Characteristics of Different Muscle Fibers
| Fibre Type | Type I fibers | Type II A fibers | Type II B Type fibers |
| Contraction time | Slow | Fast | Very Fast |
| Size of motor neuron | Small | Large | Very Large |
| Resistance to fatigue | High | Intermediate | Low |
| Activity Used for | Aerobic | Long term anaerobic | Short term anaerobic |
How many different types of fibers do muscles have?
Muscle Fiber Types 1 and 2 – An Overview. There are two main types of muscle fiber. Type 1 = Slow-twitch fibers; Type 2 = Fast-twitch fibers; There’s also two basic sub-categories of Type 2: Type 2A; Type 2X; Type 2A are somewhere in between Type 1 and Type 2X.
What are the three types of fibers?
Types Of Fibers With Pictures & Their Properties
- Cotton. Cotton is the most common natural fibers in our daily life. ...
- Bast and Leaf fibers. Bast and leaf fibers are plant fibre collected from the phloem or bast surrounding the stem of certain dicotyledonous plants.
- Wool. ...
- Silk. ...
- Synthetic fibers. ...
Are muscle cells and muscle fibers the same thing?
YES, a muscle cell is a muscle fibre, they mean the same thing, but a muscle fibre really is not a muscle cell. it is a collection of cells fussed together during embryological development. Muscle cells are huge compared to other cells and very long. Should I take collagen, or is it too late for me?
What are the longest muscle fibers found in the body?
What are the longest muscle fibers found in the body? The sartorius muscle The sartorius muscle is the longest muscle in the human body. It is strap-like, up to 600 mm in length, and contains five to seven neurovascular compartments, each with a neuromuscular endplate zone. Do skeletal muscles have long fibers? Skeletal muscle fibers are long, multinucleated cells.
How do you tell if you have type 1 or type 2 muscle fibers?
The two types of skeletal muscle fibers are slow-twitch (type I) and fast-twitch (type II). ... Slow-twitch muscle fibers have high concentrations of mitochondria and myoglobin. ... Type I fibers produce less force and are slower to produce maximal tension (lower myosin ATPase activity) compared to type II fibers.More items...
How do you know if you have type 2X muscle fibers?
3:5115:28Muscle Fiber Types Explained: Type 1, Type 2a, Type 2x - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd steady graph rather than our type twos we'll see our a higher peak. So these muscle fibers areMoreAnd steady graph rather than our type twos we'll see our a higher peak. So these muscle fibers are characteristic by being small red.
What are the 3 types of muscle fibers?
Overview. The 3 types of muscle tissue are cardiac, smooth, and skeletal. Cardiac muscle cells are located in the walls of the heart, appear striped (striated), and are under involuntary control.
What are 3 characteristics of type I muscle fibers?
Type I fibers are identified by slow contraction times and a high resistance to fatigue. Structurally, they have a small motor neuron and fiber diameter, a high mitochondrial and capillary density, and a high myoglobin content.
Are abs fast or slow twitch?
The abdomen (Abs) are muscles all the same to the rest of your body. They are derived from both slow twitch muscle fibers, which stimulate better to low weight high reps, and fast twitch muscle fibers, which stimulate better to heavy weight and low reps.
How do you tell if I have fast or slow twitch muscles?
At the start of the vertical jump, a slow-twitch athlete will tend to dip very low and slowly into a squat position before transitioning concentrically to a vertical displacement. On the other hand, a fast-twitch athlete will have a short and forceful dip to create higher acceleration for the jump.
Are fast-twitch muscles bigger?
Each muscle features a unique ratio of these fibers. The fast-twitch fibers have a larger diameter and can lead to bigger muscles, while your slow-twitch muscles are smaller and lead to smaller, more toned muscles.
Are biceps slow or fast-twitch?
The chest muscles, triceps/biceps, and hamstrings are more fast-twitch. Shoulders, forearms, and calves, however, are more slow-twitch, while quads and back muscles tend to be a mix. To train fast-twitch muscles, weight lift with lower reps (5-7) and more weight. For slow-twitch, go for 10-12 reps and lower weight.
Do humans have type 2B muscle fibers?
Based on differential myosin heavy chain (MYH) gene expression, there is further classification of fast-twitch fibers into three major subtypes (types 2A, 2X, and 2B, although humans do not appear to have MYH4-expressing type 2B fibers; Figure 1)1.
What muscles are fast-twitch?
Fast-twitch muscle fibers contract quickly and help you perform fast, high-intensity activities for short periods, like sprinting, jumping jacks, box jumping, and weightlifting and strength-training workouts. Fast-twitch muscles are a large proportion of the small muscles in hands and eyes for rapid movement.
Can you change muscle fiber types?
THE BOTTOM LINE: Yes, you can change your muscle fiber type to become a better endurance athlete or sprinter.
How do I train my fast-twitch muscles for running?
Training for fast-twitchDo sprints, jump rope or HIIT cardio.Run or power walk up a hill as fast as you can.Explosive kettlebell movements.Lift heavier weights for three to five reps.
What is the characteristics of type II 2 muscle Fibre?
Type II fibers are the fast twitch muscle fiber. They are called fast twitch due to their ability to quickly generate force compared with type I fibers (3-5x faster), however they will fatigue at a much quicker rate (McArdle et al., 2015).
Where are type 2 muscle fibers found?
Type IIB fibers are geared to generate ATP by anaerobic metabolic processes, however, they are not able to supply skeletal muscle fibres continuously with sufficient ATP, and fatigue easily. ATP at a fast rate and have a fast contraction velocity. Such fibres are found in large numbers in the muscles of the arms.
Are type 2b and 2x muscle fibers the same?
Note: Type IIb muscle fibers are actually type IIx fibers. So keep this in mind when you find yourself reading further about muscle fibers.
What are the two criteria to consider when classifying the types of muscle fibers?
Two criteria to consider when classifying the types of muscle fibers are how fast some fibers contract relative to others, and how fibers produce ATP. Using these criteria, there are three main types of skeletal muscle fibers. Slow oxidative (SO) fibers contract relatively slowly and use aerobic respiration (oxygen and glucose) to produce ATP.
Why are FO fibers important?
They are oxidative because they produce ATP aerobically, possess high amounts of mitochondria, and do not fatigue quickly. However, FO fibers do not possess significant myoglobin, giving them a lighter color than the red SO fibers. FO fibers are used primarily for movements, such as walking, that require more energy than postural control but less energy than an explosive movement, such as sprinting. FO fibers are useful for this type of movement because they produce more tension than SO fibers but they are more fatigue-resistant than FG fibers.
Why are FO fibers oxidative?
They are oxidative because they produce ATP aerobically, possess high amounts of mitochondria, and do not fatigue quickly. However, FO fibers do not possess significant myoglobin, giving them a lighter color than the red SO fibers.
Why do SO fibers have a large number of mitochondria?
The SO fibers possess a large number of mitochondria and are capable of contracting for longer periods because of the large amount of ATP they can produce , but they have a relatively small diameter and do not produce a large amount of tension. SO fibers are extensively supplied with blood capillaries to supply O 2 from the red blood cells in the bloodstream. The SO fibers also possess myoglobin, an O 2 -carrying molecule similar to O 2 -carrying hemoglobin in the red blood cells. The myoglobin stores some of the needed O 2 within the fibers themselves (and gives SO fibers their red color). All of these features allow SO fibers to produce large quantities of ATP, which can sustain muscle activity without fatiguing for long periods of time.
What is the function of myoglobin in muscle fibers?
The myoglobin stores some of the needed O 2 within the fibers themselves (and gives SO fibers their red color). All of these features allow SO fibers to produce large quantities of ATP, which can sustain muscle activity without fatiguing for long periods of time.
What is FG fiber?
FG fibers are used to produce rapid, forceful contractions to make quick, powerful movements. These fibers fatigue quickly, permitting them to only be used for short periods. Most muscles possess a mixture of each fiber type. The predominant fiber type in a muscle is determined by the primary function of the muscle.
Which fibers produce ATP?
Slow oxidative (SO) fibers contract relatively slowly and use aerobic respiration (oxygen and glucose) to produce ATP. Fast oxidative (FO) fibers have fast contractions and primarily use aerobic respiration, but because they may switch to anaerobic respiration (glycolysis), can fatigue more quickly than SO fibers.
Why do muscle fibers develop?
It’s possible for muscle fibers to develop issues. This can be due to things like direct injury, a nerve condition, or another underlying health condition. Conditions affecting muscle fibers can, in turn, affect the function of a specific muscle or muscle group. Last medically reviewed on May 12, 2020.
What type of muscle fibers are striated?
This causes the muscle tissue to be striated, or have a striped appearance. Skeletal muscle fibers are classified into two types: type 1 and type 2. Type 2 is further broken down into subtypes. Type 1. These fibers utilize oxygen to generate energy for movement.
What is the skeletal muscle made of?
Skeletal muscle. Each one of your skeletal muscles is made up of hundreds to thousands of muscle fibers that are tightly wrapped together by connective tissue. Each muscle fiber contains smaller units made up of repeating thick and thin filaments.
What are the different types of muscles?
The types of muscle tissue have different functions within your body: 1 Skeletal muscle. These muscles are attached to your skeleton by tendons and control the voluntary movements of your body. Examples include walking, bending over, and picking up an object. 2 Smooth muscle. Smooth muscles are involuntary, meaning that you can’t control them. They’re found in your internal organs and eyes. Examples of some of their functions include moving food through your digestive tract and changing the sizes of your pupil. 3 Cardiac muscle. Cardiac muscle is found in your heart. Like smooth muscle, it’s also involuntary. Cardiac muscle contracts in a coordinated way to allow your heart to beat.
What muscle is involuntary?
Cardiac muscle. Cardiac muscle is found in your heart. Like smooth muscle, it’s also involuntary. Cardiac muscle contracts in a coordinated way to allow your heart to beat. Muscle fibers and muscles work to cause movement in the body.
What are some examples of muscle tissue?
These muscles are attached to your skeleton by tendons and control the voluntary movements of your body. Examples include walking, bending over, and picking up an object.
What causes muscle tornness?
This can happen when a muscle stretches beyond its limits or is made to contract too strongly. Some of the most common causes are sports and accidents.
What type of muscle fibers are used for walking?
T here are two main types of fibers in your muscles. Slow Twitch: These are also known as Type I muscle fibers. They are responsible for long-duration, low intensity activity such as walking or any other aerobic activity.
What type of fiber is used for explosive, short-duration activity?
Type IIB fibers are built for explosive, very short-duration activity such as Olympic lifts. Type IIA fibers are designed for regular high-intensity work. T o find the predominant fiber type in a particular muscle in your body, you can try the following test. Find your one rep max here for an isolation exercise for that muscle group.
What is a fast twitch fiber?
They are responsible for long-duration, low intensity activity such as walking or any other aerobic activity. Fast Twitch: These are known as Type II fibers (divided further into A and B). They are responsible for short-duration, high intensity activity.
What type of fibers are found in the muscles of the arms?
These fibers, also called fast twitch or fast glycolytic fibers, contain a low content of Myoglobin, relatively few mitochondria, relatively few blood capillaries and large amounts glycogen. Type II B fibers are white, geared to generate ATP by anaerobic metabolic processes, not able to supply skeletal muscle fibers continuously with sufficient ATP, fatigue easily, split ATP at a fast rate and have a fast contraction velocity. Such fibers are found in large numbers in the muscles of the arms.
What are the characteristics of skeletal muscle fibers?
Faster contracting fibers have greater ability to split ATP. In addition, skeletal muscle fibers vary with respect to the metabolic processes they use to generate ATP. They also differ in terms of the onset of fatigue. On the basis of various structural and functional characteristics, skeletal muscle fibers are classified into three types: Type I fibers, Type II B fibers and type II A fibers.
How does exercise affect skeletal muscle?
Various types of exercises can bring about changes in the fibers in a skeletal muscle. Endurance type exercises, such as running or swimming, cause a gradual transformation of type II B fibers into type II A fibers. The transformed muscle fibers show a slight increase in diameter, mitochondria, blood capillaries, and strength. Endurance exercises result in cardiovascular and respiratory changes that cause skeletal muscles to receive better supplies of oxygen and carbohydrates but do not contribute to muscle mass. On the other hand, exercises that require great strength for short periods of time, such as weight lifting, produce an increase in the size and strength of type II B fibers. The increase in size is due to increased synthesis of thin and thick myofilaments. The overall result is that the person develops large muscles.
What is the skeletal muscle?
Skeletal Muscle. Skeletal muscle tissue is attached to our bones. It is striated; that is, the fibers (cells) contain alternating light and dark bands (striations) that are perpendicular to the long axes of the fibers. Skeletal muscle tissue can be made to contract or relax by conscious control (voluntary). All skeletal muscle fibers are not alike ...
What is muscle tissue?
Our muscle tissue consists of fibers (cells) that are highly specialized for the active generation of force for our muscle contraction. Muscle tissue provides motion, maintenance of our posture, and heat production. On the basis of certain structural and functional characteristics, the muscle tissue that our body has is classified ...
How to develop fast twitch muscle fiber?
You can develop your fast-twitch muscle fiber by conducting plyometrics or complex training (combination of plyometrics and weights.) to build the fast muscle (IIa), and performing weight/strength training to build the super-fast (IIb) to the point where you can release exercise-induced growth hormone.
How fast does a muscle move?
The fast muscle (what the researchers call type IIa) moves 5 times faster than the slow muscle, and the super-fast (called type IIb) moves 10 times faster than the slow muscle fiber.
How many types of muscle fibers are there?
There are three main types of muscle fiber:
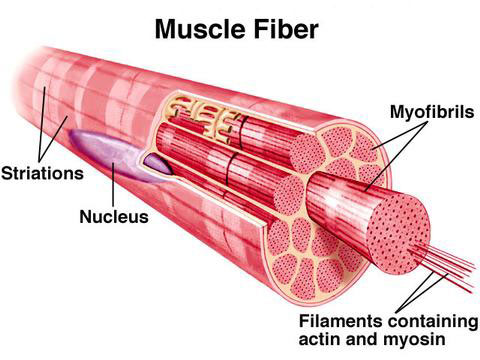
What are the fibers of skeletal muscle?
Each muscle is wrapped in a thick connective tissue called the epimysium. Within this is a number of muscle fibers which are bundled together to form a fascicle, which are held in place by the perimysium.
What is your muscle type?
As we have shown, muscle fiber types are varied between individuals, so it is highly likely that you show differences between your friends and family. Sadly, the only true way of finding out what your muscle fiber types is through a muscle biopsy – this involves taking away a tiny portion of the muscle for testing in the labs.
Why do muscle fibers change shape?
This is because muscle fibers are plastic, meaning they are capable of changing their size and shape. Even more interesting is the fact that they can also convert from one type to another! These changes to muscle fibers are due to a number of factors, these include your age but also your activity level.
What is the skeletal muscle made of?
Skeletal muscle is therefore made up of hundreds, if not thousands of muscle fibers. These fibers are singular protein dense cells which contain many nuclei, mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum. Each fiber is surrounded by a plasma membrane called the sarcolemma, and inside this sits the sarcoplasm, a gelatin-like substance which separates ...
What is the smallest connective tissue?
Within each muscle fiber we have a number of myofibrils which are aligned in parallel, each individual fiber is surrounded by endomysium – the smallest of the connective tissue.
Which muscle fibers produce the most force?
Type IIb muscle fibers are without doubt the most powerful, they produce the most force and are faster at getting to their peak force. However, they are easily fatiguable, meaning this high-level of force cannot be sustained for as long as type I fibers.
What is the body's muscle fibers?
Each of your muscle fibers is composed of 75 percent water, 20 percent protein, 5 percent phosphates, calcium, magnesium, sodium, potassium, chloride, fats, carbohydrates, and amino acids.
How many muscle fibers are there in the calf?
A muscle fiber will contract all the way, or not at all. One motor neuron may innervate 1000 muscle fibers in your calf, while another motor neuron may activate only 10 muscle fibers around your eye. Muscle takes up less space than fat. One pound of fat bulges 18 percent more than a pound of muscle.
What type of fibers have a high twitch rate?
Type II-b fibers are anaerobic with a high glycogen content and fast twitch rate. They have few capillaries and low endurance but a high power output. Your muscles need glycogen, ATP, and innervation to become active. A stimulus to a motor unit contracts your muscles on an all-or-none principle.
What is a mesomorphic body type?
Body types, play a major role in how women develop. A mesomorphic body type is one with well developed and defined muscles on the trunk and limbs. These women are broader in the shoulders and hips and narrower at the waist. They have a high muscle to fat ratio and may look fit even without exercise.
What are the two subclasses of Type II fibers?
There are two subclasses of Type II fibers. Type II a-intermediate fibers are somewhat oxidative. They use a combination of the aerobic and glycogen systems. These are recruited after Type I fibers. Type II a-intermediate fibers are fast twitch with moderate myoglobin content, capillary density, force production and endurance.
How many muscles are there in the body?
You have 430 voluntary muscles which represents 40 to 50 percent of your body weight. Skeletal muscle is the largest single tissue in your body. You have two basic types of muscle fibers. Your postural muscles are Type I, endurance, red, and are considered slow twitch muscles. These muscles hold you in an erect position all day long.
Which type of muscle is recruited first during your strength and speed work?
These muscles hold you in an erect position all day long. Type I fibers are recruited first during your strength and speed work and are capable of less force but can help you perform more repetitions (reps.) and run longer and slower than Type II fibers.
What is muscle fiber type?
Muscle fiber type can be an important factor for individualization of an athlete's training program. There are two basic muscle fiber types: type I and type II. The type I fibers are called slow-twitch because they produce low amounts of strength and power and are subsequently best suited for endurance activities.
Why are type II fibers called fast-twitch fibers?
The type II fibers are called fast-twitch because they produce high amounts of strength and power and are thus better suited for speed and explosive events. The best way to determine the general fiber make-up of a trainee is to do a vertical jump test.
How accurate is a muscle biopsy?
The only 100% accurate reading of a muscle fiber type is through a muscle biopsy, but if you're looking for a practical test that can be done in less than a minute, I highly suggest you use the vertical jump test. Stephane Cazeault February 17, 2017 Comment.
