 or more glucose units.
Is cellulose a disaccharide?
Ribose and Deoxyribose are found in the backbone structure of RNA and DNA, respectively. French word for sugar--"sucre", a disaccharide containing glucose and fructose; table sugar, cane sugar, beet sugar....CarbohydratesMonosaccharidesDisaccharidesPolysaccharidesFructoseLactoseCelluloseRiboseGlyceraldehyde2 more rows
Is cellulose a starch?
There is one major difference between Starch and Cellulose....Difference Between Starch And Cellulose.PropertiesStarchCelluloseLinkageStarch has alpha 1,4 linkageCellulose has beta 1,4 linkageUsesPlants use starch to store energyPlants use cellulose to support structure7 more rows
What are the 4 types of polysaccharides?
Types Of PolysaccharidesGlycogen: It is made up of a large chain of molecules. ... Cellulose: The cell wall of the plants is made up of cellulose. ... Starch: It is formed by the condensation of amylose and amylopectin. ... Inulin: It is made up of a number of fructofuranose molecules linked together in chains.
Is cellulose a carbohydrate or protein?
5.3. Cellulose, as is starch, is a carbohydrate. It is a structural polysaccharide, while starch is one of the storage polysaccharides.
Is cellulose made of carbohydrates?
Cellulose, a fibrous carbohydrate found in all plants, is the structural component of plant cell walls. Because the earth is covered with vegetation, cellulose is the most abundant of all carbohydrates, accounting for over 50% of all the carbon found in the vegetable kingdom.
Is cellulose a lipid or carbohydrate?
Cellulose is a polysaccharide which consists of several repeating units of monosaccharide D - Glucose. Thus, it cannot be broken down into simpler compounds. Hence, cellulose is not a simple sugar. Hence, option (b) is the only correct answer, cellulose is a carbohydrate.
What is cellulose short answer?
Cellulose is a molecule, consisting of hundreds – and sometimes even thousands – of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms. Cellulose is the main substance in the walls of plant cells, helping plants to remain stiff and upright. Humans cannot digest cellulose, but it is important in the diet as fibre.
How many glucose molecules are in cellulose?
Cellulose consists of several thousand glucose molecules linked end to end. The chemical links between the individual glucose subunits give each cellulose molecule a flat ribbonlike structure that allows adjacent molecules to band laterally together into microfibrils with lengths ranging from two to seven…
What is cellulose used for?
Of great economic importance, cellulose is processed to produce papers and fibres and is chemically modified to yield substances used in the manufacture of such items as plastics, photographic films, and rayon. Other cellulose derivatives are used as adhesives, explosives, thickening agents for foods, and in moisture-proof coatings.
What are cellulose derivatives used for?
Other cellulose derivatives are used as adhesives, explosives, thickening agents for foods, and in moisture-proof coatings. Structures of common fibres. Cellulose consists of several thousand glucose molecules linked end to end. The chemical links between the individual glucose...
What is the most abundant polymer on earth?
Cellulose, a complex carbohydrate that is the basic structural component of the plant cell wall, is the most abundant polymer on earth. The basic structure of cellulose and its derivatives is shown below.…. History at your fingertips. Sign up here to see what happened On This Day, every day in your inbox!
What percentage of plant cell walls are made of cellulose?
The basic structural component of plant cell walls, cellulose comprises about 33 percent of all vegetable matter (90 percent of cotton and 50 percent of wood are cellulose) and is the most abundant of all naturally occurring organic compounds.
Is cellulose a herbivore food?
Nondigestible by man, cellulose is a food for herbivorous animals ( e.g., cows, horses) because they retain it long enough for digestion by microorganisms present in the alimentary tract; protozoans in the gut of insects such as termites also digest cellulose.
What is the purest form of cellulose?
A triple strand of cellulose showing the hydrogen bonds (cyan lines) between glucose strands. Cotton fibres represent the purest natural form of cellulose, containing more than 90% of this polysaccharide. Compared to starch, cellulose is also much more crystalline.
What is the formula for cellulose?
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula ( C#N#6 H#N#10 O#N#5)#N#n, a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β (1→4) linked D -glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall of green plants, many forms of algae and the oomycetes. Some species of bacteria secrete it to form biofilms. Cellulose is the most abundant organic polymer on Earth. The cellulose content of cotton fiber is 90%, that of wood is 40–50%, and that of dried hemp is approximately 57%.
What is a molecule that is soluble in water?
Molecules with very small chain length resulting from the breakdown of cellulose are known as cellodextrins ; in contrast to long-chain cellulose, cellodextrins are typically soluble in water and organic solvents.
How is cellulose treated?
Cellulose pulp may also be treated with strong acid to hydrolyze the amorphous fibril regions, thereby producing short rigid cellulose nanocrystals a few 100 nm in length. These nanocelluloses are of high technological interest due to their self-assembly into cholesteric liquid crystals, production of hydrogels or aerogels, use in nanocomposites with superior thermal and mechanical properties, and use as Pickering stabilizers for emulsions.
What is the most abundant organic polymer?
Cellulose is the most abundant organic polymer on Earth. The cellulose content of cotton fiber is 90%, that of wood is 40–50%, and that of dried hemp is approximately 57%. Cellulose is mainly used to produce paperboard and paper.
How is cellulose broken down?
Cellulose is derived from D -glucose units, which condense through β (1→4)- glycosidic bonds. This linkage motif contrasts with that for α (1→4)-glycosidic bonds present in starch and glycogen.
How many units of chain length is cellulose?
Cellulose from wood pulp has typical chain lengths between 300 and 1700 units; cotton and other plant fibers as well as bacterial cellulose have chain lengths ranging from 800 to 10,000 units. Molecules with very small chain length resulting from the breakdown of cellulose are known as cellodextrins; in contrast to long-chain cellulose, cellodextrins are typically soluble in water and organic solvents.
What are carbohydrates made of?
First, all carbohydrates are made up of the same chemical elements: 1 carbon (that’s the “carbo-” part) 2 hydrogen and oxygen, in about a two-to-one proportion, just like in H 2 O (that’s the “-hydrate” part)
What is the storage form of carbohydrates in plants?
Starch is the storage form of carbohydrate in plants. Plants make starch in order to store glucose. For example, starch is in seeds to give the seedling energy to sprout, and we eat those seeds in the form of grains, legumes (soybeans, lentils, pinto and kidney beans, for example), nuts, and seeds.
What is lactose made of?
Here is the chemical structure of lactose: Lactose is made of a glucose molecule bonded to a galactose molecule. It is sometimes called “milk sugar” as it is found in dairy products like milk, yogurt, and cheese. These are the only animal foods that have significant amounts of carbohydrate.
What is maltose used for?
Maltose also plays a role in the production of beer and liquor, because this process involves the fermentation of grains or other carbohydrate sources. Maltose is formed during the breakdown of those carbohydrates, but there is very little remaining once the fermentation process is complete.
How to taste maltose?
You can taste the sweetness of maltose if you hold a starchy food in your mouth for a minute or so. Try this with a simple food like a soda cracker. Starch is not sweet, but as the starch in the cracker begins to break down with the action of salivary amylase, maltose will form, and you’ll taste the sweetness!
Where is glucose found in food?
Food sources of glucose: Glucose is found in fruits and vegetables, as well as honey, corn syrup, and high fructose corn syrup. (All plants make glucose, but much of the glucose is used to make starch, fiber, and other nutrients. The foods listed here have glucose in its monosaccharide form.)
Why do plants use glucose?
You’re already familiar with glucose, because it’s the main product of photosynthesis. Plants make glucose as a way of storing the sun’s energy in a form that it can use for growth and reproduction.
What is Cellulose?from byjus.com
Cellulose is a complex organic compound that occurs abundantly in nature. It is a polymeric carbohydrate molecule consisting of a linear chain having thousands of glycosidic linkages.
How is cellulose made?from en.wikipedia.org
Cellulose is derived from D -glucose units, which condense through β (1→4)- glycosidic bonds. This linkage motif contrasts with that for α (1→4)-glycosidic bonds present in starch and glycogen. Cellulose is a straight chain polymer. Unlike starch, no coiling or branching occurs and the molecule adopts an extended and rather stiff rod-like conformation, aided by the equatorial conformation of the glucose residues. The multiple hydroxyl groups on the glucose from one chain form hydrogen bonds with oxygen atoms on the same or on a neighbor chain, holding the chains firmly together side-by-side and forming microfibrils with high tensile strength. This confers tensile strength in cell walls where cellulose microfibrils are meshed into a polysaccharide matrix. The high tensile strength of plant stems and of the tree wood also arises from the arrangement of cellulose fibers intimately distributed into the lignin matrix. The mechanical role of cellulose fibers in the wood matrix responsible for its strong structural resistance, can somewhat be compared to that of the reinforcement bars in concrete, lignin playing here the role of the hardened cement paste acting as the "glue" in between the cellulose fibers. Mechanical properties of cellulose in primary plant cell wall are correlated with growth and expansion of plant cells. Live fluorescence microscopy techniques are promising in investigation of the role of cellulose in growing plant cells.
What is the process of synthesis of cellulose?from vedantu.com
Carbon dioxide and water are its by-products. The process of synthesis of celluloses and digestion of cellulose both occurs with the help of several species of bacteria.
Why do termites rely on cellulose?from vedantu.com
Termites rely on their own celluloses. It is believed because they have the strong activity of cellulose in the midgut. Acetic acid and other acids are released at the time of the digestion of wood cellulose.
Why do ruminants digest cellulose?from byjus.com
They are able to digest cellulose because of the presence of bacteria and enzymes in the rumen where anaerobic bacterial digestion ...
What is the material that passes through the digestive system?from science.jrank.org
Small amounts of cellulose found in vegetables and fruits pass through the human digestive system intact. Cellulose is part of the material called "fiber" that dieticians and nutritionists have identified as useful in moving food through the digestive tract quickly and efficiently.
What is the process of breaking down cellulose into smaller polysaccharides called?from en.wikipedia.org
Cellulolysis is the process of breaking down cellulose into smaller polysaccharides called cellodextrins or completely into glucose units; this is a hydrolysis reaction. Because cellulose molecules bind strongly to each other, cellulolysis is relatively difficult compared to the breakdown of other polysaccharides. However, this process can be significantly intensified in a proper solvent, e.g. in an ionic liquid.
What is the sweetest carbohydrate?
Fructose is the sweetest carbohydrate. Plants make nectar. The nectar has this fructose in high amount. Because of its sweetness the insects attract to those plants. So this factor helps to reproduction. Food sources of fructose: Fruits and vegetables, honey, high fructose corn syrup.
What are carbohydrate gums?
Carbohydrate gums are polysaccharides and have hydrophilic properties. Seeds, roots, tree sap, bacteria, seaweed are the sources of carbohydrate gums. Starches, pectin, derivative of cellulose are act like carbohydrate gums. Carbohydrate gums are used as a thickener, texturizer, emulsifier, stabilizer in food industry. Carbohydrate gums are hydrocolloids. Carbohydrate gums protect the colloidal nature of chocolate milk and also break the colloidal nature in wines and beers.
What are the two groups of sugars?
Monosaccharides can be categorized as triose, tetrose, pentose and hexose which have 3,4,5,6 carbon atoms respectively. Also monosaccharides can be classified into two groups that aldose and ketoses. Glucose is a hexose that is very important to our life. And fructose and also galactose are important too.
What are the two types of sugars that are linked by alpha 1-4?
Lactose are made by one glucose and one Galactose and also they linked by alpha 1-4 linkages. Lactose are called milk sugar. Sucrose contain one glucose and one fructose. They linked by alpha 1-2 linkages. Sucrose are called beet/ cane sugar.
What is the main product of photosynthesis?
Glucose is the main product of photosynthesis. Glucose is one of the most important fuel in human body. Also important to the brain and our nervous system. Food sources of glucose: fruits and vegetables, honey, corn syrup, high fructose corn syrup.
What is the ratio of carbohydrates to carbon?
Carbohydrates contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) as elements. Usually carbon and hydrogen ratio is 2:1. There are three main types of carbohydrates as sugars, starches and fibres. Sugars are simple carbohydrates and starch and fibres are complex carbohydrates. In this tutorial, we are going to study about types of carbohydrates;sSugars, starches and fibres
How many sugar units are in a trisachcharide?
Trisachcharides contain three sugar units. Raffinose that in beans are made by one galactose, one glucose and one fructose. Maltotriose are contained by three glucose units.
Why Is Cellulose Considered To Be A Complex Carbohydrate?
Cellulose is a carb that has more than two units of sugar linked together and that s why it is considered to be a complex carbohydrate.Feb 2 2018
Why is cellulose considered to be a complex carbohydrate quizlet?
Why is cellulose considered to be a complex carbohydrate? It is composed of a complex arrangement of glucose molecules. It is composed of a long straight chain of glucose molecules.
Is cellulose a complex carbohydrate?
cellulose a complex carbohydrate or polysaccharide consisting of 3 000 or more glucose units.
What type of complex carbohydrate is cellulose?
Polysaccharides are also referred to as complex carbohydrates . Complex carbohydrates that are found in living things include starch glycogen cellulose and chitin.
Why is it called a complex carbohydrate?
Complex carbohydrates also known as polysaccharides are starches formed by longer saccharide chains which means they take longer to break down. Chemically they usually comprise of three or more linked sugars.
Which describes a complex carbohydrate cellulose quizlet?
Which describes the complex carbohydrate cellulose? It is composed of a complex arrangement of glucose molecules. Which statement about carbohydrates is true? Carbohydrates provide energy for living things. What will most likely happen if a person does not consume the minimum daily requirement of carbohydrates.
Is galactose a complex carbohydrate?
There are two major carbohydrate subgroups: simple and complex. Simple carbohydrates contain the monosaccharide and disaccharide groups. Monosaccharides are comprised of a single simple sugar unit glucose fructose or galactose and they cannot be broken down into simple sugar units.
Which is more easily metabolized, carbohydrates or lipids?from quizizz.com
Carbohydrates are more easily metabolized than lipids. However, on a gram-for-gram basis lipids provide cells with more -
What are the differences between two molecules?from quizizz.com
The differences between two molecules include the type of sugar that forms a section of the molecules and the identify of one of the four nitrogenous bases that make up another section of the molecules. These two molecules are -. Carbohydrates are more easily metabolized than lipids.
Is fructose good for diabetics?from diabetestalk.net
Long thought to be the better sugar for people with diabetes, fructose may not be so great after all. Most people think of fructose as a natural fruit sugar. After all, its one of the main sugars (along with glucose and sucrose) in fruits. In fact, the amount of fructose in most fruits is relatively small, compared with other sources. Fruit also contains a host of greatnutrients, including fiber, which slows the absorption of sugars. The fructose found in processed foods, however, is another story. Between 1980 and 2000, Americans decreased their intake of sucrose (table sugar), but the amount of fructose consumption more than tripled. The reason for this was that food makers replaced sucrose (table sugar) with high-fructose corn syrup (HFCS) to sweeten foods and beverages. HFCS does not come from fruit. Its a highly processedblend of sugars (typically 55 percent fructose and 45 percent glucose) derived from corn. Because the fructose in HFCS is part of a man-made blend (as opposed to the natural compound of sugars found in fruit), the body metabolizes it very differently from other sugars. Also, people with diabetes were told that because fructose doesnt raise blood glucose levels, it was a good alternative to sugar. Therefore, they began using fructose-rich agave nectar under the mistaken assumption that itposed no diabetes-related risk. Unlike glucose, which enters the bloodstream and raises blood sugar levels, fructose is taken up directly to the liver. Sugar and honey contain about 50percentglucose and 50 percentfructose, so regardless of which is consumed, blood glucose will rise. By contrast, agave nectar contains about 85percentfructose, on average, so it has less of an impact on blood sugar and is considered a low glycemic sweetener. However, high fructose int Continue reading >>
Does sucrose lower insulin?from diabetestalk.net
Switching from sucrose to fructose lowers insulin and blood glucose in the obese and diabetics Blood glucose and insulin levels were lower after consuming food or drink that contained fructose, compared to those with sucrose or glucose. By Gary Scattergood Swapping table sugar for fruit-derived sugar helpsreduce blood glucose, especially in people who are overweight or have diabetes, a new review has reported. Researchers from theUniversity of Canberra'sHealth Research Institute examined the short-term and long-term effects of swapping sucrose or glucose, for fructose, the sugar found in many fruits, vegetables and honey. The research, which has been published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition,found blood glucose and insulin levels were lower after consuming food or drink that contained fructose, compared to those with sucrose or glucose. The authors wrote: "We searched the Cochrane Library, MEDLINE, EMBASE, the WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform Search Portal, and clinicaltrials.gov. We included randomised controlled trials measuring peak postprandial glycemia after isoenergetic replacement of glucose, sucrose, or both with fructose in healthy adults or children with or without diabetes. The main outcomes analyzed were peak postprandial blood glucose, insulin, and triglyceride concentrations." University of Canberra adjunct professional associate and senior author of the report Dr Kerry Mills said that in the short-term study, the reduction in blood glucose was far greater in people who were overweight or had diabetes than in those with normal blood glucose levels. The sharp rise in blood glucose after eating glucose and sucrose is a risk factor for diabetes. Fructose, on the other hand, has to be converted by the liver before it can affec Continue reading >>
Does fructose cause insulin resistance?from diabetestalk.net
The metabolism of excessive amounts of fructose leads to fatty liver, which is a key step in the development of insulin resistance, as we saw in our last post. Is there evidence that consumption of fructose leads to insulin resistance? In a word – yes. As far back as 1980, there were studies linking the use of fructose, but not glucose to the development of insulin resistance in humans. The study “Impaired cellular insulin binding and insulin sensitivity induced by high-fructose feeding in normal subjects” examined the effect of adding 1000 kcal/day of excess calories as glucose vs fructose in healthy young people. Body weight over the duration of the test did not change in either group. Intravenous insulin was injected into the subjects after the overfeeding period and blood glucose was measured. The group with excessive glucose intake did not show any statistical difference in sensitivity to insulin. The fructose group, however, showed a 25% worsening of their insulin sensitivity. After 7 days! Remember that both groups had been overfed by the same amount of calories. Fructose also caused a decrease in the binding of insulin to cells and this paralleled the increase in insulin resistance. A more recent study “Effect of Fructose Overfeeding and Fish Oil Administration on Hepatic De Novo Lipogenesis and Insulin Sensitivity in Healthy Men” showed much the same effect. Normal healthy subjects were overfed fructose. De novo Lipogenesis (DNL) – or the production of new fat in the liver increased six fold accompanied by a 79% increase in plasma triglycerides. A measure of insulin resistance in the liver increased by 28%. After 6 days! Muscle insulin resistance was not changed. Since insulin resistance is the hallmark of type 2 Diabetes, this means that these prev Continue reading >>
Does fructose cause diabetes?from diabetestalk.net
As part of the overall diabetes discussion, there lurks the misconception that somehow fructose does not contribute to diabetes. This is a major misunderstanding. Fructose is directly associated with diabetes, especially high-fructose corn syrup. When one is cellularly addicted to glucose, sucrose, and/or fructose, they become stuck in sugar metabolism for making energy. For years, limited and conventional “wisdom” has held that fructose does not affect your blood sugar. This is accurate on a superficial level but unscientific in its assumption that because fructose does not raise blood sugar, it does not affect insulin resistance and cause many metabolic disease problems from the metabolic abnormalities associated with metabolizing an excess amount of fructose. It is therefore falsely deemed a safer sugar than glucose. None of this has been proven to be true. A primary difference is that fructose is metabolized differently than glucose. Fructose is metabolized much more rapidly than any other sugar into fat via the liver. It is also primarily metabolized in the liver. Because of this it has also been associated with a high level of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and a rapid accumulation of a particular kind of fat (triglycerides) that is stored in both the liver and general fat tissue. This is related not only to NAFLD but also to heart disease and hypertension. Glucose, when combined with fructose (as in sucrose and high-fructose corn syrup), accelerates fructose absorption. These metabolic differences are further enhanced in light of recent research reported in the March 2011 Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism, which found that cortical areas around hypothalamus in the brain responded differently to fructose than to glucose. They found that in brain scans Continue reading >>
Does fructose raise blood sugar?from diabetestalk.net
On the one hand, it tends to have only a modest effect on blood glucose levels because it must be broken down gradually by an enzyme in the liver, which converts it to glucose that the body can use for energy. On the other hand, fructose has been implicated in raising triglyceride levels in the blood as well as blood pressure . Is there any way to weigh its risks and benefits? That is what scientists recently tried to do in an analysis of 18 clinical trials that studied fructose consumption, published in the journal Diabetes Care. These trials were selected on the basis that their participants had Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes, they lasted at least seven days, and they measured the effects of dietary fructose on fasting blood glucose and insulin levels as well as HbA1c . These were all randomized controlled trials in which a standard meal plan was compared with one containing more fructose but the same number of calories. According to an ANI (India) article on the analysis , the researchers found that fructose had an overall beneficial effect on blood glucose control, as measured by HbA1c. This effect was accomplished without any detected adverse effects on body weight, blood pressure, or blood cholesterol, and no change in insulin levels. Meanwhile, the average reduction in HbA1c from fructose substitution was 0.53%, representing a major impact on blo Continue reading >>
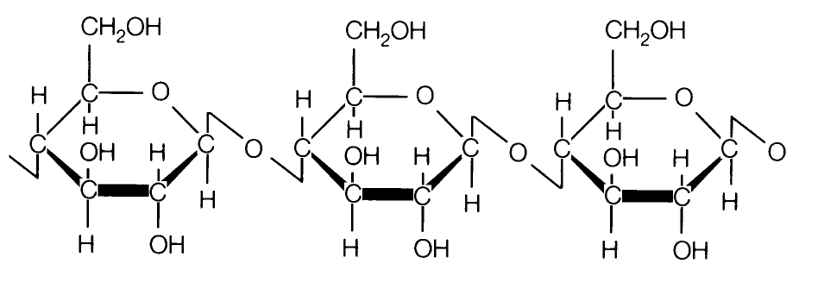
What Are Carbohydrates?
- Carbohydrates are biological molecules composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in one carbon atom(C) to one water molecule (H2O) ratio. They get their name from their chemical composition: carbon (carbo -) plus water (- hydrate). Carbohydrate chains vary in length, and biologically impo…
Table of Contents
Polysaccharides – A Type of Carbohydrate
- A polysaccharide is a long chain of monosaccharides linked by glycosidic bonds (poly– = “many”). The chain can be branched or unbranched, and it can contain various monosaccharides. Depending on the number of monomers joined, the molecular weight can reach 100,000 daltons or higher. Polysaccharides include starch, glycogen, cellulose, and chitin as primary examples.
Why Is Cellulose Considered A Complex carbohydrate?
- Cellulose is a polysaccharide, and has rigid structures that enclose the cells. Cellulose, is composed of unbranched chains of D – glucose monomers linked by 𝛃(1 → 4) glycosidic bonds. Since cellulose is made of glucose monomers in its natural state, it has very different properties. Every other glucose monomer in the chain is flipped in relation to its neighbours, resulting in lon…
Properties of Cellulose – A Carbohydrate
- Cellulose is a crystalline solid with a powdery appearance.
- It possesses a high tensile strength.
- It can be dissolved in strong acidic or alkaline conditions but not in water.
- Cellulose has no flavour or odour.
Commercial Uses of Cellulose – A Carbohydrate
- The primary commercial application of cellulose is in the production of paper.
- In the textile industry, cellulose fibres are used.
- Cotton, linen, and other natural fibres can be used directly or converted into rayon.
- Microcrystalline and powdered cellulose are used as drug fillers as well as thickeners, emulsifiers, and stabilisers in food.
Overview
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula (C 6H 10O 5) n, a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall of green plants, many forms of algae and the oomycetes. Some species of bacteria secrete it to form biofilms. Cellulose is the most abundant or…
History
Cellulose was discovered in 1838 by the French chemist Anselme Payen, who isolated it from plant matter and determined its chemical formula. Cellulose was used to produce the first successful thermoplastic polymer, celluloid, by Hyatt Manufacturing Company in 1870. Production of rayon ("artificial silk") from cellulose began in the 1890s and cellophane was invented in 1912. Hermann St…
Structure and properties
Cellulose has no taste, is odorless, is hydrophilic with the contact angle of 20–30 degrees, is insoluble in water and most organic solvents, is chiral and is biodegradable. It was shown to melt at 467 °C in pulse tests made by Dauenhauer et al. (2016). It can be broken down chemically into its glucose units by treating it with concentrated mineral acids at high temperature.
Processing
In plants cellulose is synthesized at the plasma membrane by rosette terminal complexes (RTCs). The RTCs are hexameric protein structures, approximately 25 nm in diameter, that contain the cellulose synthase enzymes that synthesise the individual cellulose chains. Each RTC floats in the cell's plasma membrane and "spins" a microfibril into the cell wall.
RTCs contain at least three different cellulose synthases, encoded by CesA (Ces is short for "cell…
Hemicellulose
Hemicelluloses are polysaccharides related to cellulose that comprise about 20% of the biomass of land plants. In contrast to cellulose, hemicelluloses are derived from several sugars in addition to glucose, especially xylose but also including mannose, galactose, rhamnose, and arabinose. Hemicelluloses consist of shorter chains – between 500 and 3000 sugar units. Furthermore, hemicelluloses are branched, whereas cellulose is unbranched.
Regenerated cellulose
Cellulose is soluble in several kinds of media, several of which are the basis of commercial technologies. These dissolution processes are reversible and are used in the production of regenerated celluloses (such as viscose and cellophane) from dissolving pulp.
The most important solubilizing agent is carbon disulfide in the presence of alkali. Other agents include Schweizer's reagent, N-methylmorpholine N-oxide, and lithium chloride in dimethylacetamide. …
Commercial applications
Cellulose for industrial use is mainly obtained from wood pulp and from cotton.
• Paper products: Cellulose is the major constituent of paper, paperboard, and card stock. Electrical insulation paper: Cellulose is used in diverse forms as insulation in transformers, cables, and other electrical equipment.
• Fibers: Cellulose is the main ingredient of textiles. Cotton and synthetics (nylons) each …
See also
• Gluconic acid
• Isosaccharinic acid, a degradation product of cellulose
• Lignin
• Zeoform
1 – Glucose
2 – Fructose
- Here’s the chemical structure of : In this class, we’ll sometimes use a simpler purple pentagon to represent fructose: Fructose is special because it is the sweetest carbohydrate. Plants make a lot of fructose as a way of attracting insects and animals, which help plants to reproduce.For example, plants make nectar, which is high in fructose and very sweet, to attract insects that wil…
3 – Galactose
- Here is the chemical structure of : In this class, we’ll sometimes use a blue hexagon to represent galactose: Food sources of galactose:Galactose is found in milk (and dairy products made from milk), but it’s almost always linked to glucose to form a disaccharide (more on that in a minute). We rarely find it in our food supply in monosaccharide form. The second type of simple carbohy…
1 – Maltose
- Here is the chemical structure of : Maltose is made of two glucose molecules bonded together. It doesn’t occur naturally in any appreciable amount in foods, with one exception: sprouted grains. Grains contain a lot of starch, which is made of long chains of glucose (more on this in a minute), and when the seed of a grain starts to sprout, it begins to break down that starch, creating malto…
2 – Sucrose
- Here is the chemical structure of : Sucrose is made of a glucose molecule bonded to a fructose molecule. It’s made by plants for the same reason as fructose — to attract animals to eat it and thereby spread the seeds. Sucrose is naturally-occurring in fruits and vegetables. (Most fruits and vegetables contain a mixture of glucose, fructose, and sucrose.) But humans have also figured o…
3 – Lactose
- Here is the chemical structure of : Lactose is made of a glucose molecule bonded to a galactose molecule. It is sometimes called “milk sugar” as it is found in dairy products like milk, yogurt, and cheese. These are the only animal foods that have significant amounts of carbohydrate. Most of our carbohydrates come from plant foods.