Is the Earth really billions of years old?
Yes, the Earth is approximately 4.543 billion years old. This is a unit of measurement, using the year as we currently define it. 1.43268048e+17 seconds is another way you can measure it, and seconds are a scientific unit whose current definition relies on atomic properties that existed that long ago. 179 views View upvotes Sponsored by Turing
What happened to the Earth thousands of years ago?
Researchers found that the combination of human encroachment with the warming contributed to the extinctions. Credit... Climate change, habitat destruction, extinctions — the Earth has seen it all before, thousands of years ago. And humans may have been partly to blame for many of those changes in nature, too.
What did earth look like one million years ago?
One million years ago, during the time of The Pleistocene Epoch, the Earth was in the midst of The Last Ice Age. This started 2.6 million years ago and lasted until about 11.700 years ago. Because of the amount of frozen water, the level of the oceans would have been lower.
What will happen to the Earth in billion years?
In 7 billion years, the Earth will probably be covered in an ocean made of lava. The Earth and Moon will then get sucked into the Sun, just before the Sun turns into a red giant. It's not looking too bright for us.

What was Earth like 25 million years ago?
This map shows how North America appeared 25 million years ago. Nebraska supported a vast savannah-like environment, and climate was cooler and drier than during the Paleocene and Eocene Epochs. Sediment from the uplifting Rocky Mountains continued to be shed across Nebraska.
What was around 25 million years ago?
The Miocene was the first epoch of the Neogene period (23-2.5 million years ago), followed by the much shorter Pliocene epoch (5-2.6 million years ago); both the Neogene and Miocene are themselves subdivisions of the Cenozoic Era (65 million years ago to the present).
What was Earth like during the Miocene era?
The Miocene Epoch, 23.03 to 5.3 million years ago,* was a time of warmer global climates than those in the preceeding Oligocene or the following Pliocene and it's notable in that two major ecosystems made their first appearances: kelp forests and grasslands.
What did the earth look like during the Paleogene period?
The beginning of the Paleogene Period was very warm and moist compared to today's climate. Much of the earth was tropical or sub-tropical. Palm trees grew as far north as Greenland! By the end of the Paleogene, during the Oligocene Epoch, the climate began to cool.
What was on Earth before dinosaurs?
At the time all Earth's land made up a single continent, Pangea. The age immediately prior to the dinosaurs was called the Permian. Although there were amphibious reptiles, early versions of the dinosaurs, the dominant life form was the trilobite, visually somewhere between a wood louse and an armadillo.
When did humans start on Earth?
The first human ancestors appeared between five million and seven million years ago, probably when some apelike creatures in Africa began to walk habitually on two legs. They were flaking crude stone tools by 2.5 million years ago.
What was on Earth 23 million years ago?
Miocene Epoch (23 – 5.3 MYA) The Miocene was a long-lasting epoch in which the earth's climate rebounded from the cooling of the Oligocene and there was a marked increase in both global temperatures and the total number of mammal species. Though warmer than the Oligocene, the polar ice caps remained in place.
Were there humans in the Miocene period?
It is generally agreed that the taproot of the human family shrub is to be found among apelike species of the Middle Miocene Epoch (roughly 16–11.6 mya) or Late Miocene Epoch (11.6–5.3 mya). Genetic data based on molecular clock estimates support a Late Miocene ancestry.
What animals were alive during the Miocene epoch?
During the later Miocene mammals were more modern, with easily recognizable canids, bears, red pandas, procyonids, equids, beavers, deer, camelids, and whales, along with now extinct groups like borophagine canids, certain gomphotheres, three-toed horses, and hornless rhinos like Teleoceras and Aphelops.
How was Earth during the Jurassic period?
The Jurassic period (199.6 million to 145.5 million years ago) was characterized by a warm, wet climate that gave rise to lush vegetation and abundant life. Many new dinosaurs emerged—in great numbers. Among them were stegosaurs, brachiosaurs, allosaurs, and many others.
What do you think would've happened if dinosaurs didn't go extinct during the Paleocene Epoch under early Cenozoic Era?
"If dinosaurs didn't go extinct, mammals probably would've remained in the shadows, as they had been for over a hundred million years," says Brusatte. "Humans, then, probably would've never been here." But Dr. Gulick suggests the asteroid may have caused less of an extinction had it hit a different part of the planet.
When did the dinosaurs go extinct?
about 65 million years agoDinosaurs went extinct about 65 million years ago (at the end of the Cretaceous Period), after living on Earth for about 165 million years.
What is the history of Earth?
The history of Earth concerns the development of planet Earth from its formation to the present day. Nearly all branches of natural science have contributed to understanding of the main events of Earth's past, characterized by constant geological change and biological evolution .
How many eons are there in the history of Earth?
In geochronology, time is generally measured in mya (million years ago), each unit representing the period of approximately 1,000,000 years in the past. The history of Earth is divided into four great eons, starting 4,540 mya with the formation of the planet. Each eon saw the most significant changes in Earth's composition, climate and life. Each eon is subsequently divided into eras, which in turn are divided into periods, which are further divided into epochs .
How did the T Tauri star form?
Meanwhile, in the outer part of the nebula gravity caused matter to condense around density perturbations and dust particles, and the rest of the protoplanetary disk began separating into rings. In a process known as runaway accretion, successively larger fragments of dust and debris clumped together to form planets. Earth formed in this manner about 4.54 billion years ago (with an uncertainty of 1%) and was largely completed within 10–20 million years. The solar wind of the newly formed T Tauri star cleared out most of the material in the disk that had not already condensed into larger bodies. The same process is expected to produce accretion disks around virtually all newly forming stars in the universe, some of which yield planets.
How are geologic timelines organized?
The history of the Earth can be organized chronologically according to the geologic time scale, which is split into intervals based on stratigraphic analysis. The following five timelines show the geologic time scale. The first shows the entire time from the formation of the Earth to the present, but this gives little space for the most recent eon. Therefore, the second timeline shows an expanded view of the most recent eon. In a similar way, the most recent era is expanded in the third timeline, the most recent period is expanded in the fourth timeline, and the most recent epoch is expanded in the fifth timeline.
What caused the Moon to form?
While the Earth was in its earliest stage ( Early Earth ), a giant impact collision with a planet-sized body named Theia is thought to have formed the Moon. Over time, the Earth cooled, causing the formation of a solid crust, and allowing liquid water on the surface.
How many species are extinct?
It is estimated that 99 percent of all species that ever lived on Earth, over five billion, have gone extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million are documented, but over 86 percent have not been described.
Why didn't planets contribute to the Earth's water?
Planetesimals at a distance of 1 astronomical unit (AU), the distance of the Earth from the Sun, probably did not contribute any water to the Earth because the solar nebula was too hot for ice to form and the hydration of rocks by water vapor would have taken too long.
How long has the Earth been around?
The timescale of Earth’s history is vast and there is still much we do not know. 4.5 billion years is an unfathomably long time and there are gaps in our understanding. The sheer longevity of Earth completely dwarfs human history; in fact, humans have existed for about 0.004% of the Earth’s total age.
What eon was the Earth during?
The Earth during the Archean eon. Credit: Nasa.gov
What is the Hadean eon?
Credit: T. Bertelink via WikiCommons CC BY-SA 4,0. The Hadean is the first geological eon of Earth’s history. Ranging from 4.6 billion to 4 billion years ago, the name “Hadean” is a reference to the Hades, the Greek god of the underworld, and describes ...
How did the moon form during the Hadean eon?
It is hypothesized that the moon formed during this time period, as a result of the collision of the Earth and a Mars-sized astronomical object. This event, dubbed the Theia Impact as a reference to the Greek titan Theia, is speculated to have occurred in the early Hadean eon, some 20 million to 100 million years after the formation of the solar system.
What was the first type of life that developed 500 million years ago?
Paleozoic Era (541 – 245 million years ago) A nautilus, one of the first kinds of invertebrate life that developed 500 million years ago. Credit: L Berger via WikiCommons CC-BYY 3.0. The beginning of the Paleozoic era in the Cambrian period signified the largest diversification of life in Earth’s history.
What caused the formation of the supercontinents?
During this time period, the Earth went through a high amount of tectonic activity resulting in the formation and fragmenting of a number of supercontinents, including ones named Columbia, Rodina, Laurentia, and Gondwana. Radiation from the sun still made land relatively inhospitable, so most life existed in the oceans. Over time, oxygen accumulation created the ozone layer which allowed life to diversify on land.
What caused the ice age?
The accumulated oxygen reacted with the methane, making carbon dioxide. The lowered greenhouse effect caused a global drop in temperatures and plunged the earth into a 300,000,000 year long ice age. During this “snowball Earth” period, the entire surface of the Earth was frozen or nearly frozen. ADVERTISEMENT.
How long ago was the Pleistocene?
In geologic terms, a million years ago was the Pleistocene age (2.5 million years BC to 11,711 years BC), and Earth was five to 10 degrees colder than it is today. Prolonged glaciation periods occurred during this time,
How much lower was the sea level between glacial epochs?
The sea levels were much lower. Geologists estimate that difference in sea level between glacial epochs was as much as almost 400 feet.
What is the name of the extinct girafid?
Sivatherium is an extinct girafid with small bumped horns that lived between five million and 10,000 years ago. The animal, related to today's giraffe, was an herbivore that was 13 feet long and weighed about one ton. It consumed 50 to 100 pounds of grass a day. Sivatherium roamed from Africa to India. It was hunted to extinction by humans at the end of the last Ice Age.
Why didn't the Great Lakes exist?
The five Great Lakes -- Superior, Huron, Michigan, Ontario, and Erie -- form the largest interconnected body of fresh water on Earth, but they didn't exist a million years ago because of the ice sheet that covered much of Canada and the northern United States.
Why did the continents experience dust storms?
Because the water levels were lower due to the Ice Age, the continents experienced dust storms.
How long ago was the Baltic Sea?
There was no Baltic Sea a million years ago. The Baltic Sea is the youngest seas in the world, appearing between 10,000 and 15,000 years ago as the ice sheets from the ice age retreated.
Where did the hominids originate?
By a million years ago, early hominids -- our human ancestors â were walking upright and making tools. They were on the move. Our ancestors originated in Africa between one and two million years ago and eventually moved to Asia and Europe. Scientists speculate that climate change had a lot to do with their migration.
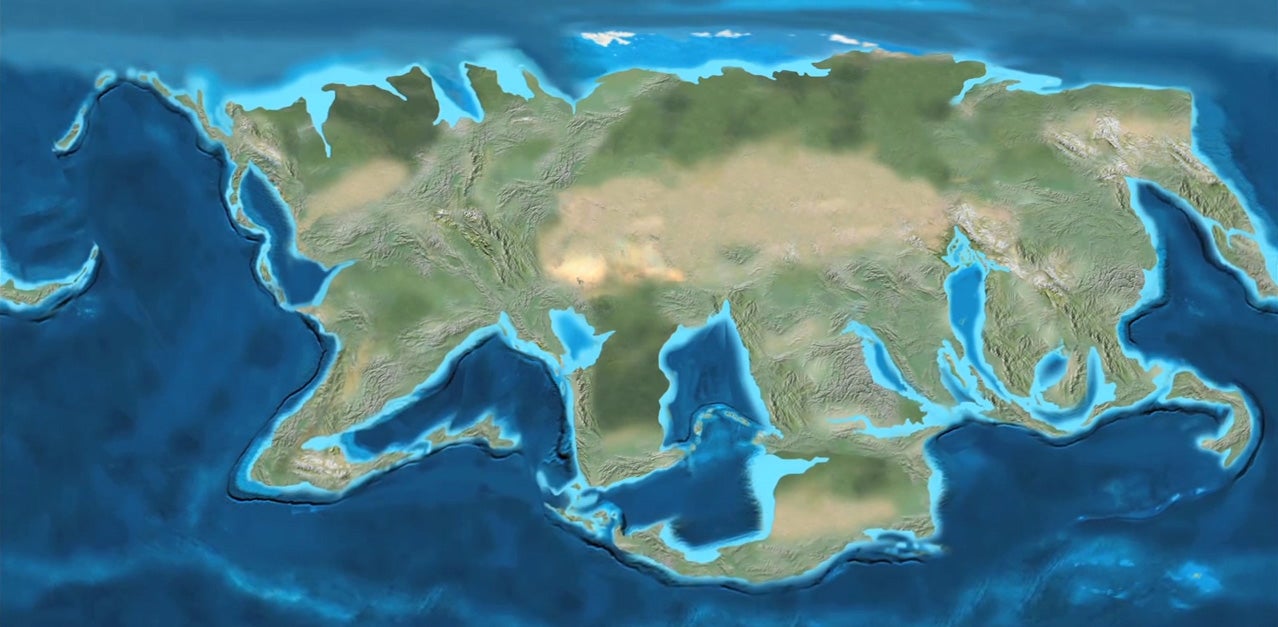
How long ago was the Earth seen?
Earth as seen from space 500 million years ago. Scientists have blended NASA images with geography and climate reconstructions to create an animation of the Earth as it would have appeared from space 500 million years ago.
What would happen if we could see light?
If we can see that light, we will be able to have an idea of the continental distribution and how much vegetation the planets have.

Overview
Eons
In geochronology, time is generally measured in mya (million years ago), each unit representing the period of approximately 1,000,000 years in the past. The history of Earth is divided into four great eons, starting 4,540 mya with the formation of the planet. Each eon saw the most significant changes in Earth's composition, climate and life. Each eon is subsequently divided into eras, which in turn are divided into periods, which are further divided into epochs.
Geologic time scale
The history of the Earth can be organized chronologically according to the geologic time scale, which is split into intervals based on stratigraphic analysis. The following five timelines show the geologic time scale to scale. The first shows the entire time from the formation of the Earth to the present, but this gives little space for the most recent eon. The second timeline shows an expanded view of the most recent eon. In a similar way, the most recent era is expanded in the t…
Solar System formation
The standard model for the formation of the Solar System (including the Earth) is the solar nebula hypothesis. In this model, the Solar System formed from a large, rotating cloud of interstellar dust and gas called the solar nebula. It was composed of hydrogen and helium created shortly after the Big Bang 13.8 Ga (billion years ago) and heavier elements ejected by supernovae. About 4.5 Ga, the nebul…
Hadean and Archean Eons
The first eon in Earth's history, the Hadean, begins with the Earth's formation and is followed by the Archean eon at 3.8 Ga. The oldest rocks found on Earth date to about 4.0 Ga, and the oldest detrital zircon crystals in rocks to about 4.4 Ga, soon after the formation of the Earth's crust and the Earth itself. The giant impact hypothesis for the Moon's formation states that shortly after formation of an in…
Proterozoic Eon
The Proterozoic eon lasted from 2.5 Ga to 538.8 Ma (million years) ago. In this time span, cratons grew into continents with modern sizes. The change to an oxygen-rich atmosphere was a crucial development. Life developed from prokaryotes into eukaryotes and multicellular forms. The Proterozoic saw a couple of severe ice ages called snowball Earths. After the last Snowball Earth …
Phanerozoic Eon
The Phanerozoic is the current eon on Earth, which started approximately 538.8 million years ago. It consists of three eras: The Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic, and is the time when multi-cellular life greatly diversified into almost all the organisms known today.
The Paleozoic ("old life") era was the first and longest era of the Phanerozoic e…
See also
• Chronology of the universe – History and future of the universe
• Detailed logarithmic timeline – Timeline of the history of the universe, Earth, and humankind
• Earth phase – Phases of the Earth as seen from the Moon